WebSocket集群方案解析与实现
一、WebSocket集群核心挑战
1.1 关键问题分析
1.2 方案对比矩阵
| 方案类型 | 实现复杂度 | 网络开销 | 可靠性 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 广播方案 | 低 | 高 | 中 | 小规模集群 |
| 目标询址 | 中 | 低 | 高 | 中大规模系统 |
| 共享存储 | 高 | 中 | 高 | 高一致性要求 |
二、广播方案深度实现
2.1 服务端核心逻辑
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{businessType}/{userId}")
@Component
public class BroadcastWebSocket {private static final Map<String, Session> LOCAL_SESSIONS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();@OnOpenpublic void onOpen(@PathParam("userId") String userId, Session session) {LOCAL_SESSIONS.put(userId, session);// 可添加Redis订阅逻辑}@MessageMapping("/topic/notify")@SendToUser("/queue/notice")public void handleBroadcast(Message message) {// 消息处理逻辑}
}
2.2 消息消费者实现
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class OrderMessageConsumer {private final SimpMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate;@RabbitListener(queues = "order.queue")public void handleOrderMessage(OrderMessage message) {messagingTemplate.convertAndSendToUser(message.getUserId(),"/queue/orders",message.getContent());}
}
三、目标询址方案完整实现
3.1 服务注册与发现
@Configuration
public class ServiceRegistryConfig {@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ServiceInstance serviceInstance(@Value("${server.port}") int port,@Value("${spring.application.name}") String appName) {return new DefaultServiceInstance(appName + "-" + IdUtil.simpleUUID(),appName,getLocalHost(),port,false);}private String getLocalHost() {try {return InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();} catch (UnknownHostException e) {return "127.0.0.1";}}
}
3.2 路由服务实现
@Service
public class RoutingService {private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;private final RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;public String getTargetService(String userId) {String serviceName = redisTemplate.opsForHash().get("ws:mapping", userId);return discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceName).stream().findFirst().map(instance -> instance.getUri().toString()).orElseThrow();}
}
3.3 Feign客户端配置
@FeignClient(name = "ws-client", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface WsClient {@PostMapping("/push/{userId}")void pushMessage(@PathVariable String userId,@RequestBody PushMessage message);class FeignConfig {@Beanpublic RequestInterceptor routingInterceptor(RoutingService routingService) {return template -> {String userId = template.pathVariables().get("userId");String baseUrl = routingService.getTargetService(userId);template.target(baseUrl);};}}
}
四、生产环境优化策略
4.1 会话健康检查
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000)
public void checkAliveSessions() {LOCAL_SESSIONS.forEach((userId, session) -> {try {session.getAsyncRemote().sendPing(ByteBuffer.wrap("HB".getBytes()));} catch (Exception e) {LOCAL_SESSIONS.remove(userId);redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete("ws:mapping", userId);}});
}
4.2 负载均衡策略
spring:cloud:loadbalancer:configurations: zone-preferencenacos:discovery:cluster-name: ${ZONE:default}
五、异常处理与容灾
5.1 回退机制实现
@Slf4j
public class WsClientFallback implements WsClient {private final MessageStore messageStore;@Overridepublic void pushMessage(String userId, PushMessage message) {messageStore.saveUndelivered(userId, message);log.warn("消息暂存,等待重试: {}", message);}
}
5.2 消息重试队列
@Bean
public MessageRecoveryRecovery recoveryStrategy() {return new ExponentialBackOffRecovery() {@Overridepublic void recover(Message message) {// 自定义重试逻辑}};
}
六、性能监控方案
6.1 监控指标采集
@Bean
public MeterBinder wsMetrics(WebSocketSessionRegistry registry) {return registry -> {Gauge.builder("websocket.sessions",() -> registry.getSessionCount()).register(registry);};
}
6.2 Grafana监控面板
{"panels": [{"title": "WebSocket Sessions","targets": [{"expr": "sum(websocket_sessions_active)","legendFormat": "Active Sessions"}]}]
}
七、方案选型决策指南
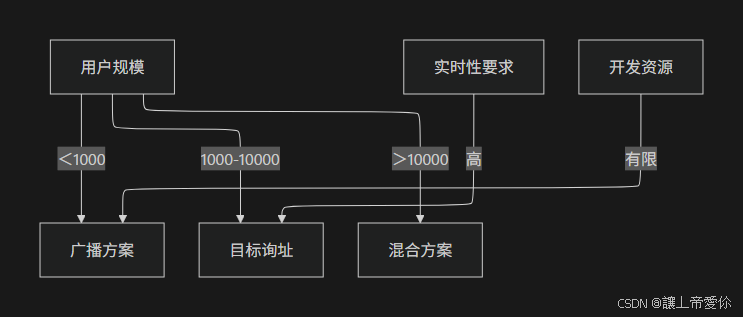
总结与建议
- 中小型项目:优先采用广播方案,配合Redis Pub/Sub实现简单集群
- 中大型系统:采用目标询址方案,确保消息精准投递
- 关键业务:实现双保险机制,结合两种方案优势
- 性能优化:重点监控会话数量和消息延迟指标
- 容灾设计:必须实现消息持久化和重试机制
示例项目结构建议:
websocket-cluster/
├── ws-common # 公共组件
├── ws-gateway # 接入层
├── ws-node1 # 节点1
├── ws-node2 # 节点2
└── ws-monitor # 监控服务
