JS 中的 this
一、this 的指向
在 JS 中,this 作为关键字,它的场景是函数,this 是函数里的内置对象,即它是JS标准中已经定义好的,无需显式创建的,用于指代的对象。
1.当 this 所在函数是事件处理函数时,它表示的是事件源。
2.当 this 所在函数是构造函数,它表示的是 new 出来的这个实例对象。也就是说当 this 单纯作为代码放在那里时,它是没有实际意义的,只有当这个对象被 new 出来的那一刻,才会赋予其指代的意义。
3.当 this 所在函数是类中的方法时,它表示调用这个方法的那个对象。
4.当 this 所在函数不是以上情况时,它表示 window对象。
所以,要分辨 this 是谁,需要看函数的调用方式,而不是只看函数被定义的位置。
箭头函数不会创建自己的 this,而是继承外层作用域的 this。也可以说箭头函数的 this 会穿透到上一级。在看 this 指向时,忽略掉箭头函数即可。
二、this 穿透的实现方式
在 JS 中,“this 穿透”是指在多层嵌套函数或回调函数中,保持外层 this 值的技术。
为什么需要 this 穿透?
JS 中的 this 是动态绑定的,在嵌套函数中往往会丢失原始上下文,因此需要特殊技术来穿透多层作用域。
class User {constructor(name) {this.name = name;}greet() {console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${this.name}`);// 嵌套函数中 this 丢失function nestedFunction() {console.log(`Nested function: Hello, ${this.name}`); // undefined}nestedFunction();}
}const user = new User("Alice");
user.greet();1.使用箭头函数(推荐)
class User {// ...greet() {console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${this.name}`);const nestedArrow = () => {console.log(`Arrow function: Hello, ${this.name}`); // Alice};nestedArrow();}
}2.保存 this 引用(经典)
class User {// ...greet() {const that = this; // 保存 this 引用console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${that.name}`);function nestedFunction() {console.log(`Nested function: Hello, ${that.name}`); // Alice}nestedFunction();}
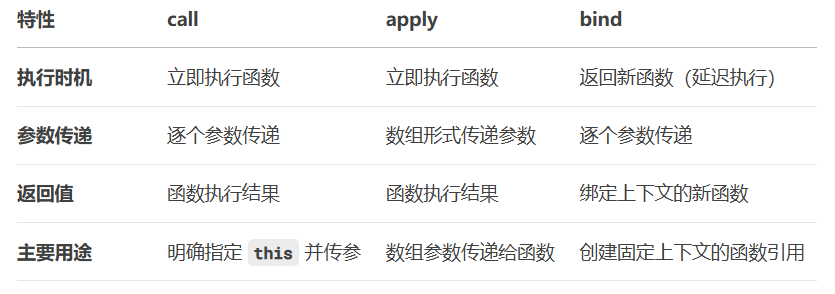
}3.使用 bind 改变 this 的指向
class User {// ...greet() {console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${this.name}`);const boundFunction = function() {console.log(`Bound function: Hello, ${this.name}`); // Alice}.bind(this);boundFunction();}
}函数.bind(对象),bind 函数里的对象(实参)就是 this。
bind 不会调用函数(延迟执行),而是产生新的函数。新产生的函数里,this永远都是绑定的 this。
4.使用 call / apply 改变 this 的指向
class User {// ...greet() {console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${this.name}`);function nestedFunction() {console.log(`Called function: Hello, ${this.name}`); // Alice}nestedFunction.call(this); // 显式绑定 this}
}函数.call(对象),call 函数里的对象(实参)就是 this。
call 或者 apply 会直接调用函数(立即执行)。this 只是临时改变一下。
5.使用 Proxy 代理(高级)
class ThisProxy {constructor(context) {return new Proxy(this, {get: (target, prop) => {if (prop in target) return target[prop];return context[prop];}});}
}class User {constructor(name) {this.name = name;this.proxy = new ThisProxy(this);}greet() {console.log(`Main function: Hello, ${this.name}`);function nestedFunction() {console.log(`Proxy function: Hello, ${this.proxy.name}`); // Alice}nestedFunction.call(this.proxy);}
}三、this 穿透在实际开发中的应用场景
1. 事件处理函数
class Button {constructor() {this.text = "Click me!";this.button = document.createElement("button");// 错误方式:this 丢失// this.button.addEventListener("click", this.handleClick);// 正确方式:箭头函数实现 this 穿透this.button.addEventListener("click", () => this.handleClick());}handleClick() {console.log(`Button text: ${this.text}`); // 正确访问}
}2. 异步操作
class DataFetcher {constructor(url) {this.url = url;this.data = null;}fetchData() {// 使用箭头函数保持 thisfetch(this.url).then(response => response.json()).then(data => {this.data = data; // 正确设置实例属性this.processData();});}processData() {console.log("Processing:", this.data);}
}3. 高阶函数
class Calculator {constructor(base) {this.base = base;}createAdder() {// 返回的函数需要访问实例的 this.basereturn (value) => this.base + value;}
}const calc = new Calculator(10);
const addFive = calc.createAdder();
console.log(addFive(5)); // 15四、call 、apply 和 bind 的区别