字符串检索算法:KMP和Trie树
目录
1.引言
2.KMP算法
3.Trie树
3.1.简介
3.2.Trie树的应用场景
3.3.复杂度分析
3.4.Trie 树的优缺点
3.5.示例
1.引言
字符串匹配,给定一个主串 S 和一个模式串 P,判断 P 是否是 S 的子串,即找到 P 在 S 中第一次出现的位置。暴力匹配的思路是:从主串 S 的每个位置开始,逐个字符与模式串 P 比较。若匹配失败,主串指针回退到起始位置的下一个位置,重新开始匹配。 时间复杂度:最坏情况下为 O(n×m)(n 为主串长度,m 为模式串长度)。缺陷:当模式串存在重复前缀或后缀时,重复比较了很多已知信息,效率低下。于是就引出了KMP算法。
2.KMP算法
要理解KMP算法,首先要搞清楚真前缀与真后缀。在一个字符串中,真前缀是指除了最后一个字符外,一个字符串的头部连续的若干字符;真后缀是指除了第一个字符外,一个字符串的尾部连续的若干字符。举个例子:
字符串:"ABCDABD"
真前缀:"A"、"AB"、"ABC"、"ABCD"、"ABCDA"、"ABCDAB"
真后缀:"BCDABD"、"CDABD"、"DABD"、"ABD"、"BD"、"D"
递推计算next数组
next 数组的求解基于“真前缀”和“真后缀”,即next[i]等于P[0]...P[i - 1]最长的相同真前后缀的长度(首先设置next[0]=-1,边界条件)。我们以表格为例:
| i | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模式串 | A | B | C | D | A | B | D | '\0' |
| next[ i ] | -1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
- i = 0,对于模式串的首字符,我们统一为
next[0] = -1; - i = 1,前面的字符串为
A,其最长相同真前后缀长度为 0,即next[1] = 0; - i = 2,前面的字符串为
AB,其最长相同真前后缀长度为 0,即next[2] = 0; - i = 3,前面的字符串为
ABC,其最长相同真前后缀长度为 0,即next[3] = 0; - i = 4,前面的字符串为
ABCD,其最长相同真前后缀长度为 0,即next[4] = 0; - i = 5,前面的字符串为
ABCDA,其最长相同真前后缀为A,即next[5] = 1; - i = 6,前面的字符串为
ABCDAB,其最长相同真前后缀为AB,即next[6] = 2; - i = 7,前面的字符串为
ABCDABD,其最长相同真前后缀长度为 0,即next[7] = 0。
那么,为什么根据最长相同真前后缀的长度就可以实现在不匹配情况下的跳转呢?举个代表性的例子:假如i = 6时不匹配,此时我们是知道其位置前的字符串为ABCDAB,仔细观察这个字符串,首尾都有一个AB,既然在i = 6处的 D 不匹配,我们为何不直接把i = 2处的 C 拿过来继续比较呢,因为都有一个AB啊,而这个AB就是ABCDAB的最长相同真前后缀,其长度 2 正好是跳转的下标位置。
思路如此简单,接下来就是代码实现了,如下:
// 生成Next数组, 示例:“GTGTGCF”
std::vector<int> buildNext(const std::string& pattern) {std::vector<int> next(pattern.size(), 0);int j = 0;for (int i = 2; i < pattern.length(); i++) {while (j != 0 && pattern[j] != pattern[i - 1]) {//从next[i+1]的求解回溯到 next[j]j = next[j];}if (pattern[j] == pattern[i - 1]) {j++;}next[i] = j;}return next;
}int kmpSearch(const std::string& text, const std::string& pattern) {//预处理,生成next数组std::vector<int> next(std::move(buildNext(pattern)));int j = 0;//主循环,遍历主串字符for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {while (j > 0 && text[i] != pattern[j]) {//遇到坏字符时,查询next数组并改变模式串的起点j = next[j];}if (text[i] == pattern[j]) {j++;}if (j == pattern.length()) {//匹配成功,返回下标return i - pattern.length() + 1;}}return -1;
}复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:
- 构建
next数组:O(m)(每个字符最多被访问两次)。 - 匹配过程:O(n)(主串指针
i仅递增,不回退)。 - 总复杂度:O(n+m),优于暴力匹配的 O(n×m)。
- 构建
- 空间复杂度:O(m)(存储
next数组)。
3.Trie树
3.1.简介
Trie树,即前缀树,又称单词查找树,字典树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计和排序大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
Trie树的核心思想是空间换时间,利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以达到提高效率的目的。 它的优点是:最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
它有3个基本性质:
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
- 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
- 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
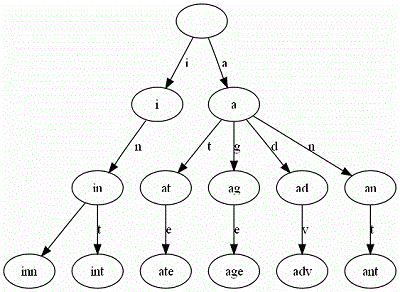
举一个例子。给出一组单词,inn, int, at, age, adv, ant, 我们可以得到下面的Trie:
3.2.Trie树的应用场景
字符串检索,词频统计,搜索引擎的热门查询
trie树在大数据查找和检索方面具有独特的优势,不过就是要求内存比较高,不过在没有内存限制的情况不适为一种好的方式,如:(节选自此文:海量数据处理面试题集锦与Bit-map详解)
a)有一个1G大小的一个文件,里面每一行是一个词,词的大小不超过16字节,内存限制大小是1M。返回频数最高的100个词。
b) 1000万字符串,其中有些是重复的,需要把重复的全部去掉,保留没有重复的字符串。请怎么设计和实现?
c)寻找热门查询:搜索引擎会通过日志文件把用户每次检索使用的所有检索串都记录下来,每个查询串的长度为1-255字节。假设目前有一千万个记录,这些查询串的重复读比较高,虽然总数是1千万,但是如果去除重复和,不超过3百万个。一个查询串的重复度越高,说明查询它的用户越多,也就越热门。请你统计最热门的10个查询串,要求使用的内存不能超过1G。
d)一个文本文件,大约有一万行,每行一个词,要求统计出其中最频繁出现的前10个词,请给出思想,给出时间复杂度分析
e) 给出一个词典,其中的单词为不良单词。单词均为小写字母。再给出一段文本,文本的每一行也由小写字母构成。判断文本中是否含有任何不良单词。例如,若rob是不良单词,那么文本problem含有不良单词。
(1) 请描述你解决这个问题的思路;
(2) 请给出主要的处理流程,算法,以及算法的复杂度。
字符串最长公共前缀
Trie树利用多个字符串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,反之,当我们把大量字符串存储到一棵trie树上时,我们可以快速得到某些字符串的公共前缀。举例:
给出N 个小写英文字母串,以及Q 个询问,即询问某两个串的最长公共前缀的长度是多少. 解决方案:
首先对所有的串建立其对应的字母树。此时发现,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即它们所在结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为了离线 (Offline)的最近公共祖先(Least Common Ancestor,简称LCA)问题。
而最近公共祖先问题同样是一个经典问题,可以用下面几种方法:
1. 利用并查集(Disjoint Set),可以采用采用经典的Tarjan 算法;
2. 求出字母树的欧拉序列(Euler Sequence )后,就可以转为经典的最小值查询(Range Minimum Query,简称RMQ)问题了;
3.3.复杂度分析
- 插入操作:时间复杂度为 O (m),这里的 m 指的是字符串的长度。
- 查找操作:时间复杂度同样为 O (m)。
- 空间复杂度:空间复杂度为 O (n),n 表示所有字符串中不同字符的总数,这一特点使得 Trie 树在处理大量字符串时非常高效。
3.4.Trie 树的优缺点
优点
- 高效前缀匹配:快速查找所有以某前缀开头的字符串(如搜索提示)。
- 避免重复存储:共享公共前缀,节省空间。
- 时间复杂度稳定:插入、查询、删除的时间复杂度均为 O(n)(n 为字符串长度)。
缺点
- 空间开销大:每个字符占用一个节点,可能浪费内存(尤其是字符集大时)。
- 实现复杂:需要处理动态节点分配和指针操作。
3.5.示例
示例一:一个字符串类型的数组arr1,另一个字符串类型的数组arr2。
- arr2中有哪些字符串,是arr1中出现的?请打印
- arr2中有哪些字符串,是作为arr1中某个字符串前缀出现的?请打印
- arr2中有哪些字符串,是作为arr1中某个字符串前缀出现的?请打印arr2中出现次数最大的前缀。
实现代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;
const int MaxBranchNum = 26;//可以扩展class TrieNode{
public:string word;int path; //该字符被划过多少次,用以统计以该字符串作为前缀的字符串的个数int End; //以该字符结尾的字符串TrieNode* nexts[MaxBranchNum];TrieNode(){word = "";path = 0;End = 0;memset(nexts,NULL,sizeof(TrieNode*) * MaxBranchNum);}};class TrieTree{
private:TrieNode *root;
public:TrieTree();~TrieTree();//插入字符串strvoid insert(string str);//查询字符串str是否出现过,并返回作为前缀几次int search(string str);//删除字符串strvoid Delete(string str);void destory(TrieNode* root);//打印树中的所有节点void printAll();//打印以str作为前缀的单词void printPre(string str);//按照字典顺序输出以root为根的所有单词void Print(TrieNode* root);//返回以str为前缀的单词的个数int prefixNumbers(string str);
};TrieTree::TrieTree()
{root = new TrieNode();
}TrieTree::~TrieTree()
{destory(root);
}void TrieTree::destory(TrieNode* root)
{if(root == nullptr)return ;for(int i=0;i<MaxBranchNum;i++){destory(root->nexts[i]);}delete root;root = nullptr;
}void TrieTree::insert(string str)
{if(str == "")return ;char buf[str.size()];strcpy(buf, str.c_str());TrieNode* node = root;int index = 0;for(int i=0; i<strlen(buf); i++){index = buf[i] - 'a';if(node->nexts[index] == nullptr){node->nexts[index] = new TrieNode();}node = node->nexts[index];node->path++;//有一条路径划过这个节点}node->End++;node->word = str;
}int TrieTree::search(string str)
{if(str == "")return 0;char buf[str.size()];strcpy(buf, str.c_str());TrieNode* node = root;int index = 0;for(int i=0;i<strlen(buf);i++){index = buf[i] - 'a';if(node->nexts[index] == nullptr){return 0;}node = node->nexts[index];}if(node != nullptr){return node->End;}else{return 0;}
}void TrieTree::Delete(string str)
{if(str == "")return ;char buf[str.size()];strcpy(buf, str.c_str());TrieNode* node = root;TrieNode* tmp;int index = 0;for(int i = 0 ; i<str.size();i++){index = buf[i] - 'a';tmp = node->nexts[index];if(--node->nexts[index]->path == 0){delete node->nexts[index];}node = tmp;}node->End--;
}int TrieTree::prefixNumbers(string str)
{if(str == "")return 0;char buf[str.size()];strcpy(buf, str.c_str());TrieNode* node = root;int index = 0;for(int i=0;i<strlen(buf);i++){index = buf[i] - 'a';if(node->nexts[index] == nullptr){return 0;}node = node->nexts[index];}return node->path;
}
void TrieTree::printPre(string str)
{if(str == "")return ;char buf[str.size()];strcpy(buf, str.c_str());TrieNode* node = root;int index = 0;for(int i=0;i<strlen(buf);i++){index = buf[i] - 'a';if(node->nexts[index] == nullptr){return ;}node = node->nexts[index];}Print(node);
}void TrieTree::Print(TrieNode* node)
{if(node == nullptr)return ;if(node->word != ""){cout<<node->word<<" "<<node->path<<endl;}for(int i = 0;i<MaxBranchNum;i++){Print(node->nexts[i]);}
}void TrieTree::printAll()
{Print(root);
}int main()
{cout << "Hello world!" << endl;TrieTree trie;string str = "li";cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.insert(str);cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.Delete(str);cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.insert(str);cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.insert(str);cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.Delete("li");cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.Delete("li");cout<<trie.search(str)<<endl;trie.insert("lia");trie.insert("lic");trie.insert("liab");trie.insert("liad");trie.Delete("lia");cout<<trie.search("lia")<<endl;cout<<trie.prefixNumbers("lia")<<endl;return 0;
}示例二:实现 Trie 树,包含插入、查找、前缀搜索和删除功能。这个实现使用智能指针管理内存,确保内存安全。代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>class TrieNode {
public:std::unordered_map<char, std::unique_ptr<TrieNode>> children;bool is_end_of_word;TrieNode() : is_end_of_word(false) {}
};class Trie {
private:std::unique_ptr<TrieNode> root;// 辅助函数:递归删除单词bool remove(TrieNode* current, const std::string& word, int index) {if (index == word.length()) {if (!current->is_end_of_word)return false;current->is_end_of_word = false;return current->children.empty();}char ch = word[index];auto it = current->children.find(ch);if (it == current->children.end())return false;bool shouldDeleteCurrentNode = remove(it->second.get(), word, index + 1) && !it->second->is_end_of_word;if (shouldDeleteCurrentNode) {current->children.erase(ch);return current->children.empty();}return false;}public:Trie() : root(std::make_unique<TrieNode>()) {}// 插入单词void insert(const std::string& word) {TrieNode* current = root.get();for (char ch : word) {if (!current->children.count(ch)) {current->children[ch] = std::make_unique<TrieNode>();}current = current->children[ch].get();}current->is_end_of_word = true;}// 查找单词bool search(const std::string& word) const {const TrieNode* current = root.get();for (char ch : word) {auto it = current->children.find(ch);if (it == current->children.end())return false;current = it->second.get();}return current->is_end_of_word;}// 查找前缀bool startsWith(const std::string& prefix) const {const TrieNode* current = root.get();for (char ch : prefix) {auto it = current->children.find(ch);if (it == current->children.end())return false;current = it->second.get();}return true;}// 删除单词void deleteWord(const std::string& word) {remove(root.get(), word, 0);}
};// 使用示例
int main() {Trie trie;trie.insert("apple");std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << trie.search("apple") << std::endl; // 输出: truestd::cout << trie.search("app") << std::endl; // 输出: falsestd::cout << trie.startsWith("app") << std::endl; // 输出: truetrie.insert("app");std::cout << trie.search("app") << std::endl; // 输出: truetrie.deleteWord("apple");std::cout << trie.search("apple") << std::endl; // 输出: falsestd::cout << trie.search("app") << std::endl; // 输出: truereturn 0;
}这个 C++ 实现具有以下特点:
- 内存安全:使用
std::unique_ptr管理节点内存,避免内存泄漏 - 高效查找:利用
unordered_map实现 O (1) 的子节点查找 - 完整功能:包含插入、查找、前缀搜索和删除操作
- 递归删除:删除操作会自动清理不再使用的节点
你可以根据需要扩展这个实现,例如添加统计单词数量、获取所有以特定前缀开头的单词等功能。
