学习:JavaScript(5)
String(字符串)对象
在 JavaScript 中, String 是用于表示文本数据的基本数据类型和对象包装器。以下是字符串的完整指南,涵盖创建、操作、方法和实际应用。
1. 字符串的基本特性
(1) 字符串表示
- 使用单引号、双引号或反引号创建:
const str1 = '单引号'; const str2 = "双引号"; const str3 = `模板字符串`;
(2) 字符串是不可变的
- 一旦创建,字符串内容无法直接修改:
let str = "Hello"; str[0] = "h"; // 无效,str 仍为 "Hello" str = "hello"; // 重新赋值
(3) 转义字符
| 转义序列 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 换行 |
|
| 制表符 |
|
| 反斜杠 |
|
| 引号 |
|
2. 字符串的创建方式
(1) 字面量(推荐)
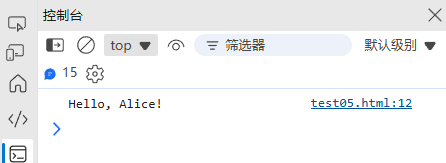
const name = "Alice";
const message = `Hello, ${name}!`; // 模板字符串
(2) 构造函数(不推荐)
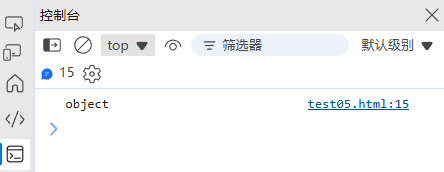
const strObj = new String("text"); // 返回对象
console.log(typeof strObj); // "object"
(3) 从其他类型转换
String(123); // "123"
String(true); // "true"
String(null); // "null"
String(undefined); // "undefined"
3. 字符串的常用方法
(1) 长度和索引
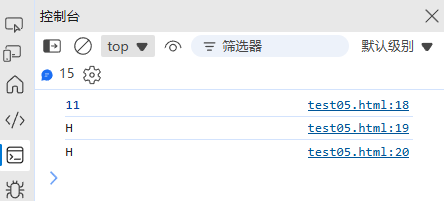
const str = "Hello World";
console.log(str.length); // 11
console.log(str[0]); // "H"
console.log(str.charAt(0)); // "H"
(2) 查找和定位
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
indexOf(search) | 返回首次出现的位置 | "hello".indexOf("l") → 2 |
lastIndexOf(search) | 返回最后出现的位置 | "hello".lastIndexOf("l") → 3 |
includes(search) | 是否包含子串 | "hello".includes("ell") → true |
startsWith(prefix) | 是否以指定字符串开头 | "hello".startsWith("he") → true |
endsWith(suffix) | 是否以指定字符串结尾 | "hello".endsWith("lo") → true |
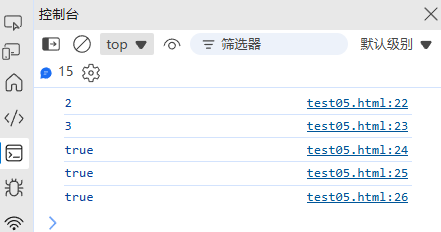
(3) 提取子字符串
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
slice(start, end) | 提取子串(支持负数索引) | "hello".slice(1, 3) → "el" |
substring(start, end) | 提取子串(不支持负数) | "hello".substring(1, 3) → "el" |
substr(start, length) | 提取指定长度子串 | "hello".substr(1, 3) → "ell" |
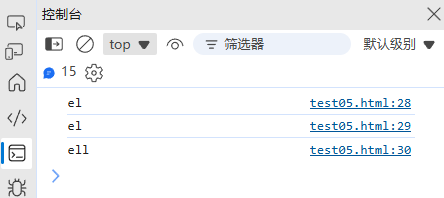
(4) 修改字符串
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
toUpperCase() | 转为大写 | "hello".toUpperCase() → "HELLO" |
toLowerCase() | 转为小写 | "HELLO".toLowerCase() → "hello" |
trim() | 去除两端空白 | " hello ".trim() → "hello" |
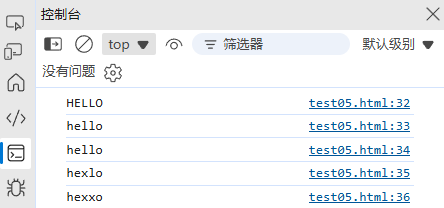
replace(search, replacement) | 替换首次匹配 | "hello".replace("l", "x") → "hexlo" |
replaceAll(search, replacement) | 替换所有匹配 | "hello".replaceAll("l", "x") → "hexxo" |
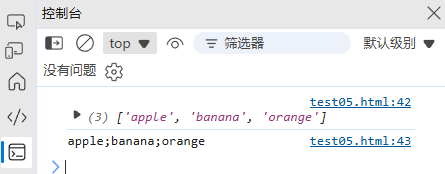
(5) 分割和连接
const str = "apple,banana,orange";
const fruits = str.split(","); // ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
const newStr = fruits.join(";"); // "apple;banana;orange"
4. 模板字符串(ES6+)
(1) 基本用法
const name = "Alice";
const age = 25;
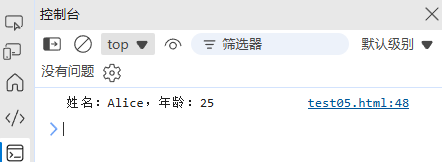
const message = `姓名:${name},年龄:${age}`;
console.log(message); // "姓名:Alice,年龄:25"
(2) 多行字符串
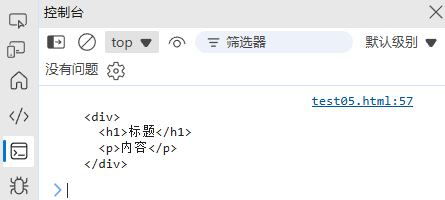
const html = `<div><h1>标题</h1><p>内容</p></div>
`;
(3) 标签模板
function highlight(strings, ...values) {return strings.reduce((result, str, i) => result + str + (values[i] ? `<mark>${values[i]}</mark>` : ""), "");
}const name = "Alice";
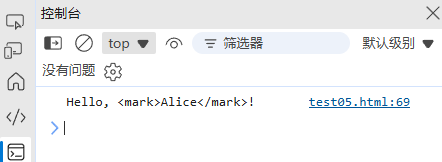
const message = highlight`Hello, ${name}!`;
console.log(message); // "Hello, <mark>Alice</mark>!"
5. 字符串的编码和 Unicode
(1) Unicode 表示
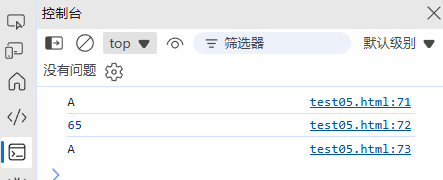
console.log("\u0041"); // "A"(Unicode 转义)
console.log("A".codePointAt(0)); // 65(获取码点)
console.log(String.fromCodePoint(65)); // "A"(码点转字符)
(2) Base64 编码
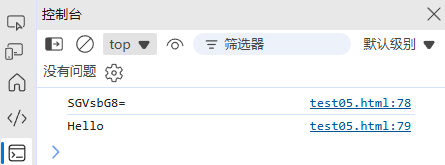
const encoded = btoa("Hello"); // "SGVsbG8="
const decoded = atob("SGVsbG8="); // "Hello"
6. 最佳实践
优先使用模板字符串
更清晰且支持表达式: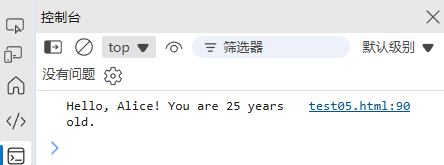
// 不推荐 const msg = "Hello, " + name + "! You are " + age + " years old.";// 推荐 const msg = `Hello, ${name}! You are ${age} years old.`;使用
includes()而非indexOf()
更语义化:// 不推荐 if (str.indexOf("needle") !== -1) { ... }// 推荐 if (str.includes("needle")) { ... }避免字符串拼接性能问题
大量拼接时使用数组:// 性能差 let result = ""; for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {result += i; }// 性能好 const parts = []; for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {parts.push(i); } const result = parts.join("");
7. 实际应用示例
(1) 字符串格式化
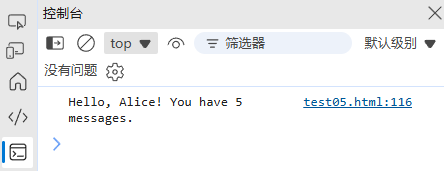
function formatString(template, data) {return template.replace(/\{(\w+)\}/g, (match, key) => data[key] || match);
}const result = formatString("Hello, {name}! You have {count} messages.", {name: "Alice",count: 5
});
console.log(result); // "Hello, Alice! You have 5 messages."
(2) URL 参数解析
function parseQueryString(query) {return query.split("&").reduce((params, pair) => {const [key, value] = pair.split("=");params[decodeURIComponent(key)] = decodeURIComponent(value || "");return params;}, {});
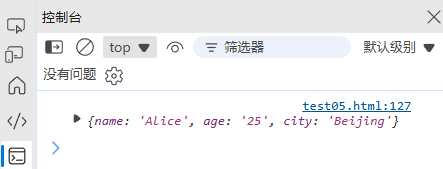
}const query = "name=Alice&age=25&city=Beijing";
console.log(parseQueryString(query));
// { name: "Alice", age: "25", city: "Beijing" }
(3) 密码强度验证
function checkPasswordStrength(password) {const checks = {length: password.length >= 8,hasUpper: /[A-Z]/.test(password),hasLower: /[a-z]/.test(password),hasNumber: /\d/.test(password),hasSpecial: /[!@#$%^&*]/.test(password)};const score = Object.values(checks).filter(Boolean).length;return { score, checks };
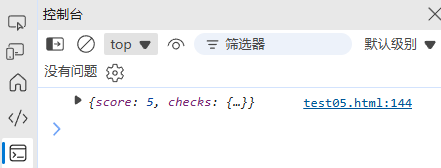
}const result = checkPasswordStrength("Pass123!");
console.log(result); // { score: 5, checks: { ... } }
Array(数组)对象
在 JavaScript 中, Array 是用于存储有序数据集合的对象。以下是数组的完整指南,涵盖创建、操作、方法和实际应用。
1. 数组的基本特性
(1) 数组表示
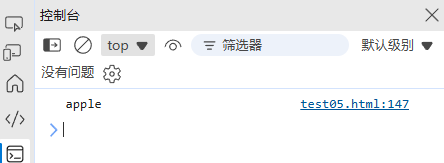
- 有序的元素集合,索引从 0 开始:
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]; console.log(fruits[0]); // "apple"
(2) 动态类型
- 数组可以包含任意类型的数据:
const mixed = [1, "text", true, { name: "Alice" }, [1, 2, 3]];
(3) 长度属性
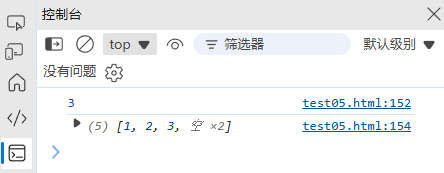
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.length); // 3
arr.length = 5; // 扩展数组
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, empty × 2]
2. 数组的创建方式
(1) 字面量(推荐)
const empty = [];
const numbers = [1, 2, 3];
const mixed = ["text", 42, true];
(2) 构造函数
const arr1 = new Array(); // []
const arr2 = new Array(5); // [empty × 5]
const arr3 = new Array(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
(3) 其他创建方法
Array.from("hello"); // ["h", "e", "l", "l", "o"]
Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
Array(5).fill(0); // [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
3. 数组的常用方法
(1) 添加/删除元素
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
push(item) | 末尾添加元素 | [1,2].push(3) → [1,2,3] |
pop() | 删除并返回末尾元素 | [1,2,3].pop() → 3 |
unshift(item) | 开头添加元素 | [1,2].unshift(0) → [0,1,2] |
shift() | 删除并返回开头元素 | [1,2,3].shift() → 1 |
splice(start, deleteCount, ...items) | 添加/删除元素 | [1,2,3].splice(1,1,4) → [1,4,3] |
(2) 遍历数组
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
forEach(callback) | 遍历每个元素 | [1,2,3].forEach(x => console.log(x)) |
map(callback) | 映射新数组 | [1,2,3].map(x => x*2) → [2,4,6] |
filter(callback) | 过滤符合条件的元素 | [1,2,3].filter(x => x>1) → [2,3] |
reduce(callback, initialValue) | 累积计算 | [1,2,3].reduce((a,b) => a+b) → 6 |
(3) 查找元素
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
indexOf(item) | 返回元素索引 | [1,2,3].indexOf(2) → 1 |
find(callback) | 返回第一个符合条件的元素 | [1,2,3].find(x => x>1) → 2 |
findIndex(callback) | 返回第一个符合条件的索引 | [1,2,3].findIndex(x => x>1) → 1 |
includes(item) | 检查是否包含元素 | [1,2,3].includes(2) → true |
(4) 排序和反转
const arr = [3, 1, 2];
arr.sort(); // [1, 2, 3]
arr.reverse(); // [3, 2, 1]// 自定义排序
[10, 2, 1].sort((a, b) => a - b); // [1, 2, 10]
(5) 切片和连接
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.slice(1, 3); // [2, 3](不修改原数组)
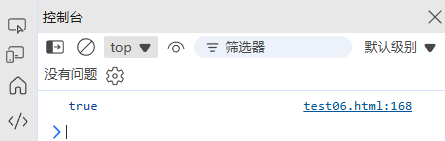
arr.concat([6, 7]); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
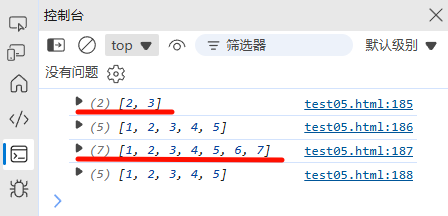
4. 数组的迭代方法对比
| 方法 | 返回值 | 是否修改原数组 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
forEach | undefined | 否 | 单纯遍历 |
map | 新数组 | 否 | 数据转换 |
filter | 过滤后的新数组 | 否 | 数据筛选 |
reduce | 累积值 | 否 | 数据聚合 |
some | 布尔值 | 否 | 是否存在满足条件的元素 |
every | 布尔值 | 否 | 是否所有元素都满足条件 |
5. 多维数组和数组解构
(1) 多维数组
const matrix = [[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[7, 8, 9]
];
console.log(matrix[1][2]); // 6
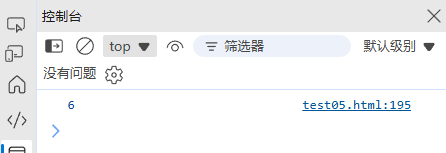
(2) 数组解构(ES6+)
const [first, second, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(first, second, rest); // 1, 2, [3, 4, 5]// 交换变量
let a = 1, b = 2;
[a, b] = [b, a];
console.log(a, b); // 2, 1
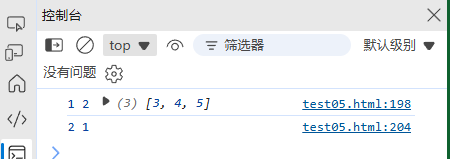
6. 数组的扩展运算符(ES6+)
(1) 复制和合并
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = [...arr1]; // 浅拷贝 [1, 2, 3]
const merged = [...arr1, 4, 5]; // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
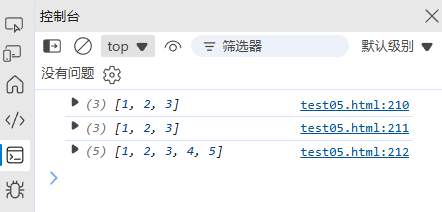
(2) 函数参数
function sum(a, b, c) {return a + b + c;
}
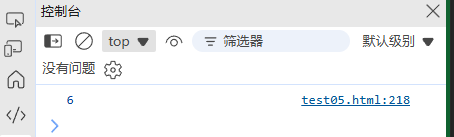
const numbers = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(sum(...numbers)); // 6
7. 最佳实践
优先使用字面量创建数组
// 不推荐 const arr = new Array(1, 2, 3);// 推荐 const arr = [1, 2, 3];使用
map/filter/reduce替代循环// 不推荐 const doubled = []; for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {doubled.push(numbers[i] * 2); }// 推荐 const doubled = numbers.map(x => x * 2);避免修改原数组的方法
const original = [1, 2, 3]; const reversed = [...original].reverse(); // 不修改原数组
8. 实际应用示例
(1) 数据分组
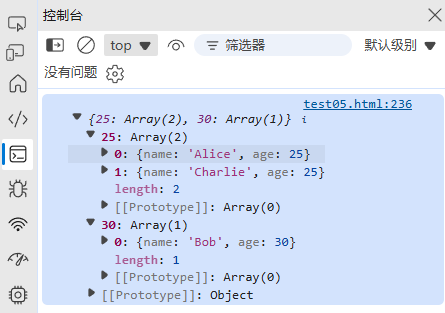
function groupBy(array, key) {return array.reduce((groups, item) => {const groupKey = item[key];if (!groups[groupKey]) {groups[groupKey] = [];}groups[groupKey].push(item);return groups;}, {});
}const users = [{ name: "Alice", age: 25 },{ name: "Bob", age: 30 },{ name: "Charlie", age: 25 }
];
console.log(groupBy(users, "age"));
// { 25: [{...}, {...}], 30: [{...}] }
(2) 数组去重
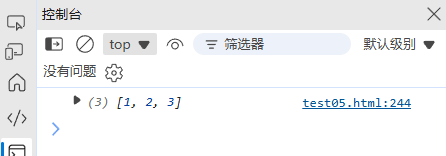
function uniqueArray(arr) {return [...new Set(arr)];// 或使用 filter: return arr.filter((item, index) => arr.indexOf(item) === index);
}console.log(uniqueArray([1, 2, 2, 3, 1])); // [1, 2, 3]
(3) 分页功能
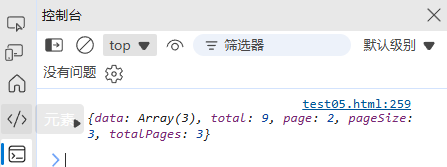
function paginate(array, page, pageSize) {const start = (page - 1) * pageSize;const end = start + pageSize;return {data: array.slice(start, end),total: array.length,page,pageSize,totalPages: Math.ceil(array.length / pageSize)};
}const data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
console.log(paginate(data, 2, 3));
// { data: [4, 5, 6], total: 9, page: 2, pageSize: 3, totalPages: 3 }
(4) 数组扁平化
function flattenArray(arr) {return arr.reduce((flat, item) => flat.concat(Array.isArray(item) ? flattenArray(item) : item), []);
}console.log(flattenArray([1, [2, [3, 4]], 5])); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]// ES6+ 简单版本
console.log([1, [2, [3, 4]], 5].flat(2)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Date(时间/日期)对象
在 JavaScript 中, Date 对象用于处理日期和时间。以下是 Date 对象的完整指南,涵盖创建、操作、格式化和实际应用。
1. Date 对象的基本特性
(1) 时间表示
- JavaScript 日期基于 Unix 时间戳(1970年1月1日至今的毫秒数)
- 时区:本地时区或 UTC(协调世界时)
(2) 精度
- 毫秒级精度(1秒 = 1000毫秒)
- 时间范围:约 1970年1月1日 ± 285,616年
2. Date 对象的创建方式
(1) 当前时间
const now = new Date(); // 当前日期时间
console.log(now); // 输出:Mon Nov 04 2024 10:30:45 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
(2) 指定时间戳
const date1 = new Date(1604476800000); // 时间戳(毫秒)
const date2 = new Date("2024-11-04T10:30:45"); // ISO 8601 字符串
const date3 = new Date(2024, 10, 4, 10, 30, 45); // 年,月(0-11),日,时,分,秒
(3) 日期字符串解析
new Date("2024/11/04");
new Date("November 4, 2024");
new Date("2024-11-04T10:30:45+08:00"); // 带时区
3. Date 对象的常用方法
(1) 获取时间组件
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例(假设日期为 2024-11-04 10:30:45) |
|---|---|---|
getFullYear() | 年份(4位) | 2024 |
getMonth() | 月份(0-11) | 10 (11月) |
getDate() | 日期(1-31) | 4 |
getDay() | 星期(0-6,0=周日) | 1 (周一) |
getHours() | 小时(0-23) | 10 |
getMinutes() | 分钟(0-59) | 30 |
getSeconds() | 秒数(0-59) | 45 |
getMilliseconds() | 毫秒(0-999) | 0 |
getTime() | 时间戳(毫秒) | 1604476845000 |
(2) 设置时间组件
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
setFullYear(year) | 设置年份 | date.setFullYear(2025) |
setMonth(month) | 设置月份(0-11) | date.setMonth(11) |
setDate(day) | 设置日期(1-31) | date.setDate(25) |
setHours(hours) | 设置小时(0-23) | date.setHours(15) |
(3) UTC 方法
const date = new Date();
console.log(date.getUTCHours()); // UTC 小时
console.log(date.getUTCMinutes()); // UTC 分钟
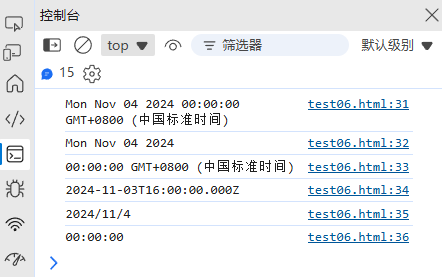
4. 日期格式化
(1) 内置格式化方法
const date = new Date(2024, 10, 4);date.toString(); // "Mon Nov 04 2024 00:00:00 GMT+0800"
date.toDateString(); // "Mon Nov 04 2024"
date.toTimeString(); // "00:00:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)"
date.toISOString(); // "2024-11-03T16:00:00.000Z"(UTC时间)
date.toLocaleDateString(); // "2024/11/4"(本地化格式)
date.toLocaleTimeString(); // "上午12:00:00"
(2) 自定义格式化函数
function formatDate(date, format = "YYYY-MM-DD") {const year = date.getFullYear();const month = String(date.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0');const day = String(date.getDate()).padStart(2, '0');const hours = String(date.getHours()).padStart(2, '0');const minutes = String(date.getMinutes()).padStart(2, '0');const seconds = String(date.getSeconds()).padStart(2, '0');return format.replace('YYYY', year).replace('MM', month).replace('DD', day).replace('HH', hours).replace('mm', minutes).replace('ss', seconds);
}const now = new Date();
console.log(formatDate(now, "YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss")); // "2024年11月04日 10:30:45"
5. 日期计算和比较
(1) 日期加减
const date = new Date();// 加一天
date.setDate(date.getDate() + 1);// 加一个月
date.setMonth(date.getMonth() + 1);// 使用时间戳计算(推荐)
const tomorrow = new Date(date.getTime() + 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000);
(2) 日期比较
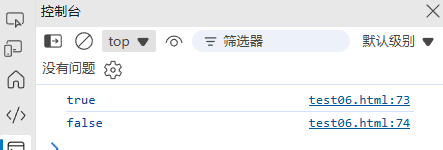
const date1 = new Date('2024-11-04');
const date2 = new Date('2024-11-05');console.log(date1 < date2); // true
console.log(date1.getTime() === date2.getTime()); // 精确比较
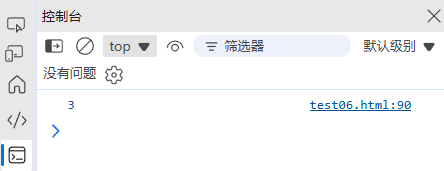
(3) 计算日期差
function dateDiff(date1, date2, unit = 'days') {const diff = date2.getTime() - date1.getTime();const units = {milliseconds: diff,seconds: diff / 1000,minutes: diff / (1000 * 60),hours: diff / (1000 * 60 * 60),days: diff / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24)};return units[unit];
}const start = new Date('2024-11-01');
const end = new Date('2024-11-04');
console.log(dateDiff(start, end, 'days')); // 3
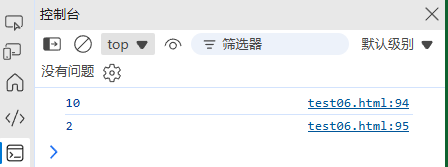
6. 时区处理
(1) 本地时间 vs UTC 时间
const date = new Date('2024-11-04T10:30:45+08:00');console.log(date.getHours()); // 10(本地时间)
console.log(date.getUTCHours()); // 2(UTC时间)
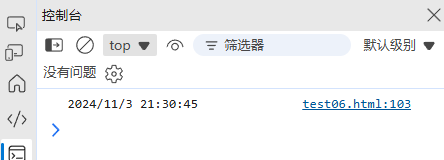
(2) 时区转换
function toTimeZone(date, timeZone) {return new Date(date.toLocaleString("en-US", { timeZone }));
}const beijingTime = new Date('2024-11-04T10:30:45+08:00');
const newYorkTime = toTimeZone(beijingTime, "America/New_York");
console.log(newYorkTime.toLocaleString()); // "11/3/2024, 9:30:45 PM"
7. 最佳实践
使用 ISO 8601 格式存储和传输日期
// 推荐 const isoString = date.toISOString(); // "2024-11-04T02:30:45.000Z"// 不推荐 const localString = date.toString(); // 时区相关,可能解析错误避免使用
getYear()方法// 不推荐(返回年份-1900) console.log(new Date().getYear()); // 124// 推荐 console.log(new Date().getFullYear()); // 2024使用时间戳进行精确计算
// 推荐 const start = new Date().getTime(); // ... 执行操作 const end = new Date().getTime(); const duration = end - start;
8. 实际应用示例
(1) 倒计时功能
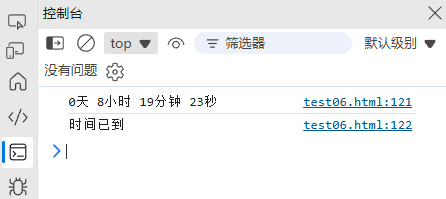
function countdown(targetDate) {const now = new Date().getTime();const target = new Date(targetDate).getTime();const diff = target - now;if (diff <= 0) return "时间已到";const days = Math.floor(diff / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));const hours = Math.floor((diff % (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24)) / (1000 * 60 * 60));const minutes = Math.floor((diff % (1000 * 60 * 60)) / (1000 * 60));const seconds = Math.floor((diff % (1000 * 60)) / 1000);return `${days}天 ${hours}小时 ${minutes}分钟 ${seconds}秒`;
}console.log(countdown("2025-11-5")); // "0天 8小时 19分钟 30秒"console.log(countdown("2024-12-31")); //时间已到
(2) 工作日计算
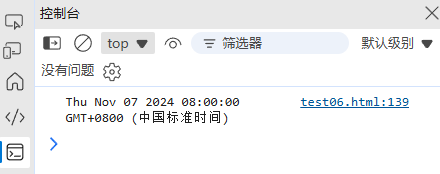
function addBusinessDays(date, days) {const result = new Date(date);let added = 0;while (added < days) {result.setDate(result.getDate() + 1);// 跳过周末(周六=6,周日=0)if (result.getDay() !== 0 && result.getDay() !== 6) {added++;}}return result;
}const start = new Date('2024-11-04'); // 周一
console.log(addBusinessDays(start, 3)); // 周四(跳过周末)
(3) 年龄计算
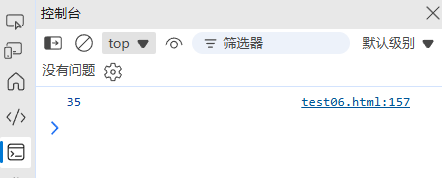
function calculateAge(birthDate) {const today = new Date();let age = today.getFullYear() - birthDate.getFullYear();const monthDiff = today.getMonth() - birthDate.getMonth();if (monthDiff < 0 || (monthDiff === 0 && today.getDate() < birthDate.getDate())) {age--;}return age;
}const birthDate = new Date('1990-05-15');
console.log(calculateAge(birthDate)); // 34
(4) 日期范围验证
function isDateInRange(date, start, end) {const time = date.getTime();return time >= start.getTime() && time <= end.getTime();
}const testDate = new Date('2024-11-04');
const rangeStart = new Date('2024-11-01');
const rangeEnd = new Date('2024-11-10');console.log(isDateInRange(testDate, rangeStart, rangeEnd)); // true