【Linux系统】1.Linux基础指令与权限
一、Linux基础指令
ls命令[list directory contents]
Linux理论知识:
1.在windows新建一个空的文件,要占据磁盘空间(文件属性也是数据),文件=文件内容+文件属性
2.Linux系统中,可以存在隐藏文件,以 . 开头
3.文件夹 == 目录
ls命令
1.语法:ls [选项] [目录或文件]
2.功能:列出该目录下的所有子目录与文件
3.选项
(1)-a[all]:列出目录下所有文件(包含隐藏文件)
(2)-l[list]:列出文件详细信息
pwd命令[print working directory]
Linux理论知识:
1.windows中,文件的唯一性通过路径标识
2.无论windows还是Linux,登陆成功后都会默认处在默认路径下
cd命令[change directory]
Linux理论知识:路径的认识
1.Linux下,一个 . 标识当前路径,两个 . 标识上一级路径
2.任何目录下,都会隐藏存在 .(当前目录) 和 …(上级目录,像一个指针指向父节点)
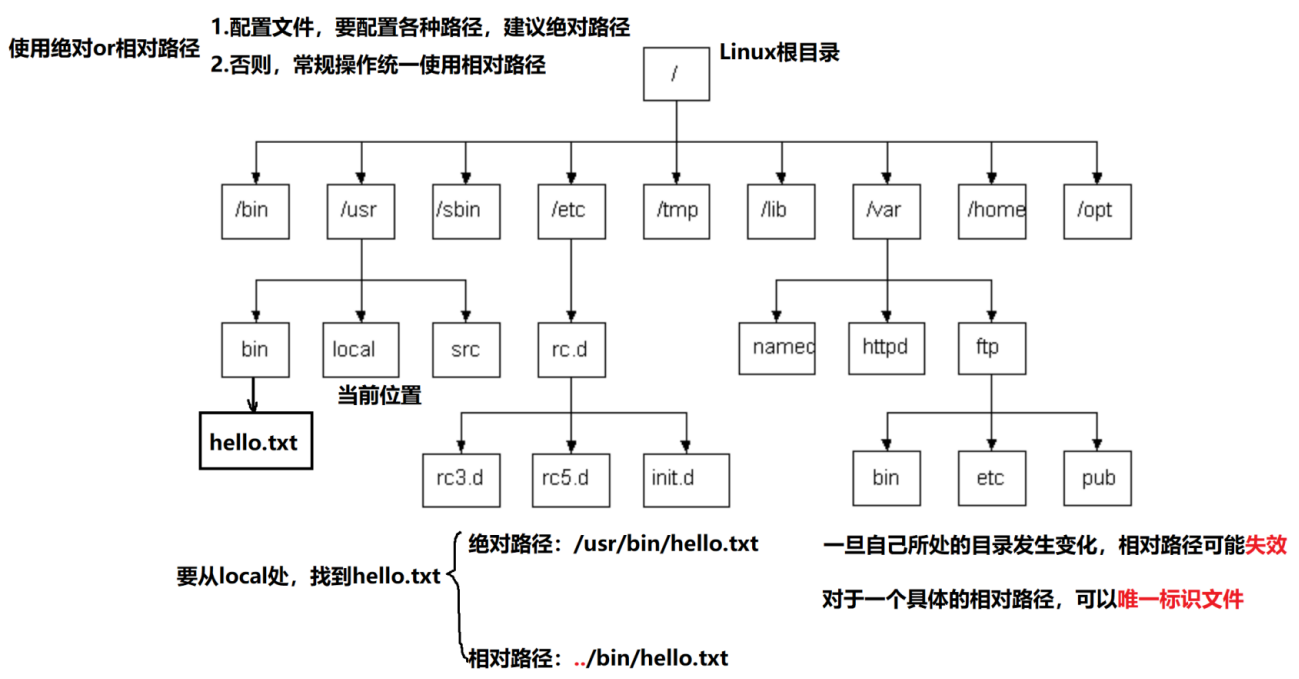
3.绝对路径:从/开始,不依赖其他目录定位文件
4.相对路径:相对于当前用户所处目录定位文件
cd命令
语法:cd 目录名
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ cd ..
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 /]$ pwd
/
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 /]$ cd ~ #快速进入家目录,root账号的家目录是:/root
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ pwd
/root
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ cd / #直接回退到最近一次所处的目录
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 /]$ pwd
/
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 /]$ cd -
/root
touch命令
功能:更改文档或目录的日期时间,包括存取时间和更改时间,或者新建一个不存在的文件
mkdir命令
Linux理论知识
Linux的文件类型——d开头表示目录文件;-开头表示普通文件,普通文件包括文本、二进制可执行程序,图片,音视频,动、静态库等
1.类型不由后缀决定
2.不代表Linux不用后缀,带后缀可以便于辨识
mkdir命令
语法:mkdir [选项] dirname
功能:在当前目录下创建一个目录
常用选项:-p,递归建立多个目录
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ mkdir dira
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ mkdir -p path1/path2/path3/path4
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ ls -l
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:07 dira#行首d开头表示目录文件
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:12 path1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 14 22:11 text.txt#行首-开头表示普通文件
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ tree
.
├── dira
├── path1
│ └── path2
│ └── path3
│ └── path4
└── text.txt
rmdir&&rm命令
最常用:rm-rf 目录名/文件名,强制删除
man命令
语法:man [选项] 命令
常用选项:num只在第num章查找
常用章节:1是普通命令,2是系统调用,3是库函数(C库函数),7是附件还有一些变量
cp命令
Linux理论知识:
1.Linux下一切皆文件
(1)向显示器打印 == 向显示器文件进行写入
(2)从键盘scanf读取数据 == 从键盘文件读
(3)终端本身也是文件,在目录 /dev/pts下
2.输出重定向与输入重定向
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ ls -l
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:07 dira
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:12 path1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 14 22:11 text.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ echo "hello world" > text.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat text.txt
hello world[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ > text.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat text.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ echo "hello world" > text.txt#输出重定向
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ echo "hello world" >> text.txt#追加重定向
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat text.txt
hello world
hello world[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat text.txt#输入重定向
hello world
hello world[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat
输入
输入

cp命令
语法:cp src dst【只能拷贝普通文件,拷贝不了目录】;cp -rf src dst【强制复制文件或目录,不论是否已经存在】
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ cp -rf test_7_14 test_7_14_backup
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ pwd
/root
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ ls -l
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:12 test_7_14
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Jul 15 09:03 test_7_14_backup
mv命令
语法:mv src dst
功能:第二个参数是文件时,mv完成重命名;第二个参数是制定目录时:剪切原来的文件,拷贝到指定路径
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ ls -l
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:07 dira
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:12 path1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24 Jul 15 09:19 text.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ mv text.txt dira#将text.txt移动到dira目录下
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ ls -l
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 15 09:41 dira
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jul 14 22:12 path1[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cd dira
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 dira]$ pwd
/root/test_7_14/dira
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 dira]$ mv text.txt test.txt#重命名
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 dira]$ ls -l
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24 Jul 15 09:19 test.txt
cat命令
语法:cat [选项] [文件]
功能:查看目标文件的内容,常用来查看小文件的内容,文件太大(如日志文件)会刷屏,用more/less更好
常用选项:
- -b:对非空输出行编号
- -n:对输出的所有行编号
- -s:不输出多行空行
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cnt=0;while [ $cnt -le 10 ]; do echo "hello ${cnt}";
let cnt++; done > temp.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cat temp.txt#从前向后查看文件
hello 0
hello 1
hello 2
hello 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
hello 10
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ tac temp.txt#从后向前查看文件
hello 10
hello 9
hello 8
hello 7
hello 6
hello 5
hello 4
hello 3
hello 2
hello 1
hello 0
more命令
语法:more [选项] 文件
功能:查看长文件,按回车向下翻
常用选项:-n指定输出行数
less命令(更强大)
语法:less [选项] 文件
功能:随意浏览文件,包括上下翻动,查关键字等
常用选项:
- /字符串:向下搜索“字符串”
- ?字符串:向上搜索“字符串”
- n:重复前一个搜索
head命令
语法:head -n 文件
功能:显示文件头n行
tail命令
Linux理论知识
管道——有入口有出口,用来传送资源(数据)
1.管道是内存级文件
2.管道可以把不同命令的功能集合在一起
tail命令
语法:tail -n 文件
功能:显示文件后n行
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ cnt=0;while [ $cnt -le 100 ]; do echo "hello ${cnt}";
let cnt++; done > temp.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_14]$ head -80 temp.txt | tail -20
hello 60
hello 61
hello 62
hello 63
hello 64
hello 65
hello 66
hello 67
hello 68
hello 69
hello 70
hello 71
hello 72
hello 73
hello 74
hello 75
hello 76
hello 77
hello 78
hello 79
date命令
主要了解时间戳:1970年1月1日物业开始到现在所经过的秒数
cal命令(了解)
显示公历日历
find命令
Linux理论知识:
1.大部分指令,本质是Linux系统固定目录下(/usr/bin)的可执行文件
2.不建议把自己定义的命令拷贝到/usr/bin路径下,会污染系统的命令池
find命令
功能:在目录结构中搜索文件
常用选项:-name 按照文件名查找文件
which命令
功能:直接在/usr/bin底下搜索文件
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'/usr/bin/ls
alias命令
功能:设置命令的别名,要删掉别名,置空即可
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ alias hello='ls -a -l -n'
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ which hello
alias hello='ls -a -l -n'/usr/bin/ls
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ hello
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 4096 Jul 16 14:43 .
dr-xr-x---. 9 0 0 4096 Jul 16 15:49 ..
file命令
功能:file+文件名,查看文件具体属性
grep命令
语法:grep [选项] 目标字符串
功能:在文件中搜索字符串,将找到的行打印出来;行文本过滤命令,默认大小写敏感
常用选项
- -n:顺便输出行号
- -v:反向选择,显示没有目标字符串内容的行
- -i:忽略大小写的不同
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ cnt=0;while [ $cnt -le 100 ]; do echo "hello ${cnt}";
> let cnt++; done > temp.txt
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ cat temp.txt | head -80 | tail -20 | grep '8'
hello 68
hello 78
应用场景:可以从日志中过滤出指定的进程
top命令
功能:调出任务管理器
常用选项
- -d:设置刷新的时间间隔
- -n:设置刷新次数
其他指令:htop
zip/unzip命令
Linux理论知识:
1.打包:多个文件形成一个文件,打包和压缩通常不区分,都是一步完成
2.为什么打包压缩?——方便网络传输or提高下载效率
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ tree
.
├── dira
│ └── test.c
└── test.txt1 directory, 2 files
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ zip -r dira.zip diraadding: dira/ (stored 0%)adding: dira/test.c (stored 0%)[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ unzip dira.zip -d dirb
Archive: dira.zipcreating: dirb/dira/extracting: dirb/dira/test.c
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ tree
.
├── dira
│ └── test.c
├── dira.zip
├── dirb
│ └── dira
│ └── test.c
└── test.txt
tar命令(重要)
压缩:tar czf test.tgz test
解压:tar xzf test.tgz #默认解压到当前目录
bc命令(了解)
bc命令可以很方便地进行浮点运算
[root@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_16]$ echo "1+2+3+4+5" | bc
15
uname -r命令
语法:uname[选项]
功能:用来获取电脑和从左系统相关信息
常用选项:-a,依次输出内核名称,主机名,内核版本号,内核版本,硬件名,处理器类型,硬件平台类型,操作系统名称
二、shell命令及运行原理
1.广义操作系统与狭义操作系统
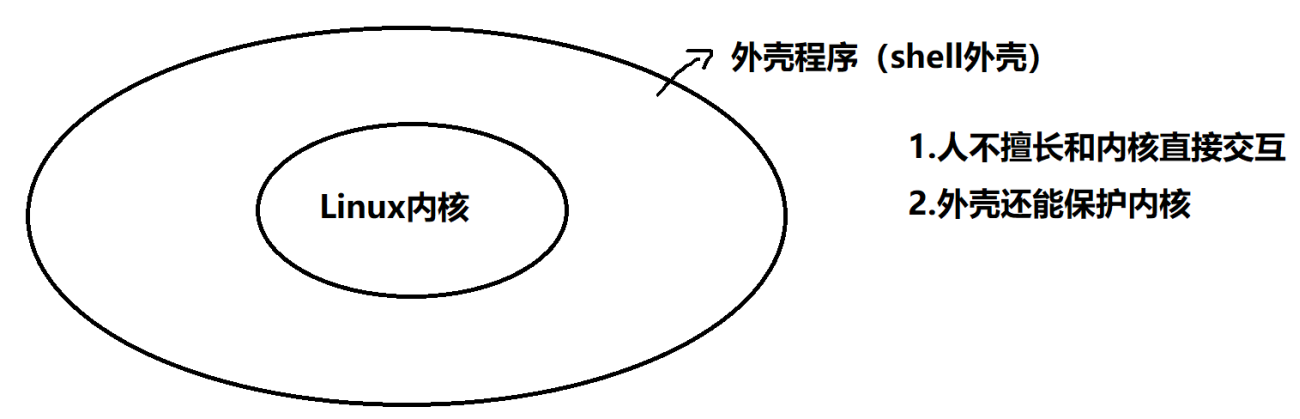
(1)广义操作系统:操作系统内核,外壳程序(shell命令行,图形化界面),必要的应用软件
(2)狭义操作系统:操作系统内核
2.shell的最简单定义
命令行解释器。把使用者的命令翻译给kernel处理,同时将kernel的处理结果翻译给使用者
3.shell外壳是所有外壳程序的统称,bash是一个具体的命令行解释器
三、Linux权限
权限相关指令:
1.chmod:设置文件的访问权限
(1)u:拥有者;g:所属组;o:other;a:所有用户
(2)例如:chmod u+r:给用户增加读权限
2.chown:更改文件拥有者
3.chgrp:更改文件所属组
4.umask:查看或修改文件掩码
1.什么叫权限?
访问资源,能还是不能的问题
2.为什么要有权限
Linux是多用户操作系统,会有多个人登录访问,权限本质是为了更好地进行用户管理
3.权限 = 人 + 文件属性
- 权限是针对特定群体的,限定人
- 目标主体必须天然具备对应的属性,才能访问(比如一个人不能在github上看视频)
- 文件属性:可读®、可写(w)、可执行(x)
(1)Linux用户的问题
①超级用户root:99%不受权限约束,属于Linux系统中的特权级别
②普通用户:受权限约束

- 如果:普通用户就要做提高权限的事情?——sudo,让普通账号短暂提权,但普通账号默认不给用sudo,因为默认不在白名单(由root管理)里,如果用户在sudoers里,则允许短暂提权
- sudo时,为啥要输普通用户的密码?——如果输的是root密码,那就相当于大家都知道root了,那么就相当于大家都掌握了root权限,都能以超级管理员的身份访问系统,这是不合理的
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ pwd
/home/pyh
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 ~]$ sudo touch test.txtWe trust you have received the usual lecture from the local System
Administrator. It usually boils down to these three things:#1) Respect the privacy of others.#2) Think before you type.#3) With great power comes great responsibility.[sudo] password for pyh:
pyh is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported.#普通用户默认不让用sudo
(2)Linux角色的问题
①权限依附于角色,角色需要人扮演
②3种角色:拥有者,所属组,other
③所属组队文件权限进行组级别的管理,是局部管理
(3)文件属性的问题
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_19]$ touch hello.txt
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_19]$ ll
total 0
-rw-rw-r-- 1 pyh pyh 0 Jul 20 10:56 hello.txt


4.没有权限会有什么表现?
(1)如果拥有者把自己的rwx权限去掉(主要为了防止误操作),此时,即使拥有者和所属组是同一个人,且所属组有rw权限,也没法读写
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_19]$ chmod u-rw hello.txt
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_19]$ ll
total 0
----rw-r-- 1 pyh pyh 0 Jul 20 10:56 hello.txt
[pyh@hcss-ecs-2126 test_7_19]$ cat hello.txt
cat: hello.txt: Permission denied

(2)关于可执行权限:文件要被执行,文件本身可执行+本身具有可执行权限=>才能成功运行
(3)文件的拥有者才有修改文件权限的能力
(4)拥有者不能改文件的拥有者和所属组
为什么?要把文件给另一个人或组,得需要别人允许,除非root来修改
5.其它三个问题
(1)目录权限:要进入一个目录需要什么权限?
① r:用户是否有权利查看制定目录下的文件属性
② w:决定用户是否有权利在该目录下新增、删除文件和修改文件名
③目录的内容:目录下文件的属性
(2)为什么:新建目录,权限是rwx rwx r-x(775),新建普通文件,权限是rw- rw- r–(664)?
①对普通文件,默认权限666;对目录文件,默认权限777
②Linux中,为了对权限作细粒度控制,产生Linux权限掩码umask,凡是出现在权限掩码中的权限,最终都应在起始权限中去掉。超级用户默认0022,普通用户默认0002
③最终权限 = 起始权限 & (~umask)
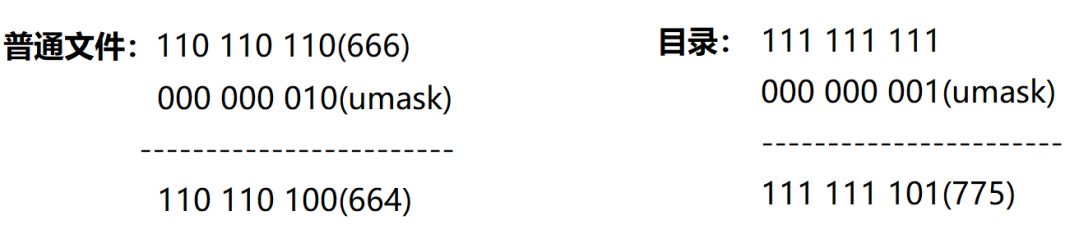
(3)文件的权限是—,可以删除吗?
可以!删一个文件,看的是目录的权限
