文章目录
- 法向量特征估计
- 估计点云子集的表面法线(error)
- 积分图进行法线估计
- 点特征直方图
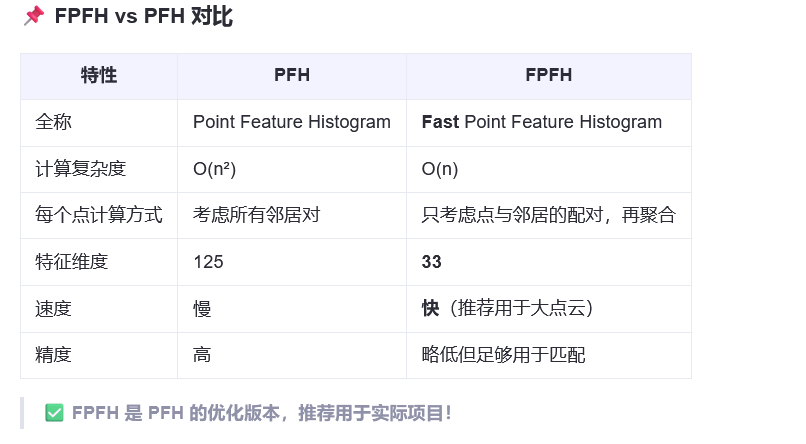
- 快速特征直方图 FPFH
- 深度图像(range image)中提取NARF特征
法向量特征估计
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono> int main()
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("../table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud) == -1){PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read the pcd file.\n");return -1;}std::cout << "Loaded " << cloud->size() << " points." << std::endl;pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud(cloud);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());ne.setSearchMethod(tree);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03); ne.compute(*cloud_normals);pcl::io::savePCDFile("../table_cloud_normals.pcd", *cloud_normals);std::cout << "Saved " << cloud_normals->size() << " normal points." << std::endl;pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer");viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, "sample cloud");viewer.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal>(cloud, cloud_normals, 10, 0.05, "normals");while (!viewer.wasStopped()){viewer.spinOnce(100);std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));}return 0;
}
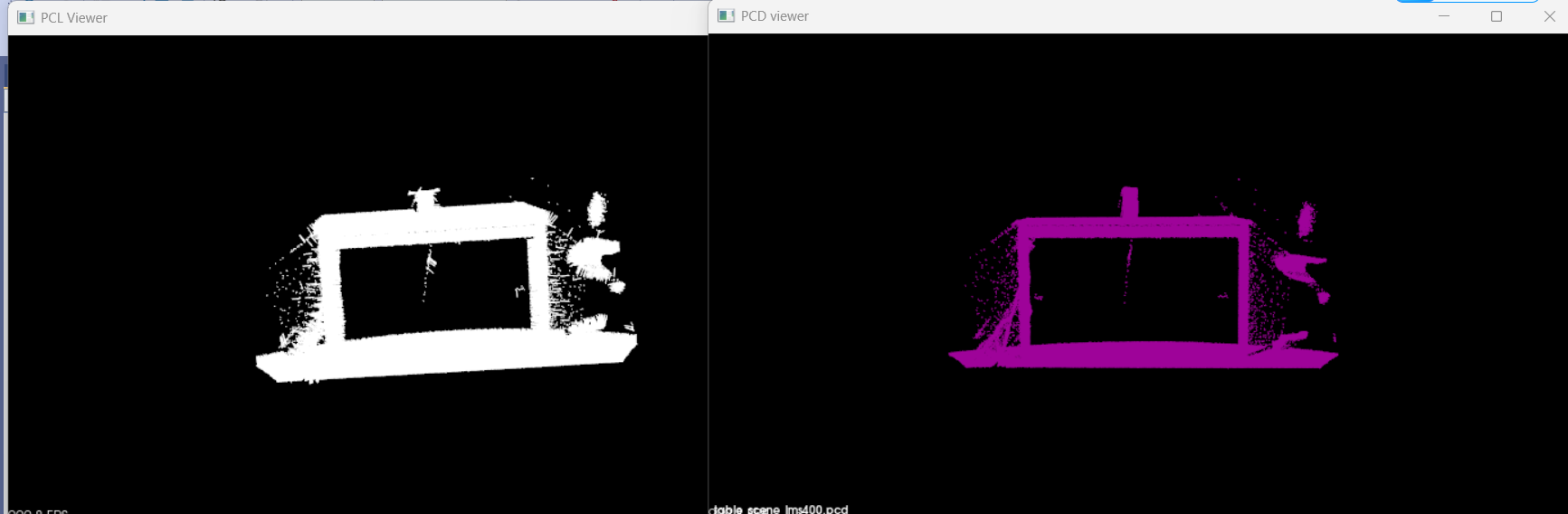
估计点云子集的表面法线(error)
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath> int main (){pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("../table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);std::vector<int> indices (std::floor (cloud->size () / 10));for (std::size_t i = 0; i < indices.size (); ++i) indices[i] = i;pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud (cloud);pcl::shared_ptr<std::vector<int> > indicesptr (new std::vector<int> (indices)); ne.setIndices (indicesptr);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ());ne.setSearchMethod (tree);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);ne.setRadiusSearch (0.03);ne.compute (*cloud_normals);}
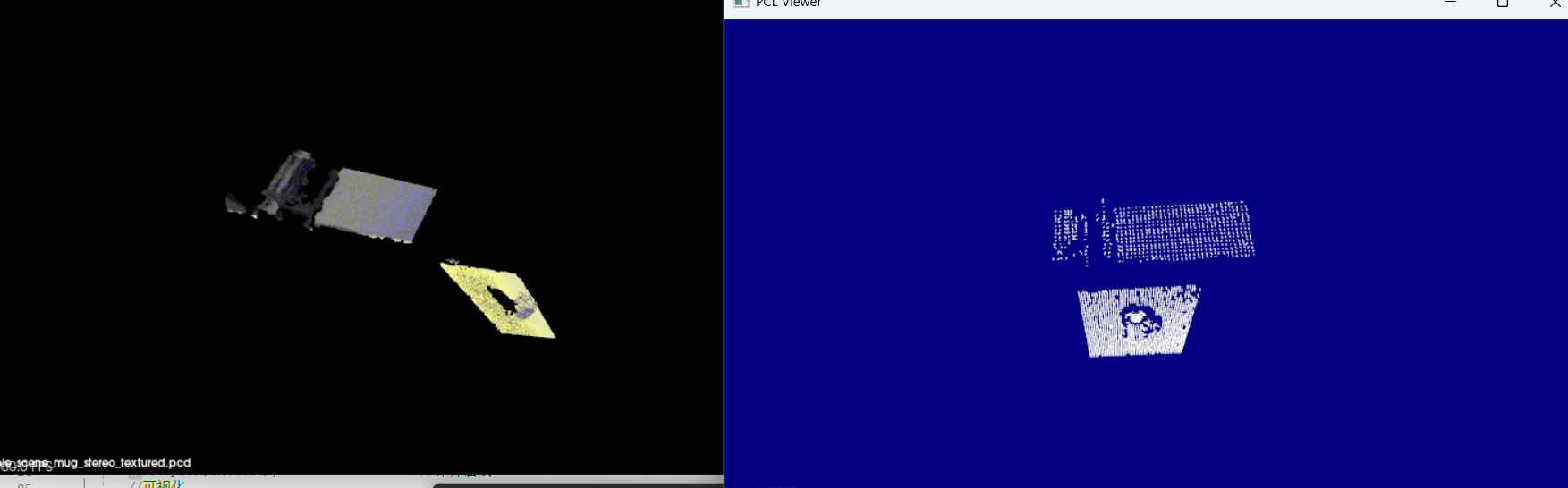
积分图进行法线估计
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/integral_image_normal.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
int main ()
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("../table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);pcl::IntegralImageNormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setNormalEstimationMethod (ne.AVERAGE_3D_GRADIENT); ne.setMaxDepthChangeFactor(0.02f); ne.setNormalSmoothingSize(10.0f); ne.setInputCloud(cloud); ne.compute(*normals); pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer"); viewer.setBackgroundColor (0.0, 0.0, 0.5); viewer.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointXYZ,pcl::Normal>(cloud, normals); while (!viewer.wasStopped ()){viewer.spinOnce ();}return 0;
}
点特征直方图
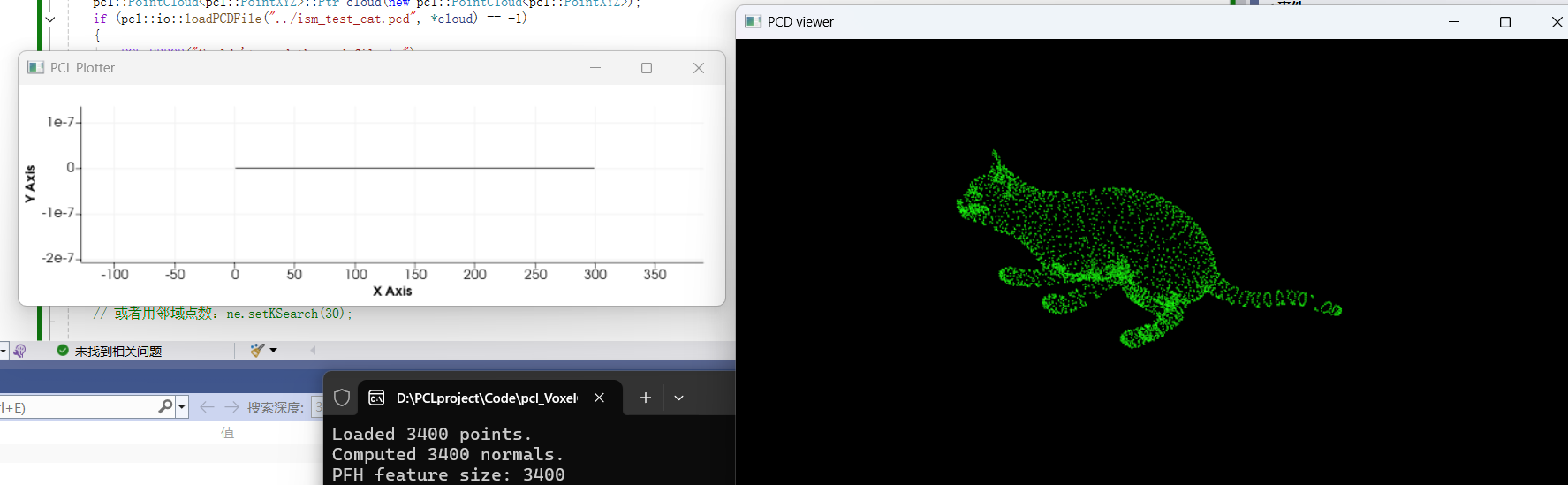
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/pfh.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_plotter.h>using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCDReader reader;reader.read("../ism_test_cat.pcd", *cloud_ptr);pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud(cloud_ptr);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());ne.setSearchMethod(tree);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>& cloud_normals = *cloud_normals_ptr;ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03);ne.compute(cloud_normals);pcl::PFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::PFHSignature125> pfh;pfh.setInputCloud(cloud_ptr);pfh.setInputNormals(cloud_normals_ptr);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree2(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());pfh.setSearchMethod(tree2);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfh_fe_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());pfh.setRadiusSearch(0.05);pfh.compute(*pfh_fe_ptr);cout << "phf feature size : " << pfh_fe_ptr->points.size() << endl;pcl::visualization::PCLPlotter plotter;plotter.addFeatureHistogram(*pfh_fe_ptr, 300); plotter.plot();return 0;
}
快速特征直方图 FPFH
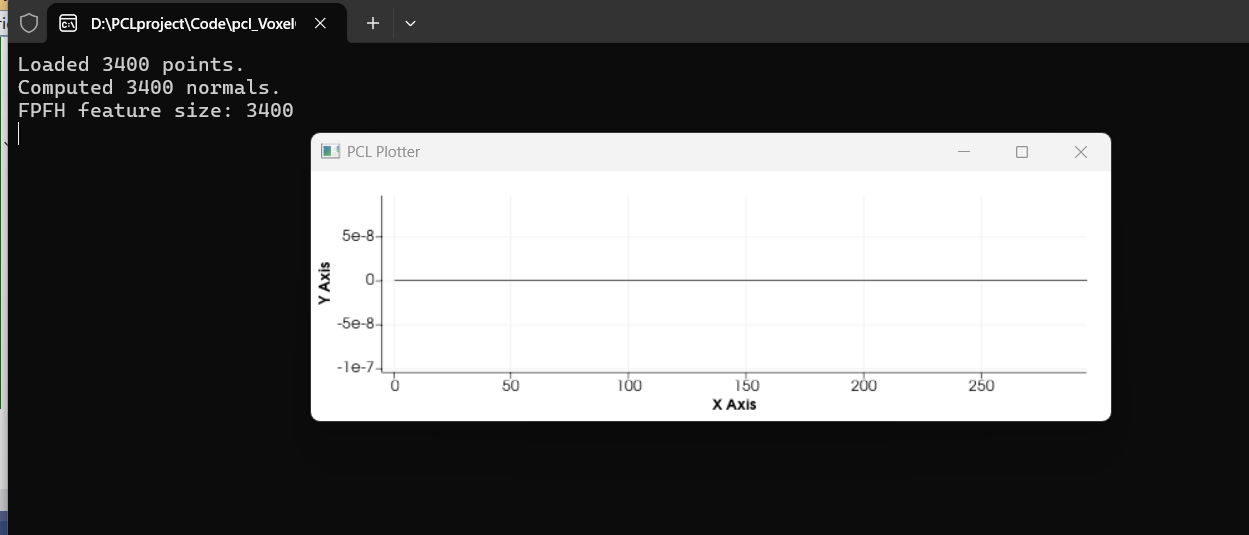
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/features/fpfh.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_plotter.h> using namespace std;int main()
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("../ism_test_cat.pcd", *cloud) == -1){PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read the pcd file.\n");return -1;}std::cout << "Loaded " << cloud->size() << " points." << std::endl;pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud(cloud);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);ne.setSearchMethod(tree);ne.setRadiusSearch(0.03); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);ne.compute(*normals);std::cout << "Computed " << normals->size() << " normals." << std::endl;pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> fpfh;fpfh.setInputCloud(cloud);fpfh.setInputNormals(normals);fpfh.setSearchMethod(tree);fpfh.setRadiusSearch(0.05); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr fpfhs(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>);fpfh.compute(*fpfhs);std::cout << "FPFH feature size: " << fpfhs->size() << std::endl;if (fpfhs->empty()){PCL_ERROR("FPFH computation failed!\n");return -1;}pcl::visualization::PCLPlotter plotter;plotter.addFeatureHistogram(*fpfhs, 300); plotter.plot();plotter.spin(); return 0;
}
深度图像(range image)中提取NARF特征
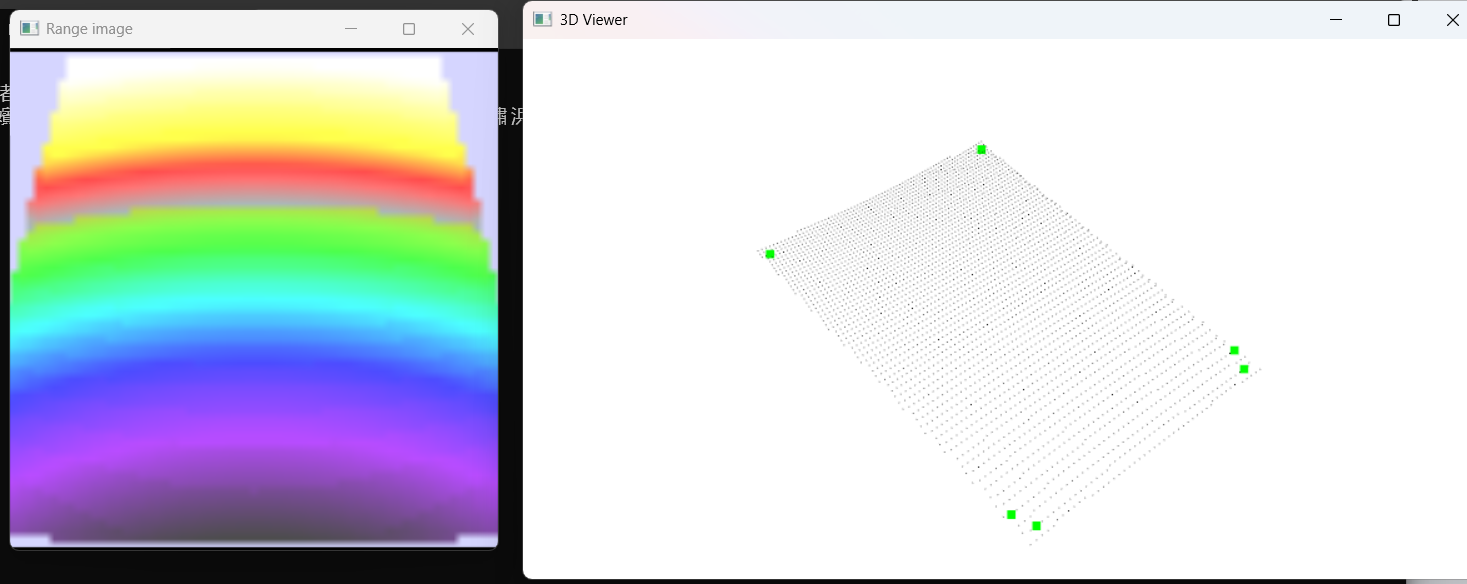
#include <iostream>#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>#include <pcl/range_image/range_image.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>#include <pcl/visualization/range_image_visualizer.h>#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/features/range_image_border_extractor.h>
#include <pcl/keypoints/narf_keypoint.h>
#include <pcl/features/narf_descriptor.h>#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
float angular_resolution = 0.5f;
float support_size = 0.2f;
pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CAMERA_FRAME;
bool setUnseenToMaxRange = false;
bool rotation_invariant = true;
void printUsage(const char* progName)
{std::cout << "\n\nUsage: " << progName << " [options] <scene.pcd>\n\n"<< "Options:\n"<< "-------------------------------------------\n"<< "-r <float> angular resolution in degrees (default " << angular_resolution << ")\n"<< "-c <int> coordinate frame (default " << (int)coordinate_frame << ")\n"<< "-m Treat all unseen points to max range\n"<< "-s <float> support size for the interest points (diameter of the used sphere - ""default " << support_size << ")\n"<< "-o <0/1> switch rotational invariant version of the feature on/off"<< " (default " << (int)rotation_invariant << ")\n"<< "-h this help\n"<< "\n\n";
}
void setViewerPose(pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer& viewer, const Eigen::Affine3f& viewer_pose)
{Eigen::Vector3f pos_vector = viewer_pose * Eigen::Vector3f(0, 0, 0);Eigen::Vector3f look_at_vector = viewer_pose.rotation() * Eigen::Vector3f(0, 0, 1) + pos_vector;Eigen::Vector3f up_vector = viewer_pose.rotation() * Eigen::Vector3f(0, -1, 0);viewer.setCameraPosition(pos_vector[0], pos_vector[1], pos_vector[2],look_at_vector[0], look_at_vector[1], look_at_vector[2],up_vector[0], up_vector[1], up_vector[2]);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{if (pcl::console::find_argument(argc, argv, "-h") >= 0){printUsage(argv[0]);return 0;}if (pcl::console::find_argument(argc, argv, "-m") >= 0){setUnseenToMaxRange = true;cout << "Setting unseen values in range image to maximum range readings.\n";}if (pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-o", rotation_invariant) >= 0)cout << "Switching rotation invariant feature version " << (rotation_invariant ? "on" : "off") << ".\n";int tmp_coordinate_frame;if (pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-c", tmp_coordinate_frame) >= 0){coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame(tmp_coordinate_frame);cout << "Using coordinate frame " << (int)coordinate_frame << ".\n";}if (pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-s", support_size) >= 0)cout << "Setting support size to " << support_size << ".\n";if (pcl::console::parse(argc, argv, "-r", angular_resolution) >= 0)cout << "Setting angular resolution to " << angular_resolution << "deg.\n";angular_resolution = pcl::deg2rad(angular_resolution);pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr point_cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);pcl::PointCloud<PointType>& point_cloud = *point_cloud_ptr;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithViewpoint> far_ranges;Eigen::Affine3f scene_sensor_pose(Eigen::Affine3f::Identity());std::vector<int> pcd_filename_indices = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument(argc, argv, "pcd");if (!pcd_filename_indices.empty()){std::string filename = argv[pcd_filename_indices[0]];if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(filename, point_cloud) == -1){std::cerr << "无法打开文件 \"" << filename << "\"。\n";printUsage(argv[0]);return -1;}scene_sensor_pose = Eigen::Affine3f(Eigen::Translation3f(point_cloud.sensor_origin_[0],point_cloud.sensor_origin_[1],point_cloud.sensor_origin_[2])) * Eigen::Affine3f(point_cloud.sensor_orientation_);}else{setUnseenToMaxRange = true;std::cout << "\n未提供 .pcd 文件 => 生成示例点云。\n\n";for (float x = -0.5f; x <= 0.5f; x += 0.01f){for (float y = -0.5f; y <= 0.5f; y += 0.01f){PointType point;point.x = x;point.y = y;point.z = 2.0f - y; point_cloud.points.push_back(point);}}point_cloud.width = static_cast<int>(point_cloud.points.size());point_cloud.height = 1;}float noise_level = 0.0; float min_range = 0.0f; int border_size = 1; boost::shared_ptr<pcl::RangeImage> range_image_ptr(new pcl::RangeImage);pcl::RangeImage& range_image = *range_image_ptr;range_image.createFromPointCloud(point_cloud, angular_resolution, pcl::deg2rad(360.0f), pcl::deg2rad(180.0f), scene_sensor_pose, coordinate_frame, noise_level, min_range, border_size );if (setUnseenToMaxRange)range_image.setUnseenToMaxRange();pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("3D Viewer");viewer.setBackgroundColor(1, 1, 1); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>::Ptr range_image_cloud_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>);pcl::copyPointCloud(range_image, *range_image_cloud_ptr);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> range_image_color_handler(range_image_cloud_ptr, 0, 0, 0);viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>(range_image_cloud_ptr, range_image_color_handler, "range image");viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "range image");pcl::visualization::RangeImageVisualizer range_image_widget("Range image");range_image_widget.showRangeImage(range_image); pcl::RangeImageBorderExtractor range_image_border_extractor; pcl::NarfKeypoint narf_keypoint_detector; narf_keypoint_detector.setRangeImageBorderExtractor(&range_image_border_extractor);narf_keypoint_detector.setRangeImage(&range_image);narf_keypoint_detector.getParameters().support_size = support_size; pcl::PointCloud<int> keypoint_indices;narf_keypoint_detector.compute(keypoint_indices); std::cout << "检测到 " << keypoint_indices.points.size() << " 个关键点。\n";pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoints_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& keypoints = *keypoints_ptr;keypoints.points.resize(keypoint_indices.points.size());for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoint_indices.points.size(); ++i)keypoints.points[i].getVector3fMap() = range_image.points[keypoint_indices.points[i]].getVector3fMap();pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> keypoints_color_handler(keypoints_ptr, 0, 255, 0);viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(keypoints_ptr, keypoints_color_handler, "keypoints");viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "keypoints");std::vector<int> keypoint_indices2;keypoint_indices2.resize(keypoint_indices.points.size());for (unsigned int i = 0; i < keypoint_indices.size(); ++i)keypoint_indices2[i] = keypoint_indices.points[i]; pcl::NarfDescriptor narf_descriptor(&range_image, &keypoint_indices2);narf_descriptor.getParameters().support_size = support_size; narf_descriptor.getParameters().rotation_invariant = rotation_invariant; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Narf36> narf_descriptors;narf_descriptor.compute(narf_descriptors); std::cout << "为 " << keypoint_indices.points.size() << " 个关键点提取了 "<< narf_descriptors.size() << " 个 NARF 描述子。\n";while (!viewer.wasStopped()){range_image_widget.spinOnce(); viewer.spinOnce(); pcl_sleep(0.01); }return 0;
}






