手写MyBatis第35弹:@Select、@Insert等注解的背后原理
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。
我们常常在当下感到时间慢,觉得未来遥远,但一旦回头看,时间已经悄然流逝。对于未来,尽管如此,也应该保持一种从容的态度,相信未来仍有许多可能性等待着我们。
目录
正文
一、SQL命令类型:框架执行的路由依据
二、解析阶段的类型识别:两种路径的汇合
三、注解解析中的命令类型识别
四、XML解析中的命令类型识别
五、MappedStatement:命令类型的承载者
六、执行阶段的路由决策:Executor的关键选择
七、设计思考:为何在解析阶段就确定命令类型?
八、总结与最佳实践
-
MyBatis源码深度解析:SQL命令类型识别的核心机制
-
手写MyBatis:如何精准识别@Select、@Insert等注解的背后原理
-
SQL命令类型判定:MyBatis执行路由的关键决策过程
-
从注解到执行:详解MyBatis的SQL命令类型解析体系
-
架构设计精髓:MyBatis如何通过sqlCommandType实现执行路由
正文
在MyBatis框架中,每一个SQL操作都需要被精确地识别其类型——是查询(SELECT)还是更新(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE)。这个看似简单的类型判定,实际上是整个框架执行路由的基石。今天,我们将深入解析MyBatis如何在不同阶段识别和记录SQL命令类型,以及这个信息如何在执行过程中发挥关键作用。
一、SQL命令类型:框架执行的路由依据
SQL命令类型的识别不仅仅是一个简单的分类问题,它决定了整个执行路径的选择:
-
查询操作(SELECT) → 调用
Executor.query()→ 返回结果集 -
更新操作(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) → 调用
Executor.update()→ 返回受影响行数
这种路由决策必须在执行前明确,因为两者的处理方式、返回值类型和资源管理策略都有本质区别。
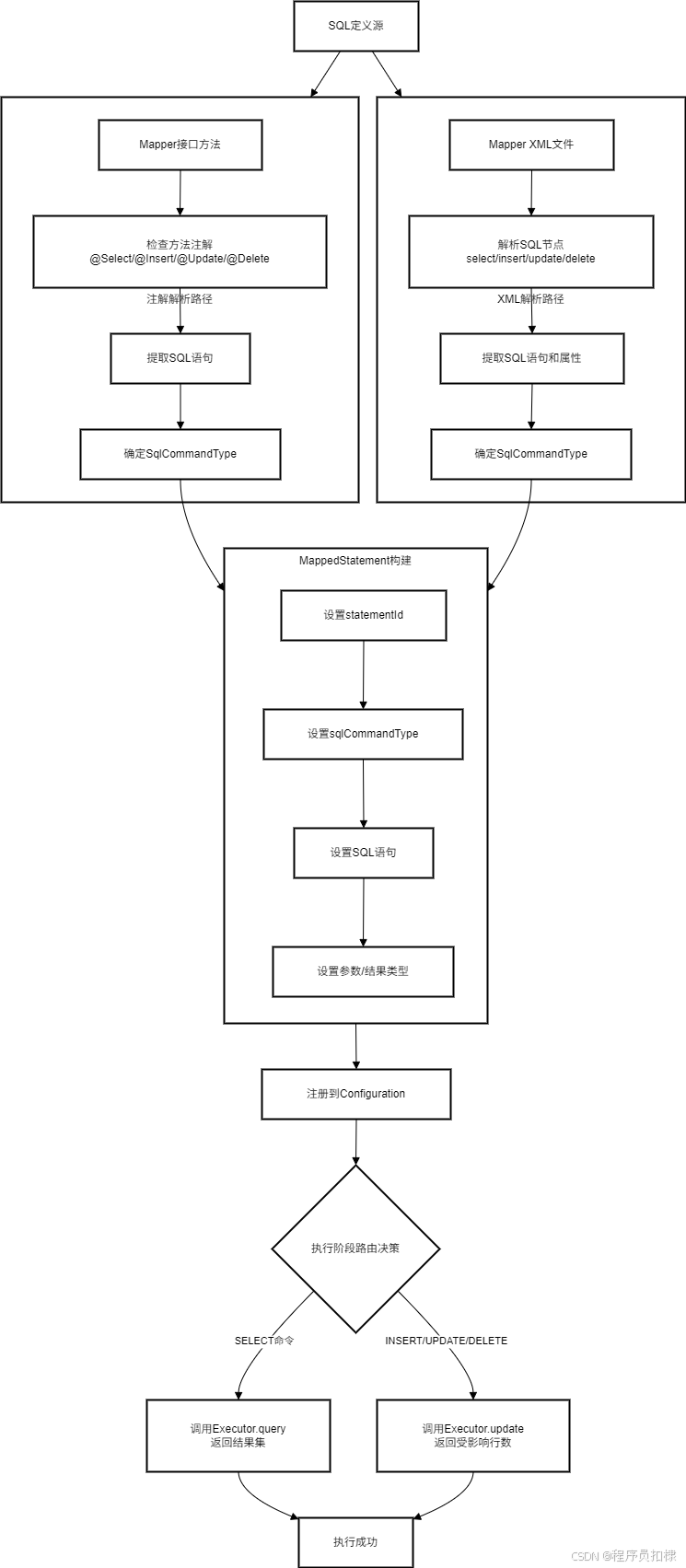
二、解析阶段的类型识别:两种路径的汇合
MyBatis支持两种方式的SQL定义:注解和XML。无论哪种方式,都需要在解析阶段准确识别SQL命令类型。
SQL命令类型枚举定义:
public enum SqlCommandType {UNKNOWN, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE;/*** 根据注解类型获取对应的SQL命令类型*/public static SqlCommandType fromAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) {if (annotationType == Select.class) {return SELECT;} else if (annotationType == Insert.class) {return INSERT;} else if (annotationType == Update.class) {return UPDATE;} else if (annotationType == Delete.class) {return DELETE;}return UNKNOWN;}/*** 根据XML节点名获取对应的SQL命令类型*/public static SqlCommandType fromXmlNode(String nodeName) {switch (nodeName) {case "select": return SELECT;case "insert": return INSERT;case "update": return UPDATE;case "delete": return DELETE;default: return UNKNOWN;}}}三、注解解析中的命令类型识别
在解析Mapper接口的注解时,我们需要检查方法上的注解类型来确定SQL命令类型:
public class MapperAnnotationParser {public void parseMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {// 检查方法上的注解Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN;String sql = null;for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.fromAnnotation(annotationType);if (sqlCommandType != SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {// 提取SQL语句if (annotation instanceof Select) {sql = ((Select) annotation).value()[0];} else if (annotation instanceof Insert) {sql = ((Insert) annotation).value()[0];} // 其他注解类似处理break;}}if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {throw new RuntimeException("No SQL annotation found on method: " + method.getName());}// 构建MappedStatementString statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();MappedStatement ms = new MappedStatement.Builder(config, statementId, sql, sqlCommandType).resultType(getReturnType(method)).parameterType(getParameterType(method)).build();config.addMappedStatement(ms);}}四、XML解析中的命令类型识别
XML解析时需要根据节点名识别命令类型:
public class XMLMapperParser {private void buildStatementFromContext(Element context, String namespace) {// 获取所有SQL操作节点List<Element> elements = context.elements();for (Element element : elements) {String nodeName = element.getName();SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.fromXmlNode(nodeName);if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {continue; // 跳过非SQL节点}String id = element.attributeValue("id");String parameterType = element.attributeValue("parameterType");String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");String sql = element.getTextTrim();String statementId = namespace + "." + id;MappedStatement ms = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, statementId, sql, sqlCommandType).parameterType(resolveClass(parameterType)).resultType(resolveClass(resultType)).build();configuration.addMappedStatement(ms);}}}五、MappedStatement:命令类型的承载者
MappedStatement是SQL命令类型的最终承载者,它在构造时就必须明确命令类型:
public class MappedStatement {private final String id;private final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;private final String sql;private final Class<?> parameterType;private final Class<?> resultType;// 使用Builder模式确保必填字段public static class Builder {private final String id;private final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;private final String sql;private Class<?> parameterType;private Class<?> resultType;public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, String sql, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {this.id = id;this.sql = sql;this.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;}public Builder parameterType(Class<?> parameterType) {this.parameterType = parameterType;return this;}public Builder resultType(Class<?> resultType) {this.resultType = resultType;return this;}public MappedStatement build() {return new MappedStatement(this);}}private MappedStatement(Builder builder) {this.id = builder.id;this.sqlCommandType = builder.sqlCommandType;this.sql = builder.sql;this.parameterType = builder.parameterType;this.resultType = builder.resultType;}}六、执行阶段的路由决策:Executor的关键选择
SQL命令类型在Executor的执行方法中被关键性地使用,它决定了调用哪个执行方法:
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) {// 只有SELECT操作才能进入查询方法if (ms.getSqlCommandType() != SqlCommandType.SELECT) {throw new RuntimeException("Only SELECT statements can be executed with query() method");}// 查询缓存逻辑...return delegate.query(ms, parameter);}@Overridepublic int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) {// 只有更新操作才能进入update方法if (ms.getSqlCommandType() == SqlCommandType.SELECT) {throw new RuntimeException("SELECT statements cannot be executed with update() method");}// 清理缓存(对于更新操作)clearLocalCache();return delegate.update(ms, parameter);}}在基础的SimpleExecutor中,这种路由更加明显:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {@Overridepublic int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) {// 验证命令类型validateUpdateStatement(ms);Statement stmt = null;try {Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter);stmt = prepareStatement(handler);return handler.update(stmt);} finally {closeStatement(stmt);}}private void validateUpdateStatement(MappedStatement ms) {SqlCommandType commandType = ms.getSqlCommandType();if (commandType != SqlCommandType.INSERT && commandType != SqlCommandType.UPDATE && commandType != SqlCommandType.DELETE) {throw new RuntimeException("Invalid statement type for update: " + commandType);}}}七、设计思考:为何在解析阶段就确定命令类型?
你可能会有疑问:为什么不在执行时解析SQL语句来判断命令类型?这样设计有几个重要原因:
-
性能优化:解析阶段一次性完成所有分析,避免每次执行时的重复解析
-
提前验证:在应用启动时就能发现配置错误,而不是运行时
-
资源准备:根据命令类型预先准备不同的执行策略和资源
-
明确性:让SQL的意图更加明确,便于代码维护和理解
八、总结与最佳实践
SQL命令类型的识别是MyBatis框架中一个看似简单却至关重要的机制。通过本文的分析,我们可以看到:
-
双重解析路径:注解和XML解析最终都汇合到统一的
MappedStatement结构中 -
早期绑定:命令类型在解析阶段就确定,为执行阶段提供明确指导
-
严格验证:在执行前后都有严格的类型验证,确保执行路径的正确性
-
扩展性设计:枚举化的命令类型为未来支持更多SQL类型预留了空间
最佳实践建议:
-
保持注解或XML配置的一致性,避免混合使用造成的 confusion
-
在自定义插件时,可以根据
sqlCommandType实现不同的拦截逻辑 -
对于复杂的动态SQL,确保XML配置中的命令类型准确反映操作意图
这个精巧的设计体现了MyBatis的一个重要哲学:通过静态分析提供运行时优化。通过在解析阶段完成尽可能多的工作,MyBatis确保了运行时的高效和执行路径的明确性。
下次当你编写一个@Insert注解时,不妨想一想这个简单的注解是如何通过精妙的架构设计,最终引导整个执行流程完成数据库插入操作的。这种从微观注解到宏观执行的转换,正是框架设计的魅力所在。
💖学习知识需费心,
📕整理归纳更费神。
🎉源码免费人人喜,
🔥码农福利等你领!💖常来我家多看看,
📕我是程序员扣棣,
🎉感谢支持常陪伴,
🔥点赞关注别忘记!💖山高路远坑又深,
📕大军纵横任驰奔,
🎉谁敢横刀立马行?
🔥唯有点赞+关注成!
