MATLAB入门教程
MATLAB Documentation![]() https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/index.html?s_tid=CRUX_topnav
https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/matlab/index.html?s_tid=CRUX_topnav
基础操作与变量
变量定义与数据类型
MATLAB中字符数组与字符串数组的区别_matlab字符串数组和字符数组的区别-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/houor/article/details/121622121
https://blog.csdn.net/houor/article/details/121622121
% 标量
a = 5; % 双精度浮点数
b = 3 + 4i; % 复数
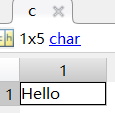
c = 'Hello'; % 字符数组
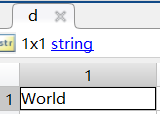
d = "World"; % 字符串% 数组和矩阵
vector = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; % 行向量
matrix = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9]; % 3x3矩阵% 特殊矩阵
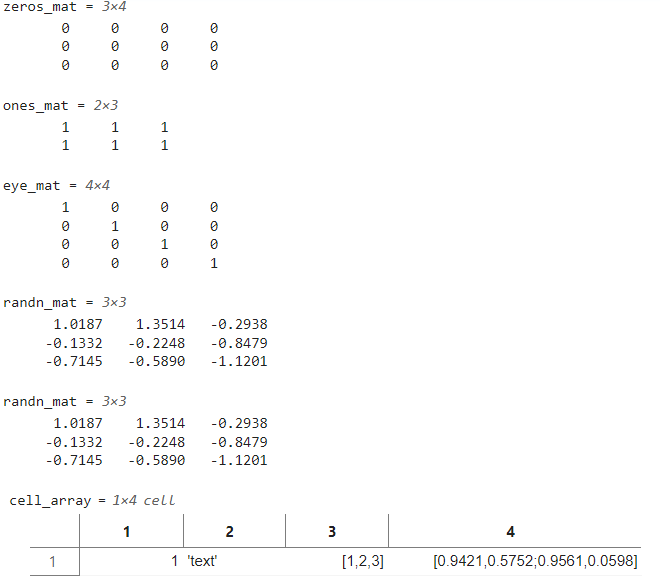
zeros_mat = zeros(3, 4); % 3x4零矩阵
ones_mat = ones(2, 3); % 2x3全1矩阵
eye_mat = eye(4); % 4x4单位矩阵
rand_mat = rand(2, 3); % 2x3随机矩阵(0-1均匀分布)
randn_mat = randn(3, 3); % 3x3正态分布随机矩阵% 元胞数组(可存储不同类型数据)
cell_array = {1, 'text', [1, 2, 3], rand(2,2)};% 结构体
person.name = 'feng';
person.age = 21;
person.scores = [85, 92, 78];使用单引号是字符数组,双引号是字符串。
| 特性 | 字符数组 | 字符串 |
|---|---|---|
| 定义方式 | 单引号 'text' | 双引号 "text" |
| 数据类型 | char | string |
| 空值表示 | '' (0×0) | "" (1×1) |
| 拼接操作 | [str1, str2] | str1 + str2 |
| 内存效率 | 更高 | 稍低 |
| 函数支持 | 传统函数 | 现代函数 |
| 数组处理 | 需要元胞数组 | 原生支持 |

常用基础函数
下面代码正常运行需要把matrix,vector数组和矩阵进行定义。
% 显示和获取信息
disp('Hello MATLAB'); % 显示文本
whos % 显示工作区变量信息
size(matrix) % 获取矩阵维度
length(vector) % 获取向量长度
numel(matrix) % 获取矩阵元素总数% 数据类型转换
str = num2str(123); % 数字转字符串
num = str2double('456'); % 字符串转数字
int_val = int8(100); % 转换为8位整数矩阵操作与运算
基本矩阵运算
A = [1, 2; 3, 4];
B = [5, 6; 7, 8];% 算术运算
C = A + B; % 矩阵加法
D = A - B; % 矩阵减法
E = A * B; % 矩阵乘法
F = A .* B; % 元素对应相乘(点乘)
G = A / B; % 矩阵右除(A*inv(B))
H = A \ B; % 矩阵左除(inv(A)*B)
I = A .^ 2; % 每个元素平方% 矩阵函数
det_A = det(A); % 行列式
inv_A = inv(A); % 逆矩阵
rank_A = rank(A); % 矩阵的秩
trace_A = trace(A); % 矩阵的迹
[eig_vec, eig_val] = eig(A); % 特征值和特征向量

索引和切片
这里不是从0开始算索引。
M = magic(5); % 创建5x5魔方矩阵% 索引访问
element = M(2, 3); % 第2行第3列元素
row = M(3, :); % 第3行所有元素
column = M(:, 4); % 第4列所有元素
submatrix = M(2:4, 1:3); % 第2-4行, 第1-3列子矩阵% 逻辑索引
idx = M > 20; % 逻辑索引矩阵
large_values = M(idx); % 获取大于20的元素% 线性索引
linear_idx = M(6); % 按列优先的第6个元素
流程控制
条件语句
这个elseif是连着一起的,和其他编程语言本质上是一样的,就是关键字和写法上有的区别。
% if-elseif-else语句
x = 10;
if x > 0disp('正数');
elseif x < 0disp('负数');
elsedisp('零');
end% switch语句
day = 'Monday';
switch daycase {'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday'}disp('工作日');case {'Saturday', 'Sunday'}disp('周末');otherwisedisp('未知日期');
end循环语句
循环也和其他语言类似,需要注意的是末尾需要end。
% for循环
sum_for = 0;
for i = 1:10sum_for = sum_for + i;
end% while循环
sum_while = 0;
n = 1;
while n <= 10sum_while = sum_while + n;n = n + 1;
end% 向量化操作(比循环更高效)
sum_vec = sum(1:10);函数编程
函数定义与使用
MATLAB函数句柄详解-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/edward_zcl/article/details/90231453MATLAB的编程与应用,匿名函数、嵌套函数、蒙特卡洛法的掌握与使用_matlab匿名函数-CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/edward_zcl/article/details/90231453MATLAB的编程与应用,匿名函数、嵌套函数、蒙特卡洛法的掌握与使用_matlab匿名函数-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Williamtym/article/details/134356032
https://blog.csdn.net/Williamtym/article/details/134356032
% 在myFunction.m文件中定义函数
function [output1, output2] = myFunction(input1, input2)% 函数说明:计算两个数的和与积output1 = input1 + input2;output2 = input1 * input2;
end% 调用函数
[a, b] = myFunction(3, 4); % a=7, b=12% 匿名函数
square = @(x) x.^2;
result = square(5); % result=25% 函数句柄
f = @sin; % 创建sin函数的句柄
y = f(pi/2); % y=1
数据可视化
基本绘图函数
% 创建数据
x = linspace(0, 2*pi, 100);
y1 = sin(x);
y2 = cos(x);% 线图
figure(1);
plot(x, y1, 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2); % 红色实线
hold on; % 保持当前图形
plot(x, y2, 'b--', 'LineWidth', 2); % 蓝色虚线
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
title('正弦和余弦函数');
legend('sin(x)', 'cos(x)');
grid on;
hold off;% 散点图
figure(2);
scatter(x(1:10:end), y1(1:10:end), 50, 'filled');
title('散点图示例');% 直方图
figure(3);
data = randn(1000, 1);
histogram(data, 30);
title('正态分布数据直方图');% 子图
figure(4);
subplot(2, 2, 1);
plot(x, y1);
title('子图1');subplot(2, 2, 2);
plot(x, y2);
title('子图2');subplot(2, 2, [3, 4]);
plot(x, y1 + y2);
title('子图3和4合并');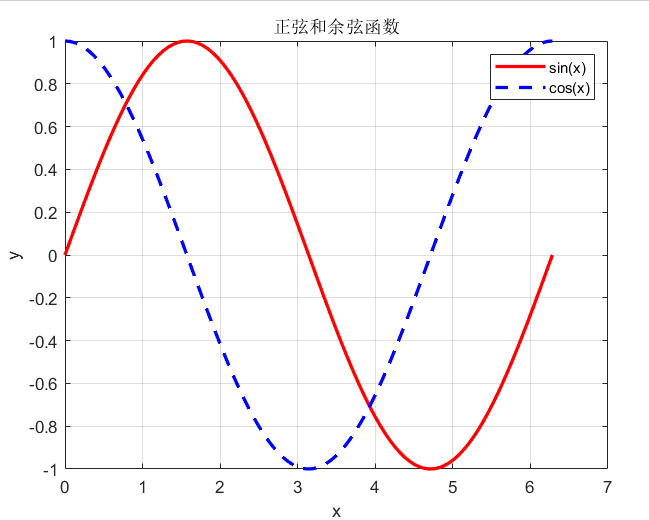
3D绘图
% 3D曲面图
[X, Y] = meshgrid(-2:0.1:2, -2:0.1:2);
Z = X .* exp(-X.^2 - Y.^2);figure(5);
surf(X, Y, Z);
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
zlabel('Z');
title('3D曲面图');
colorbar;% 3D曲线图
t = linspace(0, 10*pi, 1000);
x = sin(t);
y = cos(t);
z = t;figure(6);
plot3(x, y, z, 'LineWidth', 2);
grid on;
title('3D螺旋线');
文件I/O操作
读写数据文件
% 保存和加载.mat文件
data = rand(5, 5);
save('myData.mat', 'data'); % 保存变量到文件
clear data; % 清除变量
load('myData.mat'); % 从文件加载变量% 读写文本文件
% 写入文本文件
fid = fopen('data.txt', 'w');
fprintf(fid, '%d %f %s\n', 1, 3.14, 'pi');
fclose(fid);% 读取文本文件
fid = fopen('data.txt', 'r');
data_cell = textscan(fid, '%d %f %s');
fclose(fid);% 读写Excel文件
% 写入Excel
xlswrite('data.xlsx', magic(5), 'Sheet1');% 读取Excel
[num, txt, raw] = xlsread('data.xlsx', 'Sheet1');% 读写CSV文件
% 写入CSV
csvwrite('data.csv', rand(3, 3));% 读取CSV
csv_data = csvread('data.csv');常用内置函数
数学函数
% 基本数学函数
abs_value = abs(-5); % 绝对值
sqrt_value = sqrt(16); % 平方根
exp_value = exp(1); % 指数函数
log_value = log(10); % 自然对数
log10_value = log10(100); % 以10为底的对数% 三角函数
sin_val = sin(pi/2); % 正弦
cos_val = cos(pi); % 余弦
tan_val = tan(pi/4); % 正切% 取整函数
round_val = round(3.6); % 四舍五入
floor_val = floor(3.6); % 向下取整
ceil_val = ceil(3.2); % 向上取整
fix_val = fix(-3.6); % 向零取整% 统计函数
data = randn(100, 1);
mean_val = mean(data); % 均值
median_val = median(data); % 中位数
std_val = std(data); % 标准差
var_val = var(data); % 方差
max_val = max(data); % 最大值
min_val = min(data); % 最小值字符串操作
% 字符串创建和连接
str1 = 'Hello';
str2 = 'MATLAB';
combined = [str1, ' ', str2]; % 字符串连接% 字符串函数
length_str = length(str1); % 字符串长度
upper_str = upper(str1); % 转换为大写
lower_str = lower(str2); % 转换为小写
strcmp_result = strcmp(str1, str2); % 字符串比较
find_str = strfind(combined, 'MAT'); % 查找子串
replace_str = strrep(combined, 'MATLAB', 'World'); % 替换子串% 字符串分割和组合
split_str = split('a,b,c', ','); % 分割字符串
join_str = join(split_str, '-'); % 组合字符串高级功能
时间处理
% 当前时间
current_time = now; % 当前日期时间(序列号)
datetime_str = datestr(now); % 转换为字符串
datetime_obj = datetime('now'); % 创建datetime对象(R2014b+)% 时间计算
start_time = datetime('2023-01-01');
end_time = datetime('2023-12-31');
duration = end_time - start_time; % 时间间隔% 计时
tic; % 开始计时
pause(2); % 暂停2秒
elapsed_time = toc; % 获取经过时间错误处理
% try-catch语句
tryresult = 1/0; % 可能出错的操作
catch MEdisp(['错误发生: ', ME.message]);% 其他错误处理代码
end% 警告处理
warning('这是一个警告消息'); % 发出警告
lastwarn(''); % 清除最后警告实用技巧和最佳实践
代码优化
% 预分配内存(提高循环效率)
n = 10000;
% 不好的做法(不预分配)
% result = [];
% for i = 1:n
% result = [result, i^2];
% end% 好的做法(预分配)
result = zeros(1, n);
for i = 1:nresult(i) = i^2;
end% 向量化操作(比循环更快)
result_vec = (1:n).^2;% 使用逻辑索引
data = randn(1000, 1);
positive_data = data(data > 0); % 获取正数元素调试技巧
% 设置断点
% 在编辑器中点击行号左侧设置断点,或使用:
dbstop in myFunction at 10; % 在myFunction第10行设置断点% 调试命令
dbcont; % 继续执行
dbstep; % 单步执行
dbquit; % 退出调试模式% 检查变量
keyboard; % 暂停执行,进入调试模式