MyBatis Mapper核心组件协作关系深度解析
本篇文章为本人之前所写的《深入浅出MyBatis:Mapper接口的工作原理与使用流程》的后续。
目录
前言
一、核心三角关系图解
二、组件职责与协作时序
1. MapperProxy - 动态代理的入口
2. MapperMethod - 方法执行引擎
3. MappedStatement - SQL操作蓝图
三、三组件协作流程图解
四、关键协作节点详解
五、设计思想:职责分离
1.MapperProxy - 门面层:
2.MapperMethod - 转换层
3.MappedStatement - 元数据层
总结
前言
在之前我为大家介绍了Mapper接口的工作原理与使用流程,其中提到了三大核心组件协作,这次让我们聚焦MapperProxy、MapperMethod和MappedStatement这三个核心组件的协作逻辑,通过实际代码执行流程揭示它们的工作关系:
一、核心三角关系图解
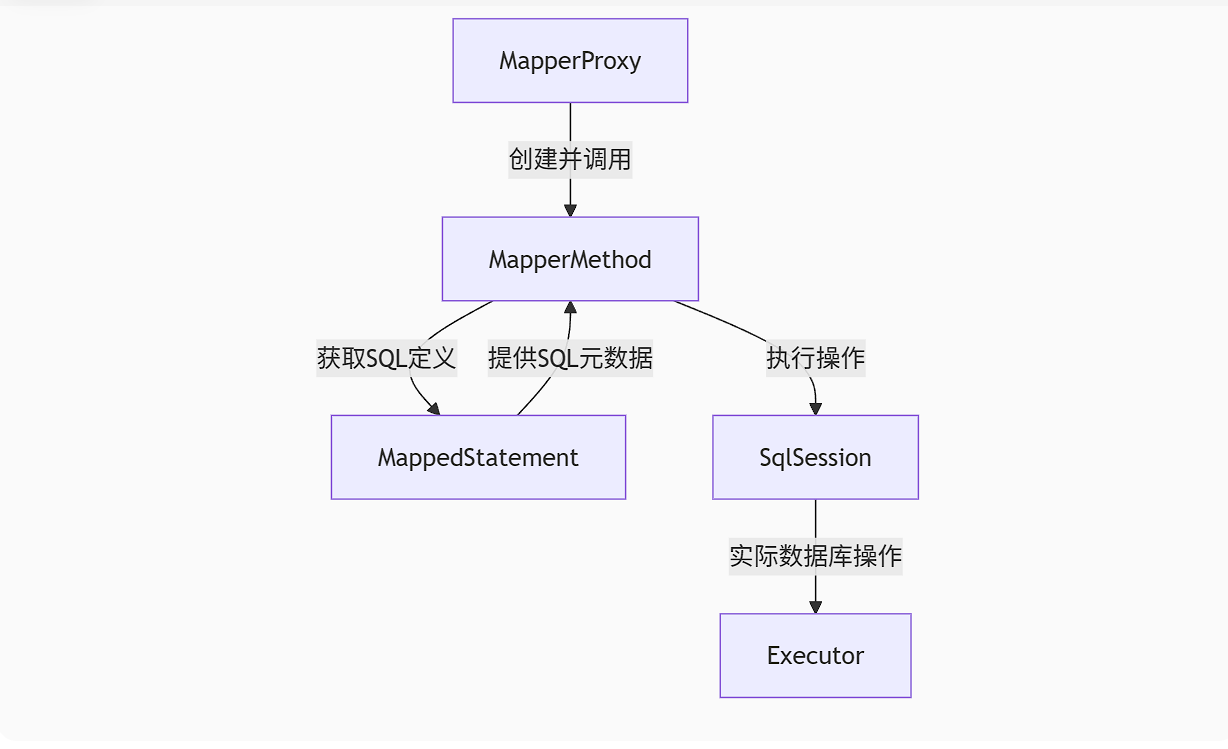
二、组件职责与协作时序
1. MapperProxy - 动态代理的入口
核心职责:拦截所有Mapper接口方法调用,路由到MapperMethod
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler {public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {// 1. 过滤Object原生方法if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);}// 2. 创建或获取MapperMethod实例(缓存优化)MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);// 3. 将调用委托给MapperMethod执行return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
}2. MapperMethod - 方法执行引擎
核心职责:将Java方法调用转化为具体的SQL操作指令
public class MapperMethod {// 两个关键子组件private final SqlCommand command; // 关联SQL类型和IDprivate final MethodSignature method; // 方法签名元数据public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {// 1. 获取MappedStatement(通过Configuration)MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());// 2. 根据SQL类型路由执行switch (command.getType()) {case SELECT:if (method.returnsVoid()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMany()) {return executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else {return executeForObject(sqlSession, args);}case INSERT:return executeInsert(sqlSession, args);// UPDATE/DELETE 类似...}}private Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {// 3. 参数转换Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 4. 执行SQL操作return sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);}
}3. MappedStatement - SQL操作蓝图
核心职责:存储SQL执行的完整元数据
public final class MappedStatement {private String id; // 全限定方法名:com.example.UserMapper.selectByIdprivate SqlSource sqlSource; // SQL脚本源码private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType; // SELECT/INSERT等// 结果映射配置private ResultMap resultMap;private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;// 参数映射配置private ParameterMap parameterMap;
}三、三组件协作流程图解
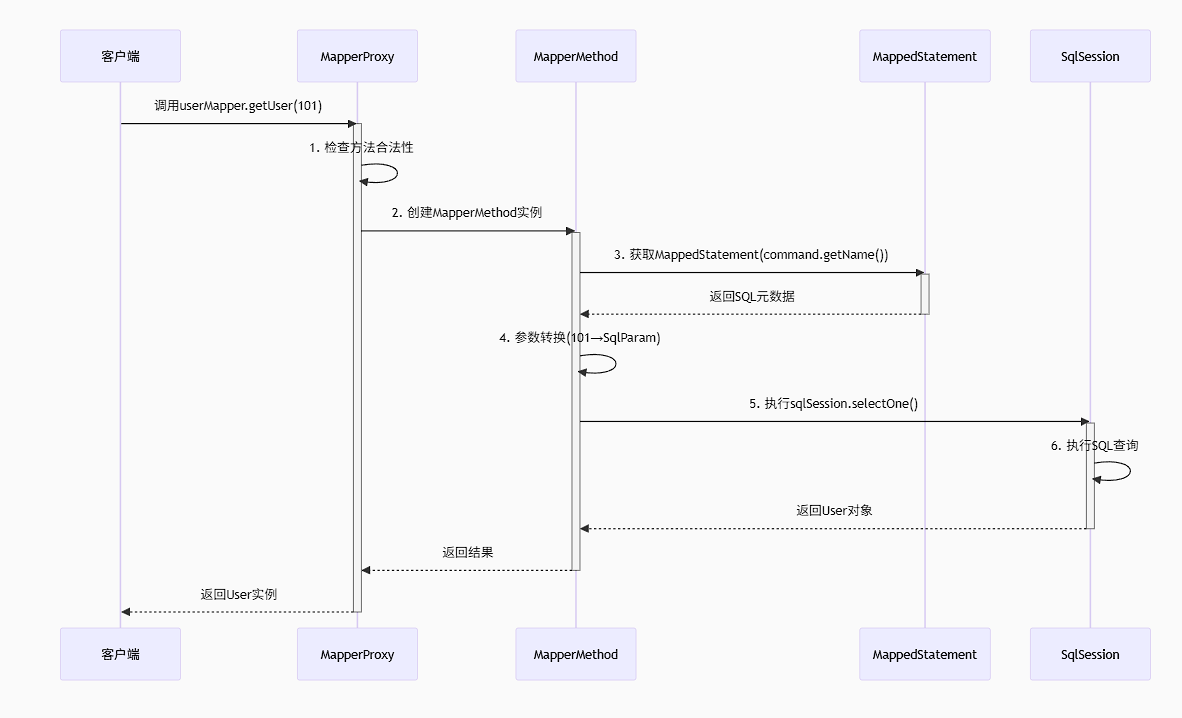
四、关键协作节点详解
节点1:方法路由(MapperProxy → MapperMethod)
触发条件:任何Mapper接口方法调用
核心操作:
// 在MapperProxy中
if ("selectUser".equals(method.getName())) {// 创建处理select操作的MapperMethodreturn new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()).execute(sqlSession, args);
}节点2:SQL元数据绑定(MapperMethod → MappedStatement)
查找逻辑:
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName()
);元数据示例:
ms.getId() // "com.example.UserMapper.selectUser"
ms.getSqlCommandType() // SqlCommandType.SELECT
ms.getResultMaps() // [UserResultMap]
节点3:参数转换与执行(MapperMethod → SqlSession)
参数处理:
// 将Java参数转换为SQL可识别格式
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 示例:将@Param注解参数转为Map
// 输入:[101, "active"] → 输出:{"id":101, "status":"active"}执行分发:
// 根据方法返回类型选择执行方式
if (method.returnsMany()) {return sqlSession.selectList(ms.getId(), param);
} else {return sqlSession.selectOne(ms.getId(), param);
}五、设计思想:职责分离
1.MapperProxy - 门面层:
负责接口层面的代理和路由
隔离Java接口与执行逻辑
2.MapperMethod - 转换层
桥接Java方法与SQL操作
处理参数转换和结果映射决策
3.MappedStatement - 元数据层
充当SQL操作的蓝图仓库
解耦SQL定义与执行环境
总结
这三个组件形成了MyBatis的执行链骨架。MapperProxy是入口,MapperMethod是转换引擎,MappedStatement是操作蓝图。它们通过严格的分层协作,将简单的Java方法调用转化为复杂的数据库操作,同时保持各层的独立性和可扩展性。这种设计使得MyBatis既能提供简洁的接口,又能处理复杂的SQL场景。
