Python实现RANSAC进行点云直线、平面、曲面、圆、球体和圆柱拟合
本节我们分享使用RANSAC算法进行点云的拟合。RANSAC算法是什么?不知道的同学们前排罚站!(前面有)
总的来说,RANSAC(Random Sample Consensus)是一种通用的迭代鲁棒估计框架,无论拟合何种几何模型,其思想完全一致: 1. 随机采样 → 2. 最小样本拟合 → 3. 内点判定 → 4. 模型评估 → 5. 迭代收敛 → 6. 输出最优模型。
下面按“直线、平面、一般二次曲面、二维圆、三维球面、圆柱面”六种情形,给出统一的实现步骤与关键公式,便于对照查阅。
--------------------------------
1. 拟合 3D 空间直线
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 每次随机抽取 2 个点 p₁、p₂(两点确定一条直线)。模型估计
- 方向向量 v = (p₂ − p₁) / ‖p₂ − p₁‖
- 直线方程:L(t) = p₁ + t v,t∈ℝ内点判定
- 点 p 到直线的距离
d = ‖(p − p₁) × v‖
若 d < d_th,则为内点。迭代终止
- 最大迭代次数 N 或内点比例达到要求即可停止。--------------------------------
2. 拟合 3D 平面
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 每次随机抽取 3 个不共线的点 p₁,p₂,p₃。模型估计
- 平面法向量 n = (p₂ − p₁) × (p₃ − p₁) 并归一化
- 平面方程:n·(x − p₁)=0,即 ax+by+cz+d=0内点判定
- 点 p 到平面距离
d = |a·x + b·y + c·z + d| / √(a²+b²+c²)
若 d < d_th,则为内点。--------------------------------
3. 拟合一般二次曲面
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 二次曲面一般式 Ax²+By²+Cz²+Dxy+Eyz+Fzx+Gx+Hy+Iz+J=0 共 10 个参数,因此最少需要 9 个点(秩缺 1,需额外约束 J=1 或 ‖参数‖=1)。模型估计
- 构造设计矩阵 A ∈ ℝ^{m×9} 和观测向量 b ∈ ℝ^m,用最小二乘解参数向量 θ=[A,B,…,I]^T。
- 得到隐式曲面方程 f(x,y,z)=0。内点判定
- 点 p 到隐式曲面的代数距离 |f(p)| / ‖∇f(p)‖ 与阈值比较。--------------------------------
4. 拟合 2D 圆
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 每次随机抽取 3 个非共线的 2D 点 (x₁,y₁),(x₂,y₂),(x₃,y₃)。模型估计
- 圆心 (a,b) 和半径 r 的闭合公式
a = [ (x₂²+y₂²−x₁²−y₁¹)(y₃−y₁) − (x₃²+y₃²−x₁²−y₁²)(y₂−y₁) ] / D
b = [ (x₃²+y₃²−x₁²−y₁²)(x₂−x₁) − (x₂²+y₂²−x₁²−y₁²)(x₃−x₁) ] / D
D = 2[(x₂−x₁)(y₃−y₁) − (x₃−x₁)(y₂−y₁)]
r = √[(x₁−a)²+(y₁−b)²]内点判定
- 点 (x,y) 到圆的距离
|√[(x−a)²+(y−b)²] − r| < d_th。--------------------------------
5. 拟合 3D 球面
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 每次随机抽取 4 个非共面 3D 点 p₁…p₄。模型估计
- 球心 c 和半径 R 的线性方程组
‖p_i − c‖² = R², i=1…4 → 4 线性方程 → 解 c、R。内点判定
- 点 p 到球面距离
|‖p − c‖ − R| < d_th。--------------------------------
6. 拟合 3D 圆柱面
--------------------------------
随机采样
- 每次随机抽取 5 个 3D 点(圆柱面有 7 个自由度,但 5 点可解唯一参数,见下)。模型估计
- 将圆柱面参数化为:
中心轴:直线 L(t)=c + t d(方向向量 d,单位化)
半径 r
- 5 点约束:任意点 p_i 到轴的距离等于 r
‖(p_i − c) × d‖ = r, i=1…5
可通过非线性最小二乘或几何代数法一次性求出 d、c、r。内点判定
- 点 p 到圆柱面距离
|‖(p − c) × d‖ − r| < d_th。
--------------------------------
下面书写一段RANSAC的统一处理流程(伪代码)
--------------------------------
输入:点云 Q,几何模型类型 T,阈值 d_th,最大迭代 N
for k = 1…N
S ← RandomSample(Q, m) # m 由模型决定(2,3,4,5…)
M ← FitModel(S, T) # 见上各小节
Inliers ← {p ∈ Q | Distance(p,M) < d_th}
if |Inliers| > best_inliers
best_model ← M
best_inliers ← Inliers
输出:best_model, best_inliers
可视化
- 用 Open3D / Matplotlib / PCL 等库将原始点云和拟合几何体(直线、平面、网格化曲面、圆环、球体、圆柱网格)同时渲染。
至此,六种常见几何模型的 RANSAC 实现步骤全部给出,可直接对照代码模板进行落地。当然,本次的数据猪脚依然是我们的老朋友——兔砸!
一、RANSAC各种拟合程序
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import pyransac3d as pyrsc
import randomFILE = "E:/CSDN/规则点云/bunny.pcd" # 改成自己的文件# ---------------- 通用工具 -----------------
def load_pcd():pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(FILE)if not pcd.has_points():raise RuntimeError("找不到 {}".format(FILE))return pcd, np.asarray(pcd.points)def show(title, in_pcd, out_pcd, geom):"""统一可视化"""o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([in_pcd, out_pcd, geom],window_name=title,width=800, height=600)# AXIS = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_coordinate_frame(size=1)# ---------------- 1. 直线 -----------------
def fit_line(pcd, pts):def ransac_3d(points, thresh=0.05, max_iter=1000):best_in, best_model = [], Nonefor _ in range(max_iter):idx = random.sample(range(len(points)), 2)p1, p2 = points[idx]vec = p2 - p1if np.linalg.norm(vec) < 1e-6:continuevec = vec / np.linalg.norm(vec)dists = np.linalg.norm(np.cross(points - p1, vec), axis=1)inliers = np.where(dists < thresh)[0]if len(inliers) > len(best_in):best_in = inliersbest_model = (p1, vec)return best_model, best_inmodel, idx = ransac_3d(pts, 0.05, 1000)if model is None:print("直线拟合失败")returnp1, vec = modelin_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])length = np.linalg.norm(pcd.get_max_bound() - pcd.get_min_bound())start, end = p1 - vec * length, p1 + vec * lengthls = o3d.geometry.LineSet(points=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector([start, end]),lines=o3d.utility.Vector2iVector([[0,1]]))ls.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector([[0,0,1]])show("1. 直线拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, ls)# ---------------- 2. 平面 -----------------
def fit_plane(pcd, pts):plane = pyrsc.Plane()eq, idx = plane.fit(pts, thresh=0.01, maxIteration=1000)in_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])# 平面网格aabb = in_pcd.get_axis_aligned_bounding_box()size = max(aabb.get_extent()) * 1.5mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_box(size, size, 0.001)mesh.translate([-size/2, -size/2, 0])mesh.rotate(in_pcd.get_rotation_matrix_from_xyz((0,0,0)), center=(0,0,0))normal = np.array(eq[:3])z = np.array([0,0,1])if np.linalg.norm(np.cross(z, normal)) > 1e-6:rot = o3d.geometry.get_rotation_matrix_from_axis_angle(np.cross(z, normal))mesh.rotate(rot, center=(0,0,0))mesh.translate(in_pcd.get_center())mesh.paint_uniform_color([0,0,1])mesh.compute_vertex_normals()show("2. 平面拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, mesh)# ---------------- 3. 二次曲面 -----------------
def fit_quadric(pcd, pts):"""拟合二次曲面 z = a x² + b y² + c xy + d x + e y + f用 RANSAC 选 6 个内点,然后用最小二乘解 6 参数。"""def quadric_model(pts_sample):A = np.c_[pts_sample[:,0]**2, pts_sample[:,1]**2,pts_sample[:,0]*pts_sample[:,1],pts_sample[:,0], pts_sample[:,1],np.ones(len(pts_sample))]b = pts_sample[:,2]coeffs, *_ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, b, rcond=None)return coeffsdef residuals(pts, coeffs):a,b,c,d,e,f = coeffsreturn np.abs(pts[:,2] - (a*pts[:,0]**2 + b*pts[:,1]**2 + c*pts[:,0]*pts[:,1] + d*pts[:,0] + e*pts[:,1] + f))best_in, best_coeff = [], Nonefor _ in range(1000):idx = random.sample(range(len(pts)), 6)sample = pts[idx]try:coeff = quadric_model(sample)except np.linalg.LinAlgError:continuedists = residuals(pts, coeff)inliers = np.where(dists < 0.05)[0]if len(inliers) > len(best_in):best_in, best_coeff = inliers, coeffif best_coeff is None:print("二次曲面拟合失败")returnin_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(best_in).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(best_in, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])# 网格可视化aabb = in_pcd.get_axis_aligned_bounding_box()xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(aabb.min_bound[0], aabb.max_bound[0], 50),np.linspace(aabb.min_bound[1], aabb.max_bound[1], 50))a,b,c,d,e,f = best_coeffzz = a*xx**2 + b*yy**2 + c*xx*yy + d*xx + e*yy + fvertices = np.stack([xx.ravel(), yy.ravel(), zz.ravel()], axis=1)mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh()mesh.vertices = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(vertices)idx = np.arange(50*50).reshape(50,50)triangles = []for i in range(49):for j in range(49):triangles.append([idx[i,j], idx[i+1,j], idx[i,j+1]])triangles.append([idx[i+1,j], idx[i+1,j+1], idx[i,j+1]])mesh.triangles = o3d.utility.Vector3iVector(np.array(triangles))mesh.paint_uniform_color([0,0,1])mesh.compute_vertex_normals()show("3. 曲面拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, mesh)# ---------------- 4. 圆 -----------------
def fit_circle(pcd, pts):pts2d = pts[:, :2] # 假设圆在 XY 平面def ransac_circle(pts2d, thresh=0.05, max_iter=1000):best_in, best_model = [], Nonefor _ in range(max_iter):idx = random.sample(range(len(pts2d)), 3)A,B,C = pts2d[idx]D = 2*((B[0]-A[0])*(C[1]-A[1]) - (B[1]-A[1])*(C[0]-A[0]))if abs(D) < 1e-6: continuecx = ((C[1]-A[1])*(B[0]**2+B[1]**2-A[0]**2-A[1]**2) - (B[1]-A[1])*(C[0]**2+C[1]**2-A[0]**2-A[1]**2)) / Dcy = ((B[0]-A[0])*(C[0]**2+C[1]**2-A[0]**2-A[1]**2) - (C[0]-A[0])*(B[0]**2+B[1]**2-A[0]**2-A[1]**2)) / Dr = np.linalg.norm([A[0]-cx, A[1]-cy])dists = np.abs(np.linalg.norm(pts2d - [cx,cy], axis=1) - r)inliers = np.where(dists < thresh)[0]if len(inliers) > len(best_in):best_in, best_model = inliers, (cx, cy, r)return best_model, best_inmodel, idx = ransac_circle(pts2d, 0.05, 1000)if model is None:print("圆拟合失败")returncx,cy,r = modelin_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)x = cx + r*np.cos(theta)y = cy + r*np.sin(theta)z = np.zeros_like(x)circle_pts = np.vstack([x,y,z]).Tls = o3d.geometry.LineSet(points=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(circle_pts),lines=o3d.utility.Vector2iVector([[i,(i+1)%100] for i in range(100)]))ls.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector([[0,0,1] for _ in range(100)])show("4. 圆拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, ls)# ---------------- 5. 球 -----------------
def fit_sphere(pcd, pts):sph = pyrsc.Sphere()center, radius, idx = sph.fit(pts, thresh=0.05, maxIteration=1000)in_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_sphere(radius=radius)mesh.translate(center)mesh.paint_uniform_color([0,0,1])mesh.compute_vertex_normals()show("5. 球拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, mesh)# ---------------- 6. 圆柱 -----------------
def fit_cylinder(pcd, pts):cyl = pyrsc.Cylinder()axis, center, radius, idx = cyl.fit(pts, thresh=0.05, maxIteration=1000)in_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx).paint_uniform_color([1,0,0])out_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(idx, invert=True).paint_uniform_color([0,1,0])height = np.linalg.norm(pcd.get_max_bound() - pcd.get_min_bound()) * 1.2mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_cylinder(radius=radius, height=height, resolution=50)mesh.compute_vertex_normals()mesh.paint_uniform_color([0,0,1])z = np.array([0,0,1])axis = axis / np.linalg.norm(axis)if np.linalg.norm(np.cross(z, axis)) > 1e-6:rot = o3d.geometry.get_rotation_matrix_from_axis_angle(np.cross(z, axis))mesh.rotate(rot, center=(0,0,0))mesh.translate(center)show("6. 圆柱拟合", in_pcd, out_pcd, mesh)# ---------------- 主菜单 -----------------
def main():pcd, pts = load_pcd()menu = """
1 直线
2 平面
3 二次曲面
4 圆
5 球
6 圆柱
q 退出
请选择(1-6):"""while True:choice = input(menu).strip()if choice == 'q': breakif choice not in {'1','2','3','4','5','6'}:print("输入无效")continueif choice == '1': fit_line(pcd, pts)if choice == '2': fit_plane(pcd, pts)if choice == '3': fit_quadric(pcd, pts)if choice == '4': fit_circle(pcd, pts)if choice == '5': fit_sphere(pcd, pts)if choice == '6': fit_cylinder(pcd, pts)if __name__ == "__main__":main()二、RANSAC各种拟合结果
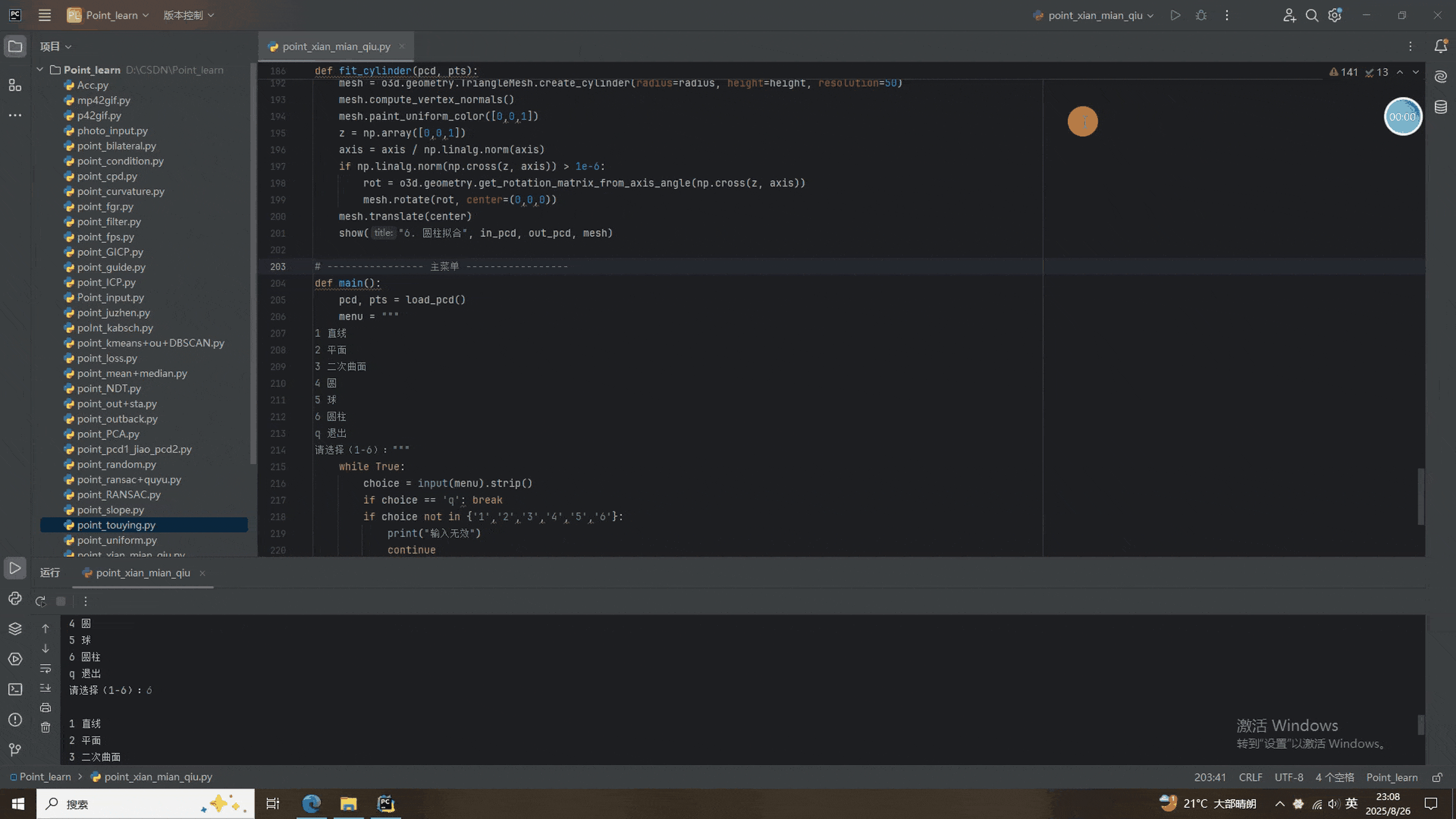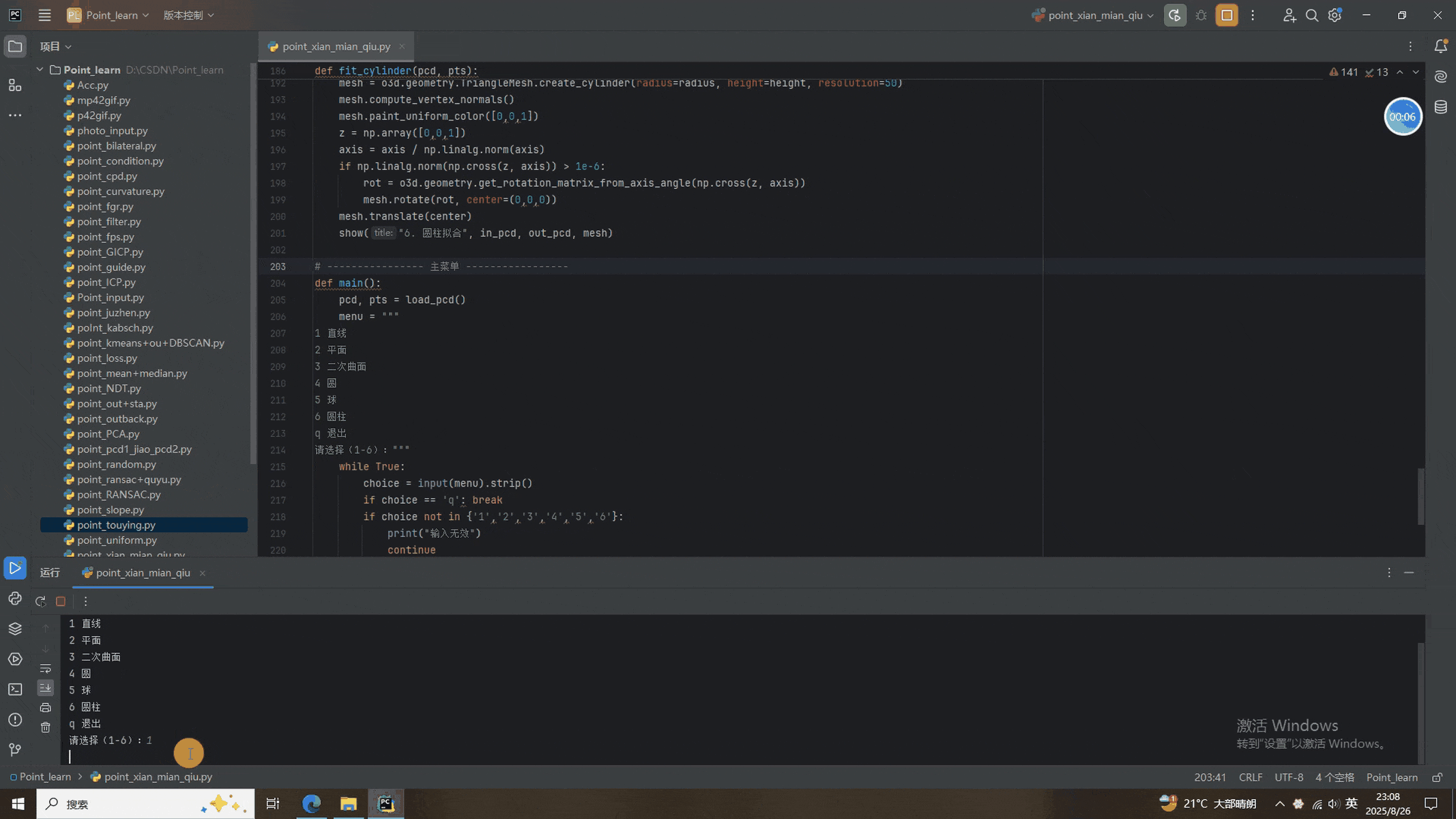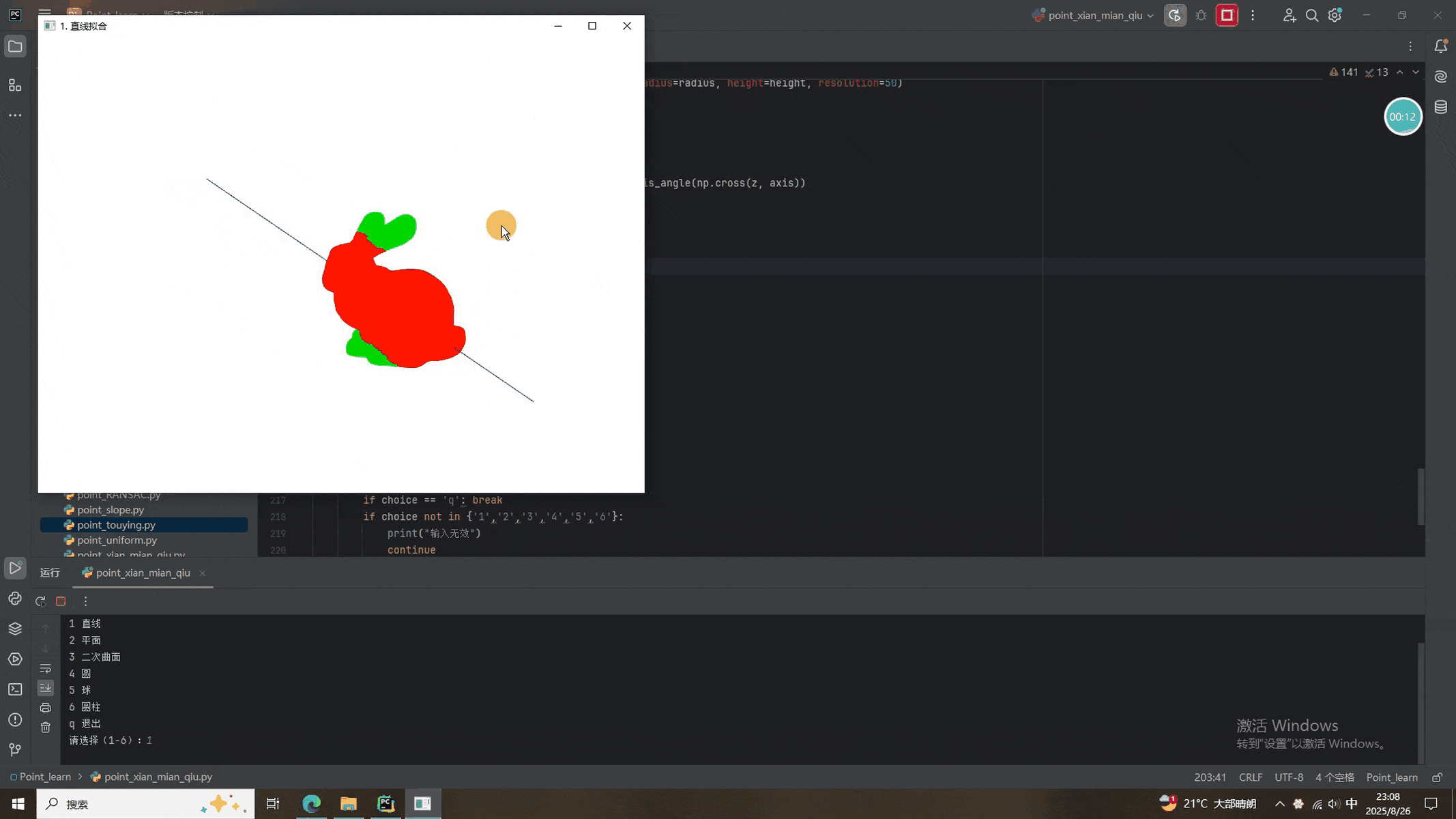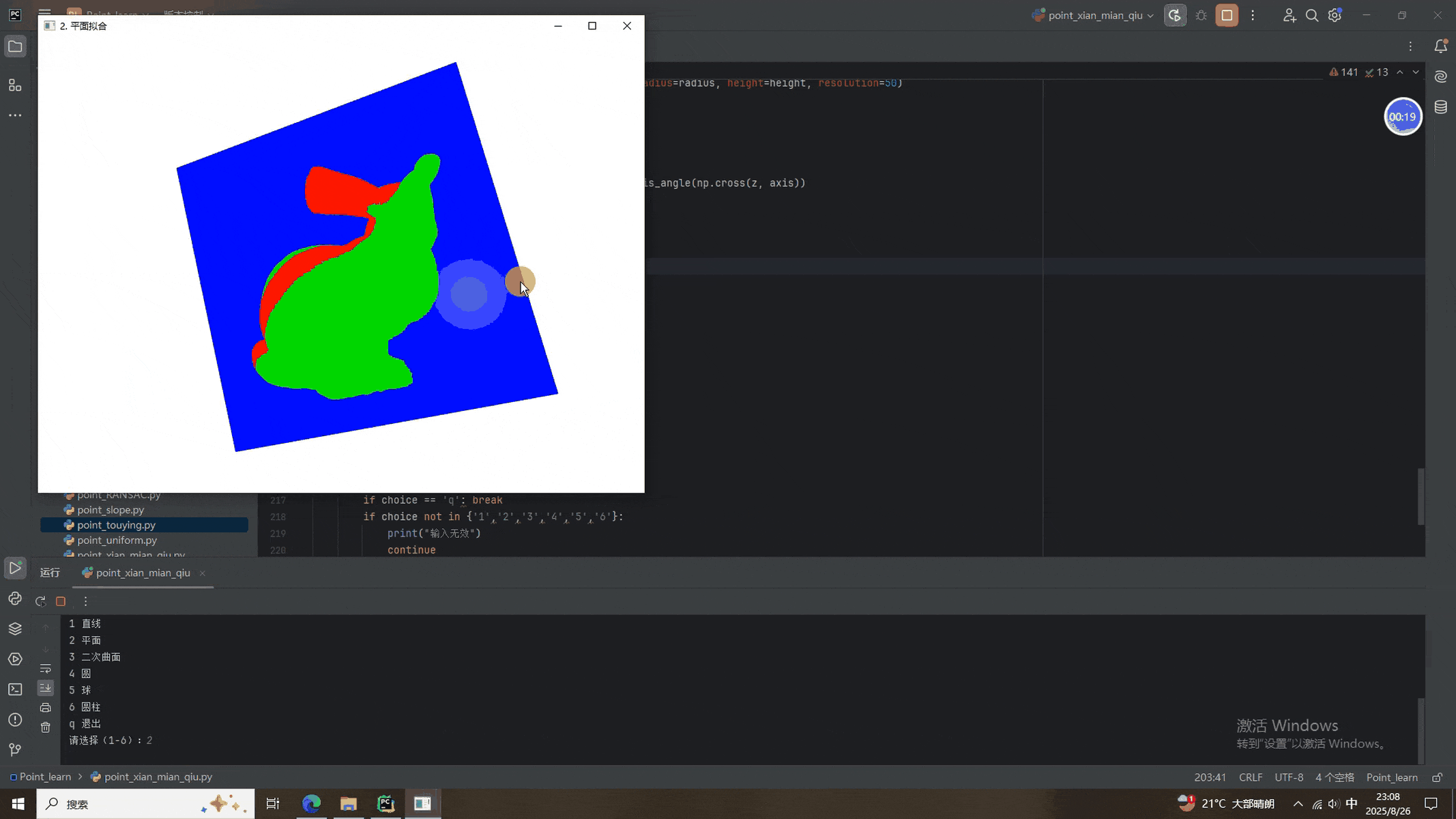
本次的程序添加了选择按钮,1-6分别是RANSAC拟合直线、平面、曲面、圆、球面、圆柱面。除了圆柱面拟合过于离谱(主要兔砸长得不像柱子),其他的都挺好。
就酱,下次见^-^
