随机链表的复制 (带random的链表深度拷贝)| C语言实现
随机链表的复制![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/以上是LeetCode原题。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/以上是LeetCode原题。
方法一:暴力求解(时间复杂度:O(N^2))
暴力求解的思路:
1.先复制一个链表
2.原链表和新链表同步找random的相对位置,找到就存。
struct Node* BuyRLNode(int val)
{struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newnode->val = val;return newnode;
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {//空链表if(head == NULL )return NULL;//新建立一个链表struct Node* newhead = BuyRLNode( head->val);newhead->random = newhead;newhead->next = NULL;struct Node* curorg = head->next;struct Node* tail = newhead;//对新链表尾插,直至和原链表一样长while(curorg){struct Node* newnode = BuyRLNode( curorg->val);tail->next = newnode;tail = newnode;curorg = curorg->next;}//尾节点置空tail->next = NULL;//设置random指针struct Node* curnew = newhead;curorg = head;while(curnew && curorg){struct Node* posorg = head;struct Node* posnew = newhead;//新链表利用旧链表的random指针同步寻找对应的random指针while(curorg->random != posorg){posnew = posnew -> next;posorg = posorg -> next;}curnew->random = posnew;curnew = curnew->next;curorg = curorg->next;}return newhead;
}方法二:要求时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(1)
以下是解题思路:
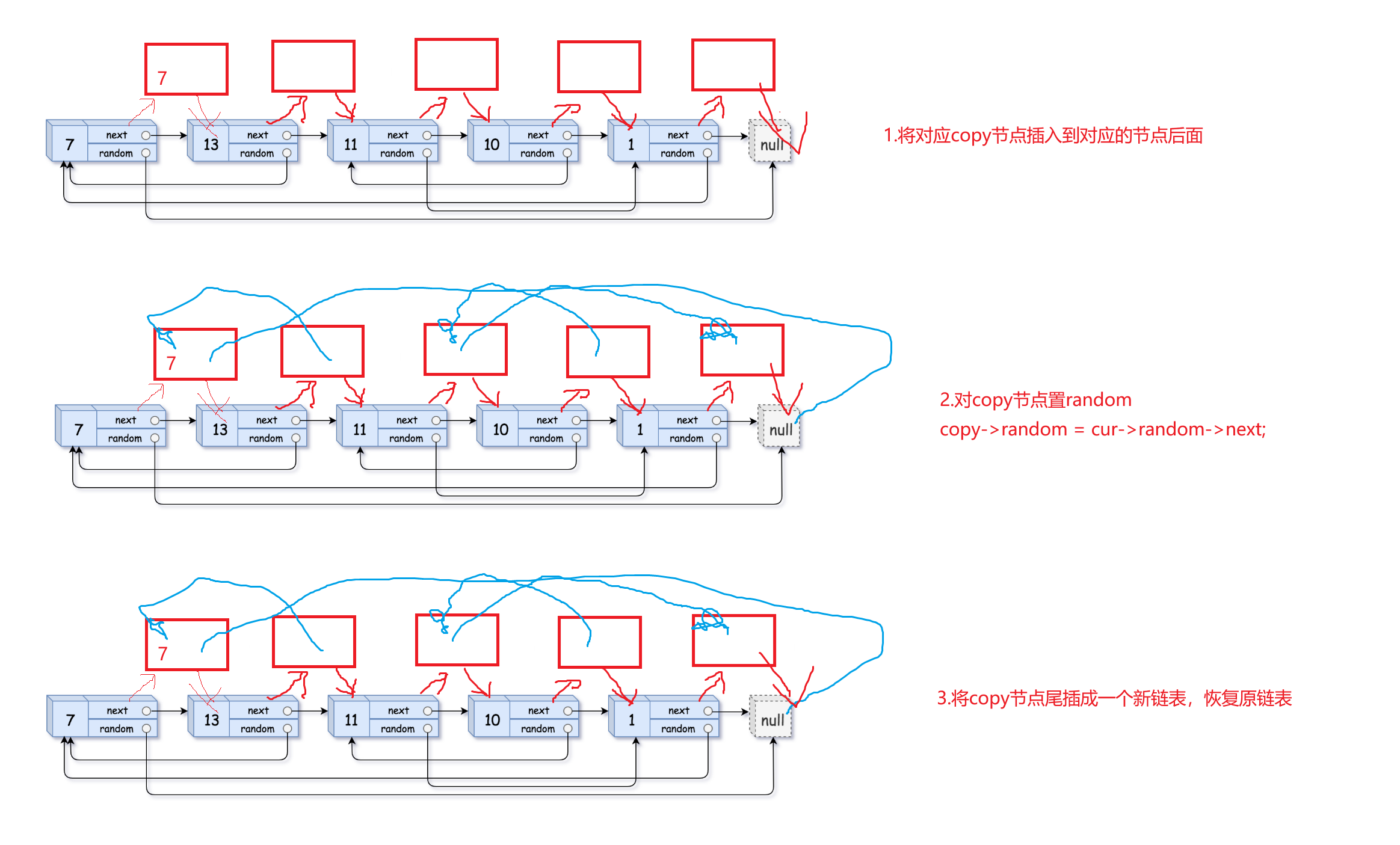
下面开始实现代码:
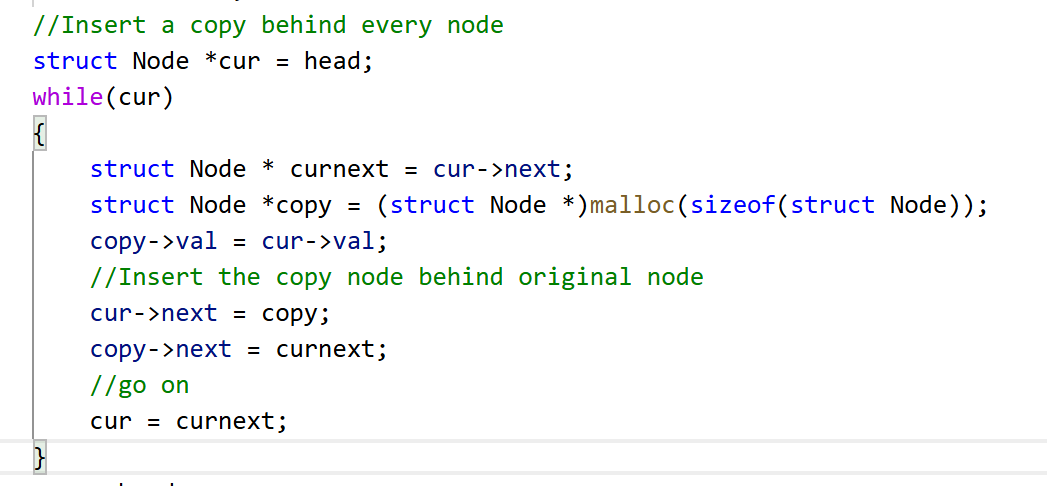
第一步:在原链表的每一个节点后面插入一个copy节点
这一步只需要开辟一个新节点,插到cur之后就可以了
下面的代码把copy的创建放到while里面而不是末尾,这样可以避免在cur到尾节点时cur = curnext后cur == NULL,curnext = cur -> next会对空指针解引用。
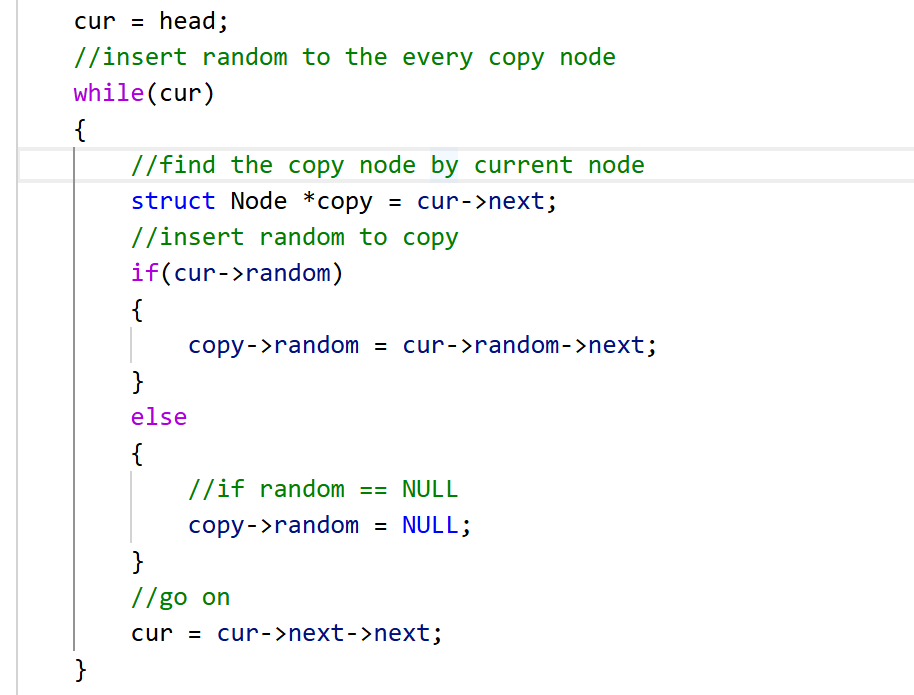
第二步:对copy节点置random
因为原节点对应的copy节点都在原节点的后面,所以用cur->random找到random后,直接访问这个random的下一个就可以了。
这里把copy的创建放在循环内,同样是为了避免对空指针解引用。
第三步:将copy节点尾插成一个新链表,恢复原链表
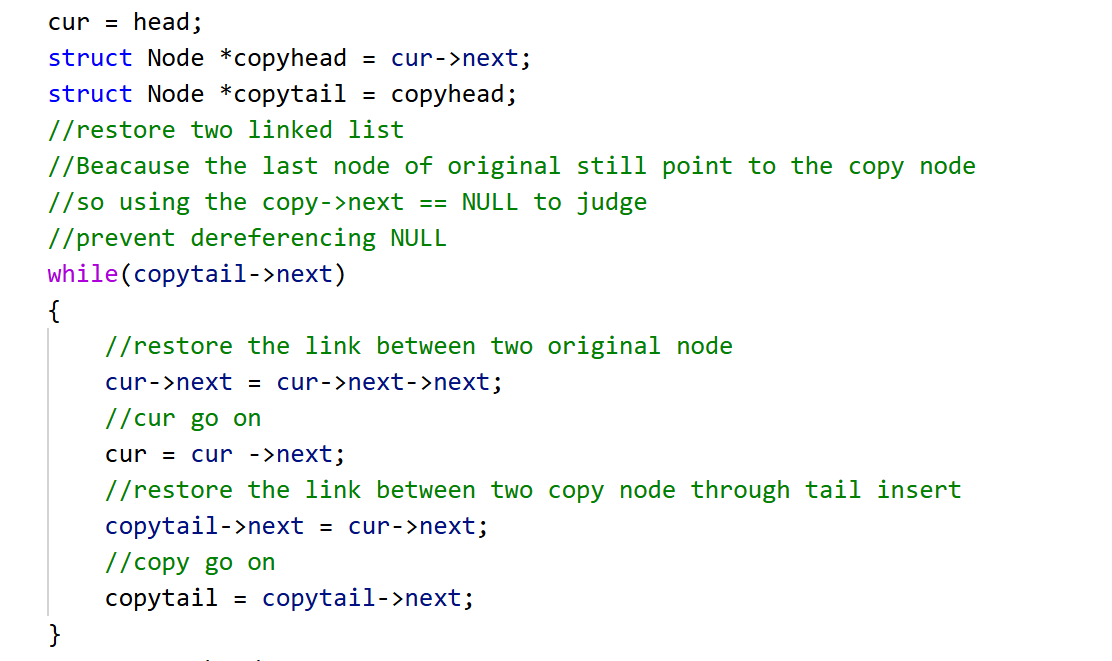
以下是一般情况下尾插copy的解释:
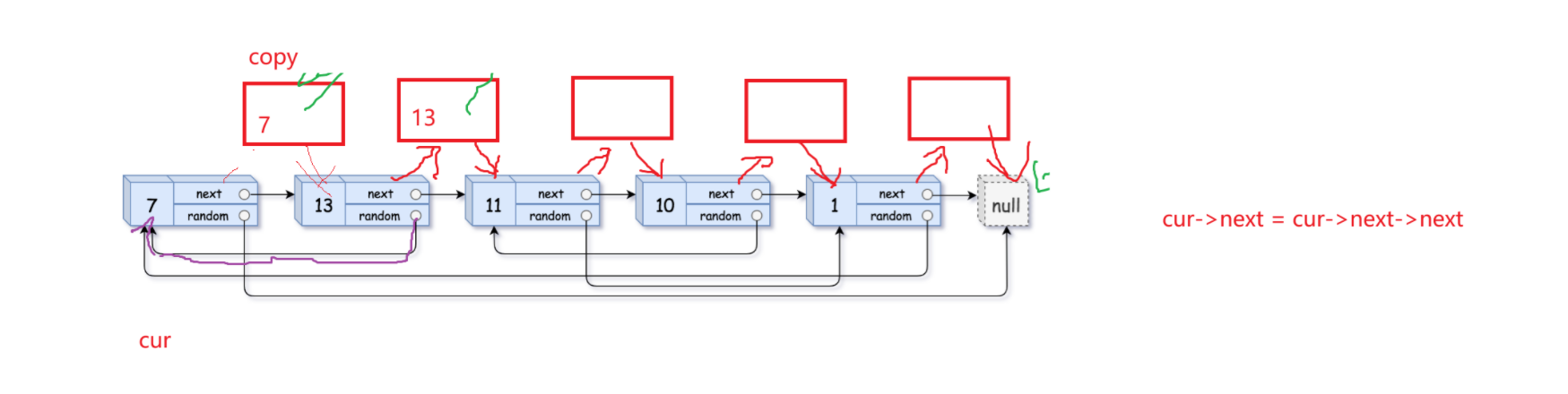
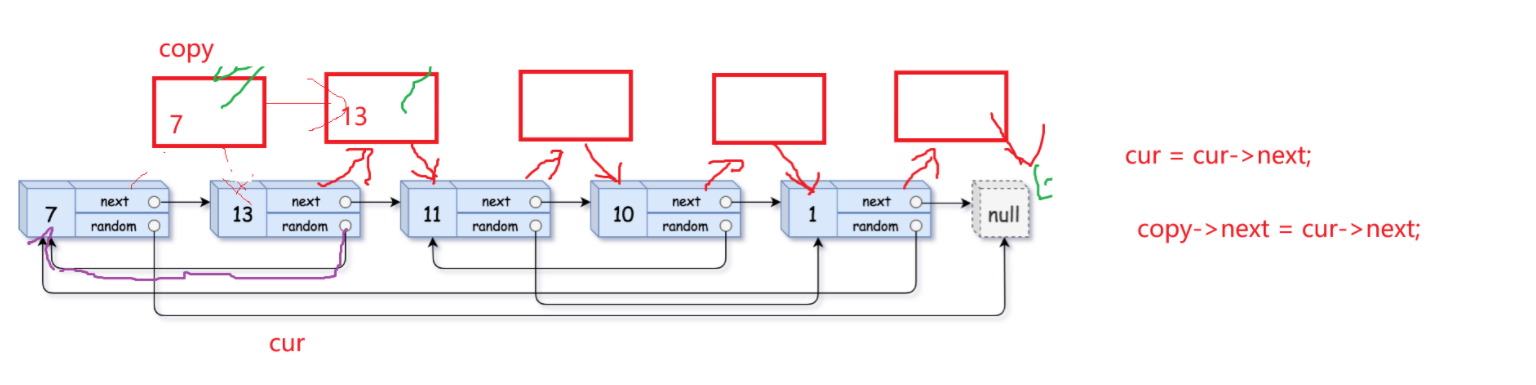
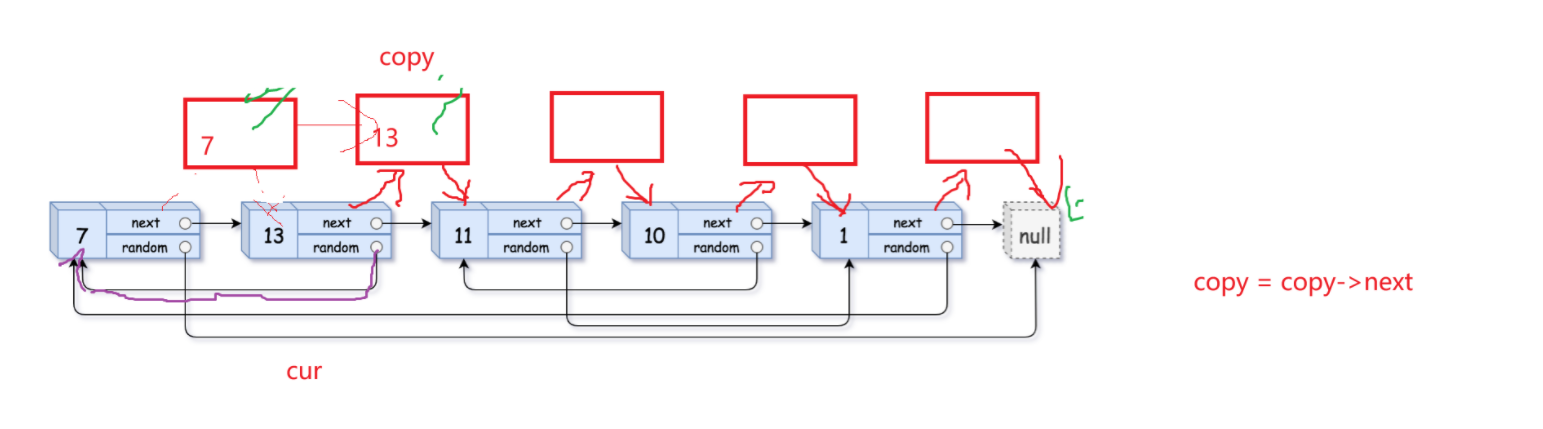
当剩下最后两个尾节点的时候需要重点注意:
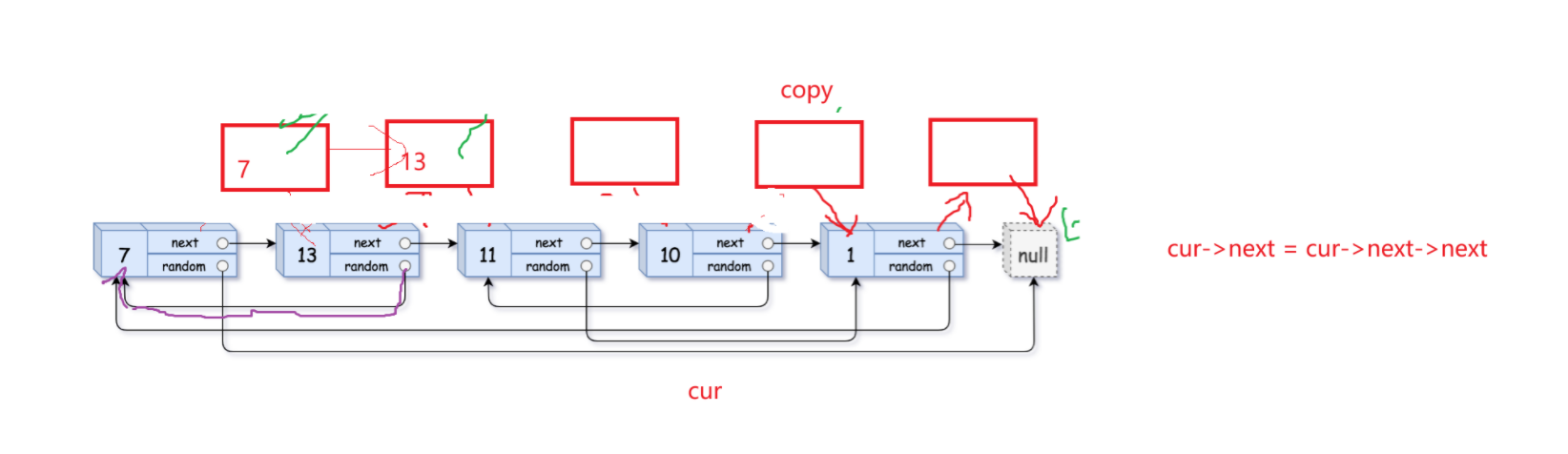
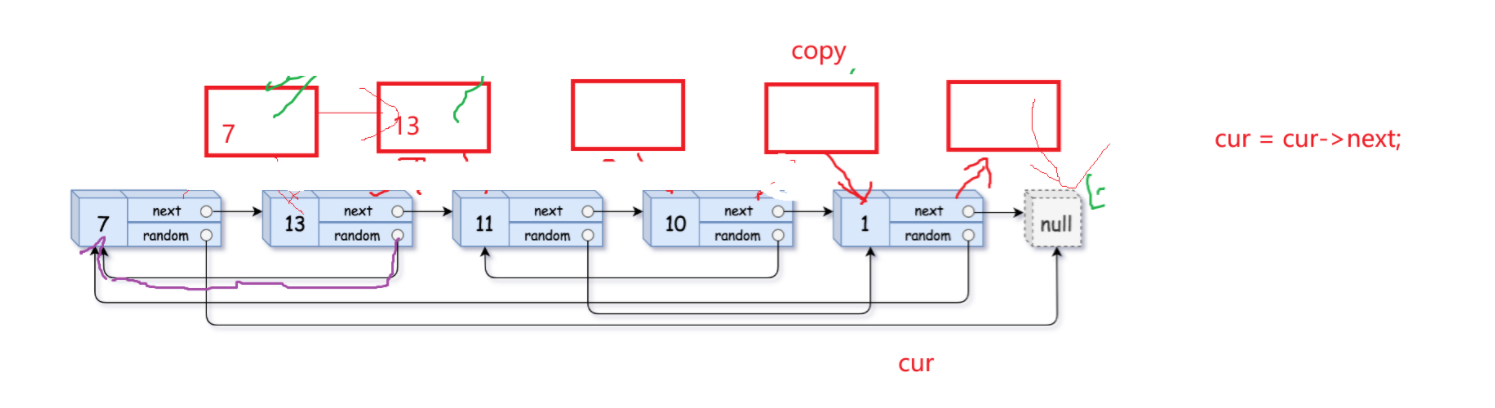

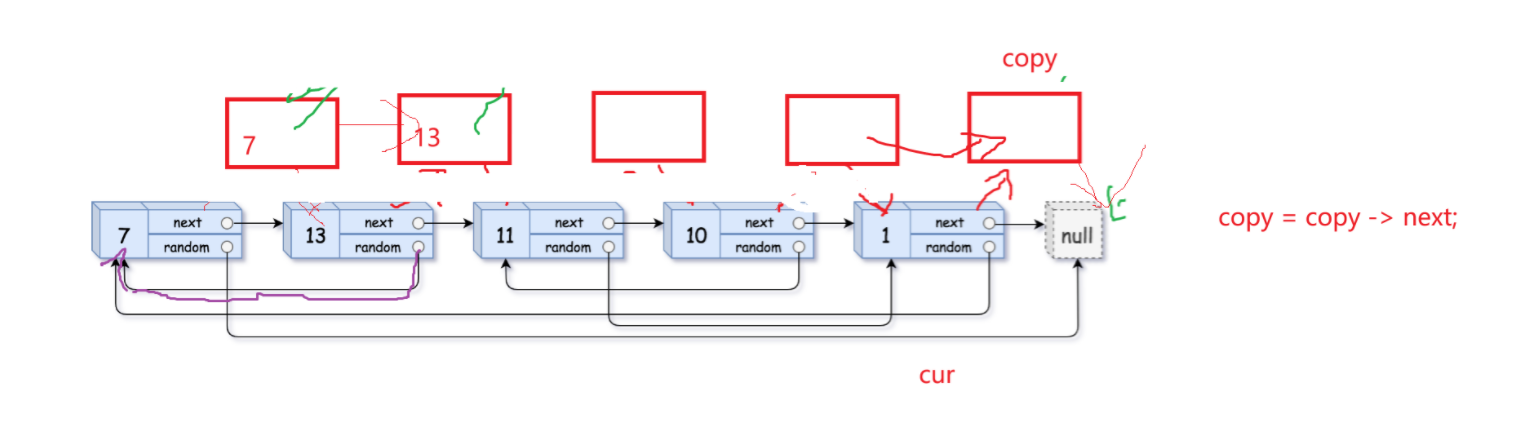
通过最后一张图解可以看到,cur的最后一个节点的next依然指向copy而不是NULL,所以应该用copy->next == NULL 当while的判定条件。
