聊聊 Pulsar:Producer 源码解析
一、前言
Apache Pulsar 是一个企业级的开源分布式消息传递平台,以其高性能、可扩展性和存储计算分离架构在消息队列和流处理领域独树一帜。在 Pulsar 的核心架构中,Producer(生产者) 是连接客户端应用与消息队列的第一步。生产者负责将消息写入指定的 Topic,从而启动整个消息流转的生命周期。
深入解析 Pulsar Producer 的源码,不仅可以了解消息生产的内部实现机制,还能帮助开发者优化客户端性能,同时为调试和扩展提供基础。在本文中,我们将从 Producer 的创建流程、消息发送逻辑以及其与 Broker 的交互机制出发,逐步剖析源码细节,以期为读者提供全面的技术视角和实践指导。
二、Producer测试类
老规矩,我们先以Producer生产下消息,来跟进Producer的相关源码流程。
@Test
public void testSimpleProducerEvents() throws Exception {final String topicName = "persistent://prop/ns-abc/topic0";// 1. producer connectProducer<byte[]> producer = pulsarClient.newProducer().topic(topicName).enableBatching(false).messageRoutingMode(MessageRoutingMode.SinglePartition).create();PersistentTopic topicRef = (PersistentTopic) pulsar.getBrokerService().getTopicReference(topicName).get();assertNotNull(topicRef);assertEquals(topicRef.getProducers().size(), 1);// 2. producer publish messagesfor (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {String message = "my-message-" + i;producer.send(message.getBytes());}rolloverPerIntervalStats();assertTrue(topicRef.getProducers().values().iterator().next().getStats().msgRateIn > 0.0);// 3. producer disconnectproducer.close();Thread.sleep(ASYNC_EVENT_COMPLETION_WAIT);assertEquals(topicRef.getProducers().size(), 0);
}
从上面的代码可以看出 Pulsar 为用户提供了非常简洁方便的 API,在使用时,只需要如下两步:
- 创建 Pulsar Producer 实例
- 调用 send 接口发送数据
三、Pulsar Producer 实例化
3.1 实例化ProducerBuilder

核心在 org.apache.pulsar.client.impl.PulsarClientImpl#createProducerAsync(org.apache.pulsar.client.impl.conf.ProducerConfigurationData, org.apache.pulsar.client.api.Schema, org.apache.pulsar.client.impl.ProducerInterceptors)
用于异步创建消息生产者(Producer)。下面是对代码的详细分析:
- 泛型 : 表示生产者的消息类型。
- CompletableFuture<Producer>: 返回一个 CompletableFuture,表示生产者的异步创建过程。
参数:- ProducerConfigurationData conf: 生产者的配置数据。
- Schema schema: 消息的模式(Schema)。
- ProducerInterceptors interceptors: 生产者的拦截器列表。
- 检查模式是否为 AutoProduceBytesSchema:
-
如果 schema 是 AutoProduceBytesSchema,并且已经初始化,直接调用 createProducerAsync 方法创建生产者。
-
如果 schema 是 AutoProduceBytesSchema,但未初始化,先从 Pulsar 服务器获取主题的模式信息:
- 如果模式信息存在,设置 AutoProduceBytesSchema 的模式。
- 如果模式信息不存在,设置 AutoProduceBytesSchema 的模式为 Schema.BYTES。
-
最后调用 createProducerAsync 方法创建生产者。
-
其他情况: 直接调用 createProducerAsync 方法创建生产者。
-
3.2 异步创建消息生产者
/*** 异步创建消息生产者* @param topic 主题名称* @param conf 生产者的配置数据* @param schema 消息的模式(Schema)* @param interceptors 生产者的拦截器列表* @return 返回一个 CompletableFuture,表示生产者的异步创建过程。* @param <T> 生产者的消息类型*/
private <T> CompletableFuture<Producer<T>> createProducerAsync(String topic,ProducerConfigurationData conf,Schema<T> schema,ProducerInterceptors interceptors) {CompletableFuture<Producer<T>> producerCreatedFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();// 取主题的分区元数据getPartitionedTopicMetadata(topic).thenAccept(metadata -> {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("[{}] Received topic metadata. partitions: {}", topic, metadata.partitions);}// 创建生产ProducerBase<T> producer;if (metadata.partitions > 0) {// 分区主题: 如果 metadata.partitions 大于 0,表示这是一个分区主题,调用 newPartitionedProducerImpl 方法创建分区生产者。producer = newPartitionedProducerImpl(topic, conf, schema, interceptors, producerCreatedFuture,metadata);} else {// 非分区主题: 否则,调用 newProducerImpl 方法创建普通生产者。producer = newProducerImpl(topic, -1, conf, schema, interceptors, producerCreatedFuture);}// 将创建的生产者添加到 producers 集合中。producers.add(producer);}).exceptionally(ex -> {log.warn("[{}] Failed to get partitioned topic metadata: {}", topic, ex.getMessage());producerCreatedFuture.completeExceptionally(ex);return null;});return producerCreatedFuture;
}
3.2.1 获取主题的分区元数据

3.2.2 创建分区生产者
public PartitionedProducerImpl(PulsarClientImpl client, String topic, ProducerConfigurationData conf, int numPartitions,CompletableFuture<Producer<T>> producerCreatedFuture, Schema<T> schema, ProducerInterceptors interceptors) {super(client, topic, conf, producerCreatedFuture, schema, interceptors);this.producers = new ConcurrentOpenHashMap<>();this.topicMetadata = new TopicMetadataImpl(numPartitions);this.routerPolicy = getMessageRouter();stats = client.getConfiguration().getStatsIntervalSeconds() > 0 ? new ProducerStatsRecorderImpl() : null;// MaxPendingMessagesAcrossPartitions doesn't support partial partition such as SinglePartition correctly// 计算最大待处理消息数: 根据配置计算每个分区的最大待处理消息数。int maxPendingMessages = Math.min(conf.getMaxPendingMessages(),conf.getMaxPendingMessagesAcrossPartitions() / numPartitions);conf.setMaxPendingMessages(maxPendingMessages);// 确定要创建的分区索引列表: 根据配置确定要创建的分区索引列表。final List<Integer> indexList;// 懒启动且共享访问模式: 只创建一个分区的生产者,选择的分区由消息路由策略决定。if (conf.isLazyStartPartitionedProducers() &&conf.getAccessMode() == ProducerAccessMode.Shared) {// try to create producer at least one partitionindexList = Collections.singletonList(routerPolicy.choosePartition(((TypedMessageBuilderImpl<T>) newMessage()).getMessage(), topicMetadata));} else {// try to create producer for all partitionsindexList = IntStream.range(0, topicMetadata.numPartitions()).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());}// 设置第一个分区索引: 设置第一个分区的索引。firstPartitionIndex = indexList.get(0);// 启动生产者: 启动指定分区索引列表中的生产者。start(indexList);// start track and auto subscribe partition increasement// 自动更新分区: 如果配置了自动更新分区,则创建监听器并启动定时任务定期检查和更新分区。if (conf.isAutoUpdatePartitions()) {topicsPartitionChangedListener = new TopicsPartitionChangedListener();partitionsAutoUpdateTimeout = client.timer().newTimeout(partitionsAutoUpdateTimerTask, conf.getAutoUpdatePartitionsIntervalSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);}
}
核心在start方法启动生产者:
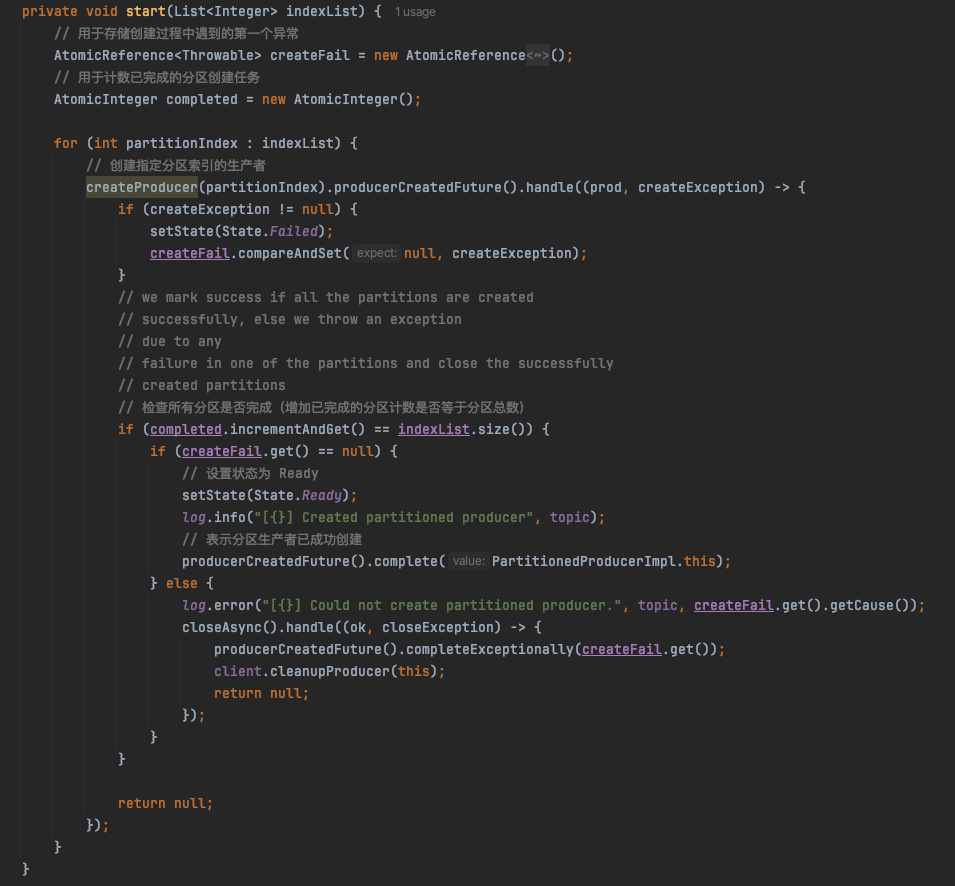
创建指定分区索引的生产者:
// 键为分区索引,值为 ProducerImpl 实例。
private final ConcurrentOpenHashMap<Integer, ProducerImpl<T>> producers;private ProducerImpl<T> createProducer(final int partitionIndex) {return producers.computeIfAbsent(partitionIndex, (idx) -> {String partitionName = TopicName.get(topic).getPartition(idx).toString();// 创建一个新的 ProducerImpl 实例,传入分区名称、分区索引、配置、模式、拦截器和一个 CompletableFuture。return client.newProducerImpl(partitionName, idx,conf, schema, interceptors, new CompletableFuture<>());});
}protected <T> ProducerImpl<T> newProducerImpl(String topic, int partitionIndex,ProducerConfigurationData conf,Schema<T> schema,ProducerInterceptors interceptors,CompletableFuture<Producer<T>> producerCreatedFuture) {return new ProducerImpl<>(PulsarClientImpl.this, topic, conf, producerCreatedFuture, partitionIndex, schema,interceptors);
}
老周对比了创建非分区生产者,创建分区生产者前面明显比创建非分区生产者封装的好,老周当时猜测肯定后面有个公共的方法调到创建非分区生产者里来。下面果然验证了老周的想法:

3.2.3 创建非分区生产者

主要看下grabCnx方法建立与 Broker 的连接
3.2.4 建立与 Broker 的连接
protected void grabCnx() {// 检查客户端连接是否已设置if (CLIENT_CNX_UPDATER.get(this) != null) {log.warn("[{}] [{}] Client cnx already set, ignoring reconnection request", state.topic, state.getHandlerName());return;}// 检查当前状态是否允许重新连接if (!isValidStateForReconnection()) {// Ignore connection closed when we are shutting downlog.info("[{}] [{}] Ignoring reconnection request (state: {})", state.topic, state.getHandlerName(), state.getState());return;}try {state.client.getConnection(state.topic) // 获取与指定主题的连接.thenAccept(cnx -> connection.connectionOpened(cnx)) // 处理连接打开事件.exceptionally(this::handleConnectionError);} catch (Throwable t) {log.warn("[{}] [{}] Exception thrown while getting connection: ", state.topic, state.getHandlerName(), t);reconnectLater(t);}
}

真正核心创建链接在这里:org.apache.pulsar.client.impl.ConnectionPool#createConnection(java.net.InetSocketAddress, java.net.InetSocketAddress, int)

其实 Pulsar 的 Producer 与 Broker 创建连接和 Kafka 的如出一辙,TCP都是走的Netty那一套。
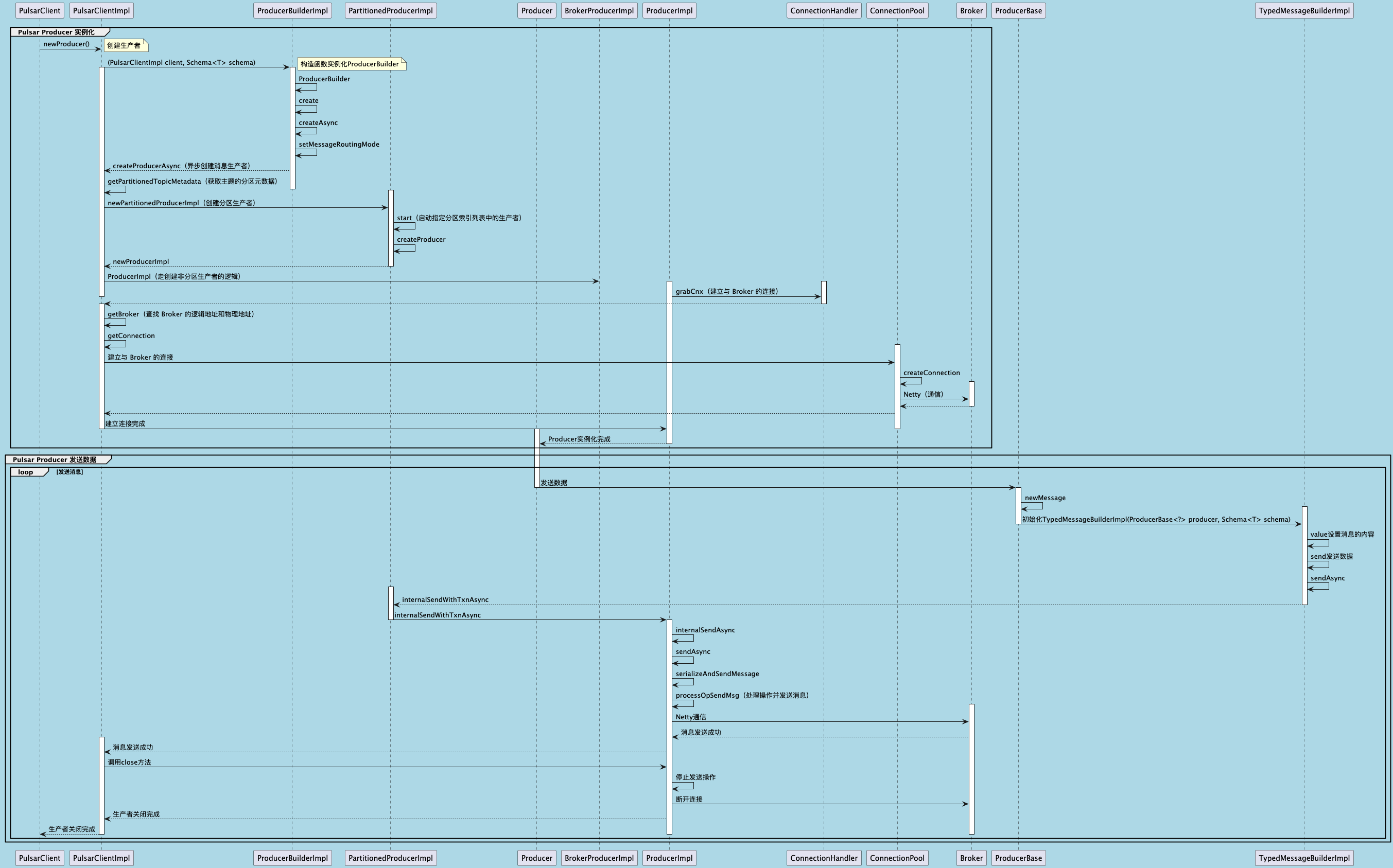
3.3 Producer 实例化时序图

四、调用 send 接口发送数据
主要看 producer.send(message.getBytes());
4.1 newMessage方法

4.2 value方法

4.3 send方法

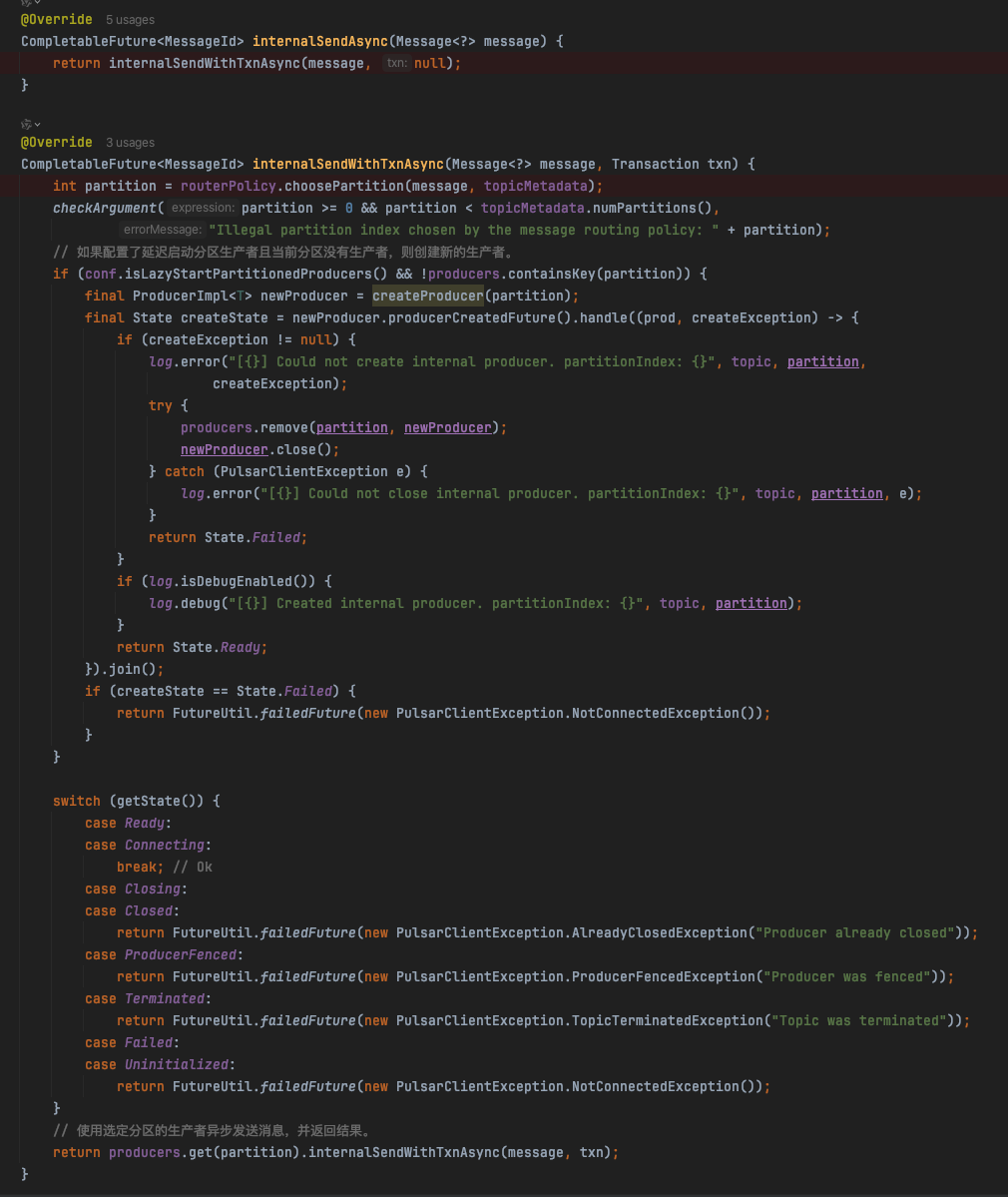
发送的核心方法在:org.apache.pulsar.client.impl.ProducerImpl#internalSendWithTxnAsync
@Override
CompletableFuture<MessageId> internalSendWithTxnAsync(Message<?> message, Transaction txn) {if (txn == null) {return internalSendAsync(message);} else {return ((TransactionImpl) txn).registerProducedTopic(topic).thenCompose(ignored -> internalSendAsync(message));}
}
继续跟到internalSendAsync方法里去:

继续跟到sendAsync方法里去:

继续跟到serializeAndSendMessage方法里去:

最后跟到processOpSendMsg处理操作并发送消息方法里去,走的Netty通信把消息发送到Broker里去。

这样分析下来,也就比较清晰了。下面老周再给大家看下整体的时序图,从创建 Pulsar Producer 实例到调用 send 接口发送数据的全生命周期。