链表相关的算法题(1)
链表相关的算法题
- 前言
- 1、移除链表元素
- 2、反转链表
- 3、链表的中间节点
- 4、合并两个有序链表
- 5、链表分割
- 6、链表的回文结构
- 7、相交链表
- 8、随机链表的复制
前言
创作文章,不仅要有知识点的总结,还要有一些算法题思路的记录。我觉得这样很好,毕竟,高中时期就没能做出来过一个像样的错题本。
当然,错题本还是要温故知新。
1、移除链表元素
移除链表元素的题目链接
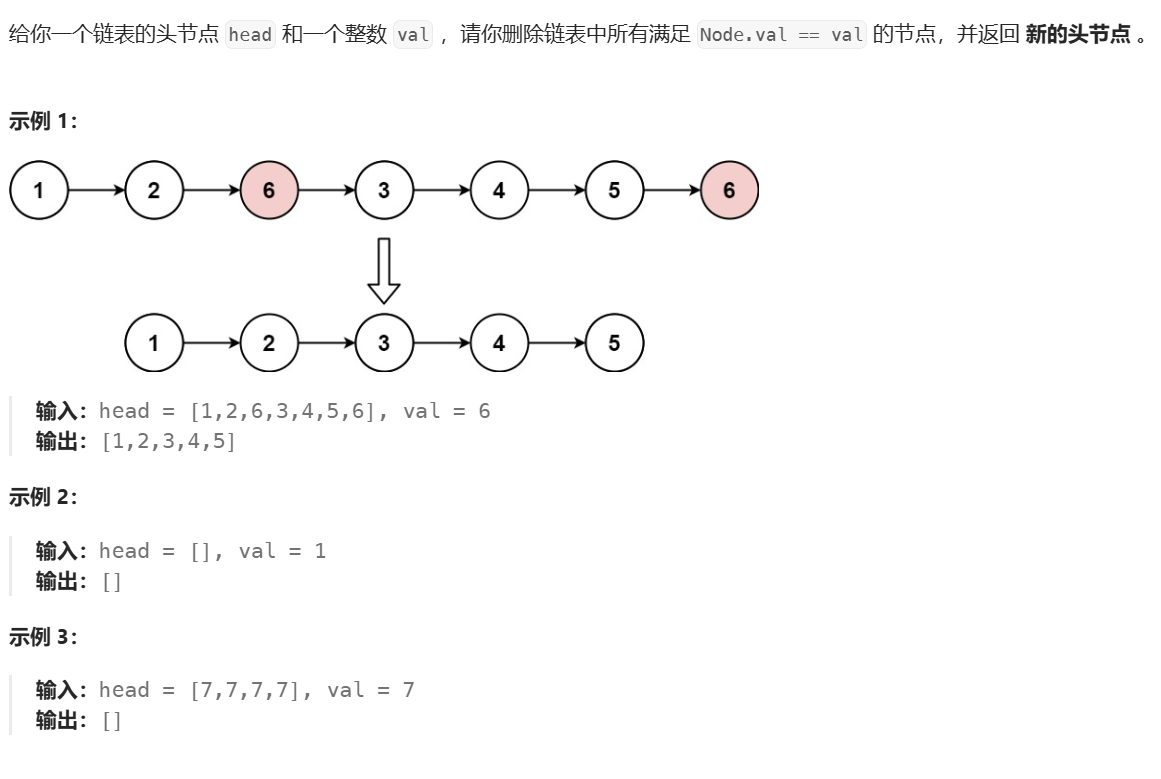
思路很简单,就是创建新链表,遍历原链表,不包含要删数据的原链表节点,尾插到新链表中。
但是,有以下注意的几点:
- 最开始,我们定义新链表的头、尾节点均为
NULL,所以需要分类讨论头节点是否为NULL。(或者可以使用哨兵位) - 插入完成,最后应切断新链表与原链表的关系。
- 由于创建新链表,额外申请常数个空间,所以空间复杂度
O(1)。
代码演示:
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {//创建新链表ListNode *newHead, *newTail;newHead = newTail = NULL;//遍历原链表ListNode* pcur = head;while (pcur)//为空就会出循环{//找非val值if (pcur->val != val){//确定新链表的头节点,和newTail的起点if (newHead == NULL){newHead = newTail = pcur;}else{//放数,找下一个newTail->next = pcur;newTail = newTail->next;}}pcur = pcur->next;//一定要记得,先写上执行操作,防止死循环}//切断与原链表的联系if (newTail){newTail->next = NULL;}return newHead;
}
2、反转链表
反转链表的题目链接
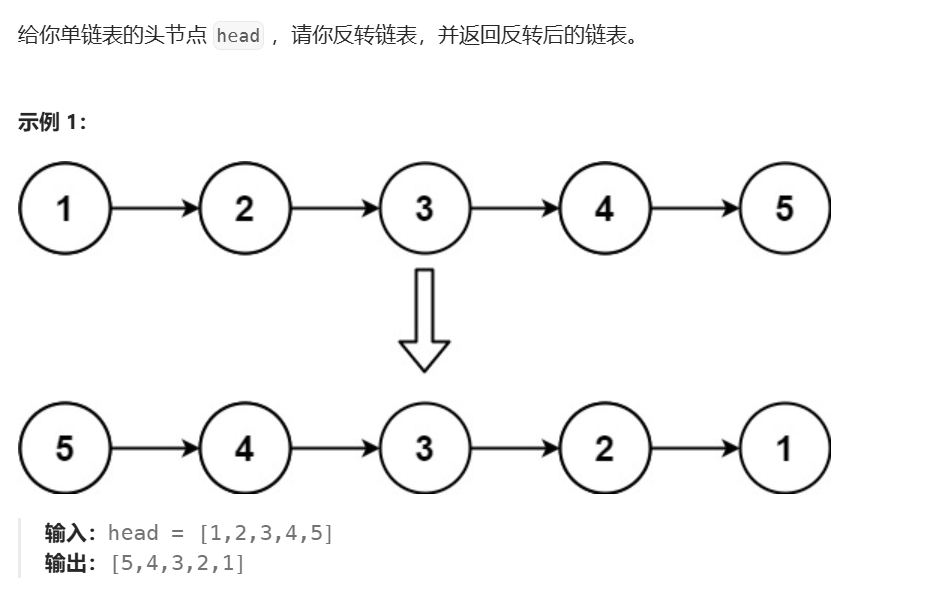
思路:
- 定义三个指针:
n1:指向NULLn2:指向原链表头节点n3:指向n2的下一个节点
- 将
n2指向n1 - 然后
n2赋值给n1,相当于头插了一个n2上的节点 n3赋值给n2,相当于n2向前一个元素位置(此时n3的辅助作用凸显)。n3也向前- 此时,
n1就是要返回的节点
图示:
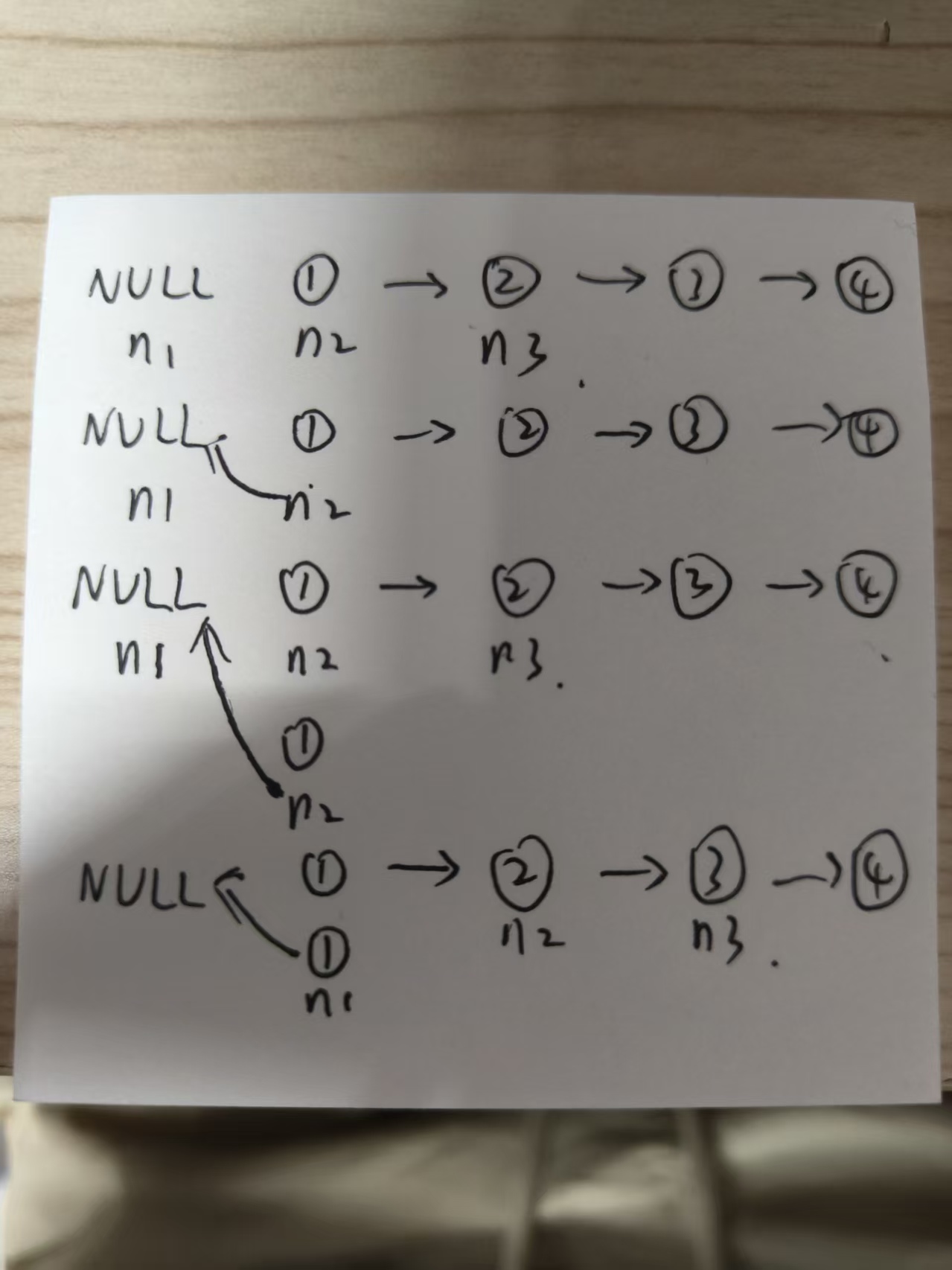
代码演示:
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {//为空,直接返回if (head == NULL)return head;ListNode* n1 = NULL;ListNode* n2 = head;ListNode* n3 = head->next;while (n2){n2->next = n1;//比如, 2 指向 1n1 = n2;//更新头指针n2 = n3;// n2 前进if (n3)// n3 的前进,需要判断{n3 = n3->next;}}return n1;
}
3、链表的中间节点
链表的中间节点题目链接
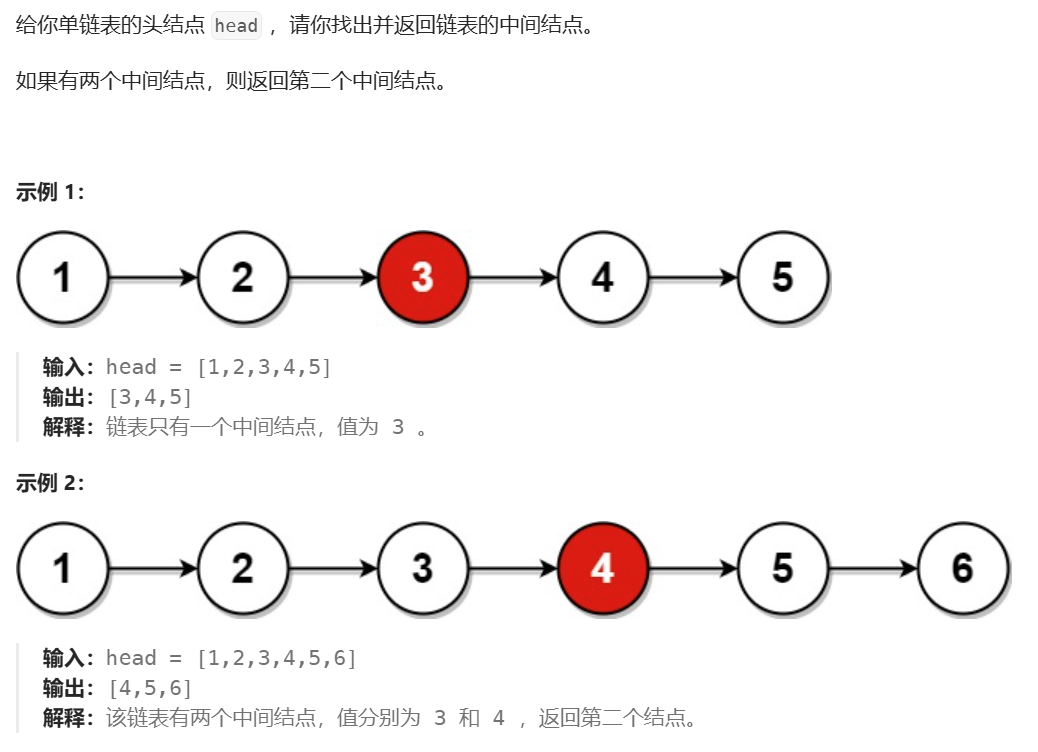
核心思路,就是快慢指针,慢指针走一步,快指针走两步(可能步数更多)。
当链表中,节点个数为奇数,则当慢指针走到中间节点时,快指针走到了NULL。
当链表中,节点个数为偶数,则当慢指针走到第二个中间节点时,快指针走到了最后一个节点。如果此时快指针为fast,则fast->next == NULL。
而为了避免对空指针进行解引用这一情况发生,我们在写循环的判断条件时,要注意先后顺序(操作符短路)。
代码演示:
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {//快慢指针ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}
4、合并两个有序链表
合并两个有序链表的题目链接
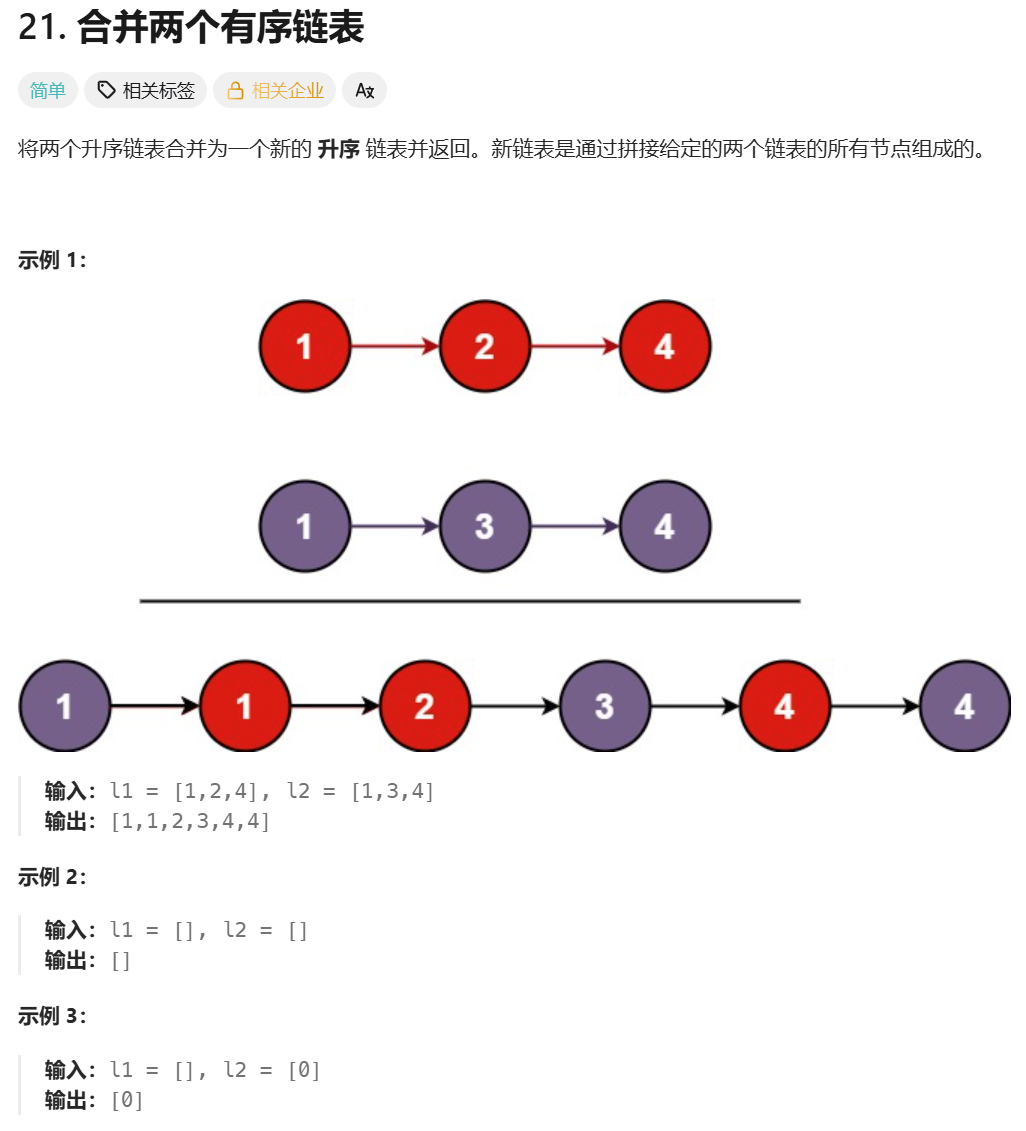
我们很容易想到,创建新链表,遍历原链表,比较,将较小数尾插入新链表。
但是,这样一来,我们就必须在遍历时,检查新链表是否为空,有点麻烦。有没有更好的办法?
这时,哨兵位就派上了用场。
思路:
- 定义一个空节点,也就是哨兵位。新链表的头、尾节点都从这开始。如果不想额外确定是否存在空链表的情况,可以让新链表头节点的
next指针指向NULL - 分别遍历两个链表,比较数据大小,将较小数尾插入新节点。
- 遍历循环结束后,分别检查原链表是否还有节点剩余。如果有,直接尾插,无需循环。
代码演示:
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {//if (list1 == NULL)// return list2;//if (list2 == NULL)// return list1;//哨兵位ListNode *newHead, *newTail;newHead = newTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newHead->next = NULL;//遍历ListNode* l1 = list1;ListNode* l2 = list2;while (l1 && l2){if (l1->val < l2->val){newTail->next = l1;newTail = newTail->next;l1 = l1->next;}else{newTail->next = l2;newTail = newTail->next;l2 = l2->next;}}//尾插剩余节点if (l1){newTail->next = l1;}if (l2){newTail->next = l2;}ListNode* ret = newHead->next;free(newHead);newHead = NULL;return ret;
}
5、链表分割
链表分割的超链接
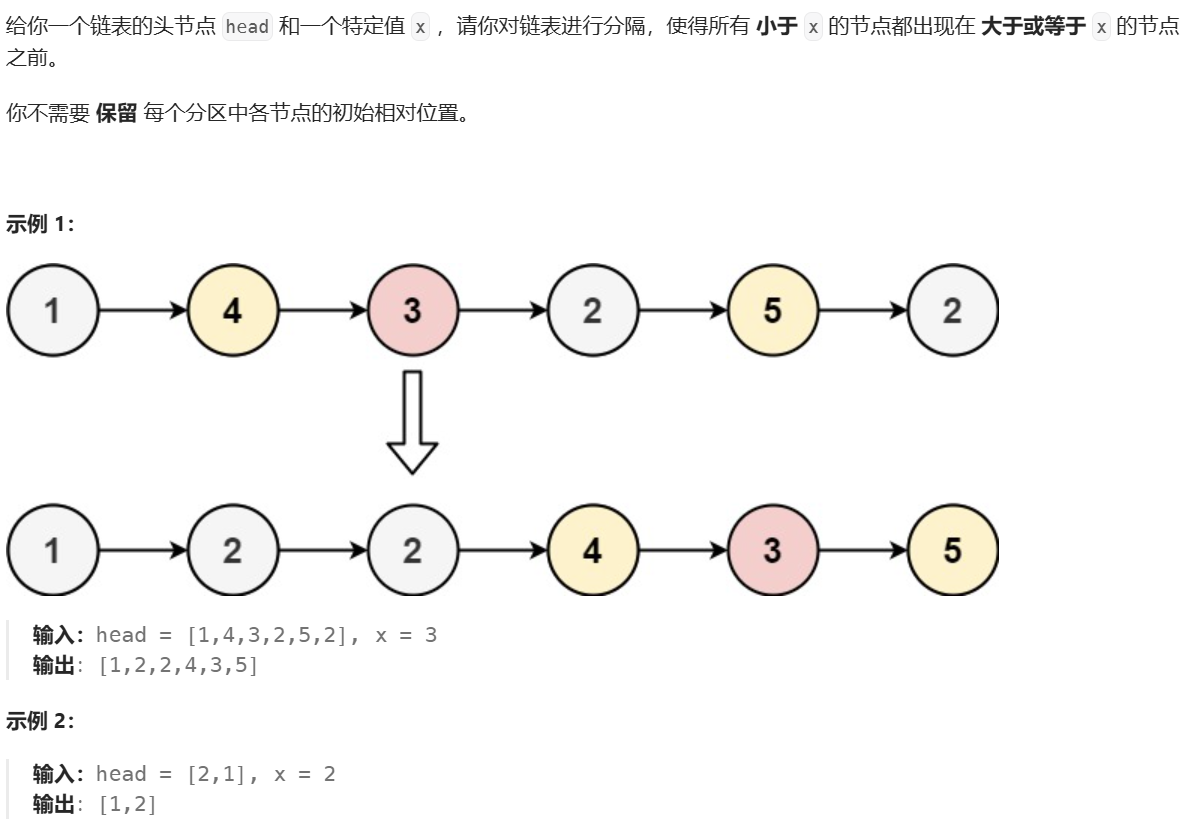
核心思路,就是哨兵位。定义两个哨兵位,按要求依次放入。
注意两点:
- 最后两个由哨兵位开始生成的两个新链表,应注意它们连接的位置
- 断开新链表与原链表的联系
代码演示:
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;
};typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x) {//原链表为空if (head == NULL)return NULL;//哨兵位ListNode* lessHead, *lessTail;lessHead = lessTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//lessHead->next = NULL;ListNode* greatHead, *greatTail;greatHead = greatTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//greatHead->next = NULL;//遍历ListNode* pcur = head;while (pcur){if (pcur->val < x){lessTail->next = pcur;lessTail = lessTail->next;}else{greatTail->next = pcur;greatTail = greatTail->next;}pcur = pcur->next;}//连接//此时,由于一开始,我们没有为哨兵位的next成员进行初始化(NULL),使得greatHead->next与greatTail->next,都是随机值//如果链表中的节点,保存的数据,都小于指定的x,那么greatTail就不会改变,greatHead->next和greatTail->next依旧都是随机值//而先连接,后置NULL,并不会改变lessTail->next,导致出错//正确的做法,是在连接之前,执行“ greatTail->next = NULL ”。//lessTail->next = greatHead->next;//greatTail->next = NULL;//切断与原链表联系greatTail->next = NULL;//切断与原链表联系lessTail->next = greatHead->next;//最好养成释放malloc的习惯ListNode* ret = lessHead->next;free(lessHead);lessHead = NULL;free(greatHead);greatHead = NULL;return ret;
}
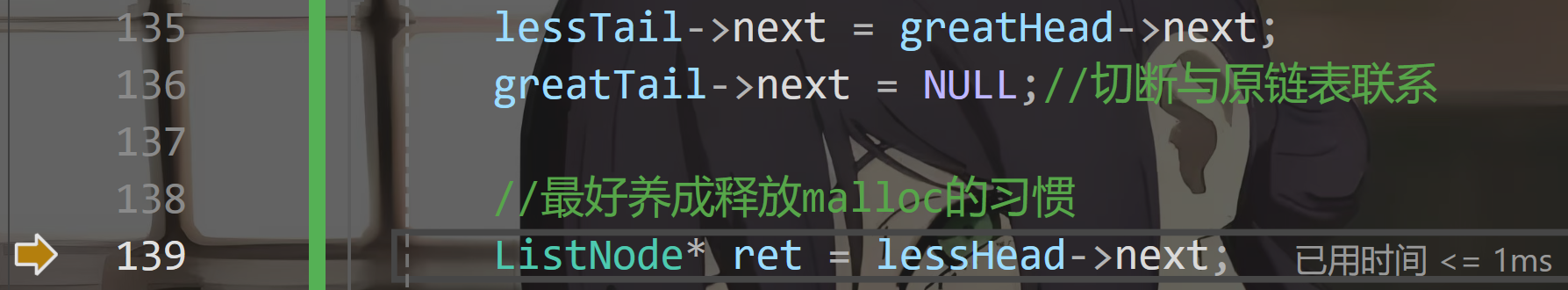
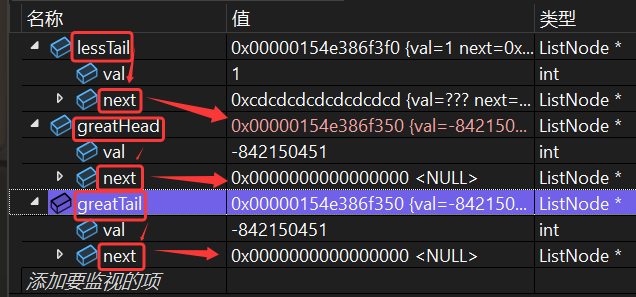
你肯定注意到了我在代码中间写的一大堆字。
所以,到底是先连接,再切断(与原链表的联系)?还是先切断,再连接?
答案是:先切断,后连接。
可以配合代码中的注释,以及下面两张图,进行理解。
6、链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构题目链接
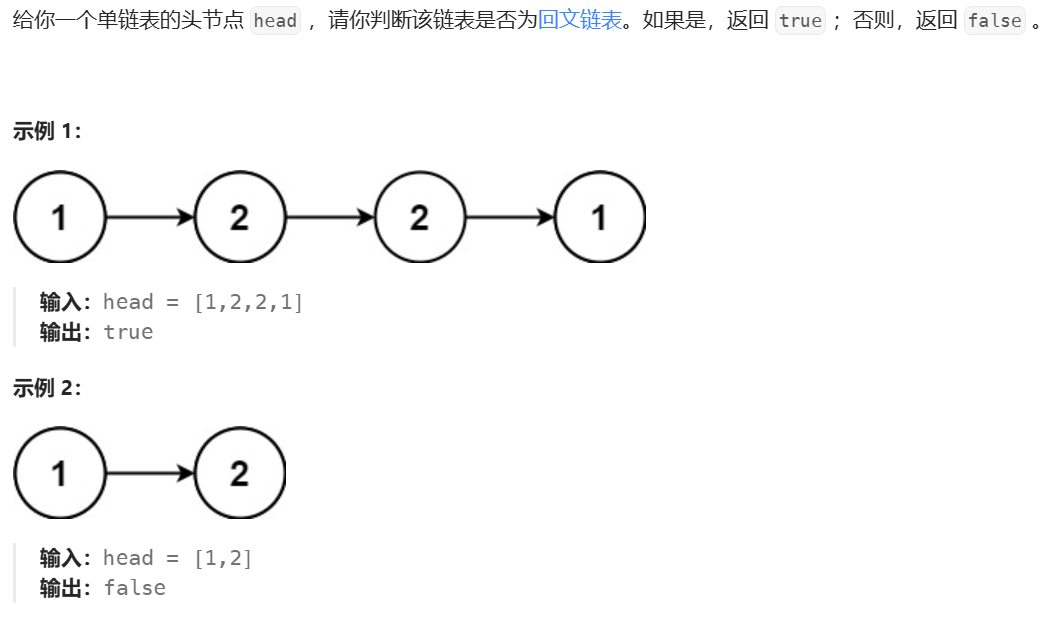
首先,我们要理解,什么是回文结构?
我们知道,回文诗句,顺着读,和倒着读,都能读顺。
类似的,数据的回文结构,就是从左往右,与从右往左,读取的每一位上的数,对应相同。比如:12321、aabcbaa……
其实这一种结构,更像是一种“ 镜像 ”的结构。
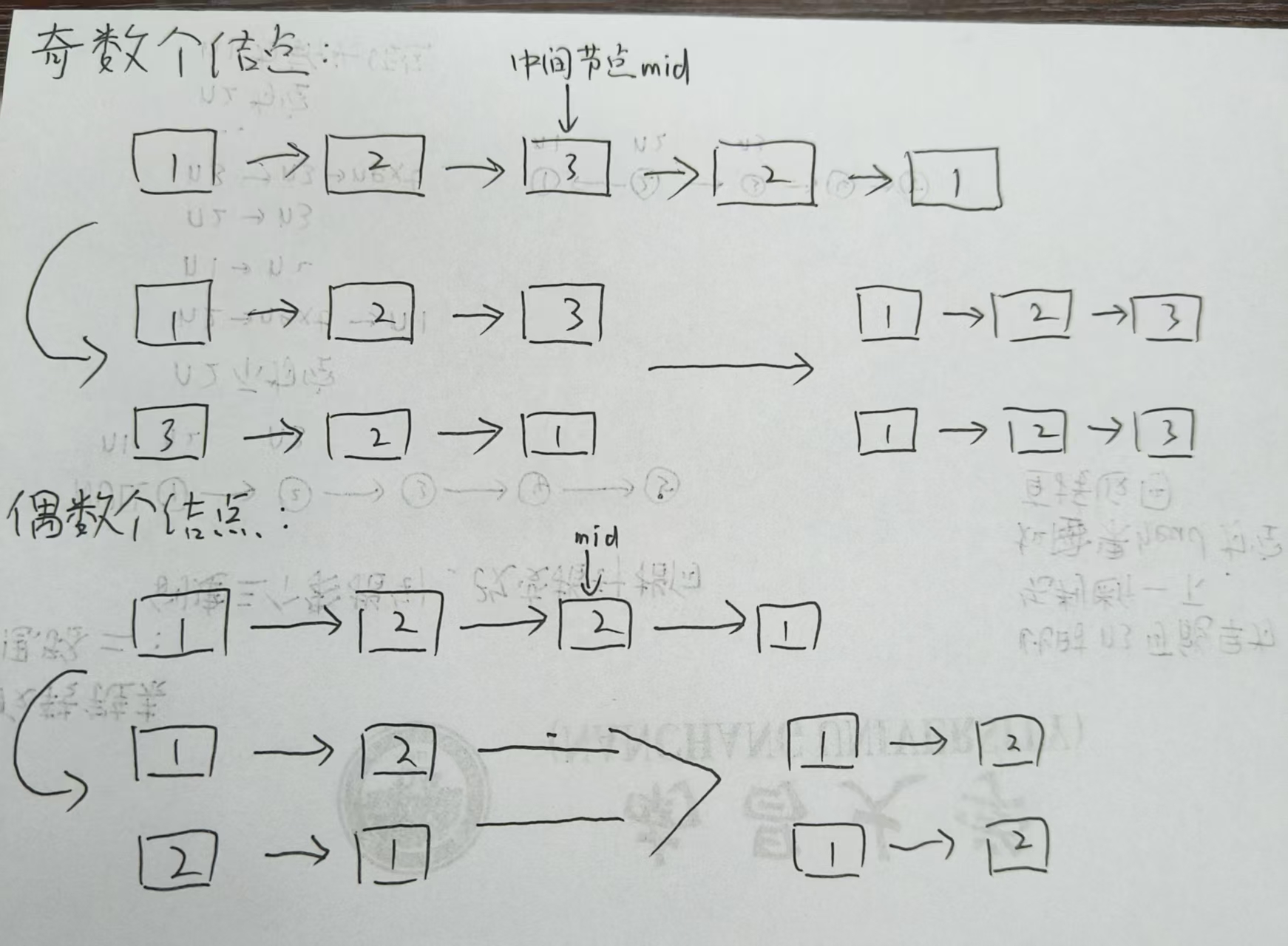
那么,思路就有了:
- 利用快慢指针,找到中间节点
- 将中间节点及以后的节点,进行反转
- 反转链表,与原链表的“ 一半 ”,遍历比较
图示:
代码演示:
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;
};typedef struct ListNode ListNode;//找中间节点
ListNode* FindMid(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* slow, *fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow;
}//链表反转
ListNode* ListSpin(ListNode* head)
{ListNode *n1, *n2, *n3;n1 = NULL;n2 = head;n3 = head->next;while (n2){n2->next = n1;n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if (n3)n3 = n3->next;}return n1;
}bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head) {//判断空链表if (head == NULL)return false;//快慢指针找中间节点ListNode* mid = FindMid(head);//反转ListNode* right = ListSpin(mid);//遍历比较ListNode* n1 = head;ListNode* n2 = right;while (n2){if (n1->val != n2->val)return false;n1 = n1->next;n2 = n2->next;}return true;
}
7、相交链表
相交链表的题目链接

思路:
- 对齐:
- 求出两链表的长度
- 计算差值
- 区分长、短链表( 利用
if语句 ) - 然后使长链表对齐短链表
- 遍历,找到相交节点
代码实现:
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;
};
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;int Count(ListNode* head)
{int count = 0;ListNode* pcur = head;while (pcur){++count;pcur = pcur->next;}return count;
}struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {//求长度int CountA = Count(headA);int CountB = Count(headB);//求差值int gap = abs(CountA - CountB);//LengthA - LengthA是什么玩意儿//定长短ListNode* Long = headA;ListNode* Short = headB;if (CountA < CountB){Long = headB;Short = headA;}//对齐while (gap--)//先使用,后++{Long = Long->next;}//遍历while (Long && Short){if (Long == Short)return Long;Long = Long->next;Short = Short->next;}return NULL;
}
8、随机链表的复制
随机链表的复制题目链接
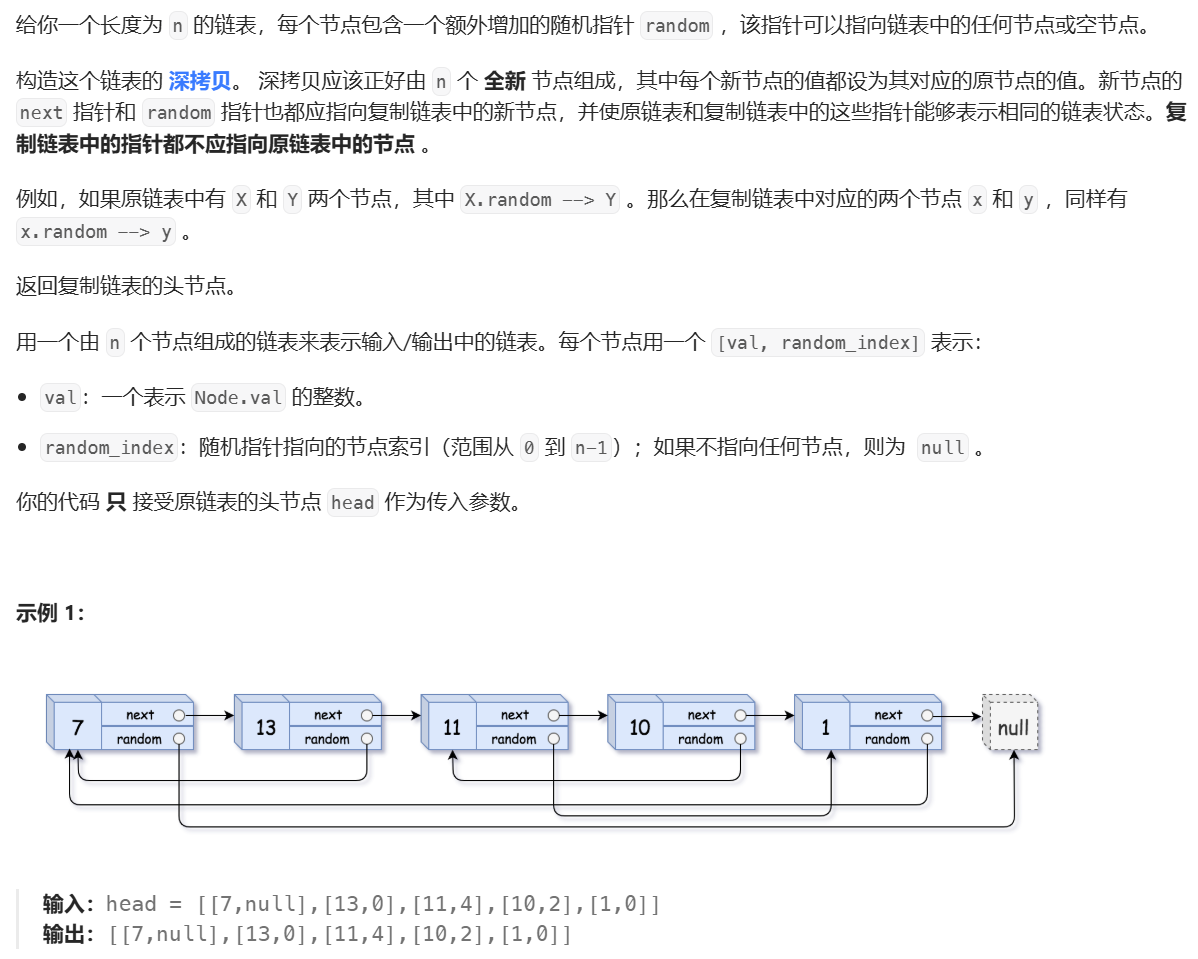
题目中说复制链表中的指针,都不应指向原链表中的节点。也就是说,我们不能直接将原链表的节点,给创建的新链表尾插。
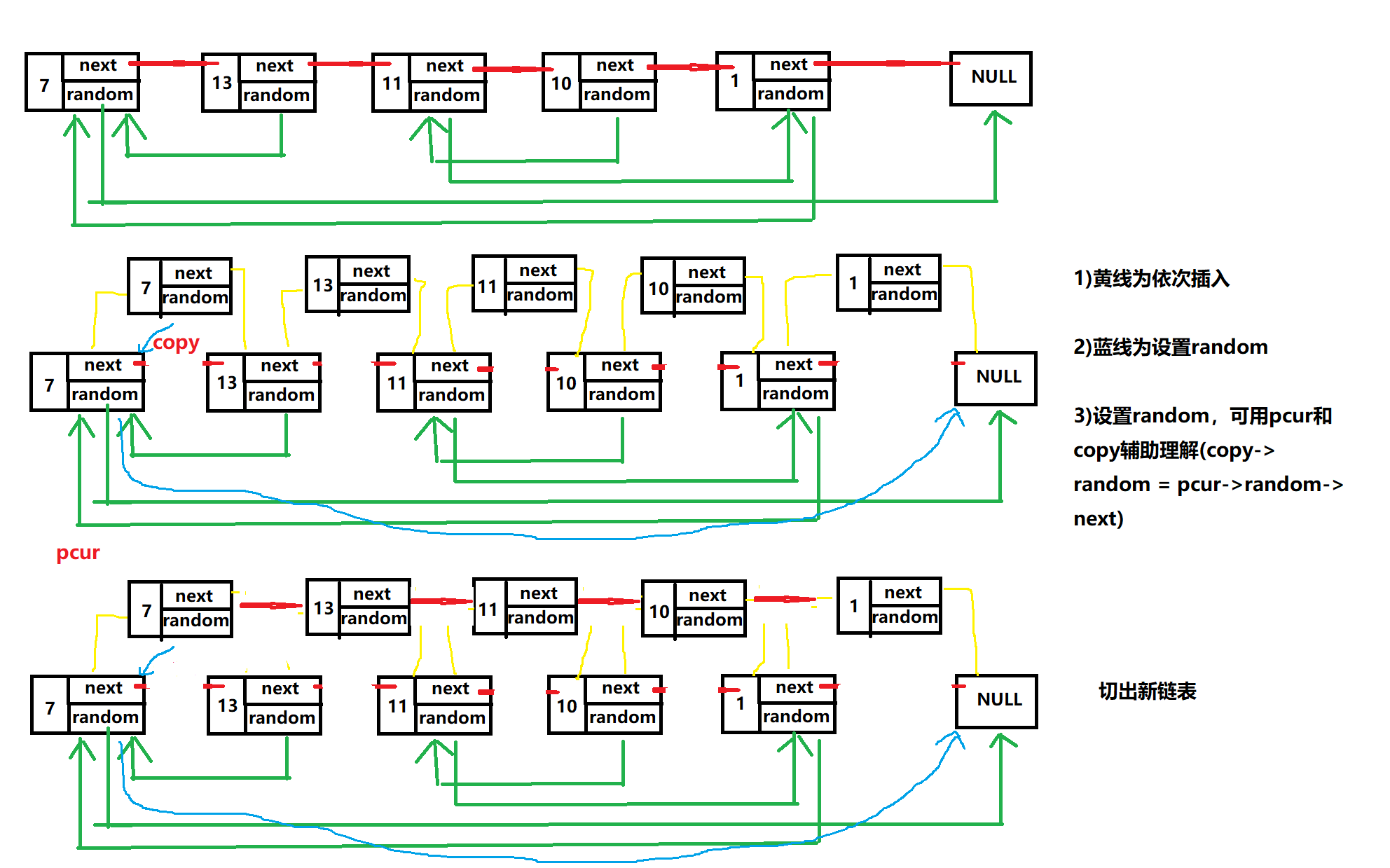
有一个比较巧妙的思路:
- 依次尾插。从原链表的头节点开始,在前一个节点与后一个节点之间,插入与前一个节点存放相同数据的节点。
- 设置插入节点的
random。每个插入节点的random,指向的就是其对应前一个节点的random指向的节点,的next指向的节点。 - 切断连接出新链表。
图示:
代码演示:
struct Node {int val;struct Node *next;struct Node *random;
};
typedef struct Node Node;Node* BuyNode(int x)
{Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newnode->next = newnode->random = NULL;newnode->val = x;return newnode;
}//依次尾插函数
void CopyPush(Node* head)
{Node* pcur = head;//用于遍历//Node* next = head->next;//用于保存pcur下一个指针while (pcur){Node* next1 = pcur->next;//pcur下一个指针,每次都要保存Node* newnode = BuyNode(pcur->val);//创建新链表//类尾插pcur->next = newnode;newnode->next = next1;pcur = next1;}
}//设置random函数
void SetRandom(Node* head)
{Node* pcur = head;while (pcur){Node* copy = pcur->next;//语句xif (pcur->random)//只有当random指向的不为NULL,才需要设置{copy->random = pcur->random->next;}pcur = copy->next;//如果语句x放到了这条语句的下面,当pcur走到NULL,会出现对空指针解引用的情况}
}struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {if (head == NULL)return head;//依次尾插CopyPush(head);//设置randomSetRandom(head);//切出新链表Node* pcur = head;Node *newHead, *newTail;newHead = newTail = head->next;while (newTail->next){pcur = newTail->next;newTail->next = pcur->next;newTail = newTail->next;}return newHead;
}
