[cpprestsdk] JSON类--数据处理 (`json::value`, `json::object`, `json::array`)
第五章:JSON (json::value, json::object, json::array)
在第四章:PPLX任务(异步编程模型)中,我们掌握了异步收发HTTP消息的技术,让应用能在网络操作时保持响应
现在我们知道如何与Web服务器通信而不阻塞程序,这很棒
但当
http_client获取到http_response后,如何处理其中的数据?
通常服务器回复中最有用的部分是消息体,其中包含结构化数据。以天气应用为例,服务器可能返回{"city": "London", "temperature": "15C", "conditions": "Cloudy"}这样的字符串。
- 如何在C++代码中轻松提取"London"、“15C"和"Cloudy”?
手动解析这类字符串既繁琐又易错。这正是JSON(JavaScript对象表示法)的用武之地。cpprestsdk提供了一套强大的类来简化JSON数据处理:json::value、json::object和json::array。
核心JSON类
json::value:通用容器
可存储任意JSON数据类型:
- 数值(整数/浮点)
- 布尔值(true/false)
- 字符串
- 空值(null)
- 对象(键值对集合)
- 数组(有序值列表)
json::object:字典结构
类似std::map<utility::string_t, json::value>,用于表示如天气数据中的层级结构:
"temperature":
{"value": 15,"unit": "C"
}
json::array:列表结构
类似std::vector<json::value>,适合存储如天气状况同级列表:
"conditions": ["Cloudy", "Windy"]
实战指南
1. JSON解析
utility::string_t json_str = U(R"({"city":"London","temp":15})");
web::json::value weather = web::json::value::parse(json_str);
std::wcout << L"城市: " << weather.at(U("city")).as_string();
2. 数据访问
// 访问嵌套对象
double temp = weather.at(U("temperature")).at(U("value")).as_double();// 遍历数组
auto conditions = weather.at(U("conditions")).as_array();
for (auto& cond : conditions) {std::wcout << cond.as_string() << L",";
}
3. 动态构建JSON
web::json::value forecast;
forecast[U("city")] = web::json::value::string(U("Paris"));
forecast[U("days")] = web::json::value::array();
forecast[U("days")][0] = web::json::value::string(U("Sunny"));
4. 序列化输出
utility::string_t output = forecast.serialize();
// 输出: {"city":"Paris","days":["Sunny"]}
完整HTTP交互示例
pplx::task<web::json::value> fetch_data() {return client.request(web::http::methods::GET, U("/api/weather")).then([](web::http::http_response resp) {return resp.extract_json(); // 自动转换响应体为JSON});
}// 发送JSON数据
web::json::value payload;
payload[U("sensor")] = web::json::value::string(U("temp-01"));
client.request(web::http::methods::POST, U("/api/data")).set_body(payload); // 自动设置Content-Type为application/json
实现原理
核心设计
- 类型擦除模式:
json::value通过std::unique_ptr持有details::_Value基类指针 - 多态派生类:
_Number、_String等子类实现具体类型存储 - 延迟构造:
operator[]在null值时自动初始化对象/数组
序列化流程
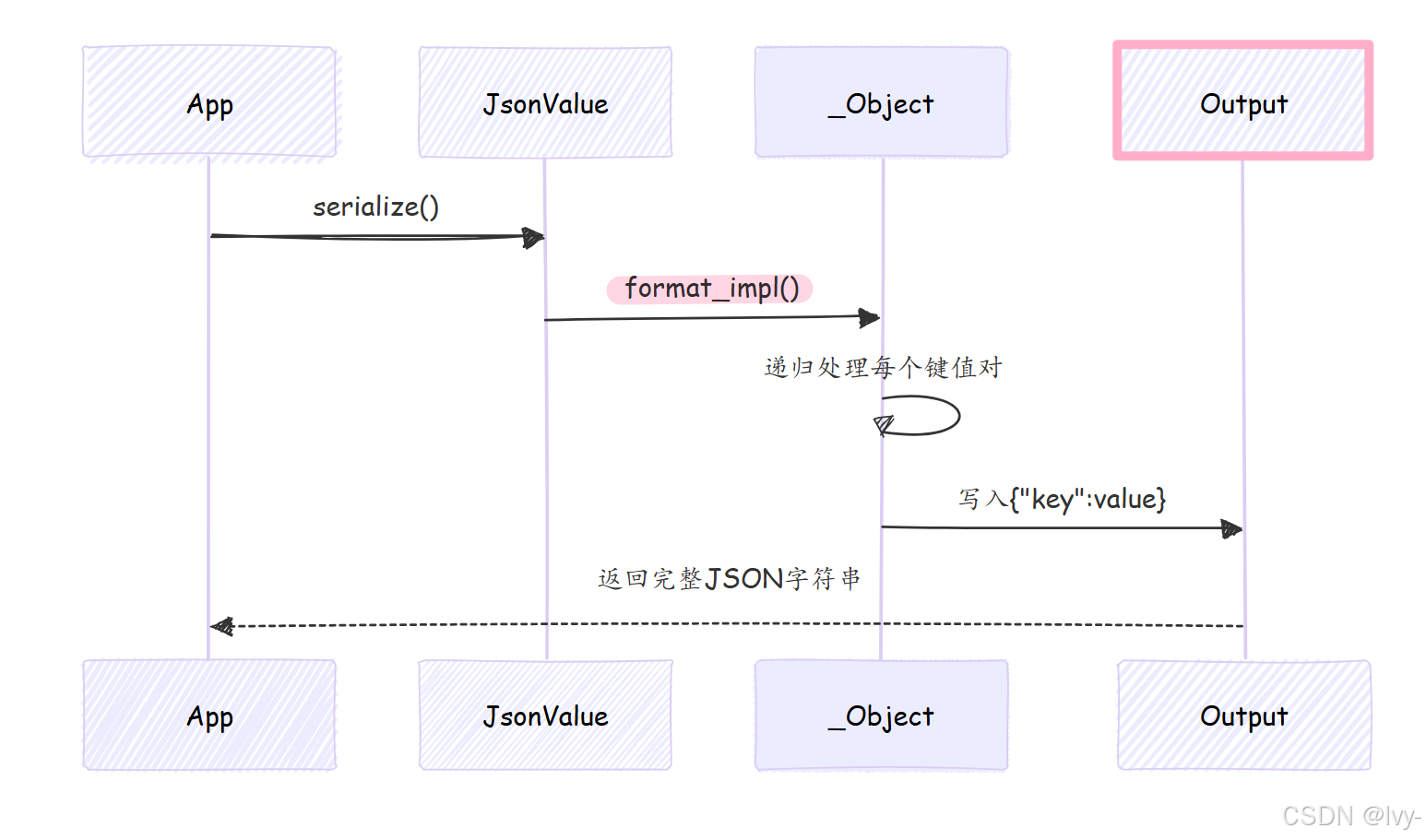
总结对比
| 功能 | json::value | json::object | json::array |
|---|---|---|---|
| 创建方式 | parse()/number()/string()等工厂方法 | 通过value::object()或operator[] | 通过value::array() |
| 类型安全 | 提供is_xxx()类型检查和as_xxx()转换 | 继承value的类型安全机制 | 同左 |
| 遍历访问 | 需先转换为具体类型 | for(auto& kv : obj)键值遍历 | for(auto& elem : arr)索引访问 |
掌握这些JSON处理技术后,我们已能:
- 高效解析网络API返回的复杂数据结构
- 动态构建符合业务需求的JSON消息
- 实现完整的HTTP请求-响应闭环处理
接下来,在第六章:异步流处理中,我们将探索大容量数据流的高效处理方法
