Leetcode 55
1 题目
797. 所有可能的路径
给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的所有路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)
graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
示例 1:
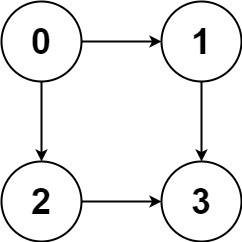
输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] 输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]] 解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
示例 2:
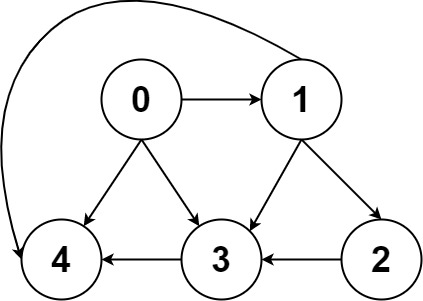
输入:graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]] 输出:[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
提示:
n == graph.length2 <= n <= 150 <= graph[i][j] < ngraph[i][j] != i(即不存在自环)graph[i]中的所有元素 互不相同- 保证输入为 有向无环图(DAG)
2 代码实现
1. LeetCode 核心代码模式(只需要实现 Solution 类)
#include <vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {
private:vector<vector<int>> result; // 存储所有路径vector<int> path; // 存储当前路径// 深度优先搜索函数void dfs(int current, const vector<vector<int>>& graph, int target) {path.push_back(current); // 当前节点加入路径// 如果到达终点,记录路径if (current == target) {result.push_back(path);} else {// 遍历所有可到达的下一个节点,递归搜索for (int next : graph[current]) {dfs(next, graph, target);}}path.pop_back(); // 回溯:移除当前节点,尝试其他路径}public:vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {int target = graph.size() - 1; // 终点是最后一个节点(n-1)dfs(0, graph, target); // 从起点0开始搜索return result;}
};
2. ACM 模式(完整可运行代码,包含输入输出)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {
private:vector<vector<int>> result;vector<int> path;void dfs(int current, const vector<vector<int>>& graph, int target) {path.push_back(current);if (current == target) {result.push_back(path);} else {for (int next : graph[current]) {dfs(next, graph, target);}}path.pop_back();}public:vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {int target = graph.size() - 1;dfs(0, graph, target);return result;}
};int main() {// 读取输入(图的邻接表)int n;cin >> n; // 节点数量vector<vector<int>> graph(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {int m;cin >> m; // 第i个节点的邻接节点数量graph[i].resize(m);for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {cin >> graph[i][j]; // 邻接节点的值}}// 计算并输出结果Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> paths = solution.allPathsSourceTarget(graph);// 按照题目要求的格式输出所有路径cout << "[";for (size_t i = 0; i < paths.size(); ++i) {cout << "[";for (size_t j = 0; j < paths[i].size(); ++j) {cout << paths[i][j];if (j != paths[i].size() - 1) {cout << ",";}}cout << "]";if (i != paths.size() - 1) {cout << ",";}}cout << "]" << endl;return 0;
}
输入输出说明(ACM 模式)
-
输入格式:第一行输入节点数量
n接下来n行,每行先输入一个整数m(表示当前节点的邻接节点数量),然后输入m个整数(邻接节点的值) -
示例输入(对应示例 1):
4 2 1 2 1 3 1 3 0 -
输出格式:按照 LeetCode 要求的格式输出所有路径(如
[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]])
可以直接将 ACM 模式代码复制到本地编译器(如 Dev-C++、VS Code)中运行,输入示例数据即可看到结果。
详解
一、彻底理解问题:什么是 “图” 和 “路径”?
1. 图的表示方式
题目里的 graph 是一个二维数组,叫做 “邻接表”,专门用来表示图。比如 graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] :
- 索引
i表示 “当前节点”(地点) graph[i]里的元素表示 “从节点i出发,能直接到达的节点”(从当前地点出发的单向路)
具体来说:
graph[0] = [1,2]→ 节点 0 有两条路:0→1,0→2graph[1] = [3]→ 节点 1 有一条路:1→3graph[2] = [3]→ 节点 2 有一条路:2→3graph[3] = []→ 节点 3 没有路(终点)
2. 什么是 “路径”?
路径就是 “从起点到终点,依次经过的节点序列”。比如上面的例子,起点是 0,终点是 3(因为 n=4,n-1=3),所以路径就是:
- 0→1→3(先从 0 到 1,再从 1 到 3)
- 0→2→3(先从 0 到 2,再从 2 到 3)
二、解题思路:如何找到所有路径?
因为要找 “所有可能的路径”,我们需要一种 “不遗漏” 的搜索方法。可以想象成 “走迷宫”:从起点出发,尝试所有岔路,走到终点就记录路线,走不通就回头换一条路。这就是深度优先搜索(DFS)。
搜索步骤(以示例 1 为例):
- 从起点 0 出发,当前路径是
[0] - 0 有两个岔路:1 和 2,先试试 1:
- 走到 1,路径变成
[0,1] - 1 只有一个岔路 3,走到 3,路径变成
[0,1,3] - 3 是终点,记录这条路径
- 回头(回溯)到 1,再回头到 0,路径变回
[0]
- 走到 1,路径变成
- 再试试 0 的另一个岔路 2:
- 走到 2,路径变成
[0,2] - 2 只有一个岔路 3,走到 3,路径变成
[0,2,3] - 3 是终点,记录这条路径
- 回溯到 2,再回溯到 0,所有路都试完了
- 走到 2,路径变成
三、代码逐行解析(超详细版)
我们用 C++ 实现,核心是用 DFS 递归 + 回溯。
1. 准备工作:定义变量
#include <iostream>
#include <vector> // 用vector存储路径和结果
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:// 存储所有找到的路径(最终要返回的答案)vector<vector<int>> result;// 存储当前正在走的路径(临时变量,随时更新)vector<int> path;
2. DFS 函数:递归探索路径
// 函数作用:从当前节点current出发,探索所有可能的路径// 参数:// current:当前所在的节点(比如0、1、2等)// graph:整个图的邻接表(地图)// target:终点(n-1,比如示例1中的3)void dfs(int current, const vector<vector<int>>& graph, int target) {// 第一步:把当前节点加入“当前路径”中path.push_back(current); // 比如当前在0,path就变成[0]// 第二步:判断是否到达终点if (current == target) {// 如果到终点了,就把当前路径存入resultresult.push_back(path); // 比如[0,1,3]存入result} else {// 没到终点,就遍历当前节点的所有“岔路”(邻居节点)for (int next : graph[current]) { // graph[current]是当前节点能去的所有节点dfs(next, graph, target); // 递归:去下一个节点探索}}// 第三步:回溯(关键!)path.pop_back(); // 把当前节点从路径中移除,回到上一步}
3. 主函数:启动搜索
// 函数作用:入口函数,返回所有从0到n-1的路径vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {int n = graph.size(); // n是节点总数(比如示例1中graph有4个元素,n=4)int target = n - 1; // 终点是最后一个节点(n-1)// 从起点0开始搜索dfs(0, graph, target);return result; // 返回所有找到的路径}
};
4. 测试代码
int main() {// 测试示例1:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]vector<vector<int>> graph1 = {{1,2}, {3}, {3}, {}};Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result1 = solution.allPathsSourceTarget(graph1);// 打印结果cout << "示例1的所有路径:" << endl;for (const auto& p : result1) { // 遍历每条路径for (int node : p) { // 遍历路径中的每个节点cout << node << " ";}cout << endl; // 每条路径换行}// 输出应该是:// 0 1 3 // 0 2 3 return 0;
}
四、关键概念:为什么需要 “回溯”?
回溯是为了 “试完一条路后,回到上一个路口试其他路”。比如在示例 1 中:
- 当我们走到 3(终点)后,需要把 3 从 path 中移除(
path.pop_back()),path 变回[0,1] - 再把 1 移除,path 变回
[0],这样才能去试另一个岔路 2
如果没有回溯,path 会一直是[0,1,3],无法记录新的路径。
五、总结
- 图的邻接表:
graph[i]存的是从 i 出发能到的节点 - 目标:找从 0 到 n-1 的所有路径
- 方法:DFS 递归探索,每到一个节点就加入路径,到终点就记录,然后回溯试其他路
你可以把代码复制到编译器里运行,结合示例一步一步调试,看看 path 和 result 的变化,会更容易理解!
【图论,深度优先搜索基础题,深搜详解 | 卡码网:98. 所有可达路径】

