C++编程技巧和规范_9_引用计数解析
字符串的实现有两种方式,eager-copy(暴力拷贝)和copy-on-write(写时复制)。
1 shared_ptr实现及string存储简单说明
1.1 智能指针
下面例子是智能指针的使用。
shared_ptr<int> p1(new int(11));int count = p1.use_count();{shared_ptr<int> p2(p1);int count = p2.use_count(); // 2cout << count << endl;}count = p1.use_count(); // cout << count << endl; // 11.2 string类型字符串存储方式的简单说明
**string的实现方式:**eager-copy(贪婪粗暴的拷贝),copy-on-write(写时赋值),small string optimization (短字符串赋值)方式。
测试std::string的实现方式。通过下面例子可以看出,字符串str str2这是两个不同的地址,但是内容是一样的,C++标准库中的string字符串的实现,采用了eager-copy方式。
string str = "hello";string str2 = str;printf("str 的地址%p\n", str.c_str()); // 000000DF35B0FC20printf("str2的地址%p\n", str2.c_str()); // 000000DF35B0FC60从上面例子可以看出,拷贝后,这两个地址不同了,可以推断出,string的实现方式是eager-copy.
2 copy-on-write方式实现字符串类
下面开始实现一个copy-on-write方式的字符串。
2.1 实现一个基本的eager-copy的字符串
下面首先实现一个eager-copy的字符串,这种方式就是std::string的实现方式。
// 实现一个基本的字符串类class MyString{public:MyString(const char * str = nullptr) : m_data(new char[1]){cout << "MyString 函数" << endl;}~MyString(){delete[] m_data;}// 拷贝构造函数MyString(const MyString& other){m_data = new char[strlen(other.m_data) + 1];// strlen每次返回字符串数量,不包括最后的 '\0'// +1目的是,拷贝时,连字符串 \0 一起拷贝strcpy(m_data, other.m_data);cout << "MyString 拷贝构造函数" << endl;}MyString& operator=(const MyString& obj){if (this == &obj){return *this;}// 删除之前内存delete[] m_data;m_data = new char[strlen(obj.m_data) + 1];strcpy(m_data, obj.m_data);return *this;}private:char* m_data = nullptr;};void test(){MyString str = "hello";MyString str2 = str; // 拷贝构造函数MyString str3;str3 = str2; // MyString& operator=}2.2 实现一个初步的copy-on-write的string
**实现思想:**把要保存的字符串以及这个字符串引用计数统一保存在一个String中。
**实现原理:**在类中自定义一个结构体StringValue,在StringValue中包含了str指针和对应的引用计数,并作为String类的私有成员,在构造函数中给该结构体赋值。
下面的拷贝构造函数:相比于之前的eager-to 方式,这种方式效率更高,因为不同频繁的拷贝内存。
class MyString{public:MyString(const char* str = ""): m_pValue(new StringValue(str)){cout << "String 构造函数" << endl;}// 拷贝构造函数MyString(const MyString& other): m_pValue(other.m_pValue){++m_pValue->refcount;cout << "MyString 拷贝构造函数" << endl;}// 返回引用计数size_t getRefCount(){return m_pValue->refcount;}private:struct StringValue{size_t refcount; // 引用计数char* point; // 指向实际字符串StringValue(const char * intValue): refcount(1) // 默认为1{refcount = 1;point = new char[strlen(intValue) + 1];strcpy(point, intValue);}~StringValue(){delete[] point;}};private:StringValue* m_pValue;};void test(){MyString str = "hello";MyString str2 = str;int size = str2.getRefCount();cout << "size = " << size << endl;/*String 构造函数MyString 拷贝构造函数size = 2*/}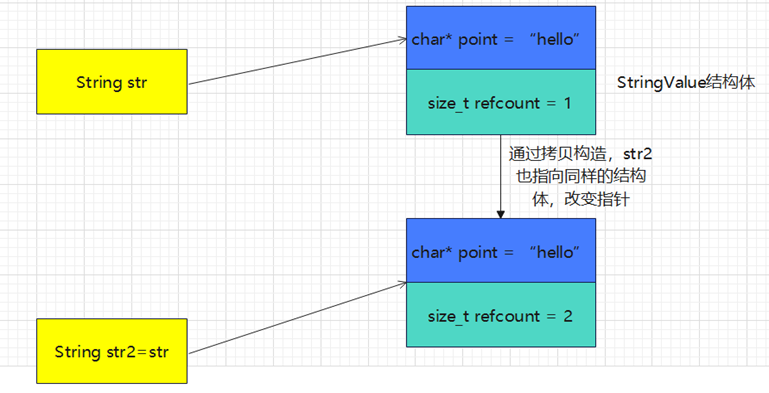
2.3 实现operator=和operator[]
在上面基础上,实现下面的operator=和operator[]。
class MyString{public:MyString(const char* str = ""): m_pValue(new StringValue(str)){cout << "String 构造函数" << endl;}// 拷贝构造函数MyString(const MyString& other): m_pValue(other.m_pValue){++m_pValue->refcount;cout << "MyString 拷贝构造函数" << endl;}// 拷贝赋值运算符MyString& operator=(const MyString& obj){if (this == &obj){return *this;}// 1 引用计数-1,如果为0就释放原来内存m_pValue->refcount--;if (m_pValue->refcount == 0){delete m_pValue;}// 2 指向当前对象m_pValue = obj.m_pValue;m_pValue->refcount++;return *this;}// const 的 operator[] 不能被修改char& operator[](int index) const{cout << "const operator[]" << endl;return m_pValue->point[index];}// 对于需要修改的[]重载,需要复制char& operator[](int index){cout << " operator[]" << endl;// 如果引用计数大于1,说明有其他对象指向,就复制一份if (m_pValue->refcount > 1) // 这里体现了“写时复制”{--m_pValue->refcount;m_pValue = new StringValue(m_pValue->point); // 复制一份}return m_pValue->point[index];}// 返回引用计数size_t getRefCount(){return m_pValue->refcount;}private:struct StringValue{size_t refcount; // 引用计数char* point; // 指向实际字符串StringValue(const char * intValue): refcount(1) // 默认为1{refcount = 1;point = new char[strlen(intValue) + 1];strcpy(point, intValue);}~StringValue(){delete[] point;}};private:StringValue* m_pValue;};void test(){MyString str = "hello";MyString str2 = str;int size = str2.getRefCount();cout << "size = " << size << endl;/*String 构造函数MyString 拷贝构造函数size = 2*/MyString str3 = "world";cout << str[0] << endl; // h }引入接口的设计方式:
1 外部加锁:
调用者负责加锁,由调用者决定跨线程使用共享对象时的加锁时机。
2 内部加锁:
对象将所有对自己的访问串行化,通过为每个成员函数加锁的方法来实现,这样就不用考虑线程安全的问题了。内部加锁并不常见,合适操作很独立,很完整的接口。
3 写时复制
有些情况下,不建议采用写时复制的技术,因为在多线程情况下,效率会明显下降,因为多线程版本往往意味着大量使用内部加锁。
2.4 完善copy-on-write技术
下面的代码会产生新的问题,
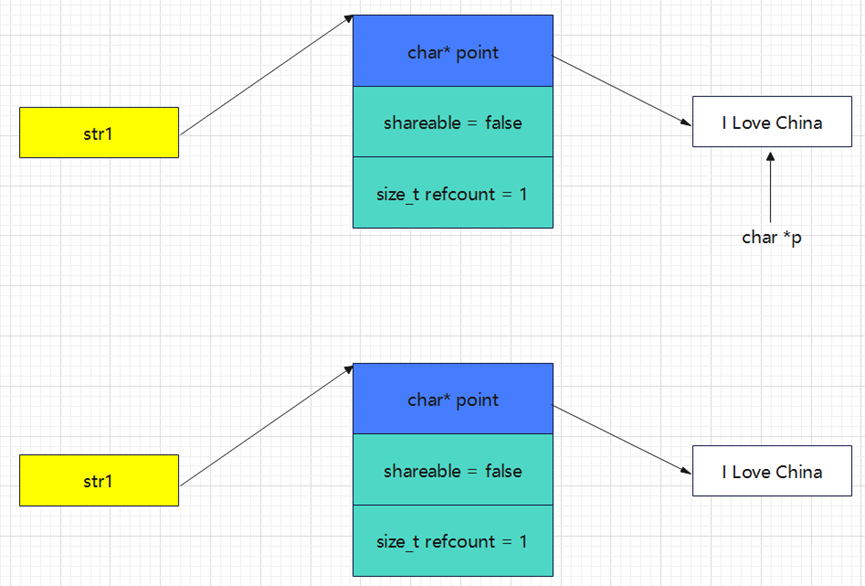
void test(){MyString str1 = "I Love China";char* p = &str1[0];MyString str2 = str1;*p = 'i';
}上边的str1和str2的内存结构如下:
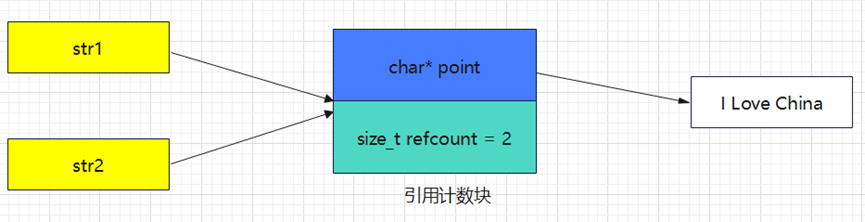
执行第二行指针p指向字符串的首字符时,内存结构如下:
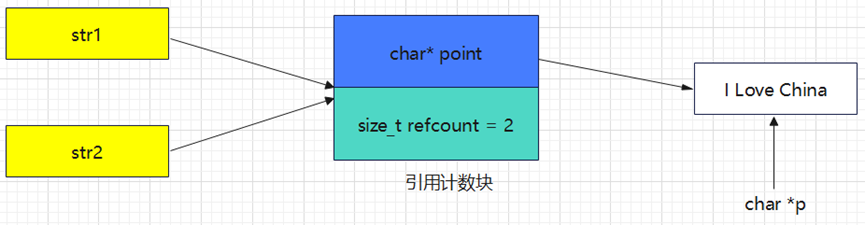
直接使用一个裸指针指向了内存中的字符串,当执行第四行代码修改字符串时,同时修改了str1和str2指向的字符串,如何避免这种现象发生呢?
解决方法1:如果该库是写给第三方用的,就要给出说明,不要尝试用裸指针修改引用计数块中的字符串指针。
解决方法2:在引用计数块中增加一个bool类型变量,对这种情况做一个特殊处理。下面的代码在引用计数块中增加一个bool类型的变量,用于判断是否可共享。
class MyString{public:MyString(const char* str = ""): m_pValue(new StringValue(str)){cout << "String 构造函数" << endl;}~MyString(){if (--m_pValue->refcount == 0){delete m_pValue;}}// 拷贝构造函数MyString(const MyString& other): m_pValue(other.m_pValue){// 旧版本//++m_pValue->refcount;//cout << "MyString 拷贝构造函数" << endl;// 改进版本if (other.m_pValue->shareable){m_pValue = other.m_pValue;++m_pValue->refcount;}else{m_pValue = new StringValue(other.m_pValue->point);}cout << "MyString 拷贝构造函数" << endl;}// 拷贝赋值运算符,根据 shareable 决定共享还是深拷贝MyString& operator=(const MyString& obj){if (this == &obj){return *this;}StringValue* newVal = nullptr;if (obj.m_pValue->shareable) // 可共享,说明只有一个指针指向{newVal = obj.m_pValue;++newVal->refcount;}else{newVal = new StringValue(obj.m_pValue->point); // 深拷贝}// 1 引用计数-1,如果为0就释放原来内存m_pValue->refcount--;if (m_pValue->refcount == 0){delete m_pValue;}// 2 指向当前对象m_pValue = newVal;return *this;}// const 的 operator[] 不能被修改char& operator[](int index) const{cout << "const operator[]" << endl;return m_pValue->point[index];}// 对于需要修改的[]重载,需要复制char& operator[](int index){cout << " operator[]" << endl;// 如果引用计数大于1,说明有其他对象指向,就复制一份if (m_pValue->refcount > 1) // 这里体现了“写时复制”{--m_pValue->refcount;m_pValue = new StringValue(m_pValue->point); // 复制一份}m_pValue->shareable = false; // 这里设置 不可共享return m_pValue->point[index];}// 返回引用计数size_t getRefCount(){return m_pValue->refcount;}private:struct StringValue{size_t refcount; // 引用计数char* point; // 指向实际字符串bool shareable; // 是否可以共享StringValue(const char* intValue): refcount(1) // 默认为1, shareable(true){point = new char[strlen(intValue) + 1];strcpy(point, intValue);}~StringValue(){delete[] point;}};private:StringValue* m_pValue;};