Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第六十八回 —— 进程主结构详解(64)
接前一篇文章:Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第六十七回 —— 进程主结构详解(63)
本文内容参考:
Linux内核进程管理专题报告_linux rseq-CSDN博客
《趣谈Linux操作系统 核心原理篇:第三部分 进程管理》—— 刘超
《图解Linux内核 基于6.x》 —— 姜亚华 机械工业出版社
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45030965/article/details/132734258
特此致谢!
进程管理核心结构 —— task_struct
12. current
前几回讲了current在x86以及ARM上的实现,本回来看本部分剩余的一个知识点:通过task_struct定位内核栈stack和通过内核栈定位task_struct。在其中还会涉及到一个重要的结构体 —— struct pt_regs。
- 通过内核栈stack找task_struct
上一回讲解对于那些struct thread_info中没有struct task_struct的体系结构,该如何通过内核栈stack找到task_struct。
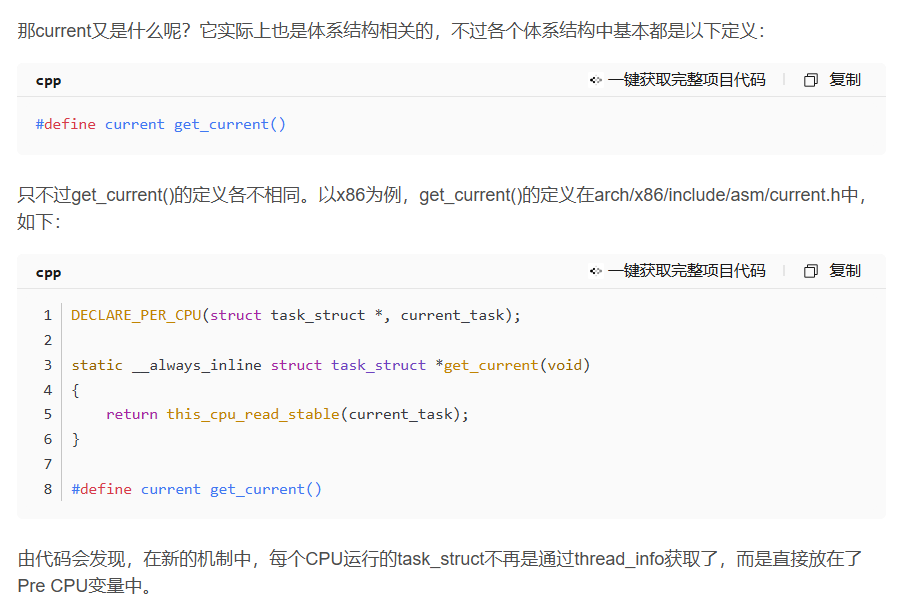
在新方案中用到了Per CPU 机制。本回对于该机制进行知识补强。
知识补强 —— Per CPU
Per CPU变量是Linux内核中的一种重要的同步机制。多核情况下,多个CPU是同时运行的,它们共同使用同一硬件资源的时候,需要解决多个CPU之间的同步问题。Per CPU变量就是为了解决这个问题应运而生的。顾名思义,Per CPU就是为每个CPU构造一个变量的副本,这样各个CPU就能够操作自己的副本而互不干涉。比如,当前进程的变量current_task就被声明为Per CPU变量。
要使用Per CPU变量,首先要声明这个变量,在arch/x86/include/asm/current.h中有:
#ifndef __ASSEMBLY__
struct task_struct;DECLARE_PER_CPU(struct task_struct *, current_task);static __always_inline struct task_struct *get_current(void)
{return this_cpu_read_stable(current_task);
}#define current get_current()#endif /* __ASSEMBLY__ */然后定义(初始化)这个变量。在arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c中有:
DEFINE_PER_CPU(struct task_struct *, current_task) = &init_task;
EXPORT_PER_CPU_SYMBOL(current_task);也就是说,系统刚刚初始化的时候,current_task都指向init_task。
后面当某个CPU上的进程进行切换的时候,current_task被修改为将要切换到的目标进程。例如,后文书要讲到的__switch_to任务切换函数就会改变current_task。以x86为例,参见arch/x86/kernel/process_32.c:

当要获取当前运行中的task_struct的时候,就需要调用this_cpu_read_stable()进行读取。而这正是current及get_current()所做的事情。

this_cpu_read_stable是一个宏,其定义在arch/x86/include/asm/percpu.h中,如下:
/** this_cpu_read() makes gcc load the percpu variable every time it is* accessed while this_cpu_read_stable() allows the value to be cached.* this_cpu_read_stable() is more efficient and can be used if its value* is guaranteed to be valid across cpus. The current users include* get_current() and get_thread_info() both of which are actually* per-thread variables implemented as per-cpu variables and thus* stable for the duration of the respective task.*/
#define this_cpu_read_stable_1(pcp) percpu_stable_op(1, "mov", pcp)
#define this_cpu_read_stable_2(pcp) percpu_stable_op(2, "mov", pcp)
#define this_cpu_read_stable_4(pcp) percpu_stable_op(4, "mov", pcp)
#define this_cpu_read_stable_8(pcp) percpu_stable_op(8, "mov", pcp)
#define this_cpu_read_stable(pcp) __pcpu_size_call_return(this_cpu_read_stable_, pcp)至此,通过task_struct寻找thread_info和通过thread_info查找task_struct的细节就讲完了。下一回讲解一个关键结构体 —— struct pt_regs。
欲知后事如何,且看下回分解。
