Java多线程进阶
目录
一、线程状态
1.线程五大状态
运行过程描述
2.线程方法
2.1停止线程
2.2线程休眠
2.3线程礼让
2.4线程插队
3.线程状态观测
4.线程优先级
5.守护(daemon)线程
二、线程同步
1.介绍
2.不安全的线程案例
3.同步方法
4.同步块
5.死锁
死锁避免办法
6.Lock(锁)
7.synchroized与Lock对比
五、线程通信问题
1.线程通信方法
2.线程通信问题解决方式
六、线程池
一、线程状态
1.线程五大状态
- 新建状态
- 就绪状态
- 运行状态
- 阻塞状态
- 死亡状态
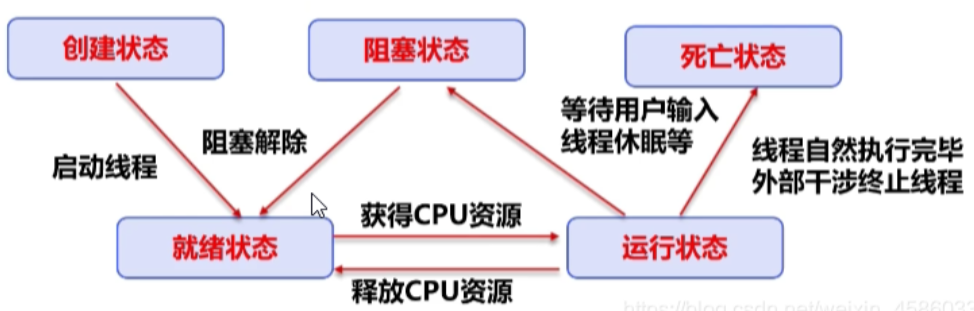
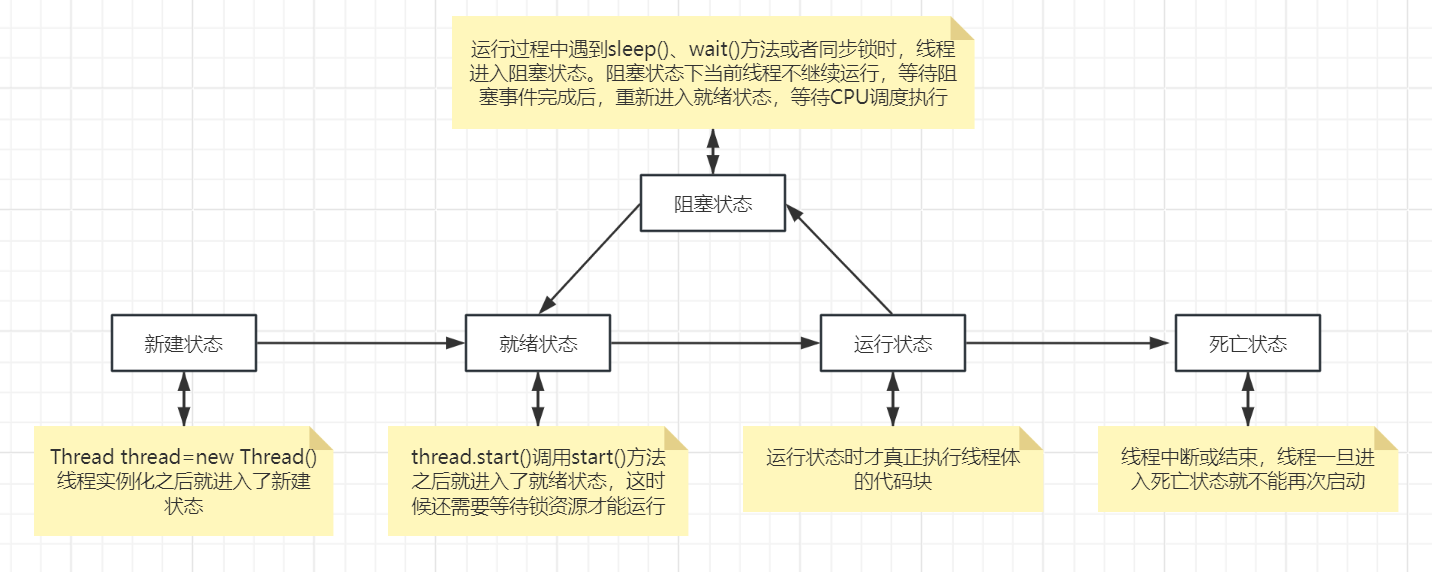
运行过程描述
2.线程方法
2.1停止线程

案例:
public class ThreadStop implements Runnable {private Boolean flag = true;@Overridepublic void run() {int count = 0;while (flag) {System.out.println("线程正在运行" + count++);}}public void stop() {this.flag = false;}public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadStop stop = new ThreadStop();new Thread(stop).start();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {System.out.println("主函数正在运行" + i);if (i == 900) {stop.stop();}}}
}
2.2线程休眠

案例:
public class ThreadSleep {public static void sleepThread() {int num = 10;while (true) {try {System.out.println("倒计时:" + num--);Thread.sleep(1000);if (num <= 0) {break;}} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {sleepThread();}
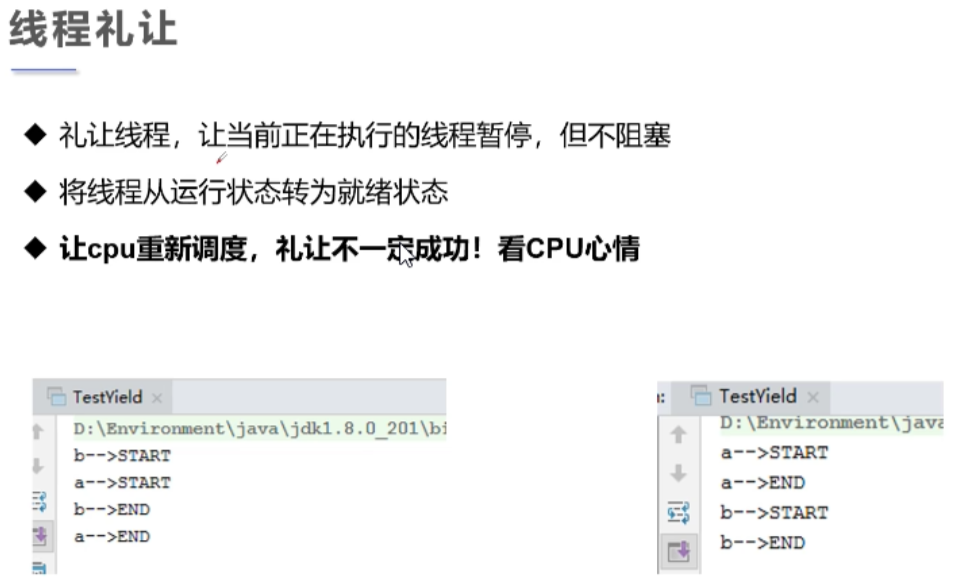
}2.3线程礼让
线程礼让只是重新抢夺CPU的调度,礼让不一定会成功、只是再给其它线程一个机会而已。
案例:
public class ThreadYield implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始运行");Thread.yield();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束运行");}public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new ThreadYield(), "线程1").start();new Thread(new ThreadYield(), "线程2").start();}
}2.4线程插队
简单的理解为线程插队就可以了
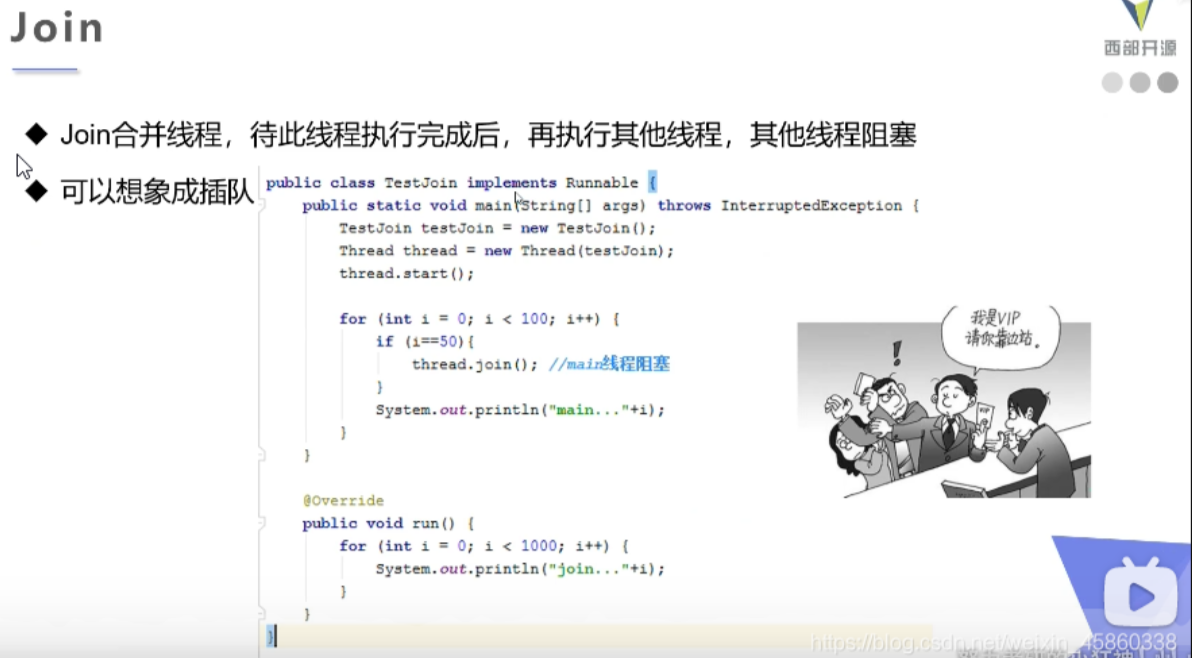
案例:
public class ThreadJoin implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {System.out.println("我是VIP我要插队" + i);}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadJoin threadJoin = new ThreadJoin();Thread thread = new Thread(threadJoin);thread.start();for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {System.out.println("我是普通用户:" + i);if (i == 50) {thread.join();}}}
}3.线程状态观测

案例:
public class GetThreadState implements Runnable {// 实现Runnable接口,重写run方法@Overridepublic void run() {// 循环一次for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {try {// 休眠500毫秒Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// 抛出运行时异常throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建GetThreadState对象Thread thread = new Thread(new GetThreadState());// 输出线程状态System.out.println(thread.getState());thread.start();System.out.println(thread.getState());while (thread.getState()!= Thread.State.TERMINATED){System.out.println(thread.getState());}System.out.println(thread.getState());}
}4.线程优先级
线程优先级的高低只是被CPU调用的概率大

案例:
public class ThreadPriority implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (ThreadPriority.class){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());}}public static void main(String[] args) {Thread one = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "one");one.setPriority(1);one.start();Thread two = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "two");two.setPriority(2);two.start();Thread three = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "three");three.setPriority(3);three.start();Thread four = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "four");four.setPriority(4);four.start();Thread five = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "five");five.setPriority(5);five.start();Thread defaultPriority = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "defaultPriority");defaultPriority.start();Thread maxPriority = new Thread(new ThreadPriority(), "maxPriority");maxPriority.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);maxPriority.start();}
}
5.守护(daemon)线程
皇上和宫女,皇上活着宫女一直在,皇上死了宫女陪葬

案例:
package com.example.threadstudy.state;public class DaemonThread {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建一个God对象God god = new God();// 创建一个Person对象Person person = new Person();// 创建一个Thread对象,并将God对象作为参数传入Thread thread = new Thread(god);// 将Thread对象设置为守护线程thread.setDaemon(true);// 启动Thread对象thread.start();// 创建一个新的Thread对象,并将Person对象作为参数传入new Thread(person, "one").start();new Thread(person, "two").start();}}class God implements Runnable {// 实现Runnable接口,重写run方法@Overridepublic void run() {// 无限循环while (true)// 输出上帝一直保佑你System.out.println("上帝一直保佑你");}
}class Person implements Runnable {// 实现Runnable接口,重写run方法@Overridepublic void run() {// 循环100次for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {// 输出"我还在坚持"System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "我还在坚持");}// 输出"坚持不住了,上帝再见"System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "坚持不住了,上帝再见");}
}
二、线程同步
1.介绍
多个线程操作同一个资源




2.不安全的线程案例
package com.example.threadstudy.unsafethread;public class BuyTicket implements Runnable {private int ticket = 10;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {if (hasTicket()) {try {Thread.sleep(50);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了第" + ticket-- + "张票");} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}} else {break;}}System.out.println("票已经卖完了");}public Boolean hasTicket() {return ticket > 0;}public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new BuyTicket(), "窗口1").start();new Thread(new BuyTicket(), "窗口2").start();new Thread(new BuyTicket(), "窗口3").start();}
}
3.同步方法

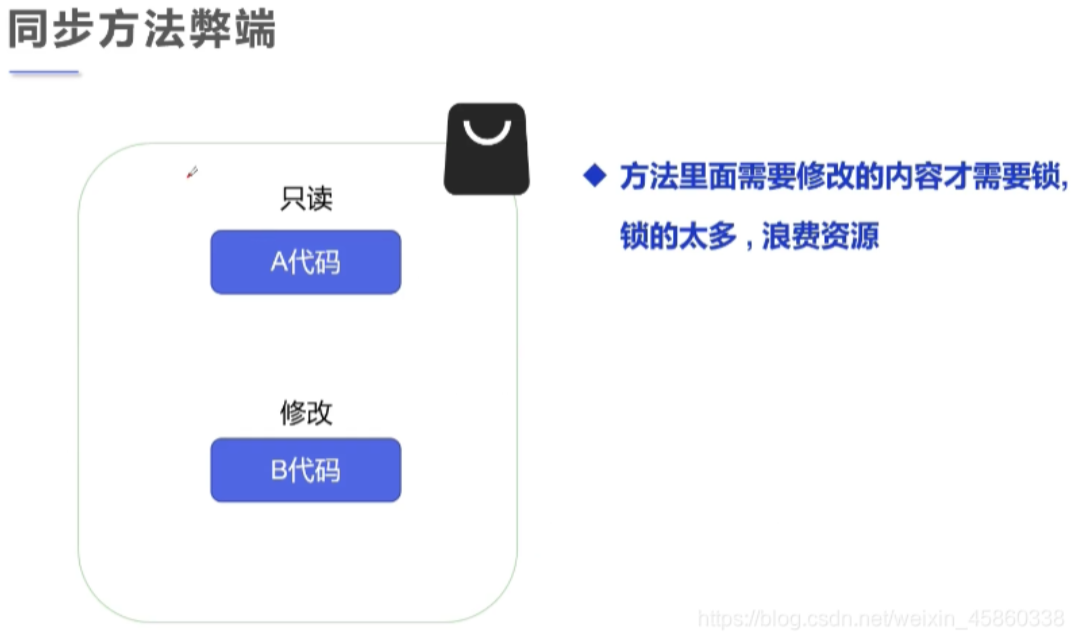
同步方法,锁的是当前对象,未添加synchronized的方法也会被锁上,浪费资源
实现:
public class BuyTicket {public static void main(String[] args) {BuyTicketThread buyTicketThread = new BuyTicketThread();Thread thread1 = new Thread(buyTicketThread, "窗口1");Thread thread2 = new Thread(buyTicketThread, "窗口2");Thread thread3 = new Thread(buyTicketThread, "窗口3");thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start();}
}
class BuyTicketThread implements Runnable {private int ticket = 10;private boolean hasTicketFlag = true;@Overridepublic void run() {while (hasTicketFlag) {buyTicket();}System.out.println("票卖完了");}public synchronized void buyTicket() {if (ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了第" + ticket + "张票");ticket--;} else {hasTicketFlag = false;}}
}4.同步块

锁的是需要修改的变量,需要增删改查的对象
实现:
package com.example.threadstudy.safethread;public class SafeBank {public static void main(String[] args) {Account1 account = new Account1(100, "结婚基金");Drawing1 you = new Drawing1(account, 50, "展堂");Drawing1 girlfriend = new Drawing1(account, 100, "sad");you.start();girlfriend.start();}
}//账户
class Account1 {int money;//余额String cardName;//卡名public Account1(int money, String cardName) {this.money = money;this.cardName = cardName;}
}//银行:模拟取款
class Drawing1 extends Thread {Account1 account;//账户int drawingMoney;//取金额int nowMoney;//你手里的钱public Drawing1(Account1 account, int drawingMoney, String name) {super(name);this.account = account;this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;}//取钱@Overridepublic void run() {//锁的对象就是变量的量,需要增删改查的对象synchronized (account) {//判断是否有钱if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "余额不足,不能进行取钱");return;}try {Thread.sleep(1000);//放大问题的发生性} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//卡内金额 = 余额-你的钱account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;//你手里的钱nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;System.out.println(account.cardName + "余额为:" + account.money);//this.getName()==Thread.currentThread().getName()System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱:" + nowMoney);}}
}5.死锁

实现:
/*** 死锁:多个线程互相抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持* 解决:一个锁只锁一个对象*/
class DeadLock {public static void main(String[] args) {Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0, "灰姑娘");Makeup makeup1 = new Makeup(1, "白雪公主");makeup.start();makeup1.start();}
}//口红
class Lipstick { }
//镜子
class Mirror { }class Makeup extends Thread {//需要的资源只有一份,用static保证只有一份static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();int choice;//选择String girlName;//使用化妆品的人public Makeup(int choice, String girlName) {this.choice = choice;this.girlName = girlName;}@Overridepublic void run() {//化妆try {makeup();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {if (choice == 0) {synchronized (lipstick) {//获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");Thread.sleep(1000);synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后想获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");}}} else {synchronized (mirror) {//获得口红镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");Thread.sleep(2000);synchronized (lipstick) {//二秒钟后想获得的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");}}}}
}
解决方式:不要相互占有资源
/*** 死锁:多个线程互相抱着对方需要的资源,然后形成僵持* 解决:一个锁只锁一个对象*/
class DeadLock {public static void main(String[] args) {Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0, "灰姑娘");Makeup makeup1 = new Makeup(1, "白雪公主");makeup.start();makeup1.start();}
}//口红
class Lipstick { }
//镜子
class Mirror { }class Makeup extends Thread {//需要的资源只有一份,用static保证只有一份static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();int choice;//选择String girlName;//使用化妆品的人public Makeup(int choice, String girlName) {this.choice = choice;this.girlName = girlName;}@Overridepublic void run() {//化妆try {makeup();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {if (choice == 0) {synchronized (lipstick) {//获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");Thread.sleep(1000);}synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后想获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");}} else {synchronized (mirror) {//获得口红镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");Thread.sleep(2000);}synchronized (lipstick) {//二秒钟后想获得的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");}}}
}
死锁避免办法

6.Lock(锁)


//测试Lock锁
public class Demo32_ThreadLock {public static void main(String[] args) {TestLock testLock = new TestLock();new Thread(testLock).start();new Thread(testLock).start();new Thread(testLock).start();}
}class TestLock implements Runnable {int tickerNums = 10;//定义Lock锁private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {//加锁try {lock.lock();if (tickerNums <= 0) {break;}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(tickerNums--);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//解锁lock.unlock();}}}
}
7.synchroized与Lock对比

五、线程通信问题
生产者消费者模式的问题
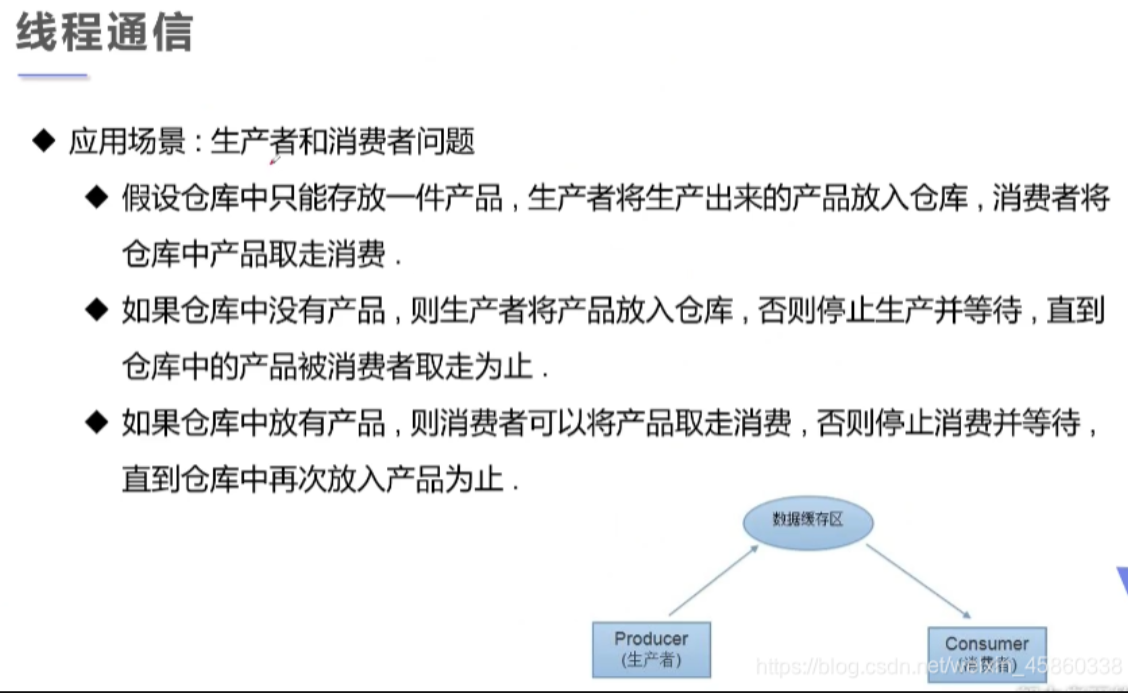
1.线程通信方法
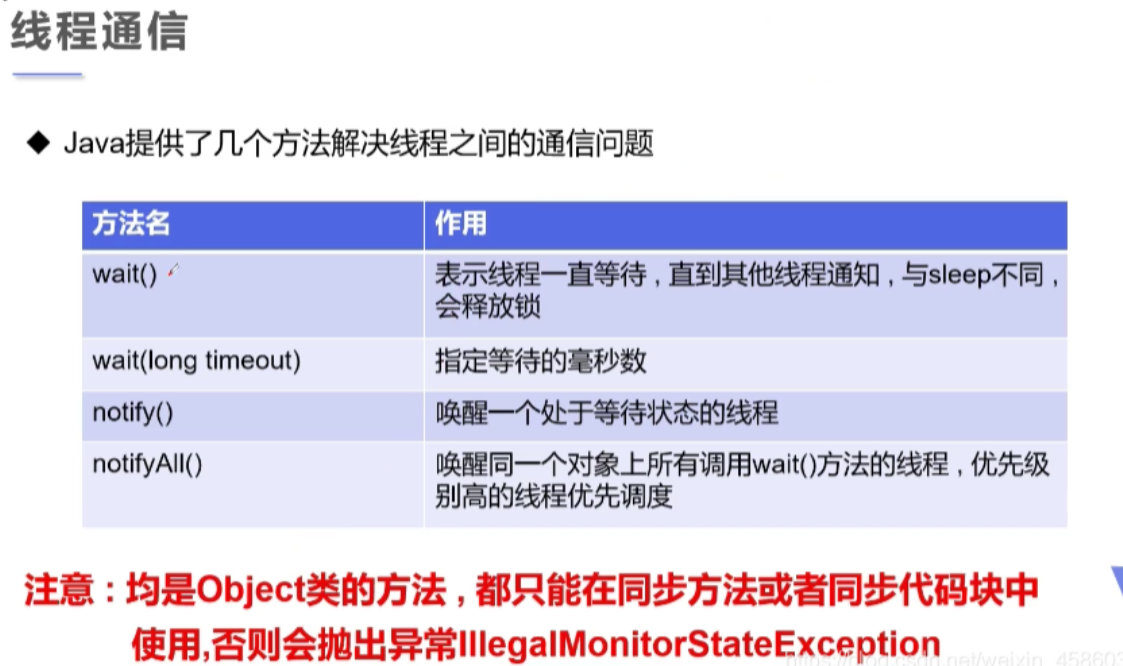

2.线程通信问题解决方式
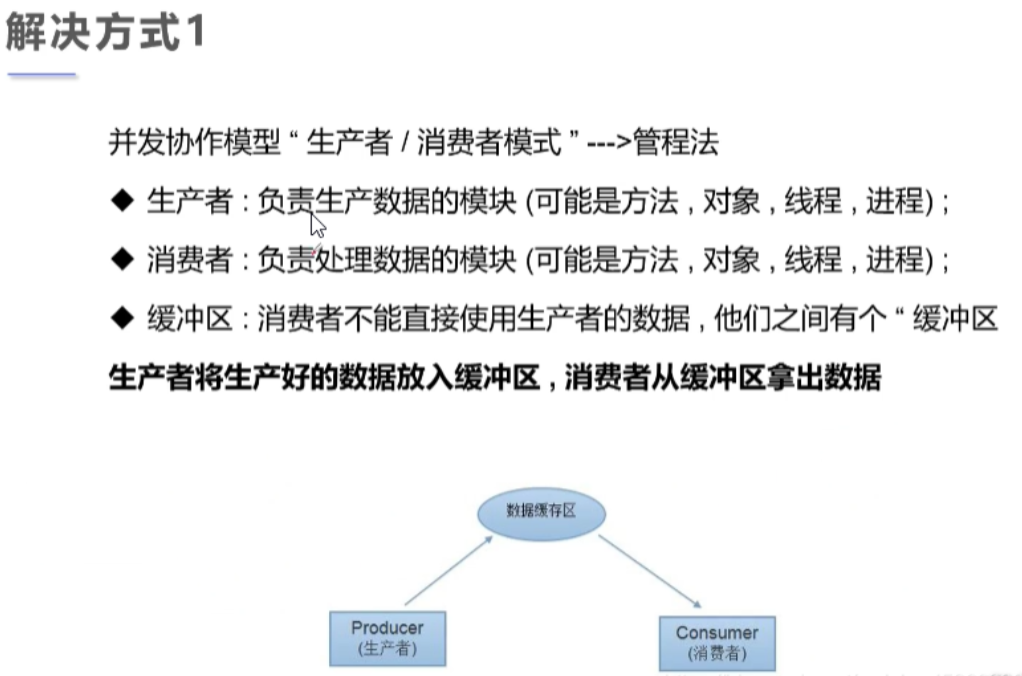
/*** 测试:生产者消费者模型-->利用缓冲区解决:管程法*/
public class ThreadPC {public static void main(String[] args) {SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer();new Producer(synContainer).start();new Consumer(synContainer).start();}
}//生产者
class Producer extends Thread {//容缓冲区SynContainer container;public Producer(SynContainer container) {this.container = container;}//生产@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {container.push(new Product(i));System.out.println("生产了" + i + "件产品");}}
}//消费者
class Consumer extends Thread {//容缓冲区SynContainer container;public Consumer(SynContainer container) {this.container = container;}//消费@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("消费了-->" + container.pop().id + "件产品");}}
}//产品
class Product {int id;//产品编号public Product(int id) {this.id = id;}
}//缓冲区
class SynContainer {//需要一个容器大小Product[] products = new Product[10];//容器计数器int count = 0;//生产者放入产品public synchronized void push(Product product) {//如果容器满了,需要等待消费者消费/*如果是if的话,假如消费者1消费了最后一个,这是index变成0此时释放锁被消费者2拿到而不是生产者拿到,这时消费者的wait是在if里所以它就直接去消费index-1下标越界,如果是while就会再去判断一下index得值是不是变成0了*/while (count == products.length) {//通知消费者消费,等待生产try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//如果没有满,需要丢入产品products[count] = product;count++;//通知消费者消费this.notifyAll();}//消费者消费产品public synchronized Product pop() {//判断是否能消费while (count <= 0) {//等待生产者生产try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//如果可以消费count--;Product product = products[count];//吃完了 通知生产者生产this.notifyAll();return product;}
}

/*** 测试:生产者消费者模型-->利用缓冲区解决:管程法*/
public class ThreadPC {public static void main(String[] args) {SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer();new Producer(synContainer).start();new Consumer(synContainer).start();}
}//生产者
class Producer extends Thread {//容缓冲区SynContainer container;public Producer(SynContainer container) {this.container = container;}//生产@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {container.push(new Product(i));System.out.println("生产了" + i + "件产品");}}
}//消费者
class Consumer extends Thread {//容缓冲区SynContainer container;public Consumer(SynContainer container) {this.container = container;}//消费@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("消费了-->" + container.pop().id + "件产品");}}
}//产品
class Product {int id;//产品编号public Product(int id) {this.id = id;}
}//缓冲区
class SynContainer {//需要一个容器大小Product[] products = new Product[10];//容器计数器int count = 0;//生产者放入产品public synchronized void push(Product product) {//如果容器满了,需要等待消费者消费/*如果是if的话,假如消费者1消费了最后一个,这是index变成0此时释放锁被消费者2拿到而不是生产者拿到,这时消费者的wait是在if里所以它就直接去消费index-1下标越界,如果是while就会再去判断一下index得值是不是变成0了*/while (count == products.length) {//通知消费者消费,等待生产try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//如果没有满,需要丢入产品products[count] = product;count++;//通知消费者消费this.notifyAll();}//消费者消费产品public synchronized Product pop() {//判断是否能消费while (count <= 0) {//等待生产者生产try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//如果可以消费count--;Product product = products[count];//吃完了 通知生产者生产this.notifyAll();return product;}
}
六、线程池


public class ThreadPool {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);//执行executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());executorService.execute(new testThreadPool());//关闭连接executorService.shutdown();}
}class testThreadPool implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}
}
至此鸣谢:狂神说多线程笔记整理_狂神多线程笔记-CSDN博客
