融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络用于舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测|文献速递-文献分享
Title
题目
Automatic prediction of depth of invasion in oral tongue squamous cellcarcinoma using a multimodal regression network fusing prior text andanatomical knowledge
融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络用于舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测
01
文献速递介绍
口腔癌是全球最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其总体发病率呈稳步上升趋势(Lo Casto 等,2022)。口腔鳞状细胞癌(OSCC)占口腔癌的 90% 以上,而舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)作为一种独特亚型,是口腔癌中最常见的类型(Ghorbanpour 等,2024)。手术切除仍是舌鳞状细胞癌的主要治疗方式,但患者预后往往较差,严重影响患者的健康和生活质量(Sultania 等,2023)。浸润深度(DOI)是舌鳞状细胞癌的关键预后因素,与淋巴结转移、手术治疗方案制定及术后复发预测密切相关,已被纳入美国癌症联合委员会(AJCC)发布的第 8 版 TNM 分期手册中的口腔癌分期系统(Lydiatt 等,2017;Minamitake 等,2021)。因此,准确预测舌鳞状细胞癌的浸润深度,对于评估肿瘤侵袭性、制定合理手术方案、预测术后复发风险及指导治疗决策至关重要。 浸润深度定义为肿瘤两侧最接近肿瘤的正常黏膜上皮基底膜与肿瘤浸润最深边缘之间的垂直距离(Tang 等,2022)。目前,病理图像中的浸润深度测量被认为是临床实践中的金标准,如图 1(a)所示。然而,该方法仅能在肿瘤手术切除后应用,作为一种有创操作,无法为术前手术规划提供及时参考。因此,众多研究者致力于探索基于术前磁共振成像(MRI)直接评估浸润深度的无创技术,多项研究表明其与病理浸润深度具有较强的相关性(Lee 和 Choi,2023)。临床实践中使用的影像学浸润深度测量方法如图 1(b-d)所示,该方法需在每个切片上确定基底膜水平线和侵蚀最深点,计算两者的垂直距离,并从中选取最大浸润深度用于对比。但这种手动测量方法存在诸多局限性:测量流程繁琐,高度依赖放射科医师的经验,预测稳定性较低;基底膜水平线和侵蚀最深点的确定易受主观因素影响,可能导致测量误差;此外,MRI 上肿瘤与水肿边界区分不清晰,成像模糊及伪影干扰也会引发测量误差。因此,迫切需要开发一种能够从术前图像中快速、准确、自动检测舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的方法。 目前,已有部分研究者探索了基于人工智能(AI)的肿瘤浸润预测方法。例如,Goto 等(2023)利用 EfficientNet-B1 网络对浸润深度小于 500 微米和 500 微米及以上的黏膜内和黏膜下胃癌进行自动分类,准确率达到 77%;Chen 等(2023)采用结合最小绝对收缩与选择算子和最大相关最小冗余特征的机器学习方法,对膀胱癌的不同浸润深度进行分类,实现了对病理性浸润、肌层浸润和外侵的准确分类;Li 等(2023)使用 ResNet 预测膀胱癌的肌层浸润,结果表明其预测性能优于放射科医师;Zhou 等(2022)提出一种两阶段专家引导的可解释预测网络,用于预测肝细胞癌的微血管侵犯,曲线下面积(AUC)达到 84.58%;Lai 等(2022)开发了一种融合先验知识感知的融合网络,通过纳入肿瘤边缘和区域特征,提高了肝细胞癌 CT 图像中大血管侵犯的预测效果。然而,这些研究主要集中于对肿瘤浸润状态进行分类,而非直接预测浸润深度数值。尽管舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动化准确预测是临床迫切需求,但目前尚未有相关研究报道。 从医学图像中自动预测数值的方法通常分为两类:基于解剖特征的自动测量法和基于回归网络的自动预测法。基于解剖特征的自动测量法需从图像中提取关键标志点、轮廓和区域,再根据解剖学原理测量浸润深度。例如,在颈动脉管腔直径和内中膜厚度的自动预测中,Lian 等(2021)提出一种基于解剖先验引导的测量方法,通过检测关键边界标志点提高测量的准确性和稳定性;Kwon 等(2024)提出一种基于深度学习的孕妇经阴道超声图像宫颈长度自动测量方法,先自动分割宫颈前、中、后解剖区域,再通过自动识别宫颈管及其端点最小化测量误差;Zou 等(2023)开发了一种脊柱 X 线图像 Cobb 角自动估计网络,结合脊柱标志点定位和倾斜度估计,通过融入带有形状先验知识的联合脊柱损失函数提高预测精度;此外,在手部 X 线图像手指关节间隙宽度的自动测量中,Ponnusamy 等(2023)先自动分割骨骼区域,再计算关节间隙宽度,使测量过程更直观。尽管基于解剖特征的自动测量法具有更好的可解释性,且能为放射科医师提供可视化结果,但该方法对解剖特征的提取精度要求较高,易受病变、噪声、图像模糊和组织变形等因素干扰。 基于回归网络的医学图像数值预测是医学成像中常用的另一种方法。由于数值预测并非总能找到合适的解剖学测量方法,回归网络通常适用于各类数值预测场景,因此应用广泛。例如,在脑年龄预测中,Peng 等(2021)提出一种轻量级卷积神经网络,结合不同预处理流程的互补信息,平均绝对误差(MAE)达到 2.14 年;Wang 等(2023a)引入偏斜损失函数校正脑年龄估计中的预测偏差;He 等(2022)考虑不同图像间的相关性,开发了一种深度关系学习回归网络,通过学习输入图像对之间的累积、相对、最大和最小关系降低平均绝对误差;Marcus 等(2023)提出一种多任务 transformer 网络,结合脑缺血病变分割和损伤年龄估计,通过互补关系学习实现优异的预测性能;在骨密度预测中,Gu 等(2023)提出一种将 X 线图像分解为骨骼分割 CT 投影的方法,利用生成对抗网络建模目标骨骼的密度分布,提高预测精度;Wang 等(2023b)提出一种基于胸部 X 线图像预测腰椎骨密度的方法,自动检测胸部 X 线中骨骼结构的局部感兴趣区域(ROI),并利用基于 transformer 的多 ROI 网络结合局部和全局信息准确估计椎体骨密度;在左心室射血分数(LVEF)预测中,Dai 等(2023)提出一种基于师生蒸馏的半监督回归网络,通过利用左心室的自监督分割作为掩码改善预测结果;Wei 等(2023)引入一种半监督回归网络用于外观和形状的协同学习,提高预测精度;此外,Dai 等(2022)开发了一种自适应对比损失函数,用于改善骨密度和左心室射血分数预测中的回归任务性能。尽管上述基于回归网络的预测方法可直接从医学图像中预测数值,实现相对简便,但其实决策过程不易解释,且未充分利用先验解剖学知识,难以准确捕捉解剖特征与预测任务之间的复杂关系。 为解决上述问题,本研究有效结合了解剖特征自动测量法与回归网络自动预测法的优势,提出一种融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络,用于舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。首先,结合 T1 加权成像(T1WI)和 T2 加权成像(T2WI)的多模态数据,采用 3D nnUNet(Isensee 等,2021)实现舌鳞状细胞癌的自动分割;其次,提出一种浸润深度自动测量方法,结合基底膜标志点自动检测与解剖学关系,确定舌鳞状细胞癌最大浸润深度的标志点及先验浸润深度;在此基础上,提出一种融合解剖学先验知识与文本信息的多模态回归网络,实现 MRI 图像中舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。本研究的主要贡献如下: 1. 据我们所知,这是首个舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动化预测方法,预测结果与病理金标准具有高度相关性,为浸润深度预测提供了一种无创手段。 2. 提出融合解剖学先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络,显著提高了舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的预测性能,预测结果优于多种最先进(SOTA)方法。 3. 基于舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的临床测量规则,提出一种结合基底膜标志点与解剖学关系的浸润深度自动测量方法,可为所提多模态回归网络提供先验文本和解剖学知识。 4. 该方法的预测结果优于住院医师和具有六年临床经验放射科医师的测量结果,表明其具有良好的临床应用潜力。
Aastract
摘要
Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (OTSCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in oral cancer.Its depth of invasion (DOI) serves as a crucial indicator for evaluating tumor invasiveness, predicting therisk of lymph node metastasis, and assessing patient prognosis. Compared to invasive measurement methodson pathology, DOI measurement on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive approach that canprovide a timely reference for preoperative surgical planning. However, this method has several limitations,including a cumbersome measurement process, strong subjectivity, high experience requirements, and poorprediction stability. To address these issues, we propose an automatic prediction algorithm for OTSCCDOI using a multimodal regression network that fuses prior text and anatomical knowledge. First, theautomatic segmentation of OTSCC is achieved using 3D nnUNet on multimodal MRI. Second, an automaticDOI measurement method that combines the detection of basement membrane landmarks with anatomicalrelationships is proposed to obtain 3D heatmap landmarks and prior DOI text. These elements are thenfused into the proposed multimodal regression network to realize the automatic prediction of OTSCC DOI.Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a mean absolute error (MAE) of 2.11 mm, aroot mean square error (RMSE) of 2.97 mm, and a mean squared error (MSE) of 8.81 mm2 , which aremarkedly better than several state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. The correlation with the pathological groundtruth reaches a Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.869, indicating high consistency. Additionally, ourmethod outperforms the manual measurements of a resident doctor and a radiologist with six years of clinicalexperience. In the future, our method will have good clinical application prospects in OTSCC DOI prediction.
舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)是口腔癌中最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。其浸润深度(DOI)是评估肿瘤侵袭性、预测淋巴结转移风险及评估患者预后的关键指标。与病理学有创测量方法相比,基于磁共振成像(MRI)的浸润深度测量是一种无创手段,可为术前手术规划提供及时参考。然而,该方法存在测量流程繁琐、主观性强、对经验要求高及预测稳定性差等局限性。为解决这些问题,本文提出一种融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络,用于舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。首先,利用3D nnUNet在多模态MRI上实现舌鳞状细胞癌的自动分割;其次,提出一种结合基底膜标志点检测与解剖学关系的浸润深度自动测量方法,获取三维热图标志点及先验浸润深度文本,并将这些元素融入所提多模态回归网络,实现舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。实验结果表明,该方法的平均绝对误差(MAE)为2.11毫米、均方根误差(RMSE)为2.97毫米、均方误差(MSE)为8.81平方毫米,显著优于多种最先进(SOTA)方法;与病理金标准的相关性达到皮尔逊相关系数(PCC)0.869,一致性较高。此外,该方法的性能优于住院医师及具有六年临床经验放射科医师的手动测量结果。未来,该方法在舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度预测方面具有良好的临床应用前景。
Method
方法
2.1. Overview of the proposed framework
The basic framework of the proposed algorithm is shown in Fig.
Given that the anatomical feature-based measurement method for
predicting OTSCC DOI is highly sensitive to the accuracy of landmarkdetection, and the regression network-based prediction method doesnot fully incorporate anatomical knowledge, we integrate prior DOIand anatomical knowledge into the multimodal regression network toimprove DOI prediction accuracy. The algorithm primarily consists ofautomatic segmentation of OTSCC, automatic acquisition of prior DOIand anatomical knowledge, and automatic prediction of OTSCC DOI.Specifically, the automatic segmentation of OTSCC is used to obtainits contour and slice range. The prior DOI and anatomical knowledgeare generated through the proposed automatic measurement methodof anatomical features. This process first predicts basement membranelandmarks using a detection network, and subsequently derives priorDOI and anatomical landmarks based on anatomical relationships.In the regression prediction phase, the OTSCC DOI is automaticallypredicted by integrating prior DOI information, anatomical landmarks,and multimodal images.
2.1 所提框架概述 所提算法的基本框架如图2所示。鉴于基于解剖特征的舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)浸润深度(DOI)测量方法对标志点检测精度高度敏感,且基于回归网络的预测方法未充分融入解剖学知识,本研究将先验浸润深度(DOI)与解剖学知识整合到多模态回归网络中,以提高浸润深度预测精度。该算法主要包括舌鳞状细胞癌自动分割、先验浸润深度与解剖学知识自动获取、舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度自动预测三个部分。具体而言,通过舌鳞状细胞癌自动分割获取其轮廓及切片范围;先验浸润深度与解剖学知识通过所提解剖特征自动测量方法生成,该过程先利用检测网络预测基底膜标志点,再基于解剖学关系推导先验浸润深度及解剖学标志点;在回归预测阶段,融合先验浸润深度信息、解剖学标志点及多模态图像,实现舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。
Conclusion
结论
This study proposes an automatic prediction algorithm for theOTSCC DOI, leveraging a multimodal regression network that integrates prior text and anatomical knowledge. Initially, the 3D nnUNetframework was employed to automatically segment the OTSCC onmultimodal MRI, thereby acquiring the tumor region and its contour.Subsequently, an automatic DOI measurement method was developed by integrating the automatic detection of basement membranelandmarks with anatomical relationships, yielding 3D heatmap landmarks and prior DOI. Ultimately, the prior DOI text and 3D heatmaplandmarks were fused into the proposed multimodal MRI regressionnetwork to facilitate the automatic prediction of OTSCC DOI. Theexperimental results demonstrate that our method not only achievesautomatic OTSCC DOI prediction but also outperforms several SOTAmethods, with prediction results exhibiting a high correlation with thepathological ground truth. Moreover, the prediction performance ofour method outperforms the manual measurements a resident doctorand a radiologist with six years of clinical experience. Our methoddemonstrates strong potential for clinical adoption in OTSCC DOIprediction.
本研究提出一种舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)浸润深度(DOI)自动预测算法,该算法基于融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络。首先,采用3D nnUNet框架在多模态磁共振成像(MRI)上实现舌鳞状细胞癌的自动分割,获取肿瘤区域及其轮廓;其次,开发一种结合基底膜标志点自动检测与解剖学关系的浸润深度自动测量方法,得到三维热图标志点及先验浸润深度;最后,将先验浸润深度文本与三维热图标志点融入所提多模态MRI回归网络,实现舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动预测。实验结果表明,该方法不仅实现了舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度的自动化预测,且性能优于多种最先进(SOTA)方法,预测结果与病理金标准具有高度相关性;此外,该方法的预测性能优于住院医师及具有六年临床经验放射科医师的手动测量结果,在舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度预测方面具有较强的临床应用潜力。
Results
结果
Figure
图
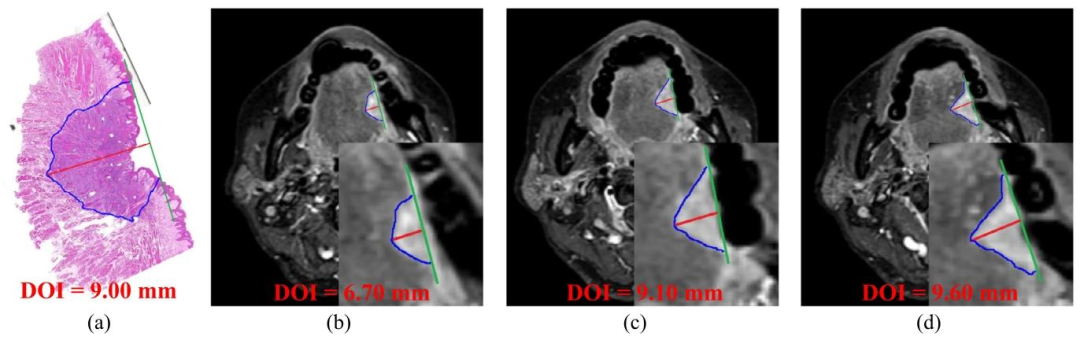
Fig. 1. (a) represents the measurement results of the OTSCC DOI on the pathological image, and (b-d) represents the DOI measured manually on different MRIslices. The blue line represents the OTSCC contour, the green line represents the horizontal line of the basement membrane, and the red line represents thevertical distance between the horizontal line of the basement membrane and the deepest edge of tumor invasion, that is the DOI.
图1 舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)浸润深度(DOI)测量示意图 (a)为病理图像上的舌鳞状细胞癌浸润深度测量结果;(b-d)为不同磁共振成像(MRI)切片上的手动浸润深度测量结果。蓝色线条代表舌鳞状细胞癌轮廓,绿色线条代表基底膜水平线,红色线条代表基底膜水平线与肿瘤浸润最深边缘之间的垂直距离,即浸润深度(DOI)。
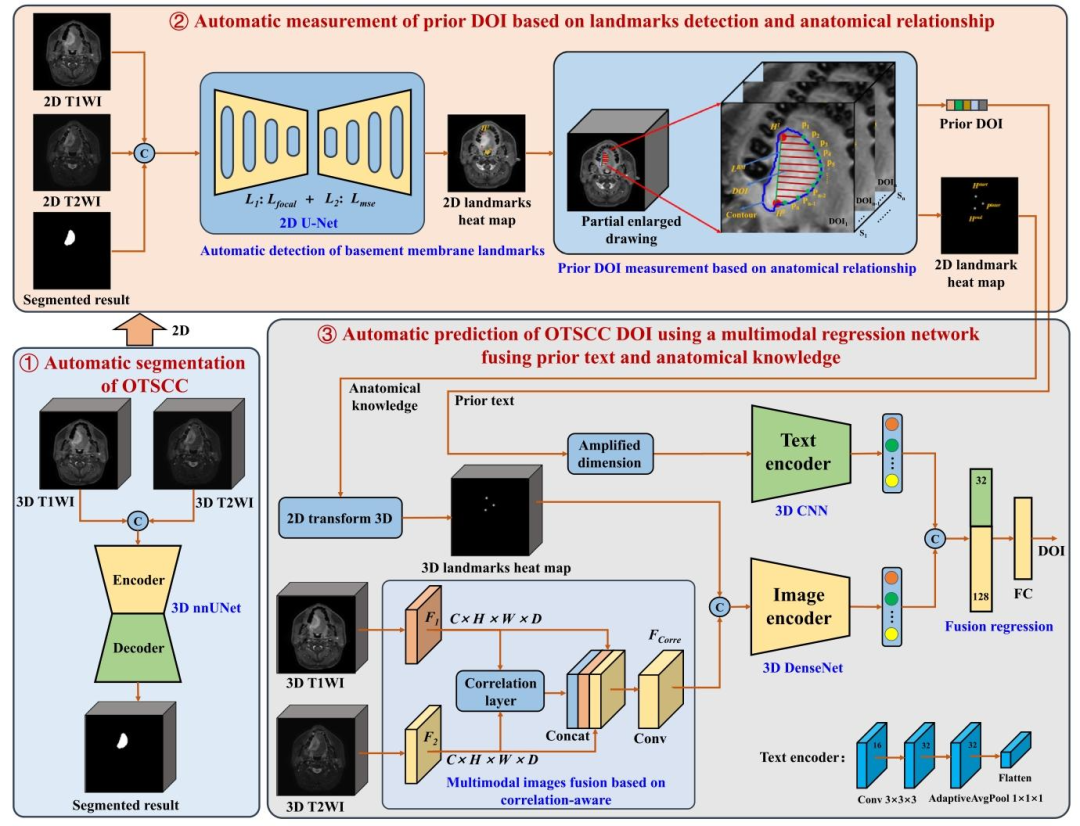
Fig. 2. A basic framework of multimodal regression network fusing prior text and anatomical knowledge to automatically predict OTSCC DOI.
图 2 融合先验文本与解剖学知识的多模态回归网络自动预测舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)浸润深度(DOI)的基本框架图
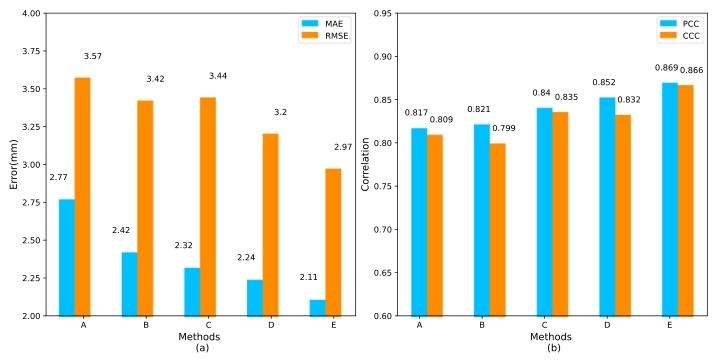
Fig. 3. The accuracy comparison bar chart of our method in ablationexperiment, where A represents the baseline, B represents baseline+landmark heatmap, C represents prior text, D represents baseline+landmarkheatmap+prior text, and E represents our method
图3 消融实验中所提方法的精度对比柱状图 其中,A代表基准模型,B代表基准模型+标志点热图,C代表先验文本,D代表基准模型+标志点热图+先验文本,E代表本文所提方法。
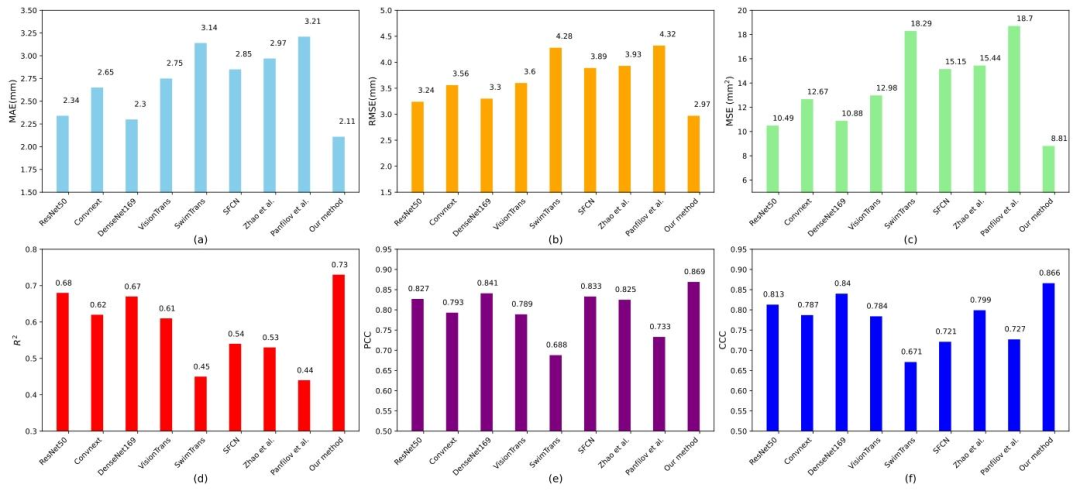
Fig. 4. Bar chart comparison of predicted DOIs between our method and several SOTA methods, evaluated using the metrics MAE, RMSE, MSE, R 2 , PCC andCCC
图4 所提方法与多种最先进(SOTA)方法的浸润深度(DOI)预测结果柱状对比图 该图基于平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)、均方误差(MSE)、决定系数(R²)、皮尔逊相关系数(PCC)及组内相关系数(CCC)六项指标进行评估。
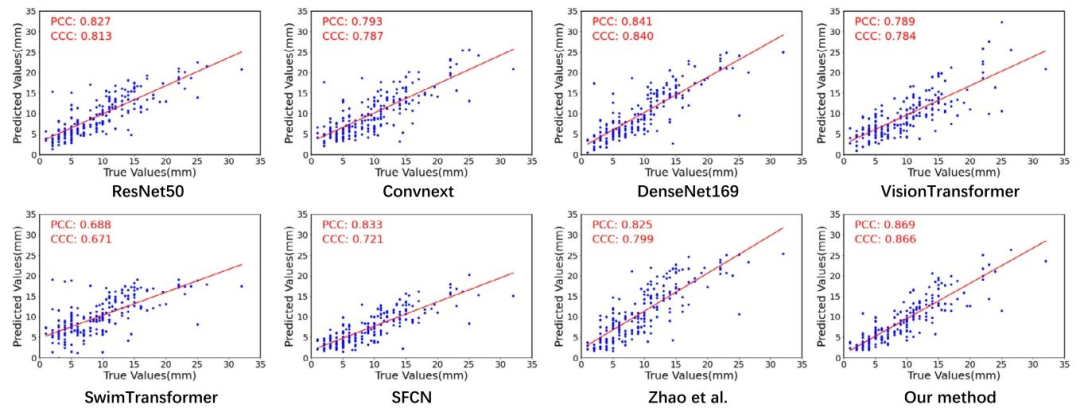
Fig. 5. Scatter plot comparison of predicted DOIs between our method and several SOTA methods, evaluated using the correlation metrics PCC and CCC
图5 所提方法与多种最先进(SOTA)方法的浸润深度(DOI)预测结果散点对比图 该图基于皮尔逊相关系数(PCC)和组内相关系数(CCC)两项相关性指标进行评估。
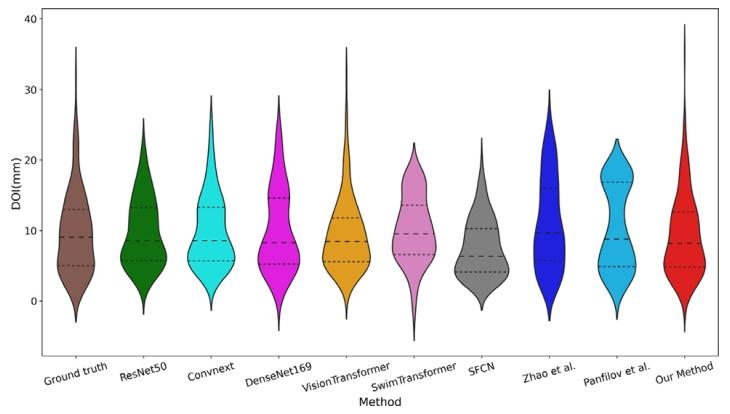
Fig. 6. Violin plot comparison of the predicted DOI distributions from ourmethod and several SOTA methods, to evaluate the distribution differencesbetween their prediction results and the ground truth.
图 6 所提方法与多种最先进(SOTA)方法的浸润深度(DOI)预测结果分布小提琴图对比该图用于评估各方法预测结果与真实值之间的分布差异
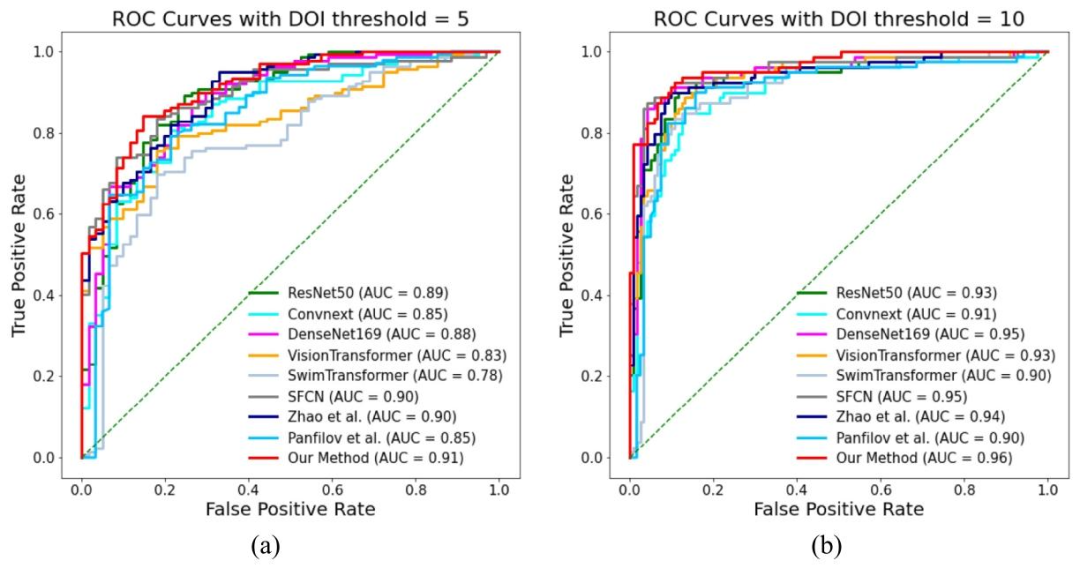
Fig. 7. ROC curve comparison of DOI prediction results between our method and several SOTA methods for binary classification at DOI thresholds of 5 and 10mm.
图7 以浸润深度(DOI)5毫米和10毫米为阈值的二分类任务中,所提方法与多种最先进(SOTA)方法的浸润深度预测结果ROC曲线对比图
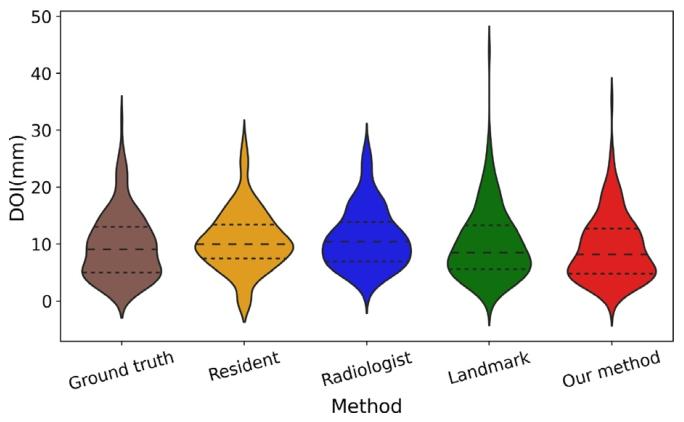
Fig. 8. Violin plot comparison of the DOI results distributions from ourmethod, landmark measurement method and, resident doctor and radiologist,to evaluate the distribution differences between their prediction results andthe ground truth.
图8 所提方法、标志点测量法、住院医师及放射科医师的浸润深度(DOI)结果分布小提琴图对比 该图用于评估各方法/人员的测量结果与真实值之间的分布差异。
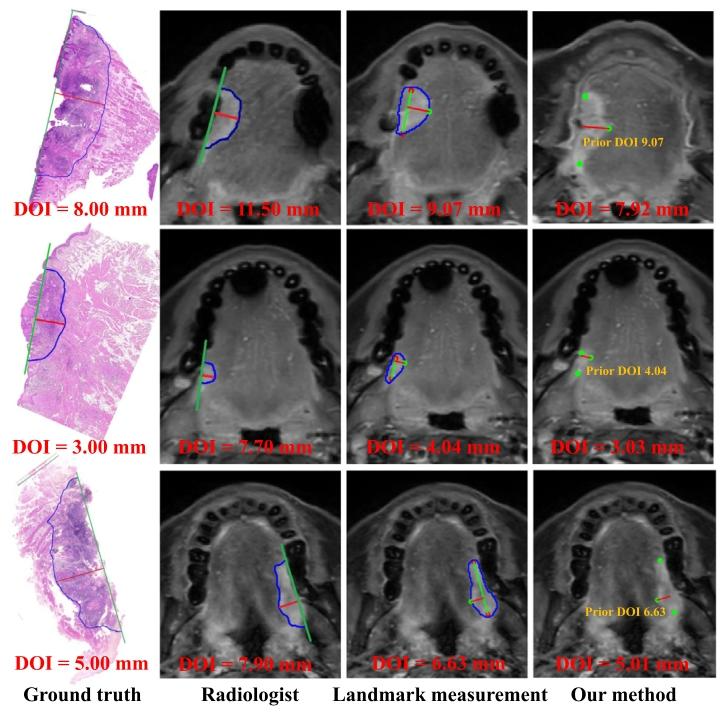
Fig. 9. Comparison of DOI results from three cases includes the manuallymeasured DOI ground truth from pathology, the manually measured DOI bythe radiologist on MRI, the automatically measured DOI using the landmarkmeasurement method on MRI, and the automatically predicted DOI usingour method on MRI. The first three methods show the basic elements of themeasurement, including the OTSCC contour line (blue), the horizontal line ofthe basement membrane (green), basement membrane landmarks (red), thevertical distance between the basement membrane and the deepest edge oftumor invasion (red), the intersection of OTSCC contour line and perpendicularline (green). Our method shows the input of three anatomical landmarks(green) and a priori DOI (red line)
图9 三例病例的浸润深度(DOI)结果对比图 包含病理手动测量的浸润深度真实值、放射科医师在磁共振成像(MRI)上的手动测量值、基于MRI的标志点测量法自动测量值,以及基于MRI的所提方法自动预测值。前三种方法标注了测量核心要素,包括舌鳞状细胞癌(OTSCC)轮廓线(蓝色)、基底膜水平线(绿色)、基底膜标志点(红色)、基底膜与肿瘤浸润最深边缘的垂直距离(红色,即浸润深度)、舌鳞状细胞癌轮廓线与垂直线的交点(绿色);所提方法标注了输入的三个解剖学标志点(绿色)及先验浸润深度(红色线条)。
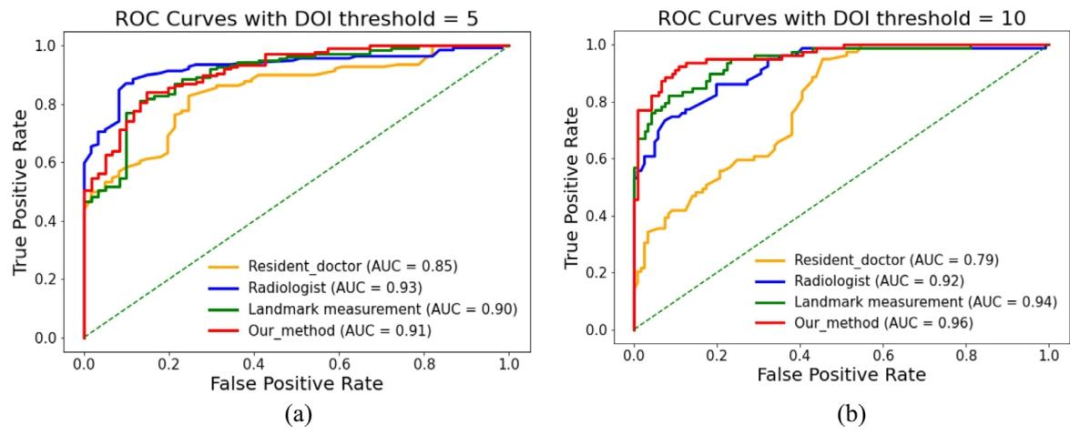
Fig. 10. ROC curves comparison of the DOI results distributions from our method, landmark measurement method and, resident doctor and radiologist in binaryclassification with DOI thresholds of 5 and 10 mm
图10 以浸润深度(DOI)5毫米和10毫米为阈值的二分类任务中,所提方法、标志点测量法、住院医师及放射科医师的浸润深度结果ROC曲线对比图
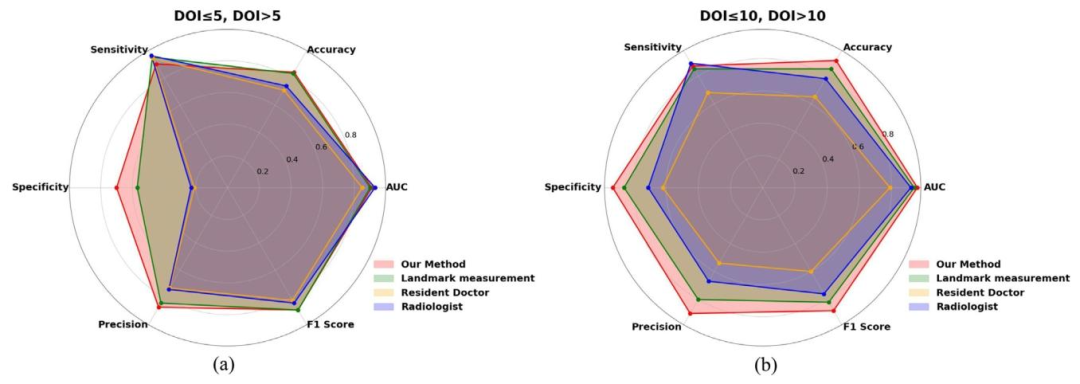
Fig. 11. Binary classification performance comparison of the DOI results distributions from our method, landmark measurement method and, resident doctor andradiologist in binary classification with DOI thresholds of 5 and 10 mm
图11 以浸润深度(DOI)5毫米和10毫米为阈值的二分类任务中,所提方法、标志点测量法、住院医师及放射科医师的浸润深度结果二分类性能对比图 要不要我帮你整理一份多主体二分类性能核心数据清单,明确各方法/人员在不同阈值下的准确率、灵敏度、特异度等关键指标,方便快速量化凸显所提方法在临床阈值判断场景中的性能优势?
Table
表
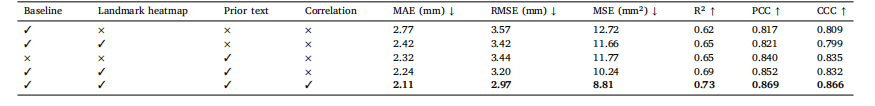
Table 1The accuracy comparison results from the ablation experiments of our method
表 1 所提方法的消融实验精度对比结果表

Table 2Ablation experiment results on convolution dimension in the text encoder
表 2 文本编码器中卷积维度的消融实验结果表
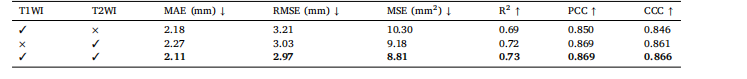
Table 3Ablation experiment results on image mode in our method
表3 所提方法在图像模态上的消融实验结果表
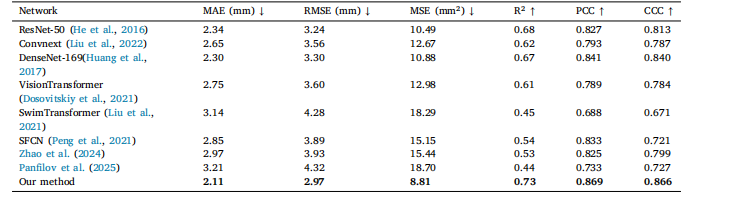
Table 4Comparison of the accuracy results between our method and several SOTA.
表 4 所提方法与多种最先进(SOTA)方法的精度对比结果表
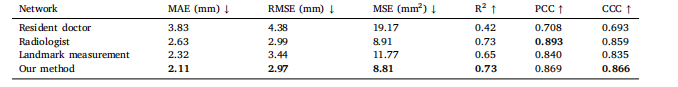
Table 5Comparison of the accuracy between proposed methods and the radiologists’ results
表5 所提方法与放射科医师测量结果的精度对比表
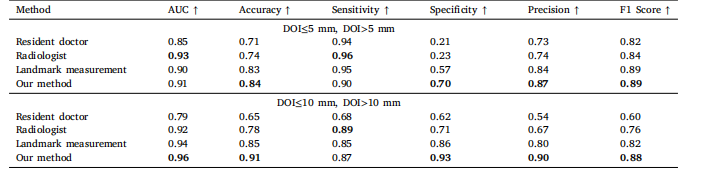
Table 6Comparison of the accuracy between proposed methods and the radiologists’ test results in binary classification with DOIthresholds of 5 and 10 mm.
表6 以浸润深度(DOI)5毫米和10毫米为阈值的二分类任务中,所提方法与放射科医师测试结果的精度对比表
