Linux arm cache 入门
ARM 架构下 Cache 的基本概念
Cache 层级:L1 I-Cache、L1 D-Cache、L2(统一 Cache),部分 SoC 还有 L3
Cache 特性:写分配 / 非写分配,写回(write-back)/ 写直达(write-through)
一致性问题:SMP 多核下的 Cache 一致性协议(MESI/MOESI 思路)
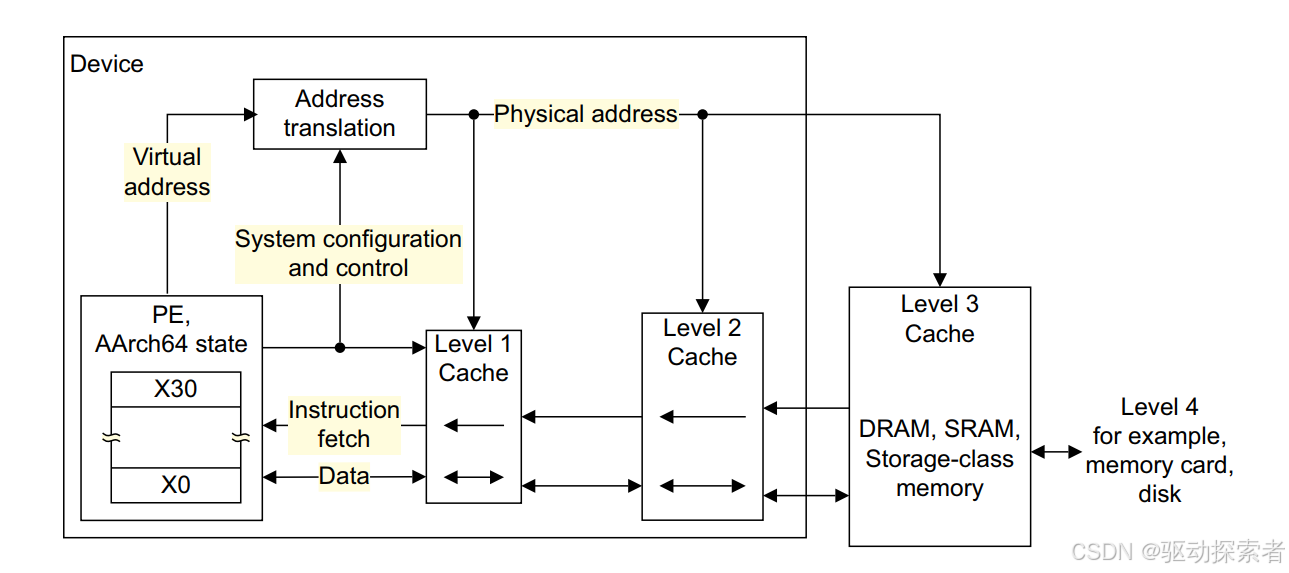
ARM 内存域划分:Normal memory vs Device memory
ARM Cache 维护指令族
ARMv8/v7 都提供了一组专门的 cache maintenance instructions,在内核驱动和系统软件里很常见。
指令分类
I-Cache(指令 Cache)相关
IC IVAU:Invalidate I-Cache by VA to PoUIC IALLUIS:Invalidate all I-Cache inner shareableIC IALLU:Invalidate all I-Cache (non-shareable)
D-Cache(数据 Cache)相关

DC CIVAC:Clean & Invalidate D-Cache line by VA to PoCDC CVAC:Clean D-Cache line by VA to PoCDC IVAC:Invalidate D-Cache line by VA to PoCDC ZVA:Zero a cache line by VADC CVAU:Clean D-Cache line by VA to PoU
关键参数
PoU (Point of Unification)
指指令流和数据流统一的位置,通常是 I-Cache 之前的层级。
比如写代码到内存后,需要清到 PoU,确保 I-Cache 能看到。
PoC (Point of Coherency)
体系保证所有 master 观察到一致性的点。
通常是 L2 Cache 出口到内存的接口。
PoP (Point of Persistence)
数据被写入“持久存储”的点(比如 NVM、持久内存系统)。
在 ARMv8.2+ 中提出,和持久化内存相关。
使用场景举例
代码自修改 / 动态加载代码:先写 D-Cache,再清到 PoU,最后无效 I-Cache。
DMA 缓冲区:CPU 和外设共享内存时,需要 Clean / Invalidate 到 PoC。
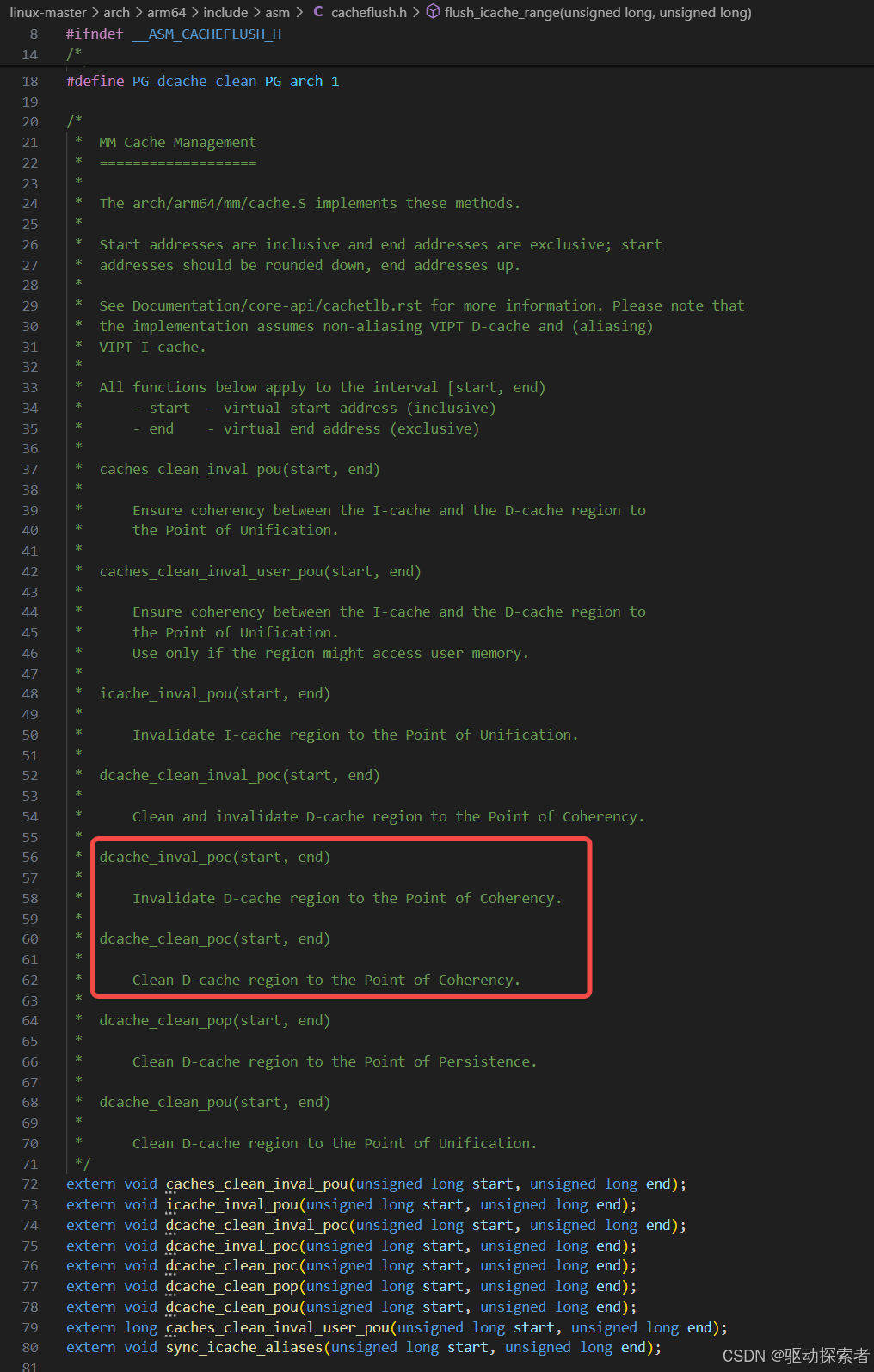
Linux 内核中的 Cache 操作接口
内核提供的 API
在 Linux 内核(arch/arm64/include/asm/cacheflush.h)中常见的接口有:
高层 API
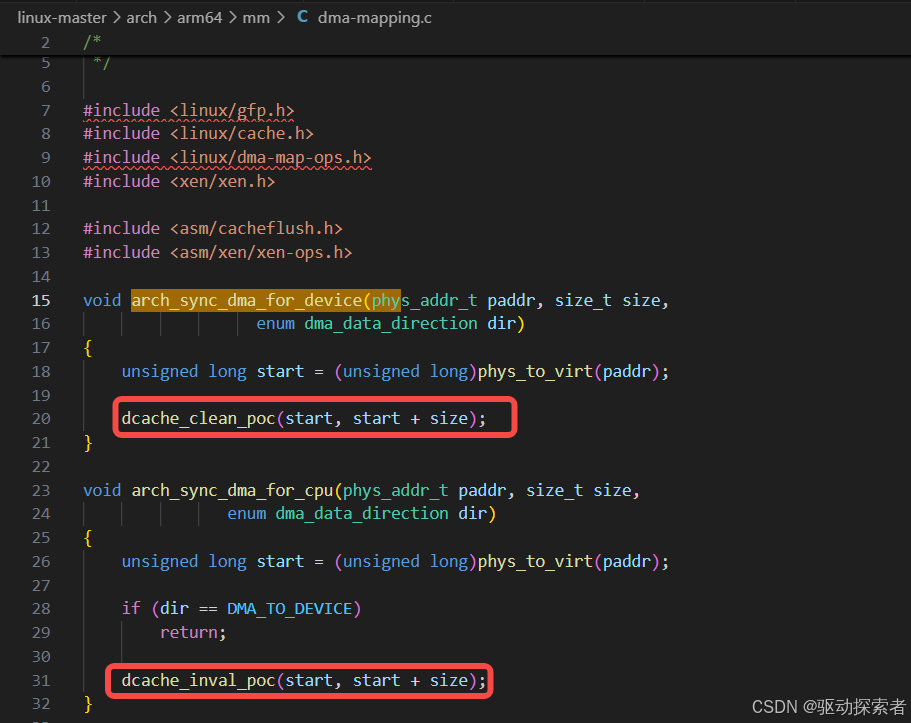
dma_map_single()/dma_unmap_single()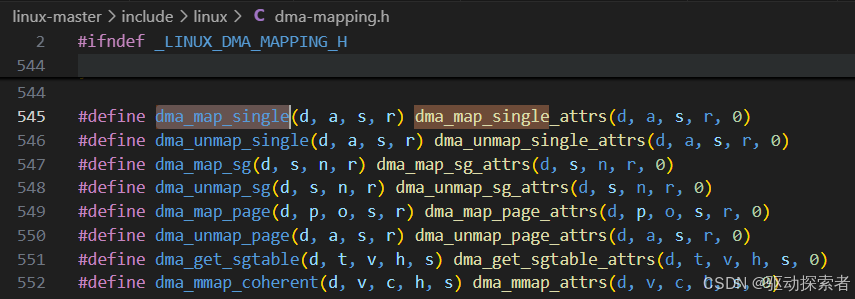
用于驱动中确保 DMA 缓冲区 Cache 与内存一致
dma_sync_single_for_device()/dma_sync_single_for_cpu()针对 CPU/设备交替访问的场景
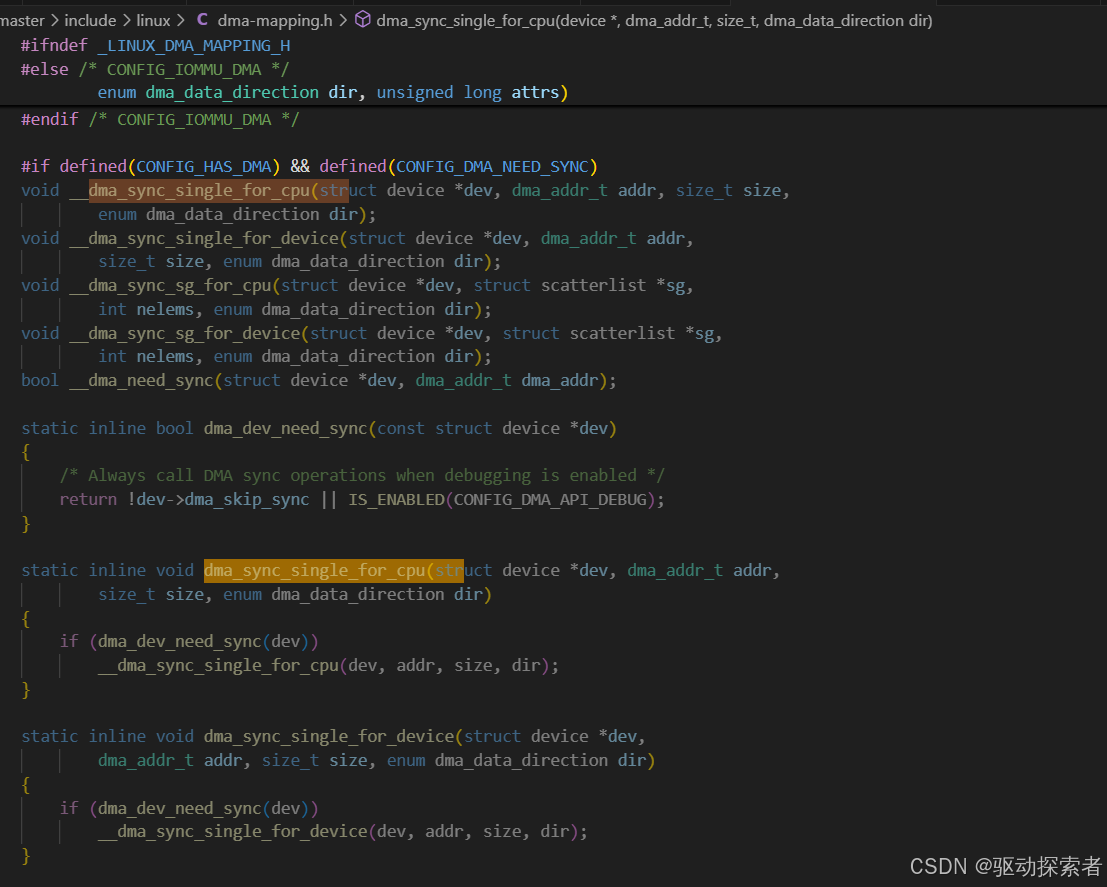
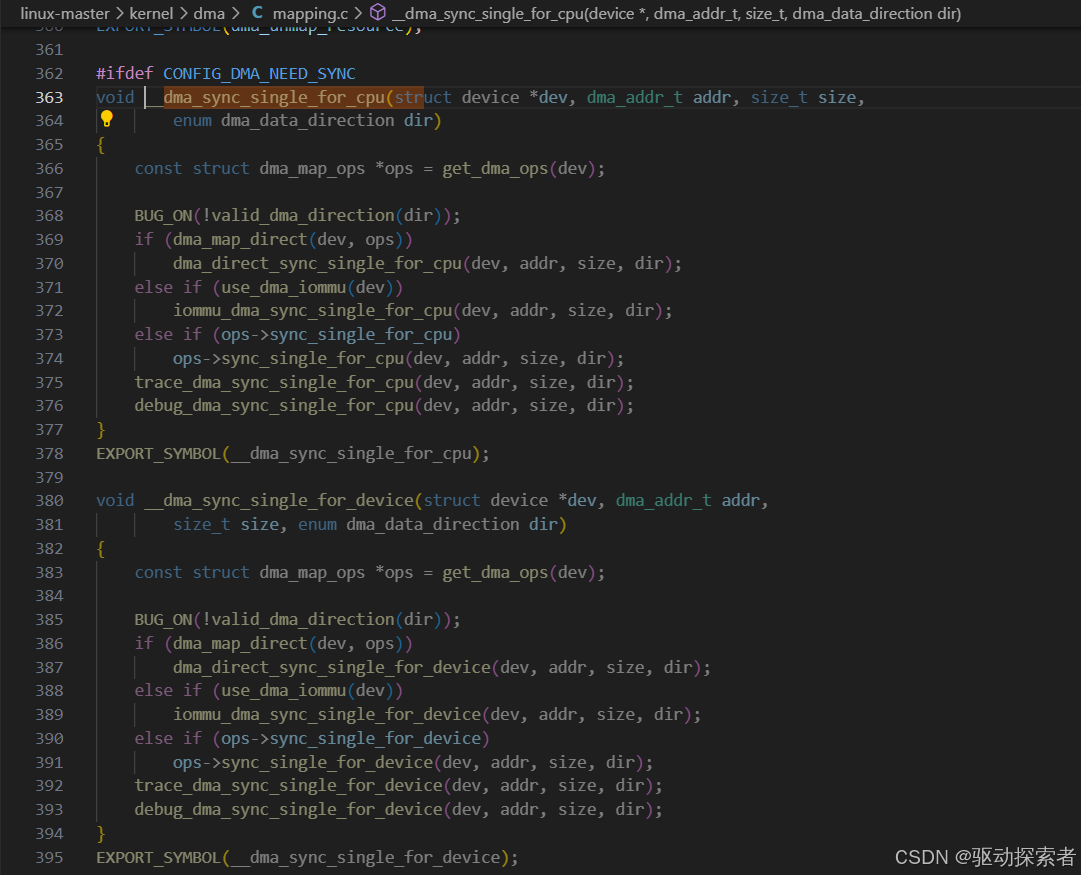
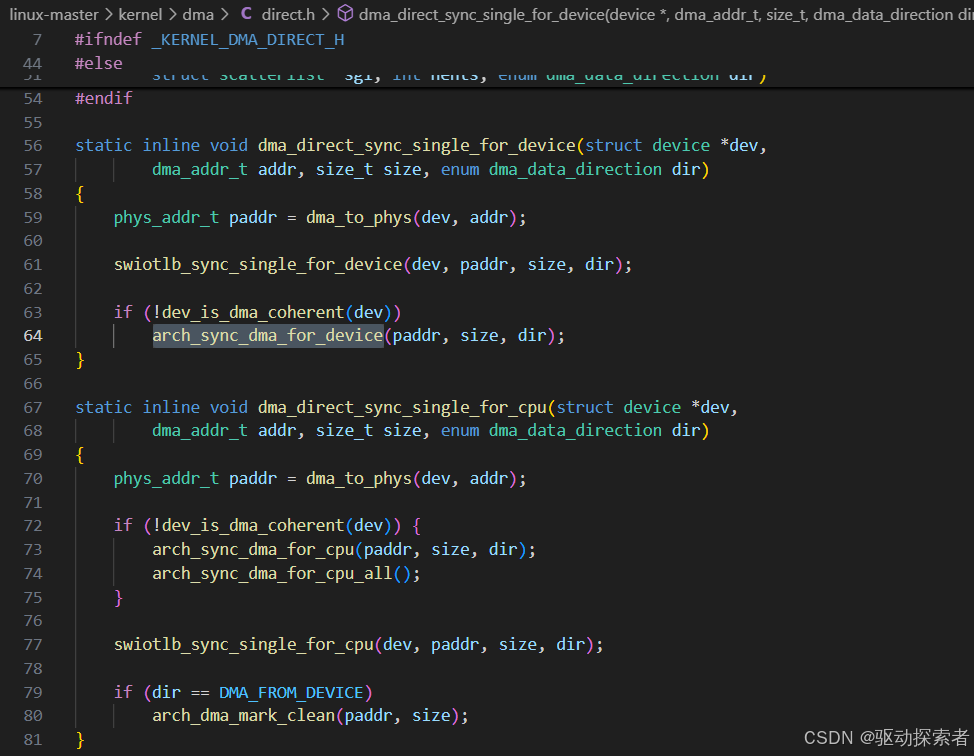
dma摸之前clean,cpu摸之前inv