使用LangChain+LangGraph自定义AI工作流,实现音视频字幕生成工具
1. 前言
前段时间做了几个短视频,之后总想着拍短视频给忘了发博客写文章了。
趁着最近AI工作流很火,趁热打铁,结合前段时间的生活,今天出一篇短文:用AI工作流做一个AI小工具,实现音视频的字幕生成。
2. langgraph简介
coze、dify、n8n都是AI工作流中的代表产品,界面炫酷且开源,在很多场景中也都得到了广泛的应用。
作为后端程序员的我,为了快速体验AI工作流带来的魅力,本文中决定使用最近同样很流行的LangChain + LangGraph来试一下。
langgraph的开源仓库地址为:https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph
与LangChain不同的是,LangGraph具有以下特性:
- 人机交互(Human-in-the-loop)
- 长短期记忆(Comprehensive memory)
- 简单易用的调试与部署(Debugging with LangSmith、Production-ready deployment)
- 长期运行(Durable execution)
简单总结就是LangChain可以让我们很方便的构建出一个智能体,而遇到比较复杂的处理流程时,则需要使用LangGraph来管理这些流程,特别是在构建多智能应用时非常有用。
关于LangGraph的详细细节这里不再展开,相关说明可移步LangGraph官方说明:LangGraph overview
3. 示例–音视频字幕生成工具流程
先用draw.io画一个流程图:
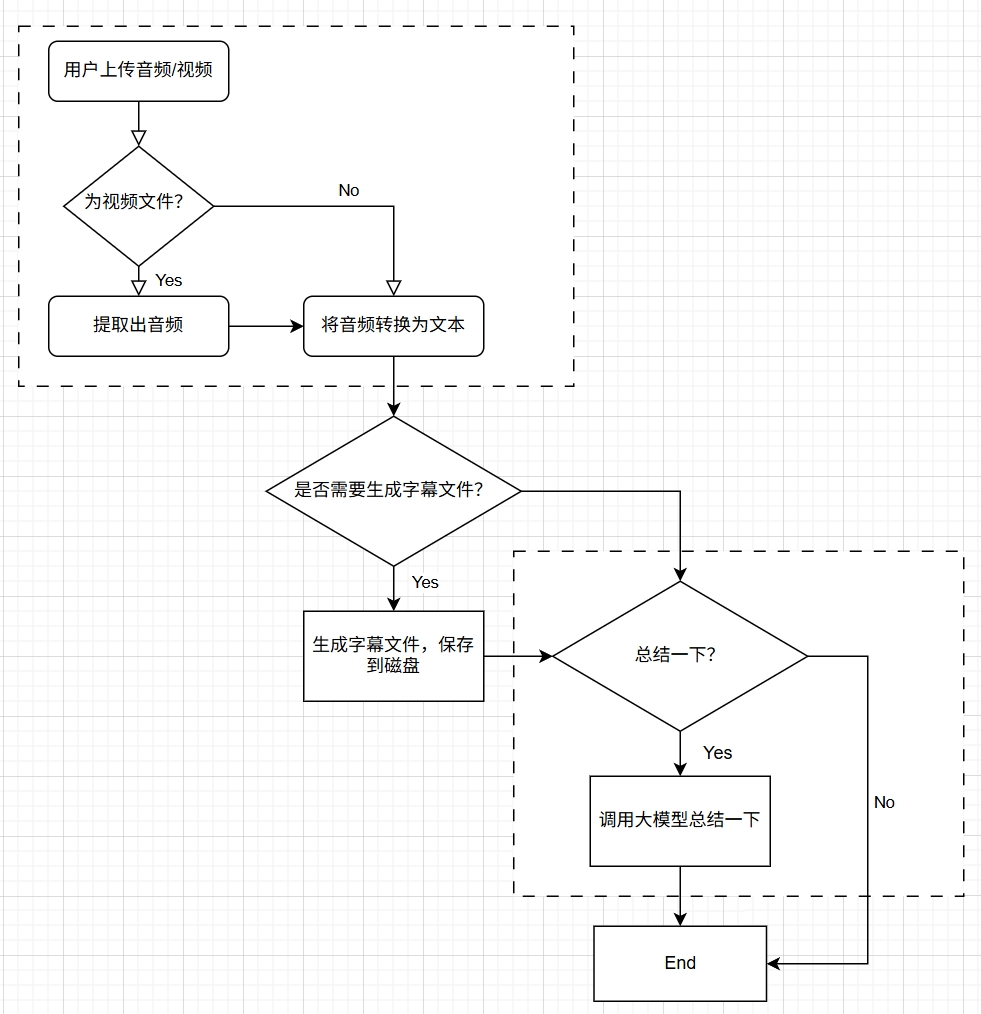
上图展示了一个将音视频转为字幕文件,并提炼总结的一个示例。
其中我们可以划分为两个智能体:
- 音视频转文本——智能体
- 总结一下——智能体
是否需要调用“总结一下”智能体由用户交互决定。
4. LangChain+LangGraph入门(可跳过)
此案例中使用的大模型为阿里的通义千问,API_KEY获取地址:https://bailian.console.aliyun.com/
4.1 LangChain构建一个智能体(HelloWorld)
在编码之前,先看一下LangChain构建一个智能体应用的代码是多么短:
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatTongyillm = ChatTongyi(model="qwen-plus",temperature=0,verbose=True,
)def get_weather(city: str) -> str:"""根据指定的城市名称获取对应的天气"""return f"今天{city}的天气很好,是一个大晴天!"agent = create_agent(model=llm,tools=[get_weather],system_prompt="你是一个非常有用的信息查询助手"
)# Run the agent
answer = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "今天成都的天气怎么样?"}]}
)# print(answer)
for i in answer["messages"]:print(i)print()定义好DASHSCOPE_API_KEY变量后再运行:
输出结果如下:
content='今天成都的天气怎么样?' additional_kwargs={} response_metadata={} id='b57bb281-6f0b-4581-a3ab-2e3619516de2'content='' additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'index': 0, 'id': 'call_fb87d30b624f4e49a380ed', 'type': 'function', 'function': {'name': 'get_weather', 'arguments': '{"city": "成都"}'}}]} response_metadata={'model_name': 'qwen-plus', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'request_id': 'ea2d43ee-1562-4bd6-99be-05c07fc6fb00', 'token_usage': {'input_tokens': 161, 'output_tokens': 19, 'total_tokens': 180, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'cached_tokens': 0}}} id='lc_run--cd6032b8-63e0-4e5c-a945-a2c4d4f4660f-0' tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'city': '成都'}, 'id': 'call_fb87d30b624f4e49a380ed', 'type': 'tool_call'}]content='今天成都的天气很好,是一个大晴天!' name='get_weather' id='36c1c579-c201-443a-b3d5-df1061d1c94d' tool_call_id='call_fb87d30b624f4e49a380ed'content='今天成都的天气很好,是一个大晴天!适合外出活动哦!' additional_kwargs={} response_metadata={'model_name': 'qwen-plus', 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'request_id': '59130a05-e0b6-4c90-9191-643d35a9b5fc', 'token_usage': {'input_tokens': 204, 'output_tokens': 16, 'total_tokens': 220, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'cached_tokens': 0}}} id='lc_run--211eeb8f-f77b-4037-85f3-89d682cb5ef5-0'4.2 LangGraph-HelloWold
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START, ENDdef mock_llm(state: MessagesState):return {"messages": [{"role": "ai", "content": "你好,世界!"}]}graph = StateGraph(MessagesState)
graph.add_node(mock_llm)
graph.add_edge(START, "mock_llm")
graph.add_edge("mock_llm", END)
graph = graph.compile()answer = graph.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi!"}]})for i in answer["messages"]:print(i)print()# Show the workflow
# png = graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()
# with open("workflow.png", "wb") as f:
# f.write(png)
# print("流程图已保存为 workflow.png")
上面代码中构建的工作流程图为:
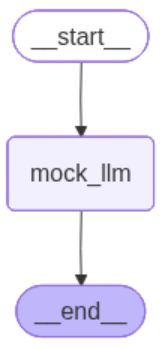
输出为:
content='hi!' additional_kwargs={} response_metadata={} id='6e5648f2-f755-4c1d-84ee-e3481e595ccb'content='你好,世界!' additional_kwargs={} response_metadata={} id='b2ede0ed-0881-420b-a971-4eb2dc93e6b0'5. 智能体实现
5.1 实现步骤
在掌握了LangChain和LangGraph的基本用法后,根据上面的目标进行拆解,并制定出以下开发步骤:
- 第1个智能体: 读取指定的文件,并让大模型来判断调用哪个工具(直接转为字幕文件,还是先转为音频后再转为字幕文件)。
此智能体中包含一个LLM和以下两个工具:- 将视频文件提取出音频
- 将音频文件转为LRC字幕文件
- 开发磁盘写入工具,将指定文件写入到磁盘
- 第2个智能体: 总结一下文本内容,并输出
- 根据应用需求,将上面的每个节点构建为一个图
- 运行构建好的图,并测试
5.2 实现代码
梳理出了实现步骤后,再编写以下代码,可以手写也可能AI辅助。上述流程的代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""
LangGraph 流程:
1) 判断文件类型 → 提取音频(如是视频)
2) Whisper → LRC 字幕
3) Qwen Plus 文本总结
4) 写入文件
"""import os, re, subprocess, logging
from pathlib import Pathfrom faster_whisper import WhisperModel
import dashscope
from http import HTTPStatusfrom langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from typing import TypedDict, Optional# ========== 配置 ==========
dashscope.api_key = os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")
if not dashscope.api_key:raise RuntimeError("❗请先设置: export DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=你的key")logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s [%(levelname)s] %(message)s")# ========== 工具函数 ==========
def ensure_file(f):if not Path(f).exists():raise FileNotFoundError(f"文件不存在: {f}")def extract_audio(video_path, wav_path):ensure_file(video_path)cmd = ["ffmpeg", "-y", "-i", video_path,"-vn", "-acodec", "pcm_s16le","-ar", "16000", "-ac", "1", wav_path]subprocess.run(cmd, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)return wav_pathdef whisper_to_lrc(audio_path, model_size="base", device="cpu"):# 加载模型model = WhisperModel(model_size, device=device)# 转写segments, info = model.transcribe(audio_path)# seg → LRC 格式函数def seg_to_lrc(seg):t = seg.startm = int(t // 60)s = t - m * 60return f"[{m:02d}:{s:05.2f}]{seg.text.strip()}"# 拼接 LRClrc_lines = [seg_to_lrc(seg) for seg in segments]lrc = "\n".join(lrc_lines)return lrcdef save_text(path, txt):Path(path).parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)with open(path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:f.write(txt)logging.info(f"✅ 文件写入: {path}")def qwen_summarize(text: str):text_clean = re.sub(r"\[\d{2}:\d{2}\.\d{2}\]", "", text).replace("\n", " ")prompt = ("总结以下字幕内容,要求简洁、中文,不超过200字,列出关键要点:\n\n"f"{text_clean}")resp = dashscope.Generation.call(model="qwen-plus",messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],temperature=0.2)if resp.status_code != HTTPStatus.OK:raise RuntimeError(f"Qwen 调用失败: {resp}")return resp.output["text"].strip()# ========== LangGraph 状态 ==========
class State(TypedDict):input_file: straudio_file: Optional[str]lrc_text: Optional[str]summary: Optional[str]output_dir: str# ========== 节点函数 ==========
def decide_and_extract(state: State):f = state["input_file"]suffix = Path(f).suffix.lower()out_dir = state["output_dir"]wav = f"{out_dir}/{Path(f).stem}.wav"if suffix in {".mp4", ".mkv", ".mov", ".avi"}:logging.info("🎬 检测到视频 → 提取音频")audio = extract_audio(f, wav)else:logging.info("🎧 音频文件,跳过提取")audio = fstate["audio_file"] = audioreturn statedef generate_lrc(state: State):logging.info("📝 Whisper 转字幕中...")lrc = whisper_to_lrc(state["audio_file"])state["lrc_text"] = lrclrc_path = f"{state['output_dir']}/{Path(state['input_file']).stem}.lrc"save_text(lrc_path, lrc)return statedef summarize(state: State):logging.info("🤖 Qwen 总结中...")summary = qwen_summarize(state["lrc_text"])state["summary"] = summarysum_path = f"{state['output_dir']}/{Path(state['input_file']).stem}.summary.txt"save_text(sum_path, summary)return state# ========== LangGraph 构建 ==========
workflow = StateGraph(State)workflow.add_node("extract", decide_and_extract)
workflow.add_node("whisper", generate_lrc)
workflow.add_node("summarize", summarize)workflow.set_entry_point("extract")
workflow.add_edge("extract", "whisper")
workflow.add_edge("whisper", "summarize")
workflow.add_edge("summarize", END)graph = workflow.compile()# ========== 运行入口 ==========
def run_pipeline(file, out="./output"):state = graph.invoke({"input_file": file, "output_dir": out})print("\n✅ 流程完成!")print(f"字幕文件: {out}/{Path(file).stem}.lrc")print(f"总结文件: {out}/{Path(file).stem}.summary.txt")if __name__ == "__main__":import argparsep = argparse.ArgumentParser()p.add_argument("file")p.add_argument("--out", default="./output")args = p.parse_args()run_pipeline(args.file, args.out)这里以抖音上的这条视频为例,测试一下:
3.87 复制打开抖音,看看【IT男海洋哥的作品】划船158公里从成都到乐山大佛 # 皮划艇 # 乐... https://v.douyin.com/zqqcl_cEhzY/ jCU:/ 09/06 f@O.XM
运行结果为:
以上代码对应的流程图为:
Tips:上面的代码实现中使用到了faster_whisper对视频和音频进行处理,底层会使用FFmpeg,运行前需要确保系统中已安装FFmpeg,并配置好环境变量。
5. LangGraphStudio
上面的代码中,我们使用LangGraph+LangChain完成一个AI工作流的开发。
也正是它是基于代码的,对于普通用户要读懂它们需要有一点的知识储备。
尽管langchain在官方博客中有说明过这篇文章:not-another-workflow-builder
但在他们也提供了对LangChain+LangGraph构建的工作流的可视化方式——LangGraph Studio
