JAVA-springboot JOSN解析库
SpringBoot从入门到精通-第12章 JOSN解析库
一、JSON解析简介
在当下流行的前后端分离的项目中,传递数据时不可或缺的。为了保证在传递数据的过程中不丢失信息,就需要一种让前端和后端都识别的传递数据的格式,这种传递数据的格式就是JSON。其中,前端需要的是以“键:值”结构保存的JSON数据,后端需要的是JavaBean。
JSON,全程是JavaScript Object Notation,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。所谓数据交换格式,指的是前端和后端之间传递数据的格式。
相比于XML格式,JSON是轻量级的。
JSON格式例子:
{“name”:“sun”}
{
“name”:“sun”,
“age”:22
}
{“arr”:[1,2,3,4]}
{“people”:{“id”:111,“name”:“sun”,“age”:22}}
对于一个前后端分离的Spring Boot项目而言,前端需要的是以“键:值”结构保存的JSON数据,后端需要的是JavaBean,这就需要使用json解析库实现序列化与反序列化。
序列化指的是JavaBean转化为JSON数据,反序列化反之。
当前常用的两种JSON解析库,一种是Spring Boot内置的Jackson,另一种是由阿里巴巴开发的FastJson。
下面程序实例使用FastJson举例。
二、Spring Boot项目中使用JSON解析
1、pom.xml文件引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.9</version></dependency>
整体pom.xml文件内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>3.5.0</version><relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --></parent><groupId>com.mr</groupId><artifactId>_20250603spring_fastjson</artifactId><version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version><name>20250603spring_fastjson</name><description>20250603spring_fastjson</description><url/><licenses><license/></licenses><developers><developer/></developers><scm><connection/><developerConnection/><tag/><url/></scm><properties><java.version>17</java.version></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.9</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId></plugin></plugins></build></project>2、编写Controller
序列化方法
String text = JSON.toJSONString(obj)
反序列化方法
VO vo = JSON.parseObject(json, VO.class)
注:
obj:被转换的对象
VO:与JSON数据对应的实体类
package com.mr._20250603spring_fastjson;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;@RestControllerpublic class Controller {
Bean bean = new Bean("sun",22);
// @GetMapping@RequestMapping("/login")public String login(@RequestBody String json){Map loginDate = JSON.parseObject(json, Map.class);String username = loginDate.get("username").toString();String password = loginDate.get("password").toString();Map<String,String> result = new HashMap<>();String code = "";String msg = "";if ("mr".equals(username) && "123".equals(password)){code = "200";msg = "登录成功";}else {code = "500";msg = "账号或密码错误";}result.put("code",code);result.put("msg",msg);return JSON.toJSONString(result);// System.out.println("wdwdwdw");
// System.out.println("bean"+bean);
// String str = JSON.toJSONString(bean);
// System.out.println("bean_json"+ str);
// return str;}
}3、apipost工具测试
3.1请求格式为json,请求参数值与程序逻辑判断值一致时
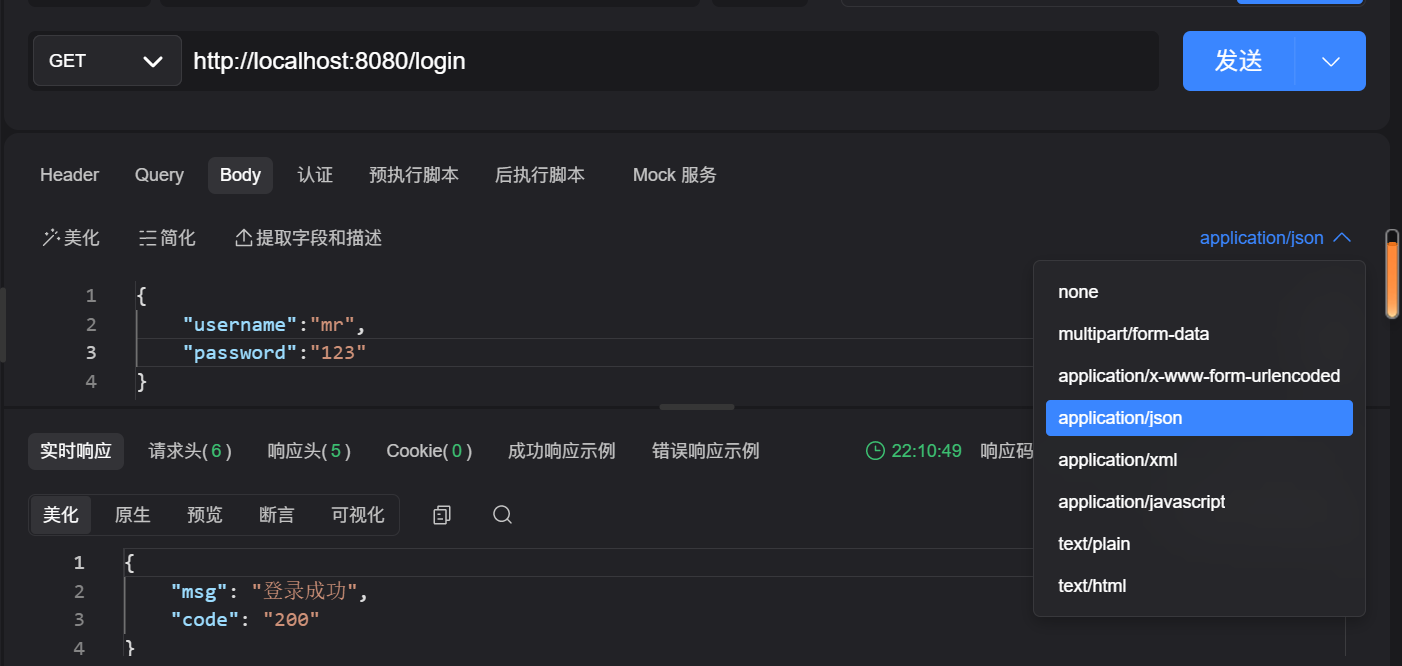
3.2请求格式为json,请求参数值与程序逻辑判断值不一致时

三、遇到的问题
-
请求时注意根据验证的请求体格式选择

