操作系统-线程
线程
线程的创建
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* threadFunc(void* arg){ // 线程函数printf("In New Thread\n");return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_t tid; // Thread id// 线程创建函数/** 参数列表:* 1.Thread id address* 2.Thread attribute address* 3.Thread function address* 4.Thread parameters address*/pthread_create(&tid, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);// 等待指定的线程结束pthread_join(tid, NULL);printf("In Main Thread\n");return 0;}
编译
gcc value.c -o value
执行
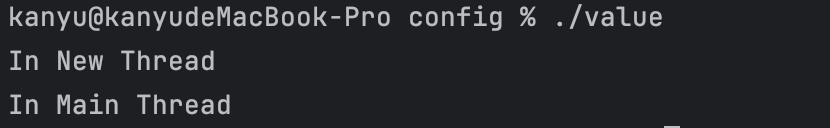
可以看到先执行子线程的语句再执行主线程的
主要是由于pthread_join语句
pthread_join
该函数的作用为等待指定线程结束才会执行后续逻辑
那这里的执行顺序一定是先执行子线程再执行主线程的?
现在把pthread_join注释掉
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* threadFunc(void* arg){ // 线程函数printf("In New Thread\n");return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_t tid; // Thread id// 线程创建函数/** 参数列表:* 1.Thread id address* 2.Thread attribute address* 3.Thread function address* 4.Thread parameters address*/pthread_create(&tid, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);// 等待指定的线程结束
// pthread_join(tid, NULL);printf("In Main Thread\n");return 0;}
重新编译再执行
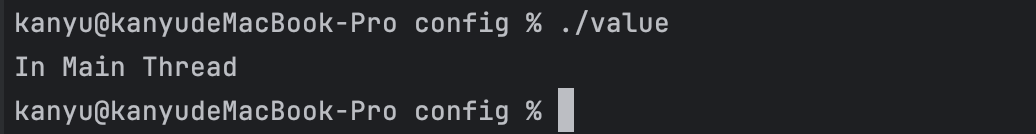
可以看到子线程没有执行就结束了!
若有的用户看不到现象仍然还是执行两条语句可以再子线程打印语句之前sleep 3s
子线程加入sleep
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* threadFunc(void* arg){ // 线程函数sleep(3);printf("In New Thread\n");return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_t tid; // Thread id// 线程创建函数/** 参数列表:* 1.Thread id address* 2.Thread attribute address* 3.Thread function address* 4.Thread parameters address*/pthread_create(&tid, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);// 等待指定的线程结束
// pthread_join(tid, NULL);printf("In Main Thread\n");return 0;}
则可以看到只打印主线程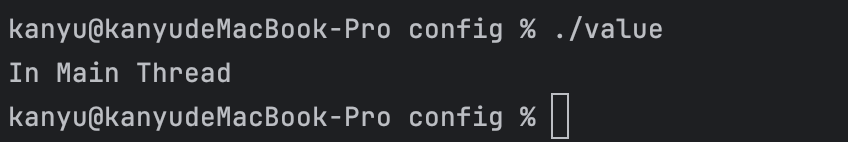
执行流程
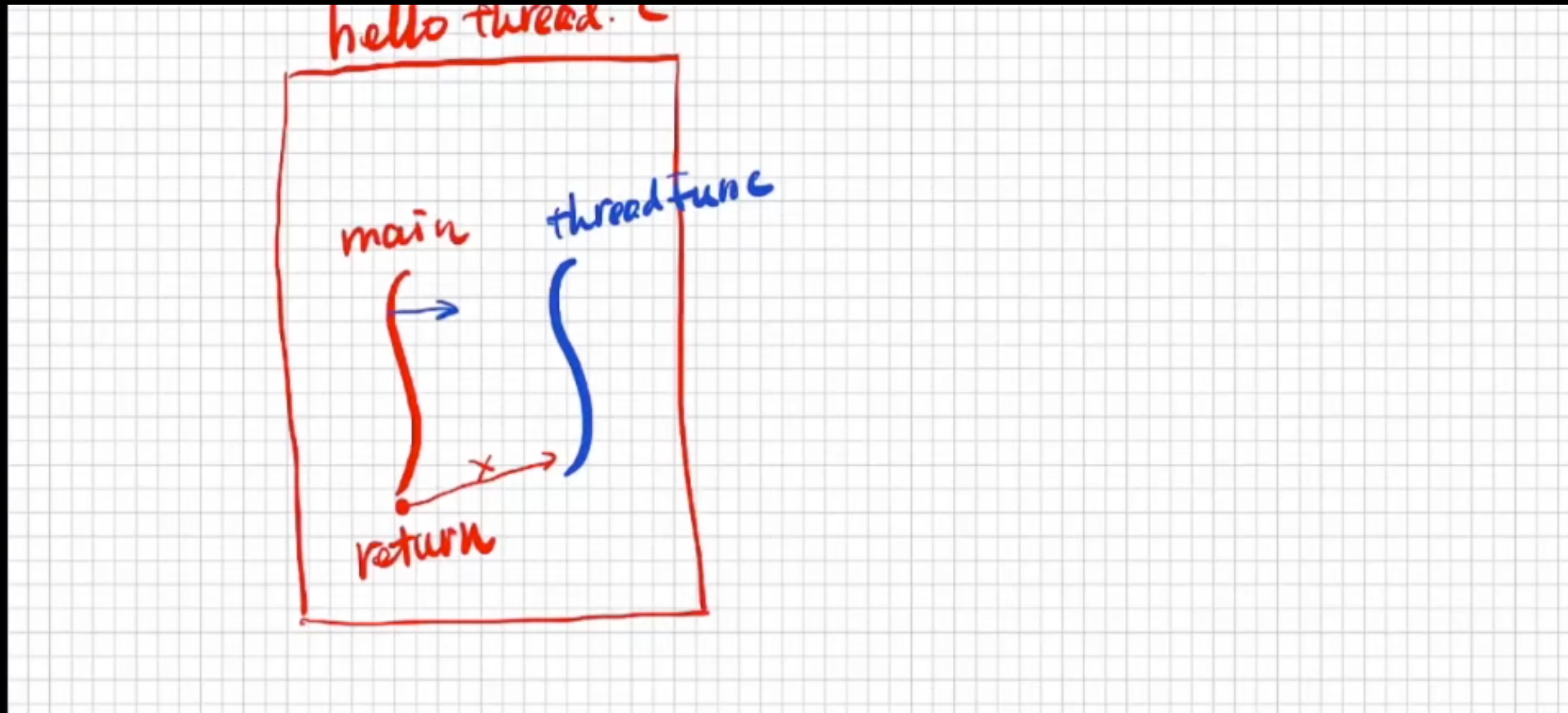
主线程开辟出子线程
当此时子线程的语句还没有打印完成的时候主线程结束,则子线程随之销毁则只会执行打印主线程的语句
join语句的关键点
将join语句移动到主函数打印语句之后
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* threadFunc(void* arg){ // 线程函数sleep(3);printf("In New Thread\n");return NULL;
}int main(){pthread_t tid; // Thread id// 线程创建函数/** 参数列表:* 1.Thread id address* 2.Thread attribute address* 3.Thread function address* 4.Thread parameters address*/pthread_create(&tid, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);// 等待指定的线程结束printf("In Main Thread\n");pthread_join(tid, NULL);return 0;}
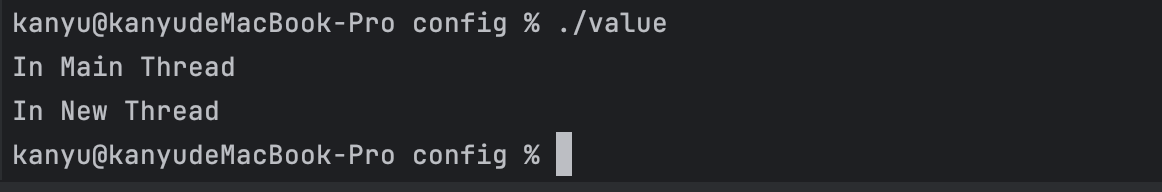
可以看到先打印出主线程的语句,过了3s之后打印出子线程的语句
多线程
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void* hello(void* args){for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++){
printf("hello(%d)\n", rand()%100);
}
return NULL;
}
void* world(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++){
printf("world(%d)\n", rand()%100);
}
return NULL;
}int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_t tid,tid2;
// 线程创建函数
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, hello, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, world, NULL);
// 等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("In Main Thread\n");
return 0;}
可以看到新建了两个子线程,同时主线程得等到两个子线程全部执行完成才会执行
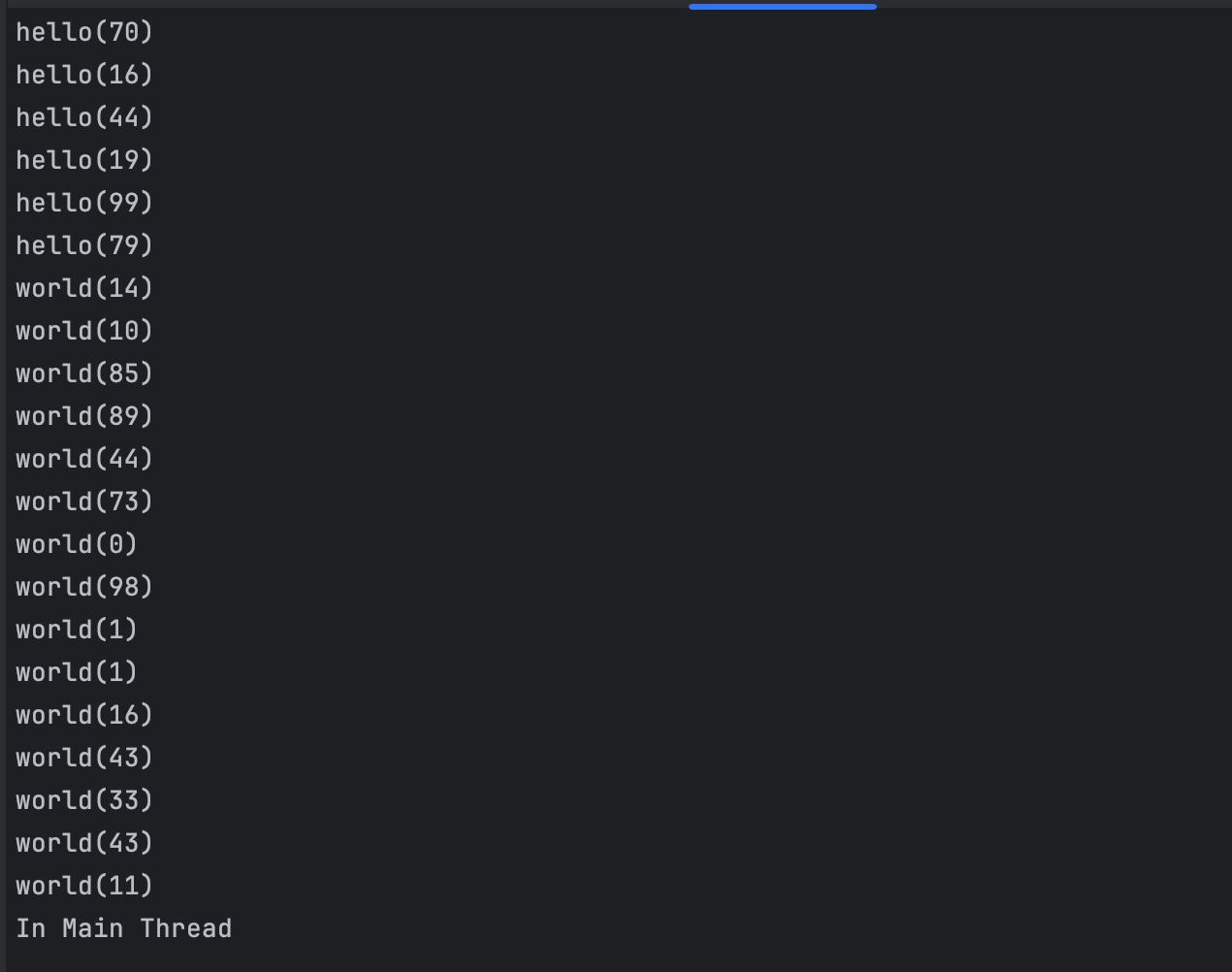
可以看到先等hello子线程全部执行完成再执行world子线程最后才会执行主线程的打印语句
实际这里由于计算机运行速度太快了看不出并发执行的效果
而且先执行hello还是world都不固定,取决于计算机处理器先调度哪个
因此在这里加上sleep语句模拟计算延迟
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void* hello(void* args){for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("hello(%d)\n", rand()%100);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
void* world(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("world(%d)\n", rand()%100);
sleep(1);}
return NULL;
}int main(){
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_t tid,tid2;
// 线程创建函数
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, hello, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, world, NULL);
// 等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("In Main Thread\n");
return 0;}
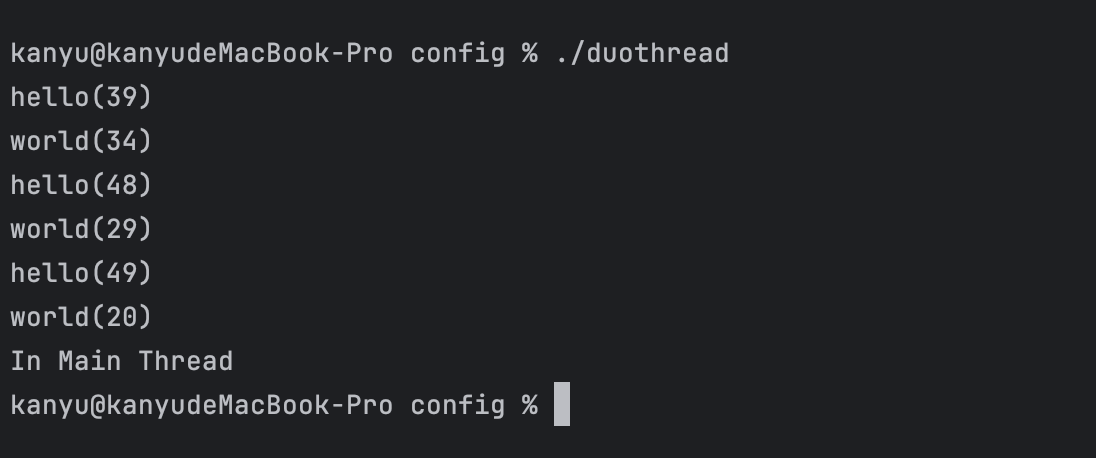
可以看到执行的语句执行不固定了
多线程之间的变量共享
定义共享变量value=100 两个子线程各进行+操作
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int value =100;
void* hello(void* args){for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("hello(%d)\n", value++);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
void* world(void* args){
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
printf("world(%d)\n", value++);
sleep(1);}
return NULL;
}int main(){
//srand(time(NULL));
pthread_t tid,tid2;
// 线程创建函数
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, hello, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, world, NULL);
// 等待指定的线程结束
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
printf("In Main Thread (%d)\n",value);
return 0;}
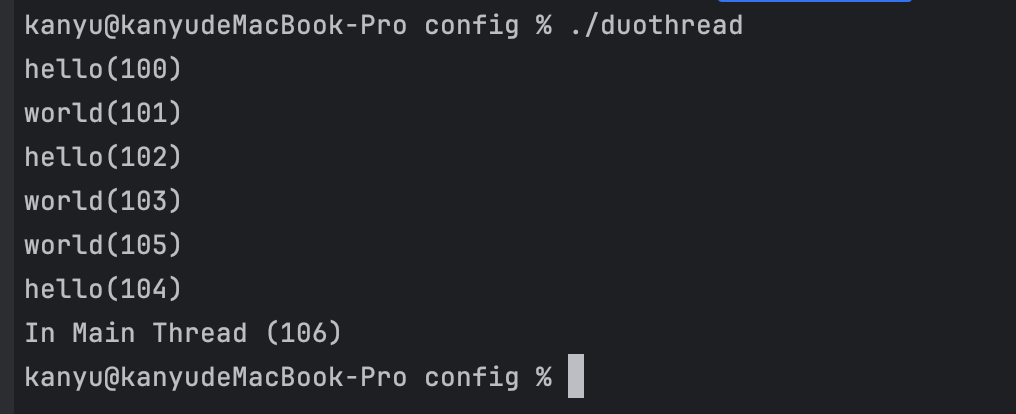
可以看到两个子线程会共享主线程的变量,且主线程同样可以拿到这个被子线程处理后的变量的值
注意value为share变量,不属于堆、不属于栈,属于全局数据段:程序启动时分配,程序结束时释放
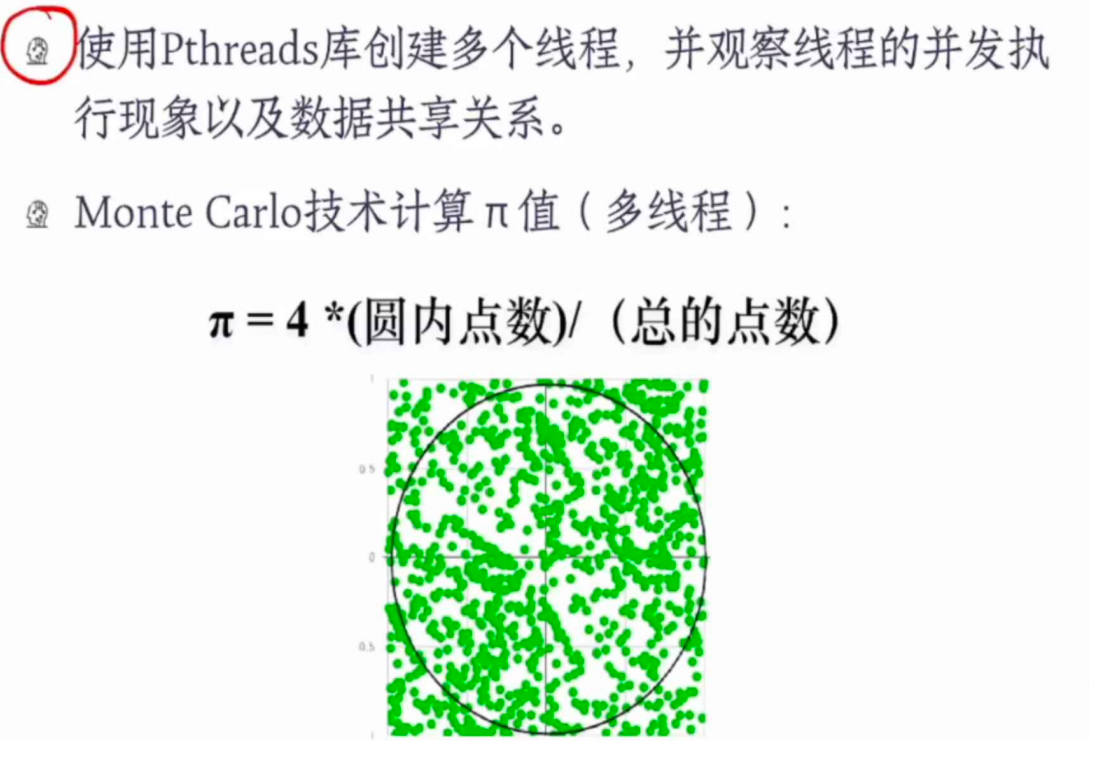
蒙特卡洛模拟
单独执行
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>void calculate_pi(int intervals){
unsigned int seed = time(NULL);
int circle_points = 0;
int square_points = 0;for (int i = 0; i < intervals * intervals; ++i)
{
double rand_x = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
double rand_y = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;if ((rand_x * rand_x) + (rand_y * rand_y) <= 1){
circle_points++;
}
square_points++;
}double pi = (double)(4.0*circle_points)/square_points;printf("The estimated PI is %lf in %d times\n", pi, intervals * intervals);}int main(){clock_t start,deleta;
double time_used;
double pi;start = clock();
// #pragma omp parallel for num_threads(10)for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
calculate_pi(1000*(i+1));
}deleta = clock() - start;printf("The time taken in total: %lf seconds\n", (double)deleta/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);return 0;}
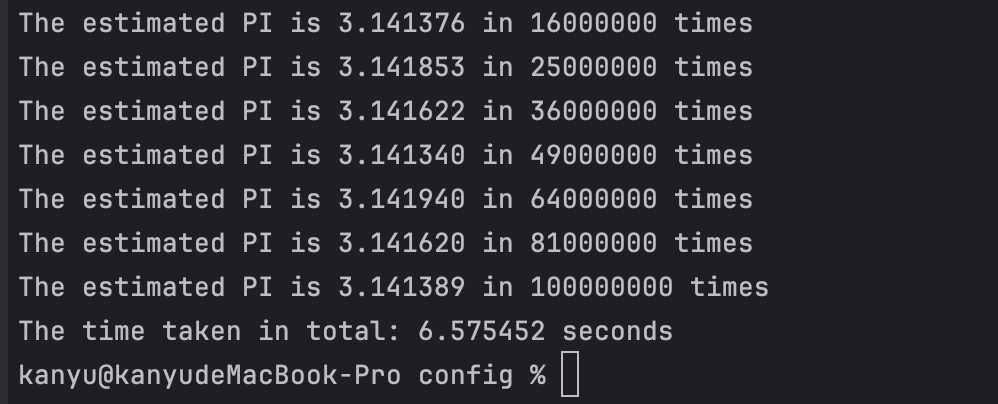
可以看到计算大概用了6s
time ./p
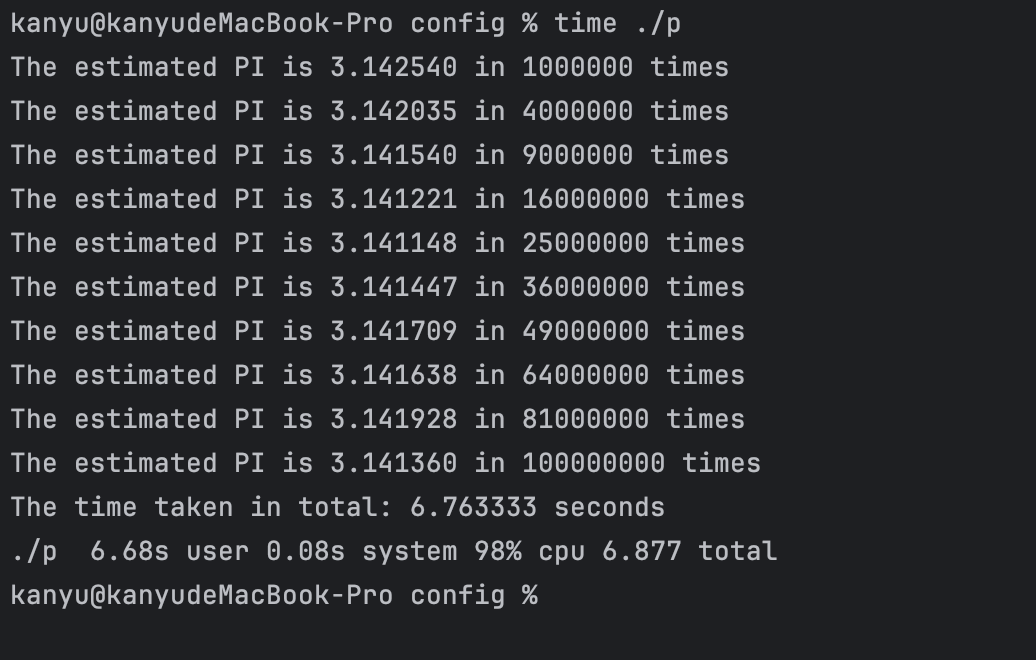
可以看到真实的运行时间 6.877 其中
接下来用多线程来执行去增加计算值多次模拟数值看计算pi值
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void* calculate_pi(void* args){
unsigned int seed = time(NULL);
int circle_points = 0;int square_points = 0;
int intervals = *((int*)args);for (int i = 0; i < intervals * intervals; ++i)
{double rand_x = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;double rand_y = (double)rand_r(&seed)/RAND_MAX;
if ((rand_x * rand_x) + (rand_y * rand_y) <= 1){
circle_points++;}square_points++;}
double pi = (double)(4.0*circle_points)/square_points;printf("The estimated PI is %lf in %d times\n", pi, intervals * intervals);pthread_exit(0);
}int main(){clock_t start,deleta;double time_used;start = clock();
pthread_t calculate_pi_threads[10];int args[10];for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){args[i] = 1000*(i+1);pthread_create(calculate_pi_threads+i,NULL,calculate_pi,args+i);}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i){pthread_join(calculate_pi_threads[i],NULL);}deleta = clock() - start;printf("The time taken in total: %lf seconds\n", (double)deleta/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
return 0;
}
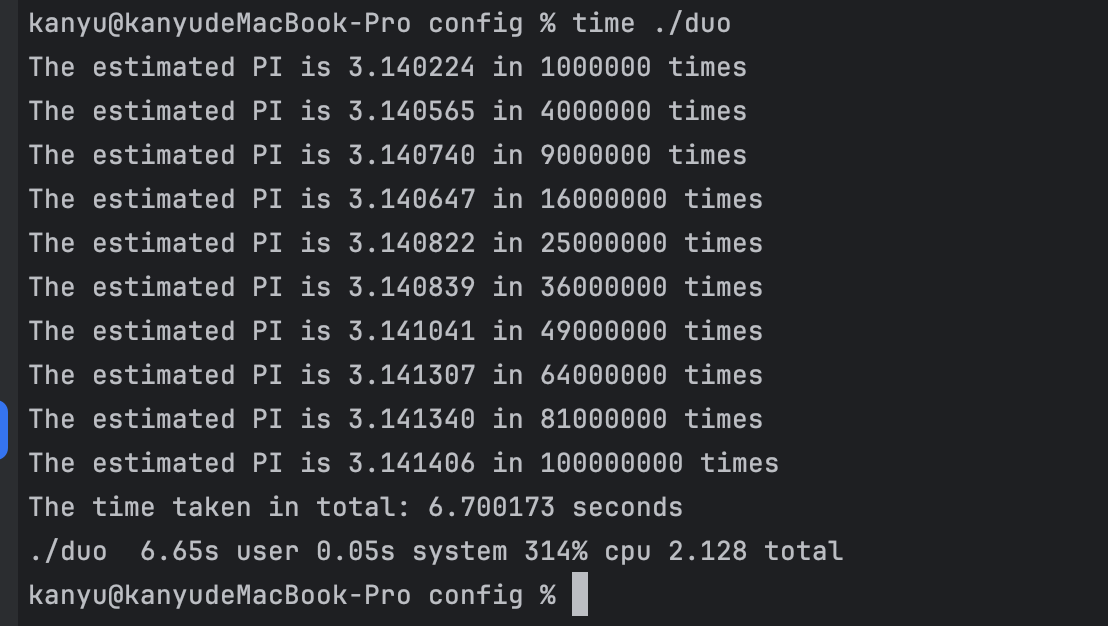
可以看到执行时间很快的
参考
操作系统原理
