C++高级数据结构:并查表
在前面的内容中我们已经接触到了一些C++的高级数据结构,如AVL数、红黑树、哈希表等,但是实际上C++常用的数据结构不仅这些,接下来我们将深入图等高级的数据结构。不过在讲解图之前我们需要了解前置的数据结构:并查表。来方便我们学习图
相关代码已经上传至作者的个人gitee:楼田莉子/CPP代码学习喜欢请点个赞谢谢
目录
并查集原理
并查集的实现
简单版本的实现
完整版实现
并查集的应用
省份数量
等式方程的可满足性
并查集原理
在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合,然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于那个集合的运算。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-find set)。
下面举例说明:
某公司今年校招全国总共招生10人,西安招4人,成都招3人,武汉招3人,10个人来自不同的学校,起先互不相识,每个学生都是一个独立的小团体,现给这些学生进行编号:{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 给以下数组用来存储该小集体,数组中的数字代表:该小集体中具有成员的个数。
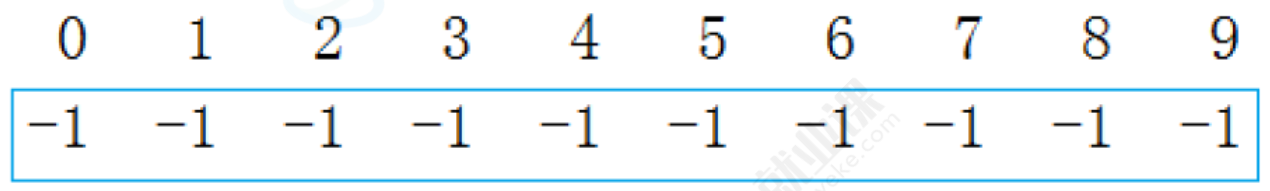
与堆类似,用数组下标表示树的关系。
初始状态用-1表示一个集合
毕业后,学生们要去公司上班,每个地方的学生自发组织成小分队一起上路,于是:
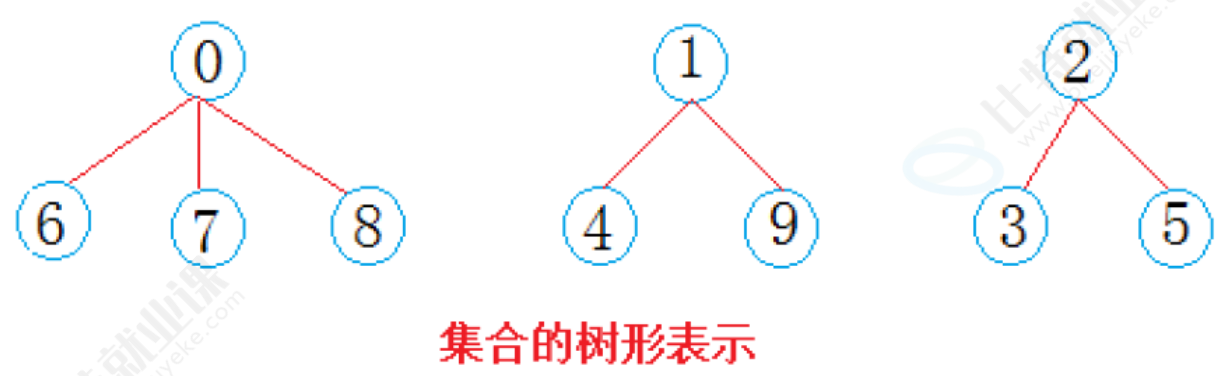
西安学生小分队s1={0,6,7,8},成都学生小分队s2={1,4,9},武汉学生小分队s3={2,3,5}就相互认识了,10个人形成了三个小团体。假设右三个群主0,1,2担任队长,负责大家的出行。我们可以用数的方式表示
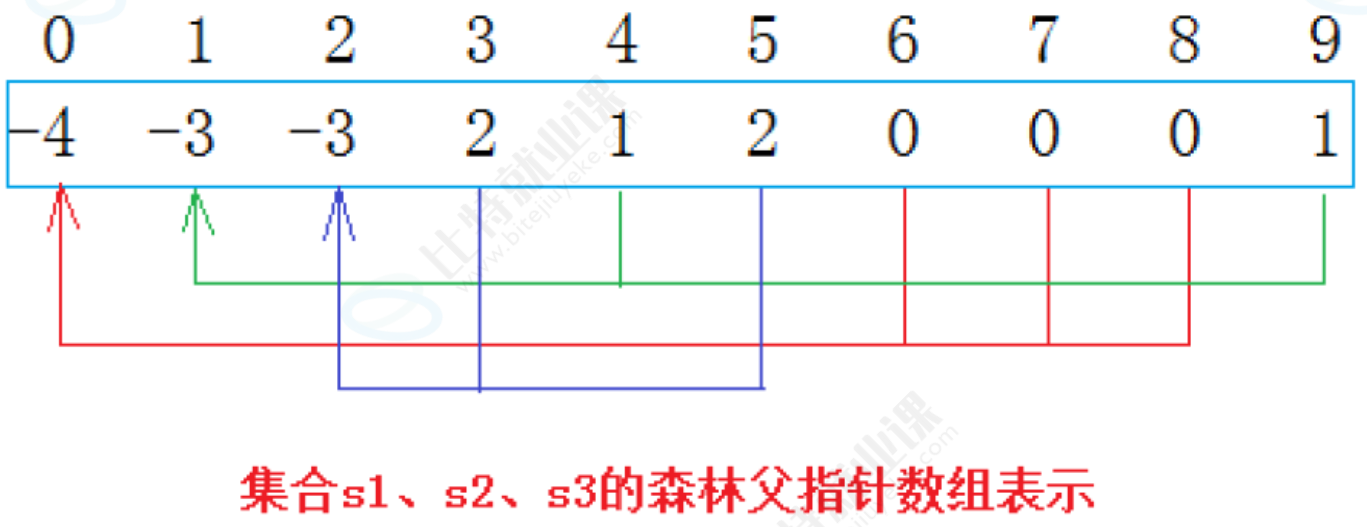
如果0跟6是朋友,那么把6所对应的-1加到0上,6号位变为0,0号位变为-2。这就是双亲表示法。
特点:
1、如果一个下标位置的值是负数,那它就是根。
2、如果一个下标位置的值是正数,那么它就是双亲的下标。
一趟火车之旅后,每个小分队成员就互相熟悉,称为了一个朋友圈。
从上图可以看出:编号6,7,8同学属于0号小分队,该小分队中有4人(包含队长0);编号为4和9的同学属于1号小分队,该小分队有3人(包含队长1),编号为3和5的同学属于2号小分队,该小分队有3个人(包含队长1)。
仔细观察数组中内融化,可以得出以下结论:
1. 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号
2. 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数
3. 数组中如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标
在公司工作一段时间后,西安小分队中8号同学与成都小分队1号同学奇迹般的走到了一起,两个小圈子的学生相互介绍,最后成为了一个小圈子:
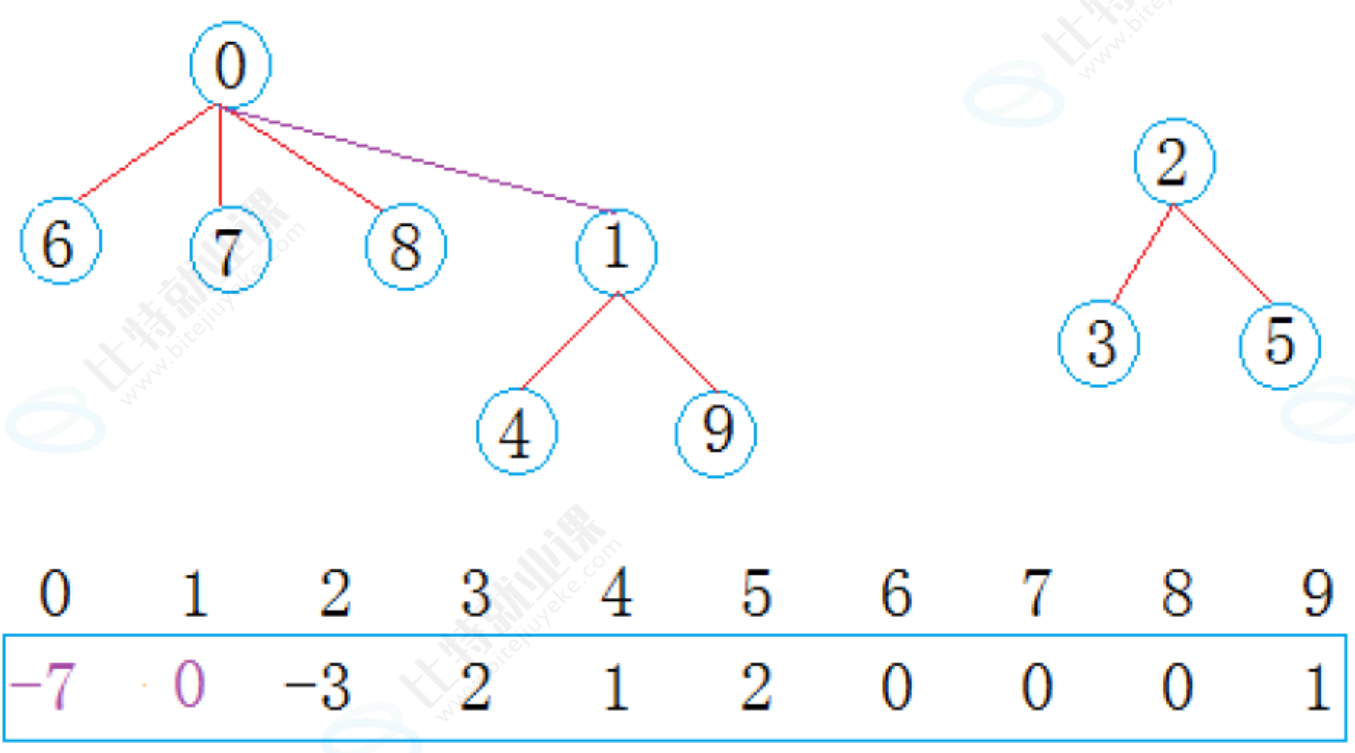
现在0集合有7个人,2集合有3个人,总共两个朋友圈。通过以上例子可知,并查集一般可以解决一下问题:
1. 查找元素属于哪个集合
沿着数组表示树形关系以上一直找到根(即:树中中元素为负数的位置)
2. 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合
沿着数组表示的树形关系往上一直找到树的根,如果根相同表明在同一个集合,否则不在
3. 将两个集合归并成一个集合
将两个集合中的元素合并
将一个集合名称改成另一个集合的名称
4. 集合的个数
遍历数组,数组中元素为负数的个数即为集合的个数。
并查集的实现
简单版本的实现
//UnionFindSet2.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using std::vector;
using std::swap;
namespace DSU
{class UnionFindSet{public:// 初始时,将数组中元素全部设置为1UnionFindSet(size_t size): _ufs(size, -1){}// 给一个元素的编号,找到该元素所在集合的名称int FindRoot(int index){// 如果数组中存储的是负数,找到,否则一直继续while (_ufs[index] >= 0){index = _ufs[index];}return index;}// 合并两个集合bool Union(int x1, int x2){int root1 = FindRoot(x1);int root2 = FindRoot(x2);// x1已经与x2在同一个集合if (root1 == root2)return false;//小的合并大的if (root1 > root2){swap(root1, root2);}// 将两个集合中元素合并_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];// 将其中一个集合名称改变成另外一个_ufs[root2] = root1;return true;}//两个集合是否相等bool Inset(int root1, int root2){return FindRoot(root1) == FindRoot(root2);}// 数组中负数的个数,即为集合的个数size_t Count()const{size_t count = 0;for (auto e : _ufs){if (e < 0)++count;}return count;}private:vector<int> _ufs;};
}
完整版实现
//UnionFindSet.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
using std::vector;
using std::map;
using std::string;
using std::unordered_map;
using std::unordered_set;
using std::initializer_list;//并查集的数据结构实现
namespace DSU
{template<class T>class UnionFindSet{public:// 默认构造函数UnionFindSet() = default;// 列表初始化构造函数UnionFindSet(std::initializer_list<T> initList){size_t i = 0;for (const T& element : initList){_data.push_back(element);_indexMap[element] = i;_parent.push_back(i);_size.push_back(1);++i;}_setCount = initList.size();}// 通过数组初始化UnionFindSet(const T* a, size_t n){for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i){_data.push_back(a[i]);_indexMap[a[i]] = i;_parent.push_back(i);_size.push_back(1);}_setCount = n;}// 通过vector初始化UnionFindSet(const vector<T>& data){for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i){_data.push_back(data[i]);_indexMap[data[i]] = i;_parent.push_back(i);_size.push_back(1);}_setCount = data.size();}// 添加新元素void AddElement(const T& element){if (_indexMap.find(element) != _indexMap.end())return;size_t newIndex = _data.size();_data.push_back(element);_indexMap[element] = newIndex;_parent.push_back(newIndex);_size.push_back(1);_setCount++;}// 批量添加元素void AddElements(std::initializer_list<T> elements){for (const T& element : elements){AddElement(element);}}// 查找元素所在集合的根节点索引int FindRoot(int index){// 路径压缩if (_parent[index] != index){_parent[index] = FindRoot(_parent[index]);}return _parent[index];}// 查找元素所在集合的根节点索引(通过元素值)int FindRoot(const T& element){auto it = _indexMap.find(element);if (it == _indexMap.end()){return -1;}return FindRoot(it->second);}// 合并两个元素所在的集合void Union(const T& a, const T& b){int rootA = FindRoot(a);int rootB = FindRoot(b);if (rootA == -1 || rootB == -1 || rootA == rootB)return;// 按秩合并:将小树合并到大树上if (_size[rootA] < _size[rootB]){_parent[rootA] = rootB;_size[rootB] += _size[rootA];}else{_parent[rootB] = rootA;_size[rootA] += _size[rootB];}_setCount--;}// 批量合并void Union(std::initializer_list<std::pair<T, T>> pairs){for (const auto& pair : pairs){Union(pair.first, pair.second);}}// 判断两个元素是否属于同一集合bool IsSameSet(const T& a, const T& b){int rootA = FindRoot(a);int rootB = FindRoot(b);return (rootA != -1 && rootB != -1 && rootA == rootB);}// 获取集合个数size_t GetSetCount() const{return _setCount;}// 根据集合根节点显示集合内所有元素void DisplaySetByRoot(const T& rootElement){int rootIndex = FindRoot(rootElement);if (rootIndex == -1){std::cout << "元素不存在或不是根节点!" << std::endl;return;}std::cout << "集合根节点 '" << _data[rootIndex] << "' 包含的元素:" << std::endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < _data.size(); ++i){if (FindRoot(i) == rootIndex){std::cout << " 编号 " << i << ": " << _data[i] << std::endl;}}}// 显示所有集合void DisplayAllSets(){std::cout << "总共 " << _setCount << " 个集合:" << std::endl;unordered_set<int> displayedRoots;for (size_t i = 0; i < _data.size(); ++i){int root = FindRoot(i);if (displayedRoots.find(root) == displayedRoots.end()){displayedRoots.insert(root);std::cout << "集合 " << root << " (根节点: '" << _data[root] << "'): ";vector<T> elements;for (size_t j = 0; j < _data.size(); ++j){if (FindRoot(j) == root){elements.push_back(_data[j]);}}for (size_t k = 0; k < elements.size(); ++k){std::cout << elements[k];if (k < elements.size() - 1) std::cout << ", ";}std::cout << std::endl;}}}// 根据编号查找元素所在集合的根节点内容T GetSetRootByIndex(int index){if (index < 0 || index >= _data.size()){return T();}int rootIndex = FindRoot(index);return _data[rootIndex];}// 根据元素值查找所在集合的根节点内容T GetSetRootByElement(const T& element){int rootIndex = FindRoot(element);if (rootIndex == -1) return T();return _data[rootIndex];}// 获取集合大小size_t GetSetSize(const T& element){int rootIndex = FindRoot(element);if (rootIndex == -1) return 0;return _size[rootIndex];}// 获取所有元素const vector<T>& GetElements() const{return _data;}// 检查元素是否存在bool Contains(const T& element) const{return _indexMap.find(element) != _indexMap.end();}private:vector<T> _data;map<T, int> _indexMap;vector<int> _parent;vector<int> _size;size_t _setCount = 0;};
}测试代码:
//test2.cpp
#include"UnionFindSet.h"
//并查集的数据结构实现
// 测试示例
int main()
{// 测试1: 使用列表初始化DSU::UnionFindSet<string> ufs1 = { "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David", "Eve" };std::cout << "测试1 - 列表初始化:" << std::endl;ufs1.DisplayAllSets();std::cout << "集合个数: " << ufs1.GetSetCount() << std::endl;std::cout << std::endl;// 测试2: 使用列表初始化 + 批量合并DSU::UnionFindSet<string> ufs2 = { "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David", "Eve" };// 使用initializer_list进行批量合并ufs2.Union({ {"Alice", "Bob"}, {"Charlie", "David"}, {"Bob", "Charlie"} });std::cout << "测试2 - 批量合并后:" << std::endl;ufs2.DisplayAllSets();std::cout << "集合个数: " << ufs2.GetSetCount() << std::endl;std::cout << std::endl;// 测试3: 默认构造 + 批量添加DSU::UnionFindSet<string> ufs3;ufs3.AddElements({ "Apple", "Banana", "Cherry", "Date", "Elderberry" });std::cout << "测试3 - 批量添加元素:" << std::endl;ufs3.DisplayAllSets();std::cout << "集合个数: " << ufs3.GetSetCount() << std::endl;std::cout << std::endl;// 合并操作ufs3.Union("Apple", "Banana");ufs3.Union("Cherry", "Date");std::cout << "测试3 - 合并后:" << std::endl;ufs3.DisplayAllSets();std::cout << "集合个数: " << ufs3.GetSetCount() << std::endl;return 0;
}并查集的应用
省份数量
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/bLyHh0/

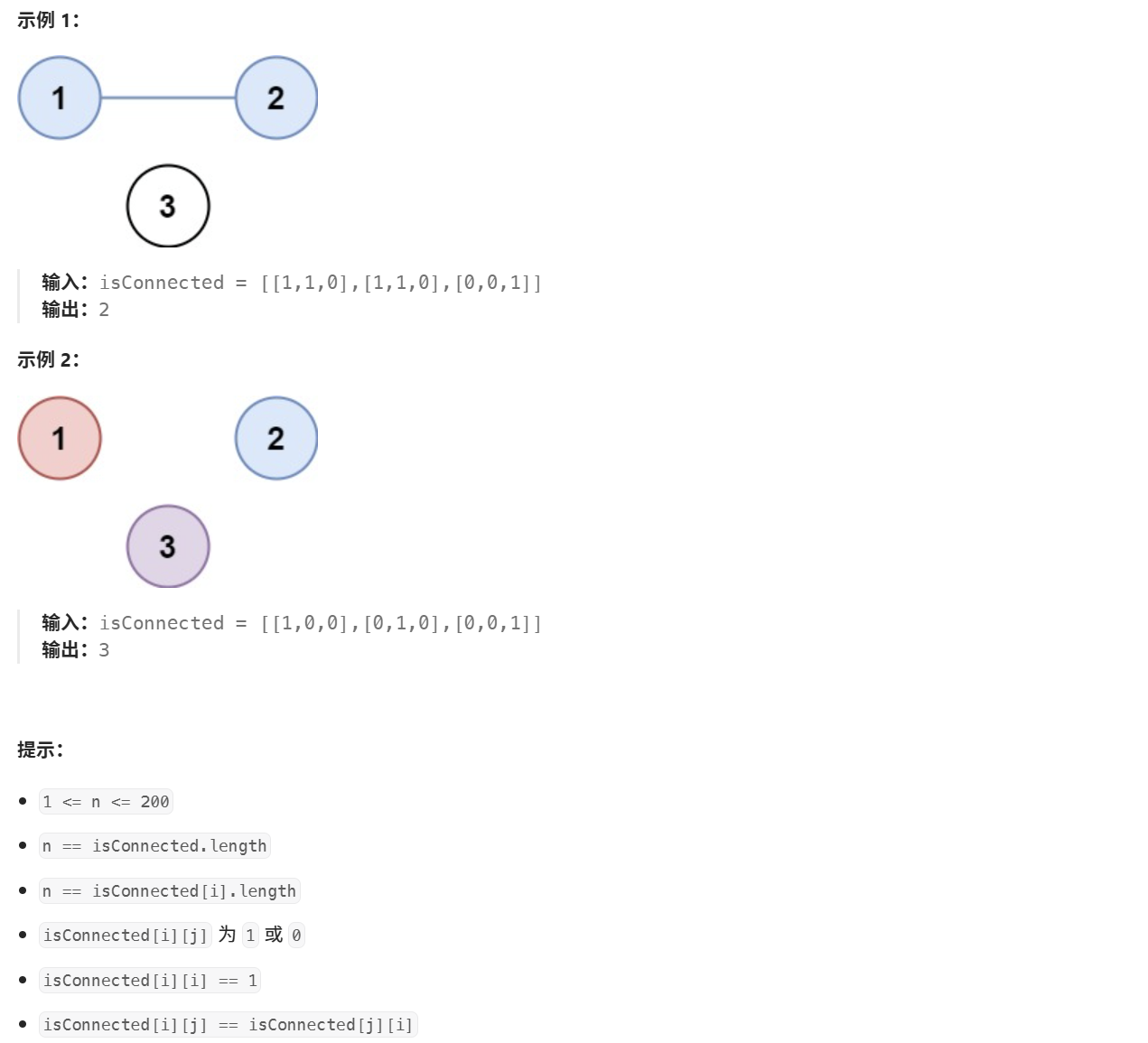
算法思路:
使用并查集(Union-Find)数据结构来解决:
-
初始化:每个城市自成一个集合
-
合并操作:遍历所有连接关系,将相连的城市合并到同一集合
-
统计结果:最后统计有多少个独立的集合
答案:
class Solution
{
public:int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected){// 手动控制并查集// ufs数组表示并查集,初始时每个元素都是根节点,值为负数表示集合大小// 例如:ufs[i] = -1 表示城市i是根节点,所在集合大小为1vector<int> ufs(isConnected.size(), -1);// 查找根节点的lambda函数// 通过不断向上查找父节点,直到找到根节点(值为负数的节点)auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x){// 一直向上查找,直到找到根节点(ufs[x] < 0)while (ufs[x] >= 0)x = ufs[x]; // 移动到父节点return x; // 返回根节点的索引};// 遍历所有城市连接关系for (size_t i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); ++i){for (size_t j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); ++j){// 如果城市i和城市j相连if (isConnected[i][j] == 1){// 查找两个城市所在的根节点int root1 = findRoot(i);int root2 = findRoot(j);// 如果根节点不同,说明属于不同集合,需要合并if (root1 != root2){// 合并策略:将小集合合并到大集合中// 更新大集合的大小(两个集合大小相加)ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];// 将小集合的根节点指向大集合的根节点ufs[root2] = root1;}}}}// 统计省份数量:即统计有多少个根节点(值为负数的元素)int n = 0;for (auto e : ufs){if (e < 0) // 负值表示这是一个根节点++n; // 每个根节点代表一个省份}return n;}
};等式方程的可满足性
题目链接:990. 等式方程的可满足性 - 力扣(LeetCode)
算法思路
使用并查集(Union-Find)数据结构来解决:
-
处理等式:将所有等式连接的变量合并到同一集合
-
验证不等式:检查所有不等式连接的变量是否在不同集合中
关键洞察
-
等式具有传递性:如果
a == b且b == c,那么a == c -
不等式必须与所有等式链保持一致
冲突检测逻辑:
if (root1 == root2) return false;答案:
class Solution {
public:bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations){// 初始化并查集,26个小写字母对应0-25的索引// 初始时每个字母自成一个集合,用-1表示(根节点,集合大小为1)vector<int> ufs(26, -1);// 查找根节点的lambda函数auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x){// 不断向上查找,直到找到根节点(值为负数的节点)while (ufs[x] >= 0)x = ufs[x]; // 移动到父节点return x; // 返回根节点索引};// 第一遍遍历:处理所有等式,构建等价关系for (auto& str : equations){// 只处理等号方程if (str[1] == '='){// 获取两个字母对应的索引('a'->0, 'b'->1, ..., 'z'->25)int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');// 如果两个字母不在同一集合,需要合并if (root1 != root2){// 合并策略:按大小合并,将小集合合并到大集合// 更新大集合的大小(两个集合大小相加)ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];// 将小集合的根节点指向大集合的根节点ufs[root2] = root1;}}}// 第二遍遍历:检查所有不等式是否与已建立的等价关系冲突for (auto& str : equations){// 只处理不等号方程if (str[1] == '!'){// 查找两个字母的根节点int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');// 如果两个字母在同一个集合中,说明它们应该相等// 但这与不等式矛盾,返回falseif (root1 == root2){return false;}}}// 所有不等式都通过了检查,没有冲突return true;}
};本期关于并查集的内容到这里就结束了,喜欢请点个赞支持一下谢谢
封面图自取:

