【Linux网络】实现简单的英译汉网络字典

本篇主要介绍基于【Linux网络】Socket编程UDP 如何实现一个简单的英译汉的网络字典。
1.字典类的设计
首先我们要准备一个单词列表,如下是随便找的一些单词,放在一个dictionary.txt文件里。这个单词列表故意设置了一些错误,如只有中文没有英文,只有英文没有中文,什么也没有的空行。
apple: 苹果
banana: 香蕉
cat: 猫
dog: 狗
book: 书
hello:
pen: 笔
happy: 快乐的
sad: 悲伤的
run: 跑
: 剩余
jump: 跳
teacher: 老师
student: 学生car: 汽车
bus: 公交车
love: 爱
hate: 恨
hello: 你好
goodbye: 再见
summer: 夏天
winter: 冬天然后还需要Dictionary.hpp文件
我们在实例化字典类的对象的时候,需要知道我们应该在哪里加载这些单词,所以需要一个路径,默认路径就是当前路径下的dictionary.txt文件,字典的映射关系就用哈希表。
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include "MyLog.hpp"using namespace MyLog;
std::string dictionary_path = "./Dictionary.txt";
class Dictionary
{
public:Dictionary(const std::string& path = dictionary_path) :_path(path){}~Dictionary() {}private:std::string _path;std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _dict; // 用哈希表映射
};
1.1 加载单词
加载单词要用到C++的文件操作。
bool Load() // 加载单词{std::ifstream in(_path);if (!in.is_open()){LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "打开字典" << _path << "失败";return false;}std::string line;while(std::getline(in, line)) // 从in文件流中读到line里去{}}while循环里面就是对前面提供的那个简单的单词本做解析,格式是英文: 中文,所以我们要用find找这个分隔符,分隔符左边是英文,右边是中文。
也有可能更找不到,就证明格式有问题,先输出一个日志然后continue解析下一个就行,也有可能有的只有英文,有的只有中文,也是错误的,也可以用日志打印一下。
然后把英文和中文插入到哈希表里就行。
std::string sep = ": "; // 把分隔符设置一下bool Load() // 加载单词{std::ifstream in(_path);if (!in.is_open()){LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "打开字典" << _path << "失败";return false;}std::string line;while (std::getline(in, line)) // 从in文件流中读到line里去{auto pos = line.find(sep); // 找分隔符if (pos == std::string::npos) // 没找到, 格式错误{LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "解析" << line << "失败";continue; // 解析下一个}std::string English = line.substr(0, pos); // 左闭右开区间// pos位置为分隔符位置,要跳过分隔符,就是pos加上分隔符的大小std::string Chinese = line.substr(pos + sep.size());if (English.empty() || Chinese.empty()){LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "缺失有效内容:" << line;continue; // 解析下一个}_dict.insert(std::make_pair(English, Chinese));LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "加载 " << line;}return true;}1.2 翻译
这里是英文翻译成中文,所以参数就是一个string类型,返回值就是返回对应的中文,也是string类型。
std::string Translate(const std::string &e){LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "进入翻译模块";auto c = _dict.find(e);if (c == _dict.end()) // 没找到{return "None";}return c->second; // 找到返回中文}2. 模块间的调用
现在我们就有了两个模块,一个是字典的模块,一个是网络服务器模块。这两个模块可以互相调用,在网络服务器模块初始化的时候传一个拉姆达表达式就行。
// UdpServer.cc文件
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include "Dictionary.hpp"
#include <memory>// 格式为:udpserver port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 2){std::cout << "Usage:" << argv[0] << " port" << std::endl;return 1;}uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]);// 字典对象提供翻译功能Dictionary dict; // 实例化dictionary的对象dict.Load(); // 加载// 网络服务器对象提供通信功能Refresh_Log_To_Console();std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> server = std::make_unique<UdpServer>(port, [&dict](const std::string &w) -> std::string{ return dict.Translate(w); });server->Init();server->Start();return 0;
}我们先运行server端,看看单词的加载结果。
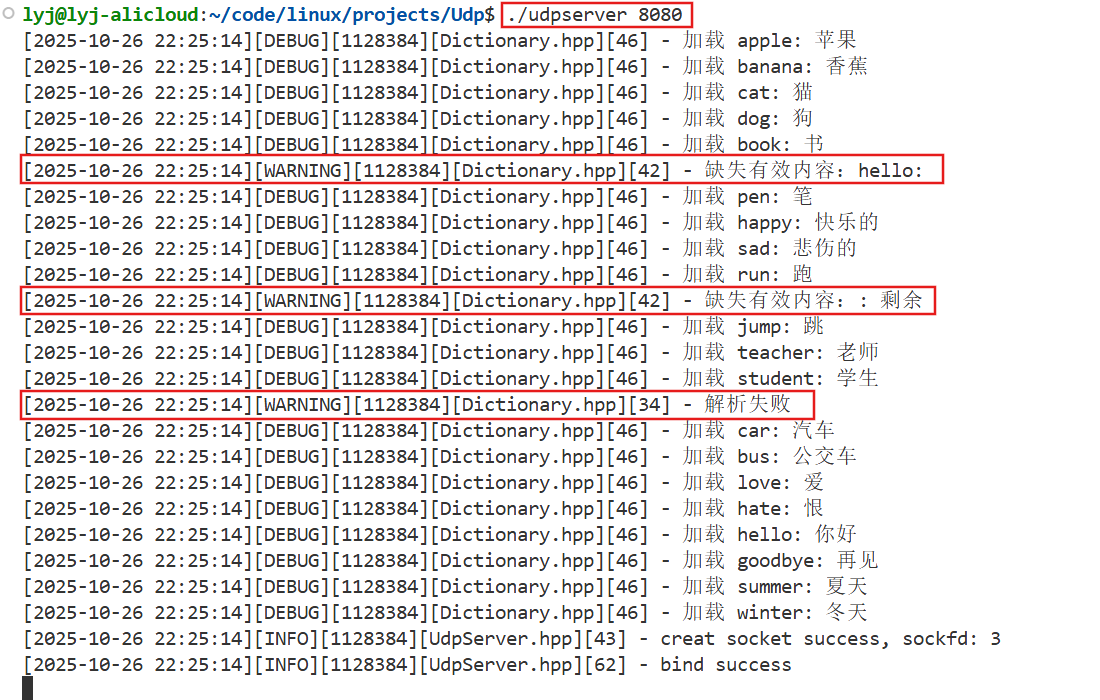
除了我们故意设置的三个错误单词格式外,其他的都正常加载。
再启动client端,并输入一些英文。
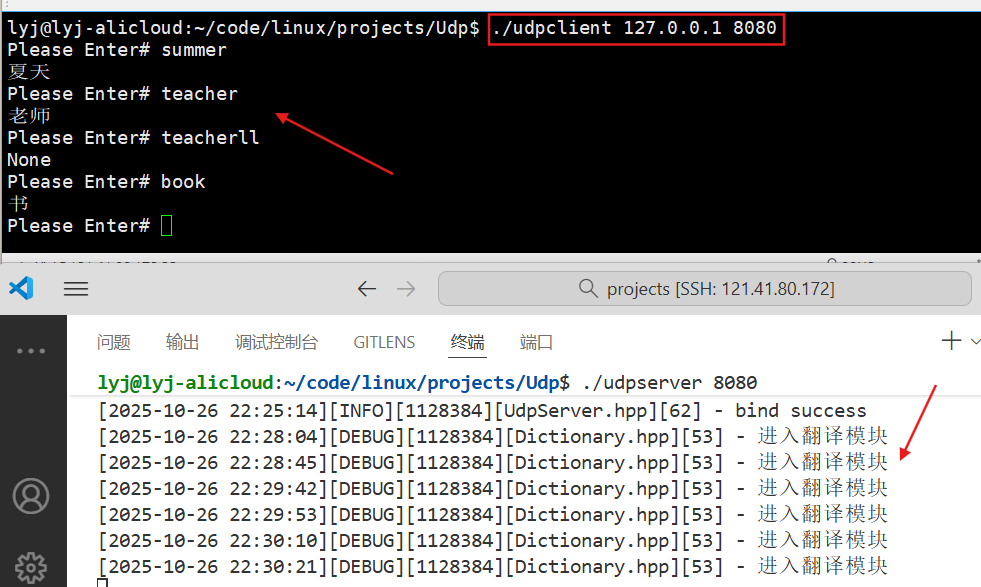
单词列表里有的,就可以直接翻译,单词列表里没有的,就会显示None。
3.获取client的信息
3.1 网络地址和主机地址之间转换的类
这里我们把网络地址与主机地址互相转换的方法提出来,新封装成一个类。
初始化的时候要求传一个结构体,通过这个类将网络序列转为主机序列,并且为外部提供能得到port和ip的接口。
// InetAddr.hpp文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>class InetAddr
{
public:InetAddr(const sockaddr_in &addr){_port = ntohs(addr.sin_port); // 网络序列转主机序列_ip = inet_ntoa(addr.sin_addr); // 4字节网络序列转点分十进制}std::string Ip(){return _ip;}uint16_t Port(){return _port;}~InetAddr() {}private:std::string _ip;uint16_t _port;
};
然后UdpServer.hpp里的Start接口就可以变为如下写法。
// UdpServer.hpp文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <strings.h>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "MyLog.hpp"
#include "InetAddr.hpp"using namespace MyLog;
using func_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &)>; // 参数和返回值都为string类型
class UdpServer
{
public://...void Start(){if (_isrunning)return; // 不要重复启动_isrunning = true;while (true){char buffer[1024];struct sockaddr_in peer;socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); // 大小要是socklen_t类型size_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);if (n > 0){buffer[n] = 0; // 手动添加字符串结束标志// 网络序列转主机序列InetAddr client(peer); // 传peer结构体过去 std::string result = _func(buffer);sendto(_sockfd, result.c_str(), result.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);}}}private:int _sockfd;uint16_t _port; bool _isrunning;func_t _func; // 服务器的回调函数
};
3.2 代码修改
我们要获取是谁进入到了翻译模块的话,在回调函数上需要新增一个参数,就是传对应的类过去。
// UdpServer.hpp文件// 返回值为string类型,参数为string和一个InetAddr类
using func_t = std::function<std::string(const std::string &, InetAddr &)>;
class UdpServer
{
public:UdpServer(uint16_t &port, func_t func): _sockfd(-1),_port(port),_isrunning(false),_func(func){}void Init(){//...}void Start(){if (_isrunning)return; // 不要重复启动_isrunning = true;while (true){char buffer[1024];struct sockaddr_in peer;socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); // 大小要是socklen_t类型size_t n = recvfrom(_sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);if (n > 0){buffer[n] = 0; // 手动添加字符串结束标志// 网络序列转主机序列InetAddr client(peer); // 传peer结构体过去std::string result = _func(buffer, client); // 把client类对象传过去sendto(_sockfd, result.c_str(), result.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);}}}~UdpServer() {}private:int _sockfd;uint16_t _port; // 端口号bool _isrunning;func_t _func; // 服务器的回调函数
};
// UdpServer.cc文件
#include "UdpServer.hpp"
#include "Dictionary.hpp"
#include <memory>// 格式为:udpserver port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 2){std::cout << "Usage:" << argv[0] << " port" << std::endl;return 1;}uint16_t port = std::stoi(argv[1]);// 字典对象提供翻译功能Dictionary dict; // 实例化dictionary的对象dict.Load(); // 加载// 网络服务器对象提供通信功能Refresh_Log_To_Console();// lambda表达式的参数变为两个std::unique_ptr<UdpServer> server = std::make_unique<UdpServer>(port, [&dict](const std::string &w, InetAddr &addr) -> std::string { return dict.Translate(w, addr); });server->Init();server->Start();return 0;
}// Dictionary.hpp文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include "MyLog.hpp"using namespace MyLog;
std::string dictionary_path = "./Dictionary.txt";
std::string sep = ": "; // 把分隔符设置一下class Dictionary
{
public:Dictionary(const std::string &path = dictionary_path): _path(path){}bool Load() // 加载单词{//...}std::string Translate(const std::string &e, InetAddr &addr){// 获得客户端信息LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "[" << addr.Ip() << ":" << addr.Port() << "]进入翻译模块";auto c = _dict.find(e);if (c == _dict.end()) // 没找到{return "None";}return c->second; // 找到返回中文}~Dictionary() {}private:std::string _path;std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _dict; // 用哈希表映射
};
前面三个对应的文件内容都要改。
改好之后运行两个.c文件,client端用不同的ip进行bind,得到如下结果。
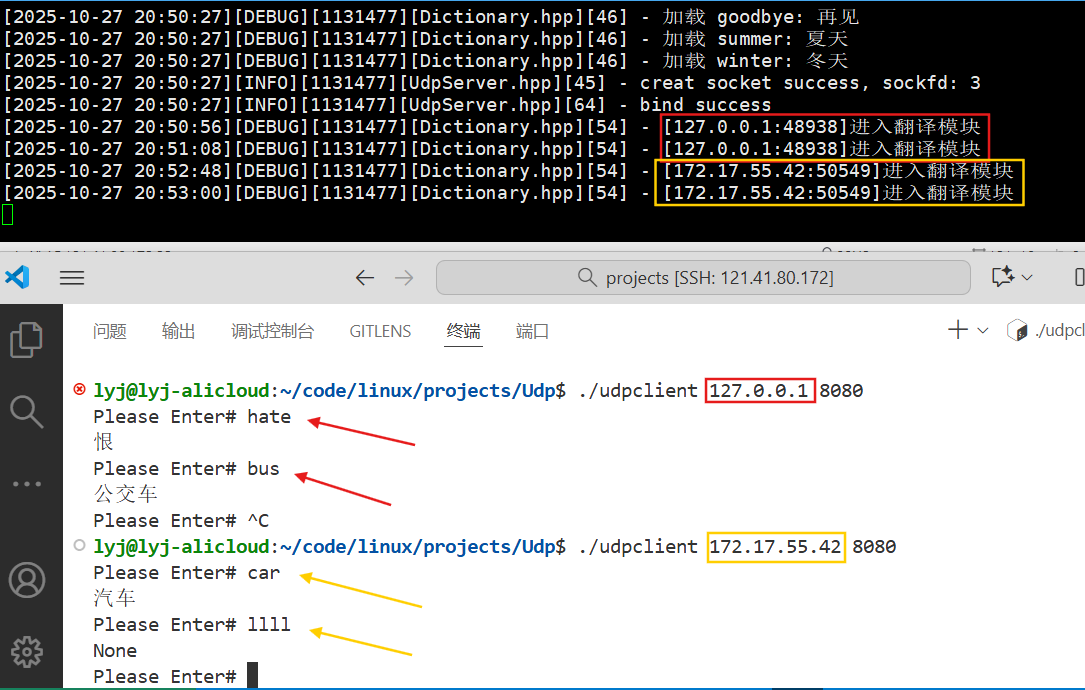
现在优化后就可以知道是哪个client在访问server了。
本篇分享就到这里,我们下篇见~

