篇章七 数据结构——栈和队列
目录
1. 栈(Stack)
1.1 概念
1.图示栈概念:
2.栈在现实生活中的例子:
1.2 栈的使用
1.3 栈的模拟实现
1.接口
2.数组实现
1.4 栈的应用场景
1. 改变元素的序列
2.单链表是否可以实现栈?
2.1 数组实现:顺序栈
2.2 链表实现:链式栈
1. 单链表:
2. 双链表:
3.将递归转化为循环
4.括号匹配
5. 逆波兰表达式求值
6. 出栈入栈次序匹配
1.5 概念区分
栈、虚拟机栈、栈帧有什么区别呢?
2. 队列(Queue)
2.1 概念
1.队列接口图及含义编辑
2.2 队列的使用
2.3 队列模拟实现
2.4 循环队列
3. 双端队列 (Deque)
4. 练习
4.1 用队列实现栈。OJ链接
4.2 用栈实现队列。OJ链接
1. 栈(Stack)
1.1 概念
1.图示栈概念:

栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。
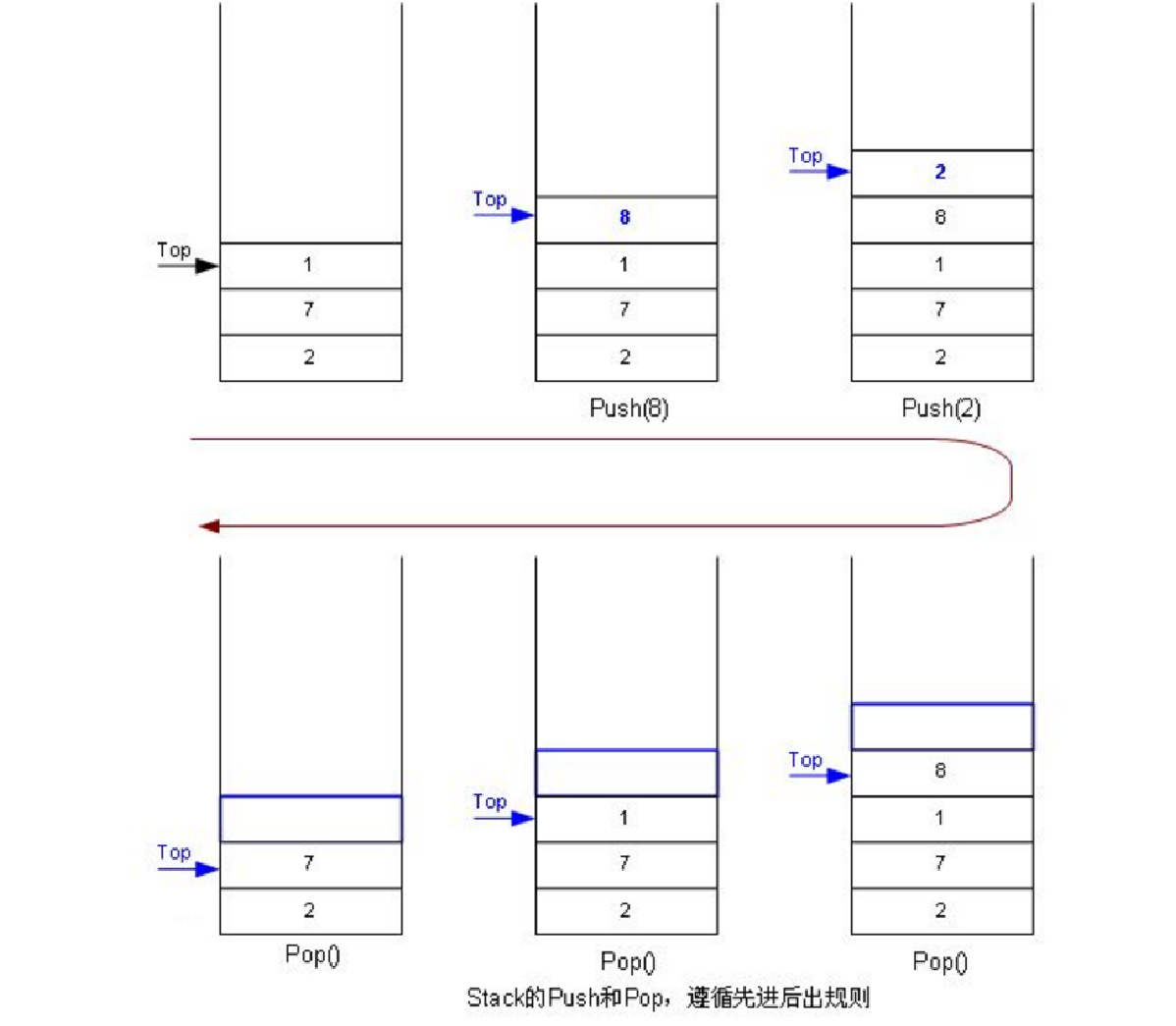
2.栈在现实生活中的例子:

1.2 栈的使用

public static void main(String[] args) {Stack<Integer> s = new Stack();s.push(1);s.push(2);s.push(3);s.push(4);System.out.println(s.size()); // 获取栈中有效元素个数---> 4System.out.println(s.peek()); // 获取栈顶元素---> 4s.pop(); // 4出栈,栈中剩余1 2 3,栈顶元素为3System.out.println(s.pop()); // 3出栈,栈中剩余1 2 栈顶元素为3if(s.empty()){System.out.println("栈空");}else{System.out.println(s.size());}
}1.3 栈的模拟实现
1.接口

从上图中可以看到,Stack继承了Vector,Vector和ArrayList类似,都是动态的顺序表,不同的是Vector是线程安全的。
public class MyStack {int[] array;int size;public MyStack(){array = new int[3];}public int push(int e){ensureCapacity();array[size++] = e;return e;}public int pop(){int e = peek();size--;return e;}public int peek(){if(empty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素");}return array[size-1];}public int size(){return size;}public boolean empty(){return 0 == size;}private void ensureCapacity(){if(size == array.length){array = Arrays.copyOf(array, size*2);}}
}2.数组实现

注意:
此处usedSize的值 —— pop逻辑

import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA* Description* User: 王杰* Date: 2025-05-30* Time: 13:42*/
public class MyStack {public int[] elem;public int usedSize;public MyStack() {this.elem = new int[10];}public void push(int val) {if (isFull()) {this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem, 2 * elem.length);}elem[usedSize++] = val;}public boolean isFull() {return usedSize == elem.length;}public int pop() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new EmptyStackException();}int val = elem[usedSize - 1];usedSize--;return val;}public int peek() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return elem[usedSize - 1];}public boolean isEmpty() {return usedSize == 0;}
}
1.4 栈的应用场景
1. 改变元素的序列
1. 若进栈序列为 1,2,3,4 ,进栈过程中可以出栈,则下列不可能的一个出栈序列是()
A: 1,4,3,2 B: 2,3,4,1 C: 3,1,4,2 D: 3,4,2,1

2.一个栈的初始状态为空。现将元素1、2、3、4、5、A、B、C、D、E依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,则元素出栈的顺
序是( )。
A: 12345ABCDE B: EDCBA54321 C: ABCDE12345 D: 54321EDCBA

2.单链表是否可以实现栈?
2.1 数组实现:顺序栈

2.2 链表实现:链式栈
1. 单链表:

2. 双链表:

LinkedList 拿双向链表实现栈
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();stack.push(12);stack.push(23);stack.push(34);stack.push(45);System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println(stack.peek());
}3.将递归转化为循环
逆序打印链表
// 递归方式
void printList(Node head){if(null != head){printList(head.next);System.out.print(head.val + " ");}
}
// 循环方式
void printList(Node head){if(null == head){return;}Stack<Node> s = new Stack<>();// 将链表中的结点保存在栈中Node cur = head;while(null != cur){s.push(cur);cur = cur.next;}// 将栈中的元素出栈while(!s.empty()){System.out.print(s.pop().val + " ");}
}4.括号匹配

class Solution {public boolean isValid(String s) {Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {char ch = s.charAt(i);if(ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[') {stack.push(ch);}else {if(stack.isEmpty()) {return false;}// 此时开始判断是否匹配char ch1 = stack.peek();if(ch1 == '(' && ch == ')' || ch1 == '{' && ch == '}' || ch1 == '[' && ch == ']') {stack.pop();}else {return false;}}}if(!stack.isEmpty()) {return false;}return true;}
}5. 逆波兰表达式求值

class Solution {public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();for(String str : tokens) {if(!isOperator(str)) {int x = Integer.parseInt(str);stack.push(x);}else {int val2 = stack.pop();int val1 = stack.pop();switch(str) {case "+":stack.push(val1 + val2);break;case "-":stack.push(val1 - val2);break;case "*":stack.push(val1 * val2);break;case "/":stack.push(val1 / val2);break;}}}return stack.pop();}private boolean isOperator(String str) {if(str.equals("+") || str.equals("-") || str.equals("*") || str.equals("/")) {return true;}return false;}
}6. 出栈入栈次序匹配

import java.util.*;public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pushV int整型一维数组 * @param popV int整型一维数组 * @return bool布尔型*/public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();int j = 0;for(int i = 0; i < pushV.length; i++) {stack.push(pushV[i]);while(!stack.empty() && j < popV.length && stack.peek() == popV[j]) {stack.pop();j++;}}return stack.empty();}
}7.155. 最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class MinStack {public Stack<Integer> stack;public Stack<Integer> minStack;public MinStack() {stack = new Stack<>();minStack = new Stack<>();}public void push(int val) {stack.push(val);if(minStack.empty()) {minStack.push(val);}else {if(val <= minStack.peek()) {minStack.push(val);}}}public void pop() {if(stack.empty()) {return;}int popVal = stack.pop();if(popVal == minStack.peek()) {minStack.pop();}}public int top() {if(stack.empty()) {return -1;}return stack.peek();}public int getMin() {if(minStack.empty()) {return -1;}return minStack.peek();}
}
1.5 概念区分
栈、虚拟机栈、栈帧有什么区别呢?

2. 队列(Queue)
2.1 概念
1.队列接口图及含义
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(FirstIn First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)

2.2 队列的使用
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的。

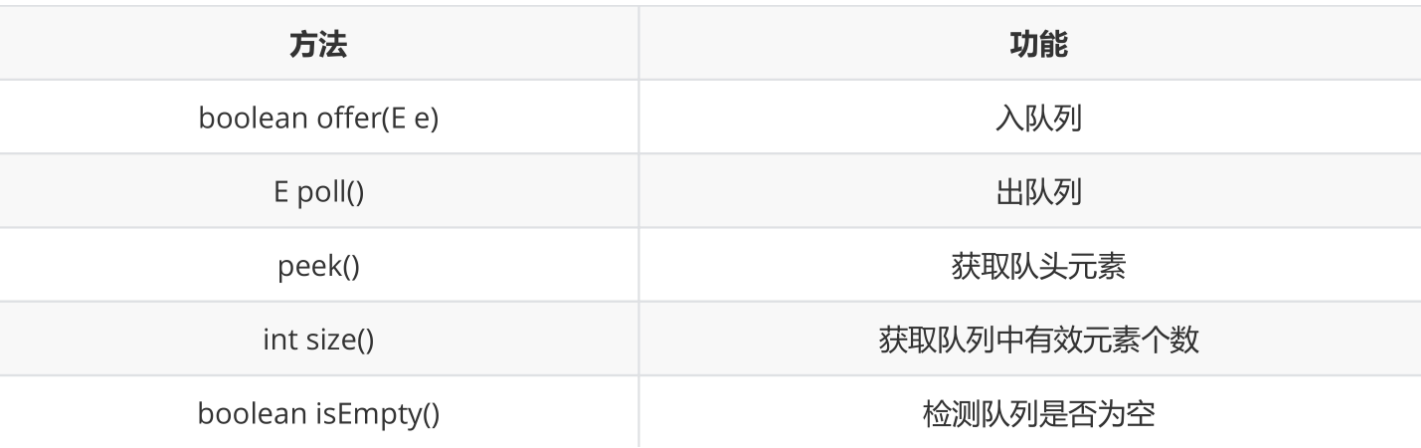
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
public static void main(String[] args) {Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(1);q.offer(2);q.offer(3);q.offer(4);q.offer(5); // 从队尾入队列System.out.println(q.size());System.out.println(q.peek()); // 获取队头元素q.poll();System.out.println(q.poll()); // 从队头出队列,并将删除的元素返回if(q.isEmpty()){System.out.println("队列空");}else{System.out.println(q.size());}
}2.3 队列模拟实现
队列中既然可以存储元素,那底层肯定要有能够保存元素的空间,通过前面线性表的学习了解到常见的空间类型有两种:顺序结构 和 链式结构。
此处为链表实现队列

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA* Description 栈和队列测试* User: 王杰* Date: 2025-05-30* Time: 13:36*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();queue.offer(1);queue.offer(2);queue.offer(3);queue.offer(4);System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());}public static void main5(String[] args) {Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(1);queue.offer(2);queue.offer(3);queue.offer(4);System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.peek());}public static void main4(String[] args) {MinStack minStack = new MinStack();minStack.push(-2);minStack.push(0);minStack.push(-3);System.out.println(minStack.getMin());minStack.pop();System.out.println(minStack.top());System.out.println(minStack.getMin());}public static void main3(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();stack.push(12);stack.push(23);stack.push(34);stack.push(45);System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println(stack.peek());}public static void main2(String[] args) {MyStack stack = new MyStack();stack.push(12);stack.push(23);stack.push(34);stack.push(45);System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println(stack.peek());}public static void main1(String[] args) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();stack.push(12);stack.push(23);stack.push(34);stack.push(45);System.out.println(stack.pop());System.out.println(stack.peek());}}
2.4 循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。循环队列通常使用数组实现。
此处为数组实现的循环队列

此处我们采用浪费一个空间的方案
class MyCircularQueue {public int front;public int rear;public int[] elem;public MyCircularQueue(int k) {elem = new int[k + 1]; }public boolean enQueue(int value) {if(isFull()) {return false;}elem[rear] = value;rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length;return true;}public boolean deQueue() {if(isEmpty()) {return false;}front = (front + 1) % elem.length;return true;}public int Front() {if(isEmpty()) {return -1;}return elem[front];}public int Rear() {if(isEmpty()) {return -1;}int index = (rear == 0) ? elem.length - 1 : rear - 1;return elem[index];}public boolean isEmpty() {return rear == front;}public boolean isFull() {return (rear + 1) % elem.length == front;}
}
3. 双端队列 (Deque)
双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。

Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。

在实际工程中,使用Deque接口是比较多的,栈和队列均可以使用该接口
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列的链式实现4. 练习
4.1 用队列实现栈。OJ链接

class MyStack {public Queue<Integer> qu1;public Queue<Integer> qu2;public MyStack() {qu1 = new LinkedList();qu2 = new LinkedList();}public void push(int x) {if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {qu1.offer(x);}else if(!qu2.isEmpty()) {qu2.offer(x);}else {qu1.offer(x);}}public int pop() {if(empty()) {return -1;}if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {int size = qu1.size();for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {qu2.offer(qu1.poll());}return qu1.poll();}else {int size = qu2.size();for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {qu1.offer(qu2.poll());}return qu2.poll();}}public int top() {if(empty()) {return -1;}if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {int size = qu1.size();int val = 0;for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {val = qu1.poll();qu2.offer(val);}return val;}else {int size = qu2.size();int val = 0;for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {val = qu2.poll();qu1.offer(val);}return val;}}public boolean empty() {return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();}
}4.2 用栈实现队列。OJ链接
注意:
使用 isEmpty():统一判断是否为空的接口

class MyQueue {public ArrayDeque<Integer> stack1;public ArrayDeque<Integer> stack2;public MyQueue() {stack1 = new ArrayDeque<>();stack2 = new ArrayDeque<>();}public void push(int x) {stack1.push(x);}public int pop() {if(empty()) {return -1;}if(stack2.isEmpty()) {while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.pop();}public int peek() {if(empty()) {return -1;}if(stack2.isEmpty()) {while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {stack2.push(stack1.pop());}}return stack2.peek();}public boolean empty() {return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();}
}
