RHCE : NFS实验1
🔧 1. 配置NFS服务端
1.1 安装必要软件包
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
sudo yum install nfs-utilsUbuntu/Debian:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server1.2 创建共享目录并设置权限
创建一个你打算共享给其他机器的目录,并设置适当的权限。
mkdir /srv/nfs/share1.3 配置NFS导出规则
编辑NFS的主要配置文件 /etc/exports,定义共享目录以及哪些客户端可以访问它及其权限
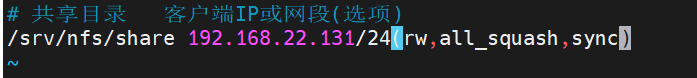
sudo vim /etc/exports在文件末尾添加一行配置,格式为:共享目录 客户端IP或网段(选项1,选项2,...)
示例:
允许IP地址为 192.168.22.131的客户端读写访问:
/srv/nfs/share 192.168.22.131(rw,all_squash,sync)允许 192.168.1.0/24网段的所有客户端只读访问:
/srv/nfs/share 192.168.1.0/24(ro,sync,no_subtree_check)
rw/ro: 读写/只读权限
sync/async: 同步/异步写入,sync更安全(数据先写入磁盘再返回成功),async性能可能更好但风险稍高
no_subtree_check: 禁用子树检查,通常能提升兼容性和性能
no_root_squash/root_squash: 是否将客户端root用户映射为服务端的nobody用户。出于安全考虑,除非必要,否则不建议使用no_root_squash
1.4 启动NFS服务并使配置生效
systemctl enable --now nfs-server1.5 配置防火墙
使用firewalld(CentOs/RHEL等)
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=nfs
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=rpc-bind
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=mountd
sudo firewall-cmd --reload使用ufw (Ubuntu/Debian等):
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port nfs # 替换为你的客户端网段[2,6](@ref)1.6 验证服务端共享
sudo showmount -e localhost
🖥️ 2. 配置NFS客户端
2.1 安装NFS客户端软件
dnf install nfs-utils -y2.2 创建本地挂载点
在客户端创建一个目录,作为NFS共享的挂载位置。
mkdir /nfs_client2.3 手动挂载NFS共享
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.22.135:/srv/nfs/share /nfs_client![]()
请将 192.168.22.135替换为你的NFS服务器的实际IP地址。
2.4 验证挂载是否成功
使用 df -h或 mount命令查看挂载情况。
df -h | grep nfs
如果挂载成功,你会看到类似 192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/share的输出。
2.5 设置开机自动挂载
如果希望客户端每次启动时自动挂载NFS共享,需要编辑 /etc/fstab文件。
sudo vim /etc/fstab在末尾添加一行:
192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/share /mnt/nfs-share nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0