tslib库介绍与使用
一、tslib 框架分析
1. tslib介绍
tslib 是一个触摸屏的开源库,可以使用它来访问触摸屏设备。编译 tslib 后,可以得到 libts 库,还可以得到各种工具:较准工具、测试工具。
tslib主要代码架构如下

“plugins”目录里的“插件”,或称为“module”。这个目录下的每个文件都是一个 module,每个 module 都提供 2 个函数:read、read_mt,前者用于读取单点触摸屏的数据,后者用于读取多点触摸屏的数据。
2. tslib框架
要分析 tslib 的框架,先看看示例程序怎么使用,我们参考 ts_test.c 和ts_test_mt.c,前者用于一般触摸屏(比如电阻屏、单点电容屏),后者用于多点触摸屏。
tslib的架构如下:
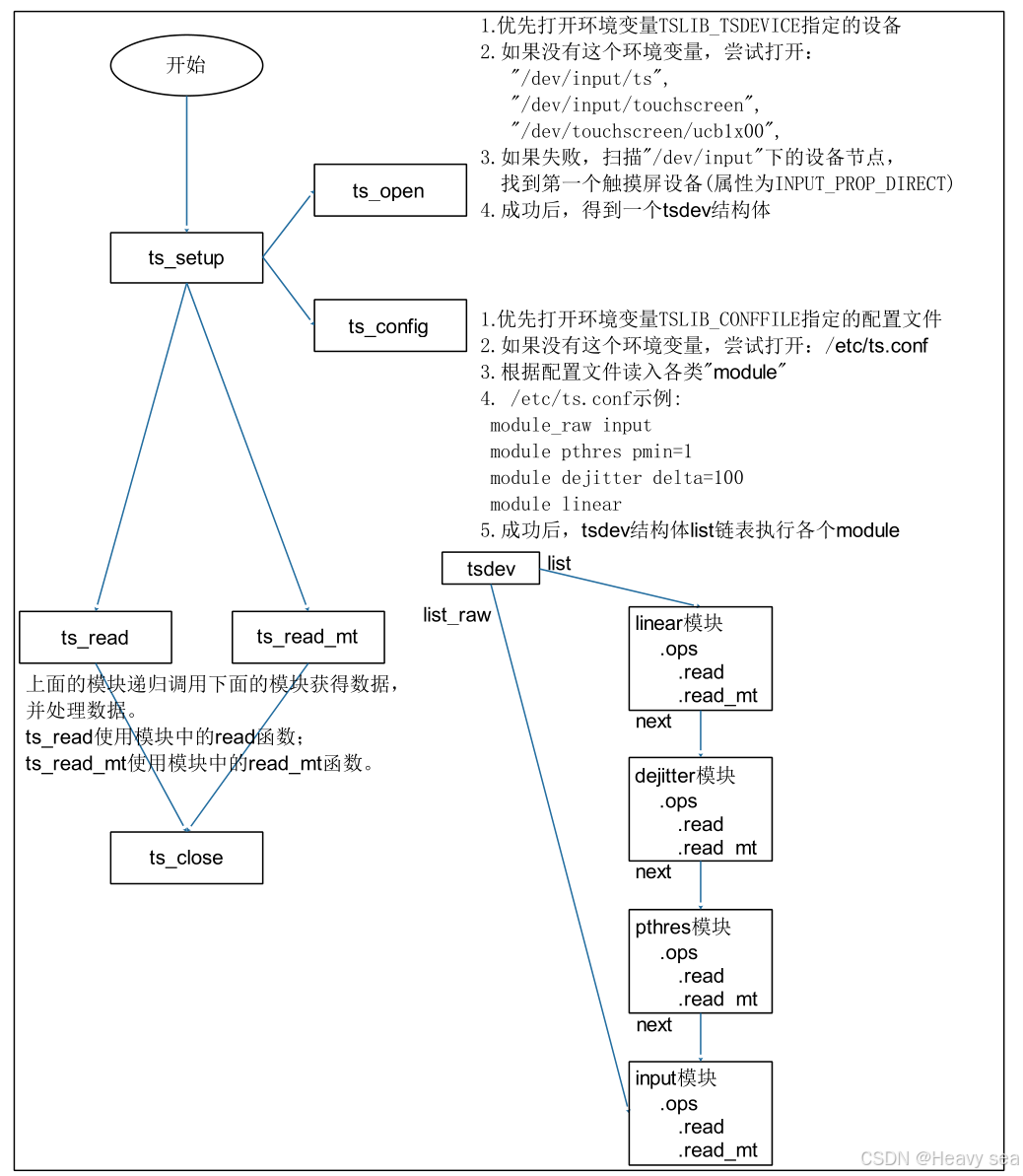
进入测试程序ts_test.c,使用ts_setup进行初始化。
ts_setup调用了ts_open,调用 ts_open 后,可以打开某个设备节点,构造出一个 tsdev 结构体。然后调用 ts_config 读取配置文件(/etc/ts.conf)的处理,假设/etc/ts.conf 内容如下:
module_raw input
module pthres pmin=1
module dejitter delta=100
module linear
每行表示一个“module”(普通模块)或“moduel_raw”(原始模块)。
对于所有的“module”,会调用ts_load_module,最终调用__ts_attach将新module插入 tsdev.list 链表头。
int __ts_attach(struct tsdev *ts, struct tslib_module_info *info)
{info->dev = ts;info->next = ts->list;ts->list = info;return 0;
}
info代表新module,假设设备ts已有一个模块链:A -> B(模块 A 是链表头,ts->list 指向模块 A;模块 A 的 next 指向模块 B,模块 B 的 next 为 NULL)。
__ts_attach函数执行三步操作,最终将新模块 info 插入到链表头部:
- info->dev = ts:新模块关联到设备 ts;
- info->next = ts->list:新模块的 next 指向原有链表头(模块 A);
- ts->list = info:设备的链表头更新为新模块 info。
- 新的模块链变为:新模块 info -> 模块 A -> 模块 B。
同理对于所有的“module_raw”,都会插入 tsdev.list_raw 链表头,一般只有一个“module_raw”。但注意这里tsdev.list 中最后一个“module”会指向 ts_dev.list_raw 的头部。
int __ts_attach_raw(struct tsdev *ts, struct tslib_module_info *info)
{struct tslib_module_info *next, *prev, *prev_list = ts->list_raw;// 头插法info->dev = ts;info->next = prev_list;ts->list_raw = info;/** ensure the last item in the normal list now points to the* top of the raw list.*/// 普通模块链为空,或已指向原原始链头部if (ts->list == NULL || ts->list == prev_list) {/* main list is empty, ensure it points here */ts->list = info; // 让普通链头部直接指向新原始模块(连接两个链)return 0;}// 普通模块链有其他模块,需找到其末尾并连接for (next = ts->list, prev = next;next != NULL && next != prev_list;next = prev->next, prev = next);prev->next = info; // 让普通链的末尾节点指向新原始模块(连接两个链)return 0;
}
无论是调用 ts_read 还是 ts_read_mt,都是通过 tsdev.list 中的模块来处理数据的。这里写模块是递归调用的,比如linear模块的read函数。
static int linear_read(struct tslib_module_info *info, struct ts_sample *samp,int nr_samples)
{struct tslib_linear *lin = (struct tslib_linear *)info;int ret;int xtemp, ytemp;// 使用链表的下一个模块来读取ret = info->next->ops->read(info->next, samp, nr_samples);if (ret >= 0) {int nr;for (nr = 0; nr < ret; nr++, samp++) {#ifdef DEBUGfprintf(stderr,
linear模块的readmt函数
static int linear_read_mt(struct tslib_module_info *info,struct ts_sample_mt **samp,int max_slots, int nr_samples)
{struct tslib_linear *lin = (struct tslib_linear *)info;int ret;int xtemp, ytemp;int i;int nr;if (!info->next->ops->read_mt)return -ENOSYS;ret = info->next->ops->read_mt(info->next, samp, max_slots, nr_samples);if (ret < 0)return ret;for (nr = 0; nr < ret; nr++) {#ifdef DEBUG
因为是递归调用,所有最先使用 input 模块读取设备节点得到原始数据,再依次经过 pthres 模块、dejitter 模块、linear 模块处理后,才返回最终数据。
二、交叉编译tslib
设置环境变量
// 对于 IMX6ULL ,命令如下
export ARCH=arm
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-
export PATH=$PATH:/home/vsea/100ask_imx6ull_mini-sdk/ToolChain/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf_sdk-buildroot/bin
交叉编译 tslib
//交叉编译 tslib:
cd tslib-1.21
./configure --host=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/
make
make install DESTDIR=$PWD/tmp
注意这里不能写–prefix=$(pwd)/tmp,ts_config函数会通过宏定义TS_CONF找到配置文件的路径。
如果设置了–prefix=$(pwd)/tmp会导致宏定义TS_CONF对应路径为
/home/vsea/linux_study/tslib-1.21/tmp/etc/ts.conf,如果移植到开发板上去就要创建同样过长的路径。
使用–prefix=/和DESTDIR=$PWD/tmp 导致宏定义TS_CONF对应路径为/etc/ts.conf
在tslib-1.21目录下使用grep命令可以查询对应路径
grep “TS_CONF” * -nwr
TS_CONF = ${sysconfdir}/ts.conf
grep “sysconfdir” * -nwr
sysconfdir = ${prefix}/etc
grep “prefix” * -nwr
prefix = /
这样我们在移植ts.conf文件时只需把文件拷贝到开发板的/etc目录下。
把头文件、库文件放到工具链目录下:
// 对于 IMX6ULL ,命令如下
cd tslib-1.21/tmp/
cp include/* /home/vsea/100ask_imx6ull_mini-sdk/ToolChain/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf_sdk-buildroot/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf/sysroot/usr/include
cp -d lib/*so* /home/vsea/100ask_imx6ull_mini-sdk/ToolChain/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf_sdk-buildroot/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf/sysroot/usr/lib/
测试tslib
先在开发板上使用 NFS 挂载 Ubuntu的目录,再把前面编译出来的 tslib-1.21/tmp/部分文件复制到板子上
cp /mnt/tslib-1.21/tmp/lib/ts -rfd /lib // 复制库文件
cp /mnt/tslib-1.21/tmp/lib/*so* -d /lib
cp /mnt/tslib-1.21/tmp/bin/* /bin // 复制测试文件
cp /mnt/tslib-1.21/tmp/etc/ts.conf -d /etc // 复制/etc/ts.conf
cp -rfd是处理 “包含符号链接的目录” 时的高效命令:
-r保证目录递归复制;-f确保强制操作,适合自动化;-d保留符号链接,不解析实际内容,维持原始目录结构。
对于 IMX6ULL,首先需要关闭默认的 qt gui 程序,才可以执行 ts_test_mt
mv /etc/init.d/*hmi* /root
mv /etc/init.d/*lvgl* /root
reboot
执行测试文件
export TSLIB_PLUGINDIR=/lib/ts
ts_test_mt
三、基于tslib编写程序
需求:当两个手指点击屏幕时,不断打印 2 个触点的距离。
用两个手指点击屏幕时,会得到以下数据
开发板上电容屏对应的设备节点是/dev/input/event1
hexdump /dev/input/event1

当ABS_MT_SLOT 0和ABS_MT_SLOT 1表示要上报一个触点信息
ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID -1 表示对应的触点被松开了
驱动程序使用 slot、tracking_id 来标识一个触点;当 tracking_id 等于-1 时,标识这个触点被松开了。
触摸屏可能支持多个触点,比如 5 个:tslib 为了简化处理,即使只有 2 个触点,ts_read_mt 函数也会返回 5 个触点数据,可以根据标志位判断数据是否有效。
int ts_read_mt(struct tsdev *ts, struct ts_sample_mt **samp, int max_slots,int nr)
假设nr设置为1,max_slots设置为5,那么读到的数据保存在:samp[0][0]、
samp[0][1]、samp[0][2]、samp[0][3]、samp[0][4]中。
假设nr设置为2,max_slots设置为5,那么读到的数据保存在:samp[0][0]、
samp[0][1] 、 samp[0][2] 、 samp[0][3] 、 samp[0][4] 和 samp[1][0] 、
samp[1][1]、samp[1][2]、samp[1][3]、samp[1][4]中。
ts_sample_mt结构体
struct ts_sample_mt {/* ABS_MT_* event codes. linux/include/uapi/linux/input-event-codes.h* has the definitions.*/int x;int y;unsigned int pressure;int slot;int tracking_id;int tool_type;int tool_x;int tool_y;unsigned int touch_major;unsigned int width_major;unsigned int touch_minor;unsigned int width_minor;int orientation;int distance;int blob_id;struct timeval tv;/* BTN_TOUCH state */short pen_down;/* valid is set != 0 if this sample* contains new data; see below for the* bits that get set.* valid is set to 0 otherwise*/short valid;
};
当valid非0时,表示含有新数据。
参照测试程序ts_test_mt.c编写程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include "tslib.h"
// #include "fbutils.h"
// #include "testutils.h"int distance(struct ts_sample_mt *point1, struct ts_sample_mt *point2)
{int x = point1->x - point2->x;int y = point1->y - point2->y;return x * x + y * y;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{struct tsdev *ts;int ret;int i;int max_slots = 1;struct ts_sample_mt **samp_mt = NULL;struct ts_sample_mt **pre_samp_mt = NULL;struct input_absinfo slot;int point_pressed[20] = {0};// 初始化触摸屏设备ts = ts_setup(NULL, 0);if (!ts){printf("ts_setup failed\n");return -1;}// 计算触摸屏支持最大触摸点数if (ioctl(ts_fd(ts), EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &slot) < 0){perror("ioctl EVIOGABS");ts_close(ts);return errno;}max_slots = slot.maximum + 1 - slot.minimum;samp_mt = malloc(sizeof(struct ts_sample_mt *));if (!samp_mt){ts_close(ts);return -1;}// 分配的内存 会被自动初始化为0samp_mt[0] = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_sample_mt));if (!samp_mt[0]){free(samp_mt);ts_close(ts);return -1;}pre_samp_mt = malloc(sizeof(struct ts_sample_mt *));if (!pre_samp_mt){ts_close(ts);return -1;}pre_samp_mt[0] = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_sample_mt));if (!pre_samp_mt[0]){free(pre_samp_mt);ts_close(ts);return -1;}for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++){pre_samp_mt[0][i].valid = 0;}while (1){// 读取当前帧的多点触摸数据ret = ts_read_mt(ts, samp_mt, max_slots, 1);for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++){if (samp_mt[0][i].valid){memcpy(&pre_samp_mt[0][i], &samp_mt[0][i], sizeof(struct ts_sample_mt));}}int cnt = 0;for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++){// tracking_id != -1 表示触摸未结束if (pre_samp_mt[0][i].valid && pre_samp_mt[0][i].tracking_id != -1){// 记录有效触摸点的索引point_pressed[cnt++] = i;}}// 若检测到两个触摸点,计算并打印距离if (cnt == 2){printf("distance = %08d\n", distance(&pre_samp_mt[0][point_pressed[0]], &pre_samp_mt[0][point_pressed[1]]));}}return 0;
}编译程序
arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc 10_mt_cal_distance.c -o mt_cal_distance -lts
