【Linux网络】多路转接select
IO多路转接之select
文章目录
- IO多路转接之select
- 初识select
- 理解select执行过程
- select的特点
- select的缺点
- select使用示例:检测标准输入输出
- select使用示例
初识select

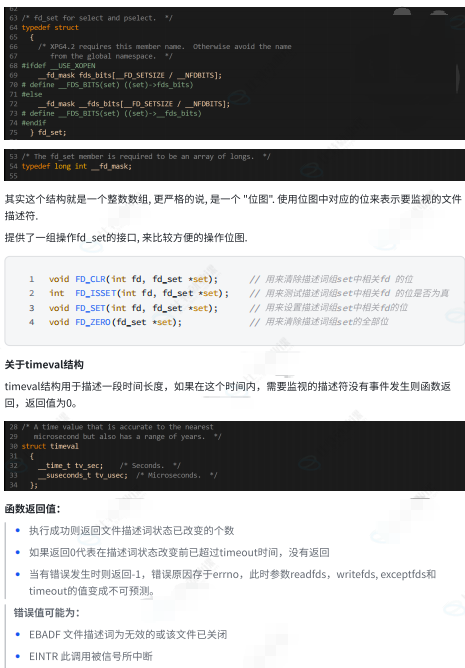
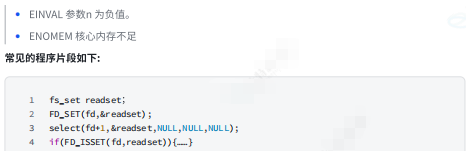



理解select执行过程


select的特点

select的缺点

select使用示例:检测标准输入输出
只检测标准输⼊:
代码如下(示例):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
int main() {fd_set read_fds;FD_ZERO(&read_fds);FD_SET(0, &read_fds);for (;;) {printf("> ");fflush(stdout);int ret = select(1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);if (ret < 0) {perror("select");continue;}if (FD_ISSET(0, &read_fds)) {char buf[1024] = { 0 };read(0, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1);printf("input: %s", buf);}else {printf("error! invaild fd\n");continue;}FD_ZERO(&read_fds);FD_SET(0, &read_fds);}return 0;
}

select使用示例
使用select是实现字典服务器
tcp_select_server.hpp
代码如下(示例):
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include "tcp_socket.hpp"
// 必要的调试函数
inline void PrintFdSet(fd_set* fds, int max_fd) {printf("select fds: ");for (int i = 0; i < max_fd + 1; ++i) {if (!FD_ISSET(i, fds)) {continue;}printf("%d ", i);}printf("\n");
}
ypedef std::function<void(const std::string& req, std::string* resp)>
Handler;
// 把 Select 封装成⼀个类. 这个类虽然保存很多 TcpSocket 对象指针, 但是不管理内存
class Selector {
public:Selector() {// [注意!] 初始化千万别忘了!!max_fd_ = 0;FD_ZERO(&read_fds_);}bool Add(const TcpSocket& sock) {int fd = sock.GetFd();printf("[Selector::Add] %d\n", fd);if (fd_map_.find(fd) != fd_map_.end()) {printf("Add failed! fd has in Selector!\n");return false;}fd_map_[fd] = sock;FD_SET(fd, &read_fds_);if (fd > max_fd_) {max_fd_ = fd;}return true;}bool Del(const TcpSocket& sock) {int fd = sock.GetFd();printf("[Selector::Del] %d\n", fd);if (fd_map_.find(fd) == fd_map_.end()) {printf("Del failed! fd has not in Selector!\n");return false;}fd_map_.erase(fd);FD_CLR(fd, &read_fds_);// 重新找到最⼤的⽂件描述符, 从右往左找⽐较快for (int i = max_fd_; i >= 0; --i) {if (!FD_ISSET(i, &read_fds_)) {continue;}max_fd_ = i;break;}return true;}// 返回读就绪的⽂件描述符集bool Wait(std::vector<TcpSocket>* output) {output->clear();// [注意] 此处必须要创建⼀个临时变量, 否则原来的结果会被覆盖掉fd_set tmp = read_fds_;// DEBUGPrintFdSet(&tmp, max_fd_);int nfds = select(max_fd_ + 1, &tmp, NULL, NULL, NULL);if (nfds < 0) {perror("select");return false;}// [注意!] 此处的循环条件必须是 i < max_fd_ + 1for (int i = 0; i < max_fd_ + 1; ++i) {if (!FD_ISSET(i, &tmp)) {continue;}output->push_back(fd_map_[i]);}return true;}
private:fd_set read_fds_;int max_fd_;// ⽂件描述符和 socket 对象的映射关系std::unordered_map<int, TcpSocket> fd_map_;
};
class TcpSelectServer {
public:TcpSelectServer(const std::string& ip, uint16_t port) : ip_(ip),port_(port) {}bool Start(Handler handler) const {// 1. 创建 socketTcpSocket listen_sock;bool ret = listen_sock.Socket();if (!ret) {return false;}// 2. 绑定端⼝号ret = listen_sock.Bind(ip_, port_);if (!ret) {return false;}// 3. 进⾏监听ret = listen_sock.Listen(5);if (!ret) {return false;}// 4. 创建 Selector 对象Selector selector;selector.Add(listen_sock);// 5. 进⼊事件循环for (;;) {std::vector<TcpSocket> output;bool ret = selector.Wait(&output);if (!ret) {continue;}// 6. 根据就绪的⽂件描述符的差别, 决定后续的处理逻辑for (size_t i = 0; i < output.size(); ++i) {if (output[i].GetFd() == listen_sock.GetFd()) {// 如果就绪的⽂件描述符是 listen_sock, 就执⾏ accept, 并加⼊到 select 中TcpSocket new_sock;listen_sock.Accept(&new_sock, NULL, NULL);selector.Add(new_sock);}else {// 如果就绪的⽂件描述符是 new_sock, 就进⾏⼀次请求的处理std::string req, resp;bool ret = output[i].Recv(&req);if (!ret) {selector.Del(output[i]);// [注意!] 需要关闭 socketoutput[i].Close();continue;}// 调⽤业务函数计算响应handler(req, &resp);// 将结果写回到客⼾端output[i].Send(resp);}} // end for} // end for (;;)return true;}
private:std::string ip_;uint16_t port_;
};