Huggingface入门实践 图像处理CV与多模态模型调用(二)
9.object detection.zh_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
目录
1. Object Detection 目标检测
2. Image Segmentation → 图像分割(抠图)
3. Image-Text Matching → 图文匹配
4. Image Captioning → 给图像生成标题
5. Multi-Modal Visual Q&A → 多模态视觉问答
6. Zero_Shot_Image_Classification → 图像属于哪个文本 分类
7. Text-to-Image 文本生成图像
试用一下Huggingface中的一些CV模型 和多模态模型 如BLIP CLIP
1. Object Detection 目标检测
https://huggingface.co/tasks/object-detection
https://huggingface.co/facebook/detr-resnet-50
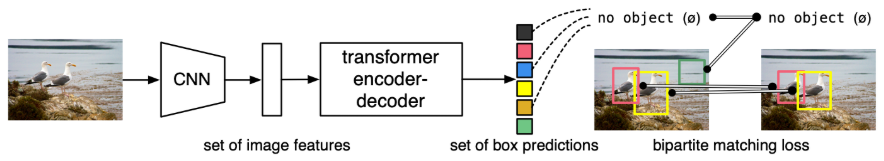
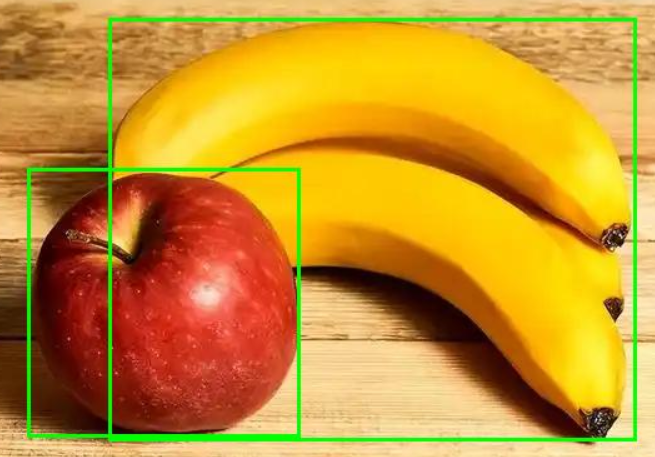
调用模型 设置置信度阈值 在draw中把方框可视化
results中可以得到 scores置信度 labels什么物体 boxes左上右下角位置
import torch
from PIL import Image
from transformers import DetrImageProcessor, DetrForObjectDetection# 1. 加载模型和处理器
processor = DetrImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50", revision="no_timm")
model = DetrForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50", revision="no_timm")# 2. 打开本地图片
image = Image.open("input.jpg").convert("RGB")# 3. 前处理 + 推理
inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)# 4. 后处理(阈值0.9)
target_sizes = torch.tensor([image.size[::-1]])
results = processor.post_process_object_detection(outputs, target_sizes=target_sizes, threshold=0.9)[0]# 5. 打印结果
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
for score, label, box in zip(results["scores"], results["labels"], results["boxes"]):box = [round(i, 2) for i in box.tolist()]print(f"Detected {model.config.id2label[label.item()]} with confidence "f"{round(score.item(), 3)} at location {box}")x0, y0, x1, y1 = [float(v) for v in box]draw.rectangle([x0, y0, x1, y1], outline=(0, 255, 0), width=3)
image.save("output.jpg")
![]()
2. Image Segmentation → 图像分割(抠图)
https://huggingface.co/tasks/image-segmentation
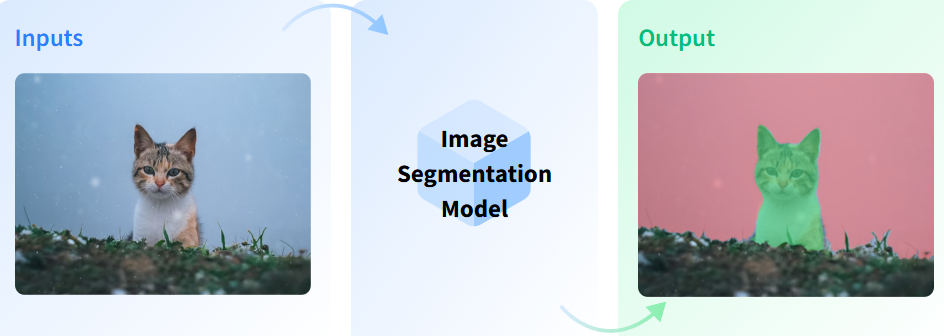
RMBG v1.4 会自动识别图片中的前景主体 实现人物和背景分开
分别实现1. 灰度掩码(白色=前景,黑色=背景)
2. putalpha 合成到原图得到 前景保留、背景透明的图片
比如对这张科比投篮的图片跑图像分割
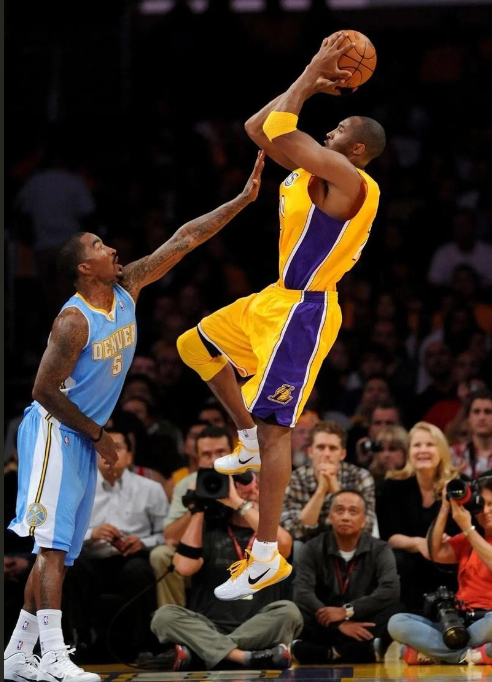

from PIL import Image
from transformers import pipeline# 1) 加载背景移除管线(RMBG v1.4)
pipe = pipeline("image-segmentation",model="briaai/RMBG-1.4",trust_remote_code=True) # 该模型需要信任自定义代码# 2) 读取你的图片
img = Image.open("input.jpg").convert("RGB")# 3) 取得前景掩码(Pillow 图像,白=前景,黑=背景)
mask = pipe(img, return_mask=True)# 4) 合成透明背景图(把掩码作为 alpha 通道)
rgba = img.copy()
rgba.putalpha(mask)# 5) 保存结果
mask.save("mask.png") # 灰度掩码
rgba.save("output_no_bg.png") # 透明背景图可以得到下面两张图像
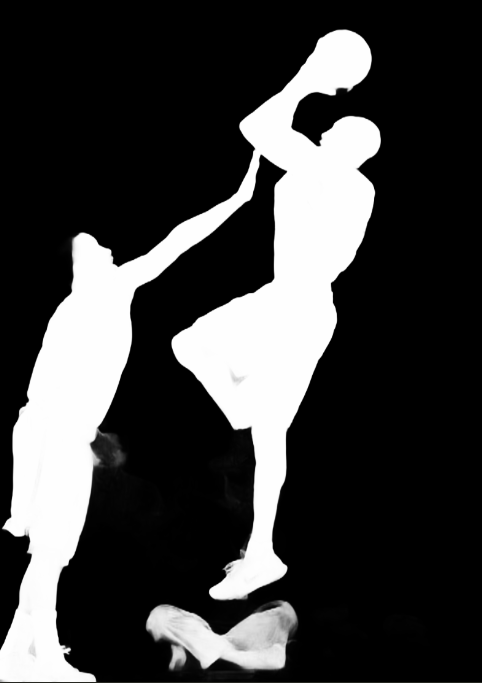
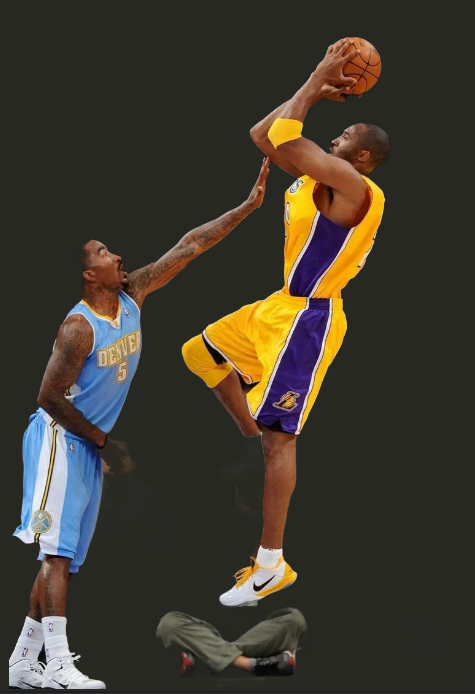


后面我们开始学习一些图文理解/生成的多模态模型
主要用到BLIP Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training
3. Image-Text Matching → 图文匹配
https://huggingface.co/Salesforce/blip-itm-base-coco
图文匹配的概率和预先相似度
"A woman and a dog sitting together in a beach."
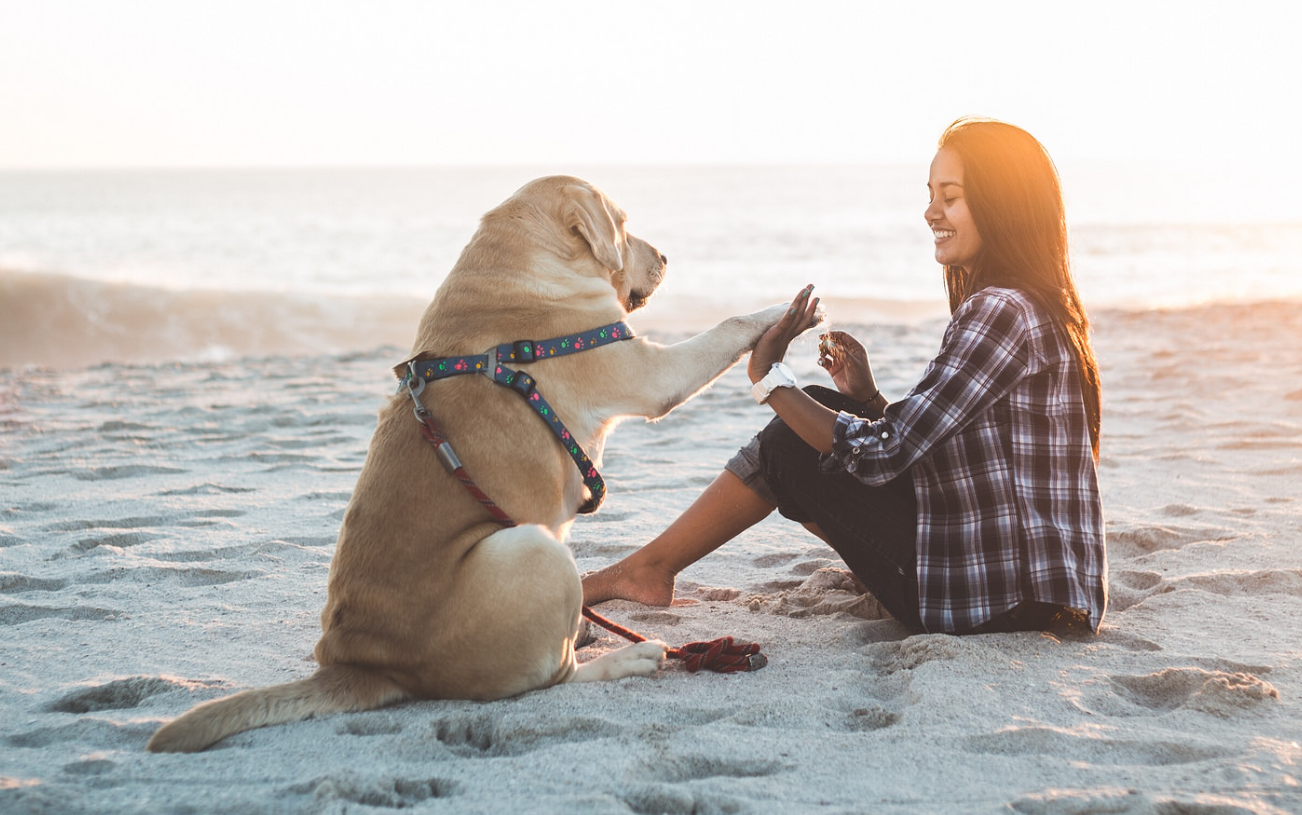

import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import BlipProcessor, BlipForImageTextRetrieval
# -------- 加载模型与处理器 --------
processor = BlipProcessor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-itm-base-coco")
model = BlipForImageTextRetrieval.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-itm-base-coco", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
# -------- 准备数据 --------
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
text = "A woman and a dog sitting together in a beach."
inputs = processor(raw_image, text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)# 计算图像与文本是否匹配的概率
out_itm = model(**inputs, return_dict=True)
probs = F.softmax(out_itm.itm_score, dim=-1) # 概率分布softmax 前为不匹配 后为匹配
print(f"ITM -> P(match)={probs[0, 1].item():.4f}, P(not match)={probs[0, 0].item():.4f}")# 计算图像与文本的余弦相似度
out_cos = model(**inputs, use_itm_head=False, return_dict=False)
print(f"Cosine similarity (image-text) -> {out_cos[0].item():.4f}")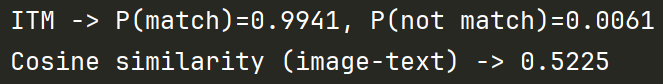
4. Image Captioning → 给图像生成标题
https://huggingface.co/Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-base
让模型文字描述这张图片 还是刚才上面那个“女生和小狗的例子”
可以给定生成的文本的开头;也可以让模型自由发挥
通过process转化为张量inputs -> generate生成张量out -> decode生成文字
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import BlipProcessor, BlipForConditionalGenerationprocessor = BlipProcessor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-base")
model = BlipForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip-image-captioning-base", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')# -------- 示例:条件式(更可控的语气/风格) --------
text = "a photography of"
inputs = processor(raw_image, text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))# -------- 示例:无条件(模型自由发挥) --------
inputs = processor(raw_image, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))比如 是否给定text 开头为"a photography of" 两个输出分别为

5. Multi-Modal Visual Q&A → 多模态视觉问答
https://huggingface.co/Salesforce/blip-vqa-base
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import BlipProcessor, BlipForQuestionAnsweringprocessor = BlipProcessor.from_pretrained("ybelkada/blip-vqa-base")
model = BlipForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("ybelkada/blip-vqa-base", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')for question in ["how many dogs are in the picture?", "how many cats are in the picture?"]:inputs = processor(image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)out = model.generate(**inputs)print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))6. Zero_Shot_Image_Classification → 图像属于哪个文本 分类
CLIP 把图片和文字投射到同一个语义空间,从而可以直接比较图片和文字是否相关
from PIL import Image
import requests
from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModelmodel = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
inputs = processor(text=["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"], images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)outputs = model(**inputs)
print(outputs.logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1)) # 图片属于每个文本的概率分别可以得到 图片分类为inputs里的文本的概率 下面代表99.9%的概率属于前者(图片是猫)
![]()
7. Text-to-Image 文本生成图像
https://huggingface.co/tasks/text-to-image
使用 diffusers Hugging Face 的 扩散模型工具库
UNet 配置加载 Lightning 蒸馏权重; 替换调度器为 EulerDiscrete + “trailing” 时间步
潜空间多步去噪 → 解码为图像
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, EulerDiscreteScheduler
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
from safetensors.torch import load_filebase = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
repo = "ByteDance/SDXL-Lightning"
ckpt = "sdxl_lightning_4step_unet.safetensors" # 使用4步UNet权重# 1. 加载基础 UNet 架构
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_config(base, subfolder="unet").to("cuda", torch.float16)# 2. 加载 Lightning 蒸馏权重
unet.load_state_dict(load_file(hf_hub_download(repo, ckpt), device="cuda"))# 3. 构建 pipeline
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(base, unet=unet, torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
).to("cuda")# 4. 设置 scheduler
pipe.scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config, timestep_spacing="trailing"
)# 5. 文本生成图片 (4步推理 + guidance_scale=0)
image = pipe("A dog smiling", num_inference_steps=4, guidance_scale=0).images[0]
image.save("output.png")

