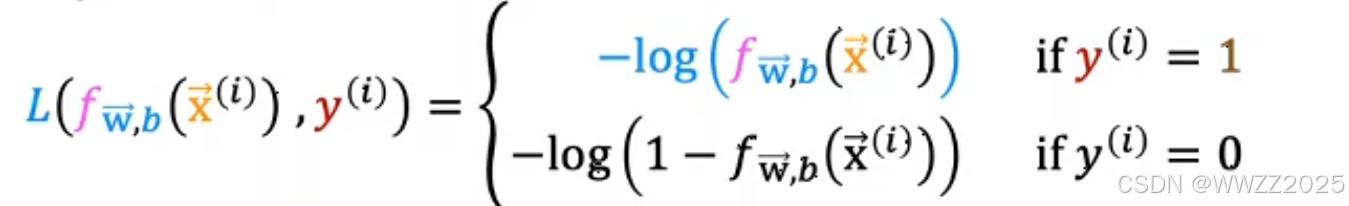快速上手大模型:机器学习5(逻辑回归及其代价函数)
目录
1 逻辑回归
1.1 肿瘤分类示例
1.2 逻辑函数(Logistic function)
1.3 逻辑回归模型
1.4 代码表达
2 决策边界(Decision boundary)
2.1 定义
2.2 推导
3 逻辑回归的代价函数
3.1 数据集
3.2 代价函数构建
3.3 简化代价函数
4 梯度下降
1 逻辑回归
1.1 肿瘤分类示例
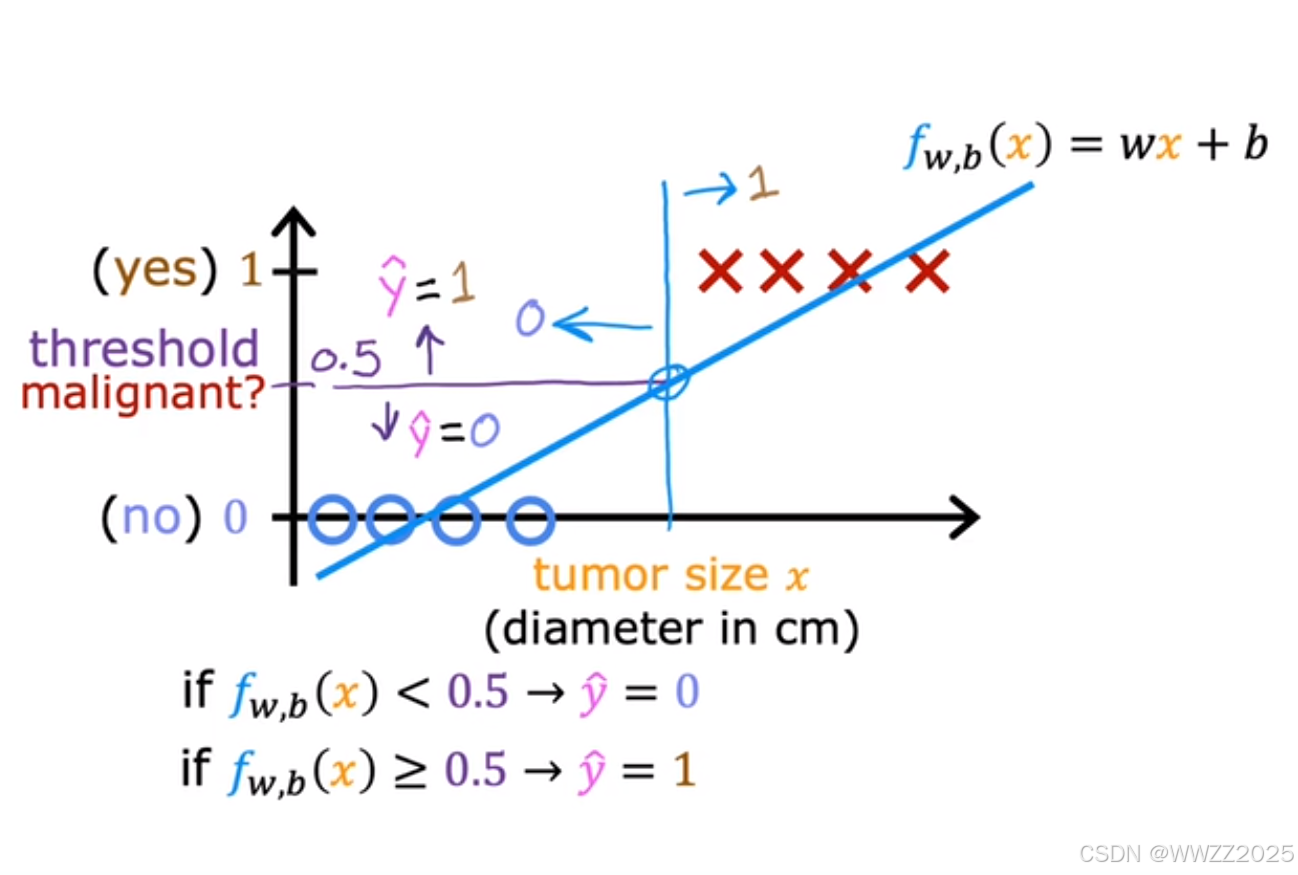
线性回归不适用这种分类,会改变肿瘤判断的标准,详情如下:
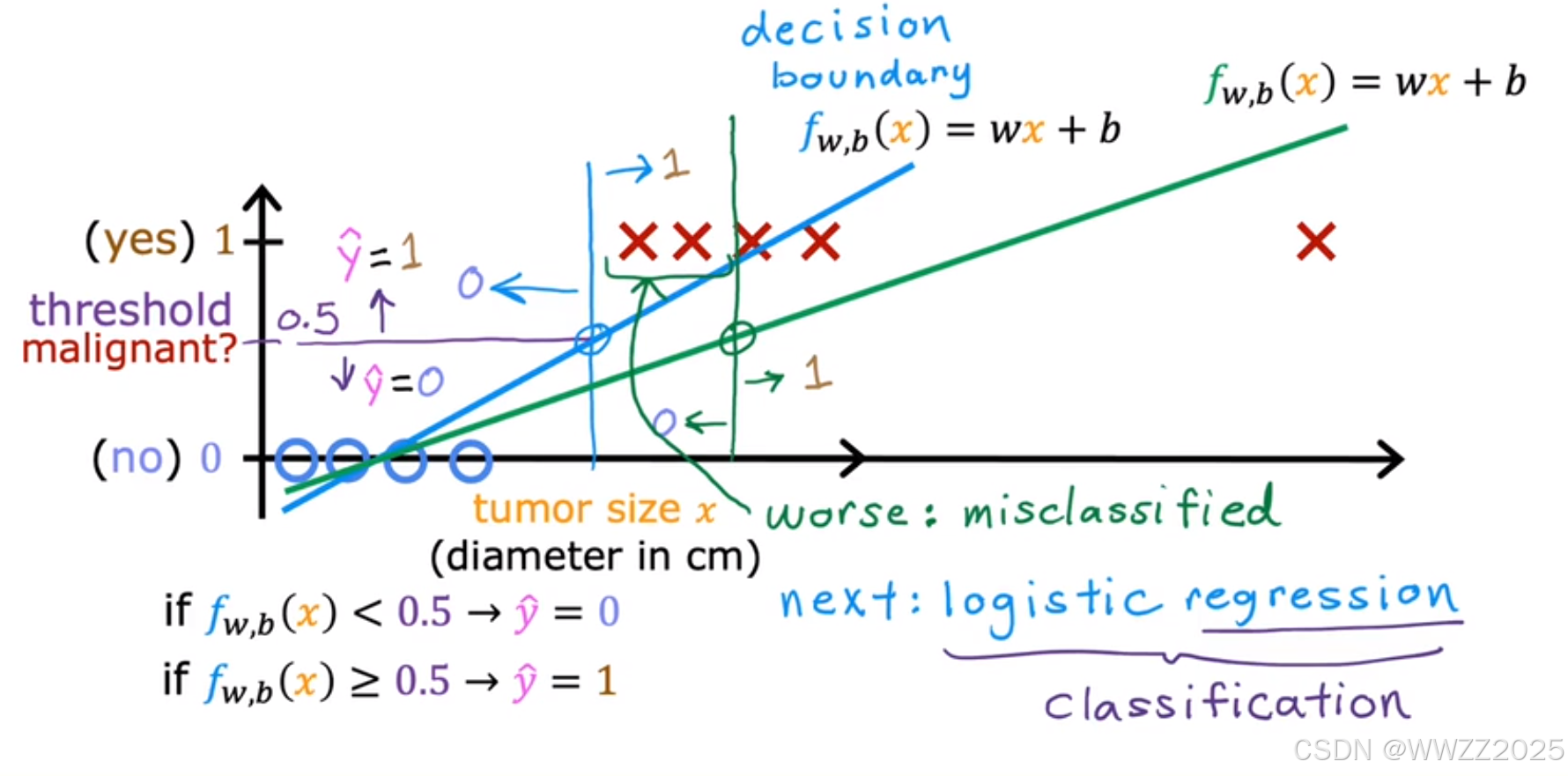
图中o为良性、x为恶性,是否为肿瘤阀值假设为0.5,则蓝色竖线(决策边界Decision boundary)左侧被判断为良性、右侧被判断为恶性;
当新增一个恶性肿瘤样本,线性回归最佳拟合曲线变成绿色的,阀值继续使用0.5时,样本中是恶性肿瘤的被判断为良性,原判断结论改变,预测有误。
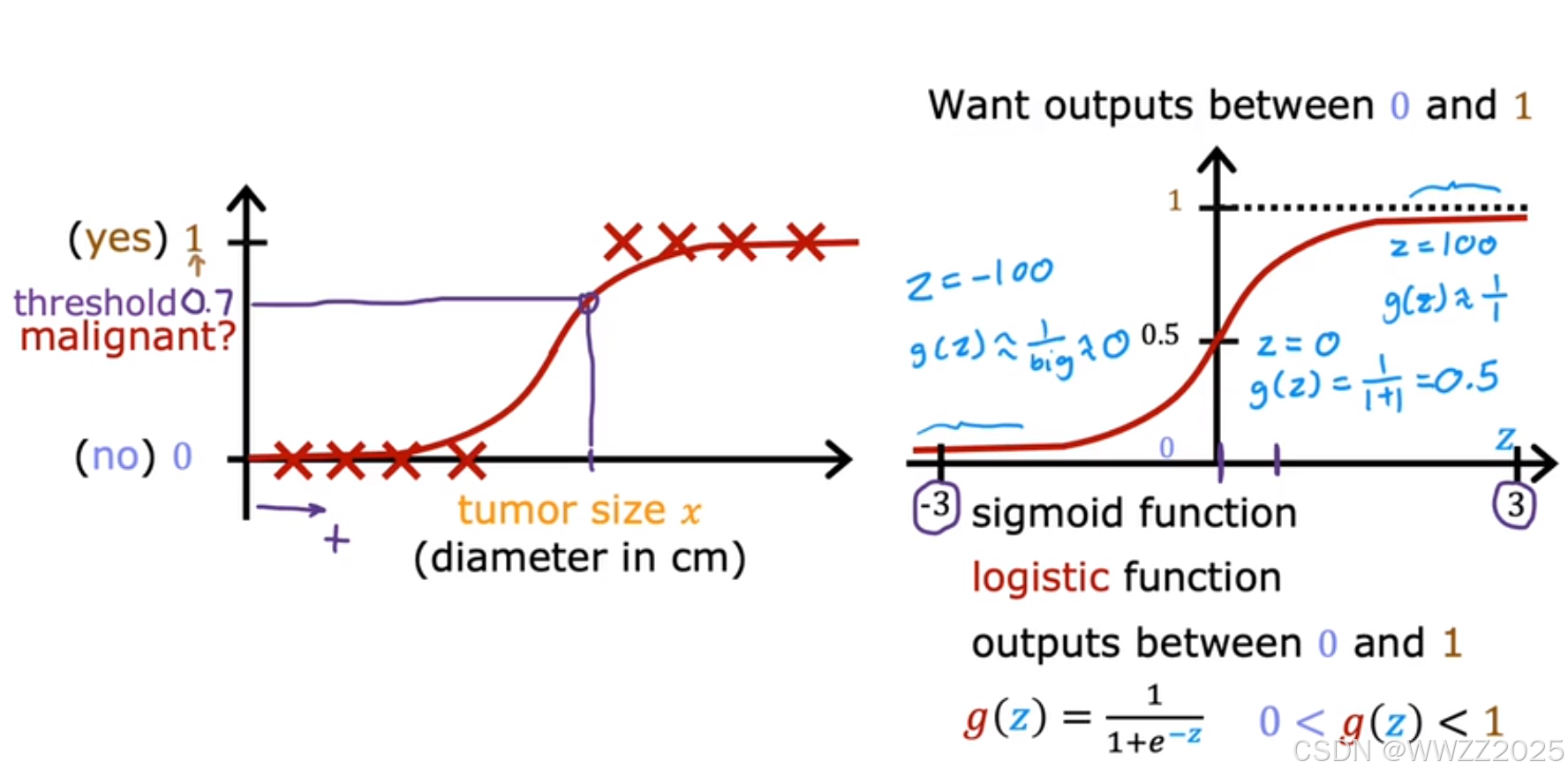
1.2 逻辑函数(Logistic function)
逻辑函数也称(sigmoid function),定义式为
,图像如下右图。
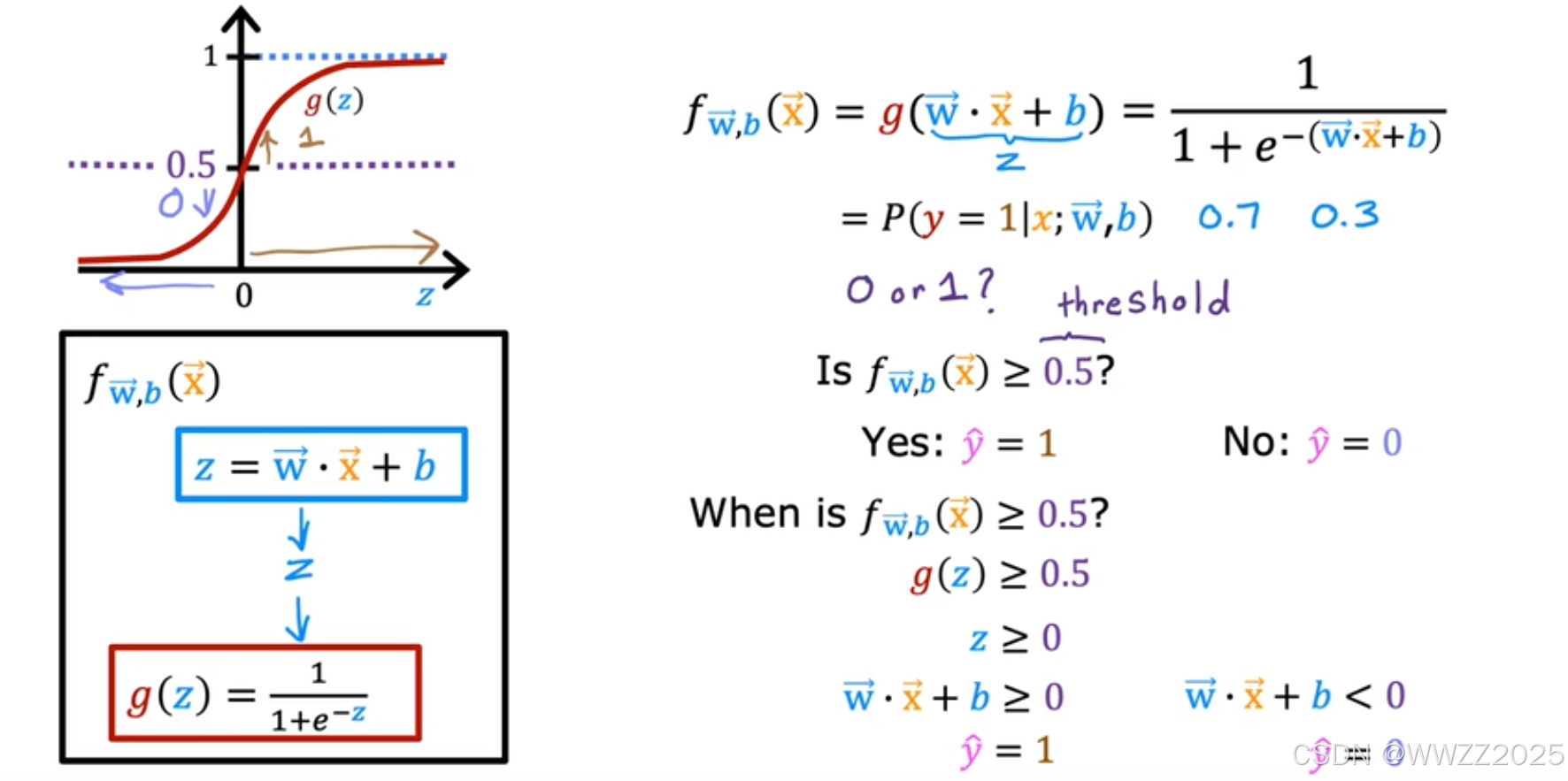
1.3 逻辑回归模型
模型:
逻辑函数:
逻辑回归模型:
肿瘤分类例子:
x:肿瘤大小
y:肿瘤良性/恶性的概率
如果
,则表示70%的概率肿瘤为恶性。
1.4 代码表达
import numpy as np %matplotlib widget import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from plt_one_addpt_onclick import plt_one_addpt_onclick from lab_utils_common import draw_vthresh plt.style.use('./deeplearning.mplstyle')# Input is an array. input_array = np.array([1,2,3]) exp_array = np.exp(input_array)print("Input to exp:", input_array) print("Output of exp:", exp_array)# Input is a single number input_val = 1 exp_val = np.exp(input_val)print("Input to exp:", input_val) print("Output of exp:", exp_val)def sigmoid(z):"""Compute the sigmoid of zArgs:z (ndarray): A scalar, numpy array of any size.Returns:g (ndarray): sigmoid(z), with the same shape as z"""g = 1/(1+np.exp(-z))return g# Generate an array of evenly spaced values between -10 and 10 z_tmp = np.arange(-10,11)# Use the function implemented above to get the sigmoid values y = sigmoid(z_tmp)# Code for pretty printing the two arrays next to each other np.set_printoptions(precision=3) print("Input (z), Output (sigmoid(z))") print(np.c_[z_tmp, y])输出:
Input (z), Output (sigmoid(z)) [[-1.000e+01 4.540e-05][-9.000e+00 1.234e-04][-8.000e+00 3.354e-04][-7.000e+00 9.111e-04][-6.000e+00 2.473e-03][-5.000e+00 6.693e-03][-4.000e+00 1.799e-02][-3.000e+00 4.743e-02][-2.000e+00 1.192e-01][-1.000e+00 2.689e-01][ 0.000e+00 5.000e-01][ 1.000e+00 7.311e-01][ 2.000e+00 8.808e-01][ 3.000e+00 9.526e-01][ 4.000e+00 9.820e-01][ 5.000e+00 9.933e-01][ 6.000e+00 9.975e-01][ 7.000e+00 9.991e-01][ 8.000e+00 9.997e-01][ 9.000e+00 9.999e-01][ 1.000e+01 1.000e+00]]
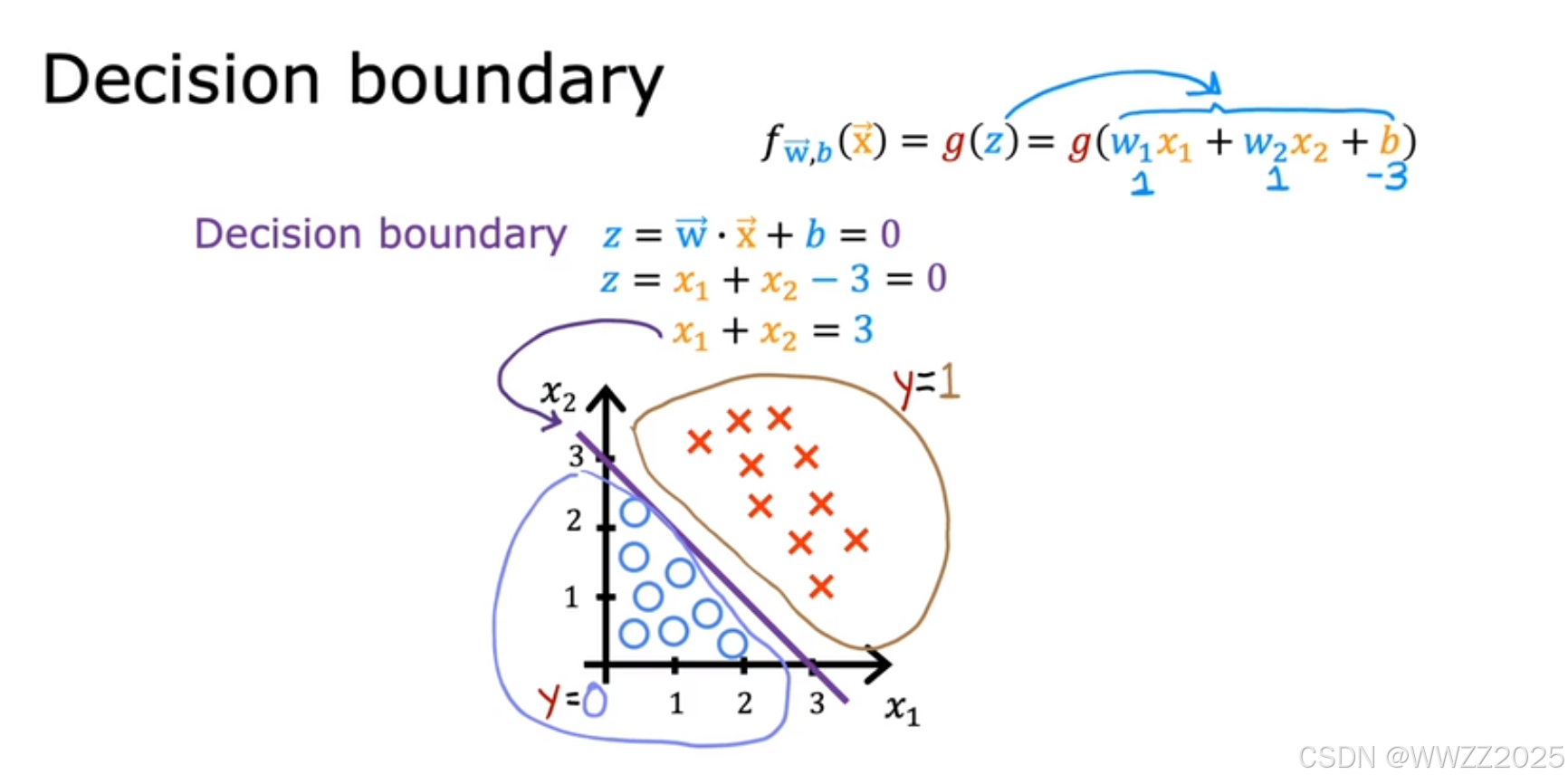
2 决策边界(Decision boundary)
2.1 定义
用于决策判断的分割线。
2.2 推导
当逻辑回归模型为
,
如果
,则
、
、
,输出
,此时预测为恶性。
另w1=w2=1,b=-3
则决策边界为
,即
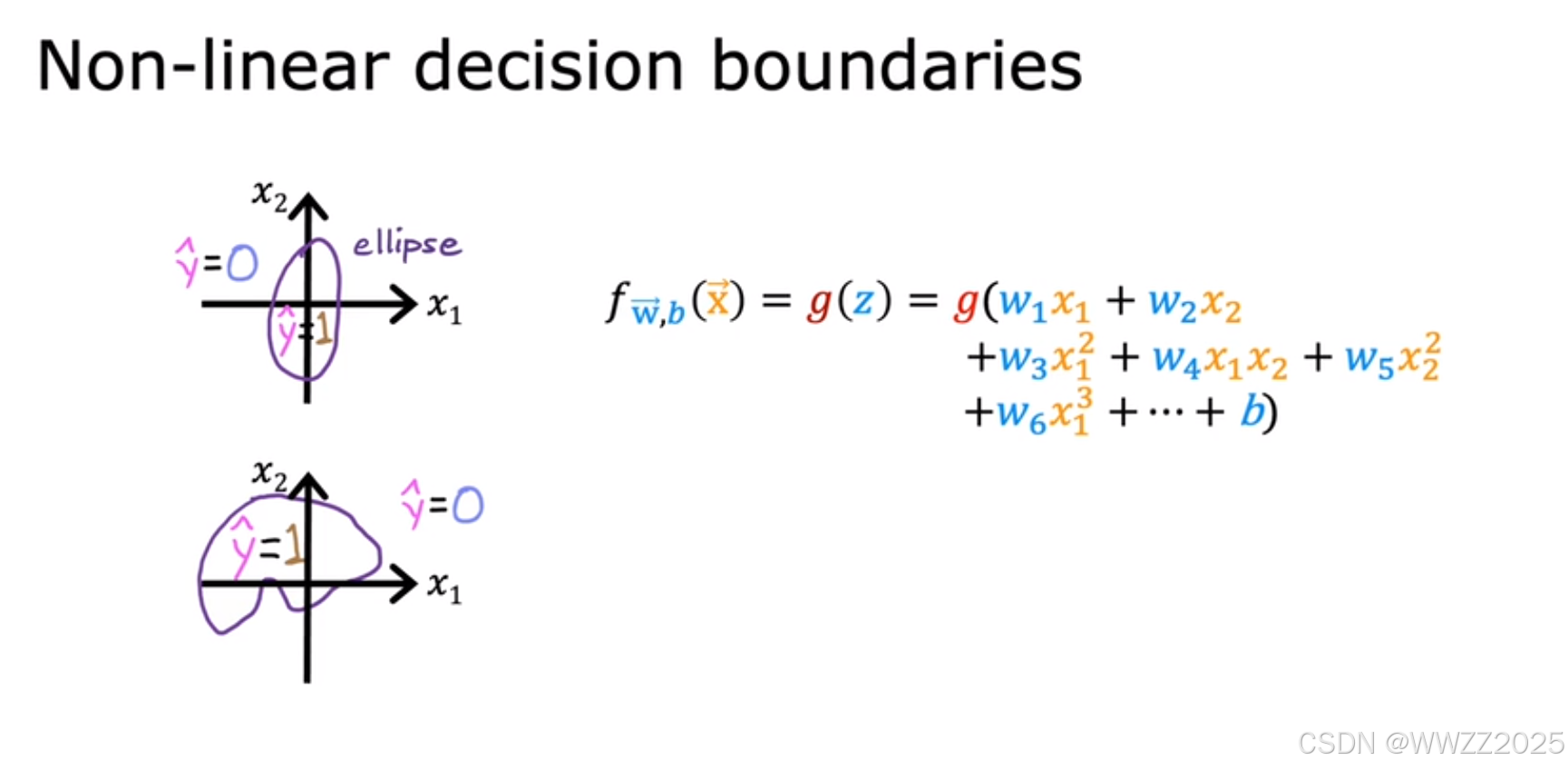
非线性决策边界同理。
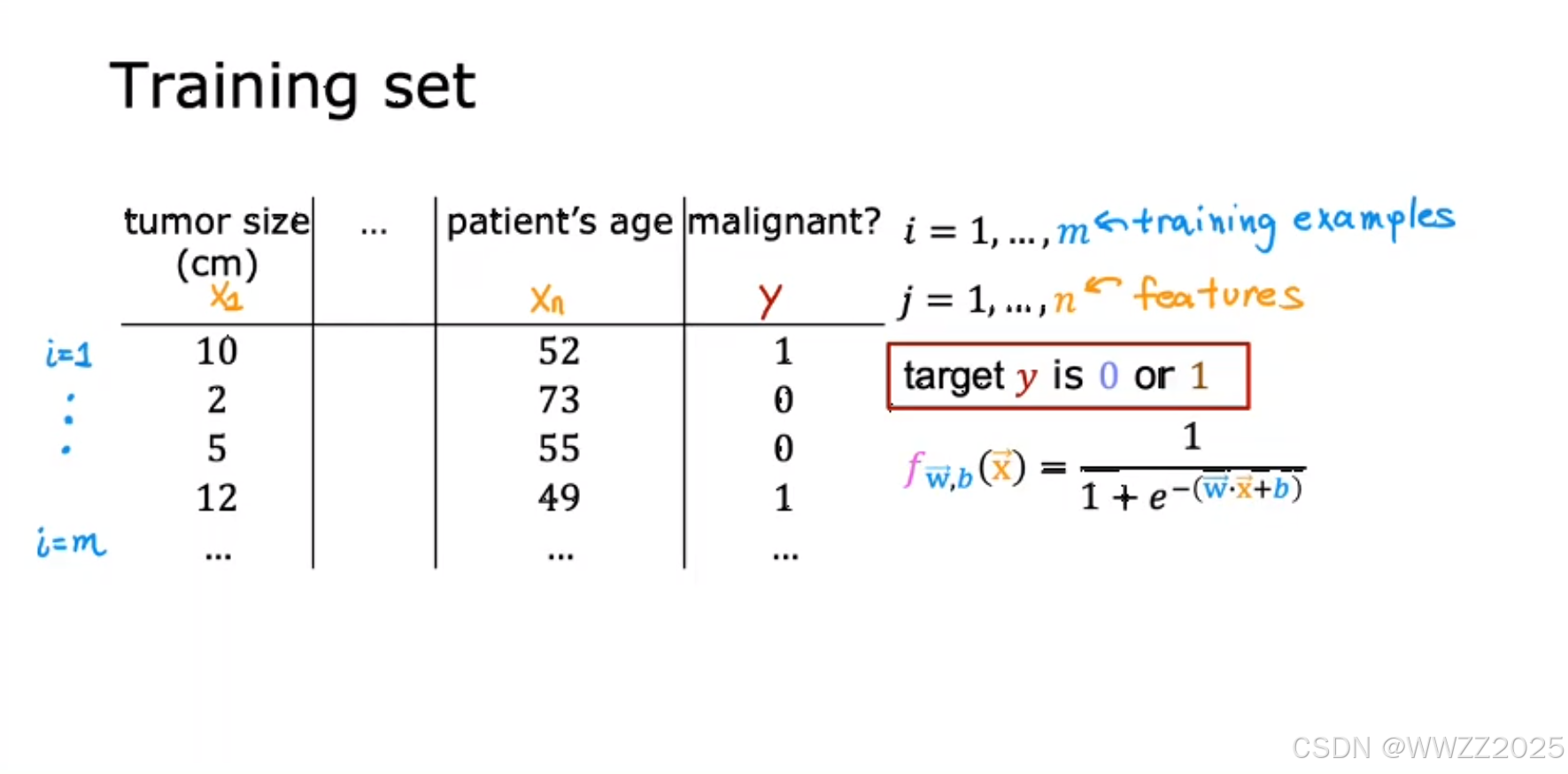
3 逻辑回归的代价函数
3.1 数据集
m为训练样本数量,m为特征,y为目标标签,逻辑回归模型为
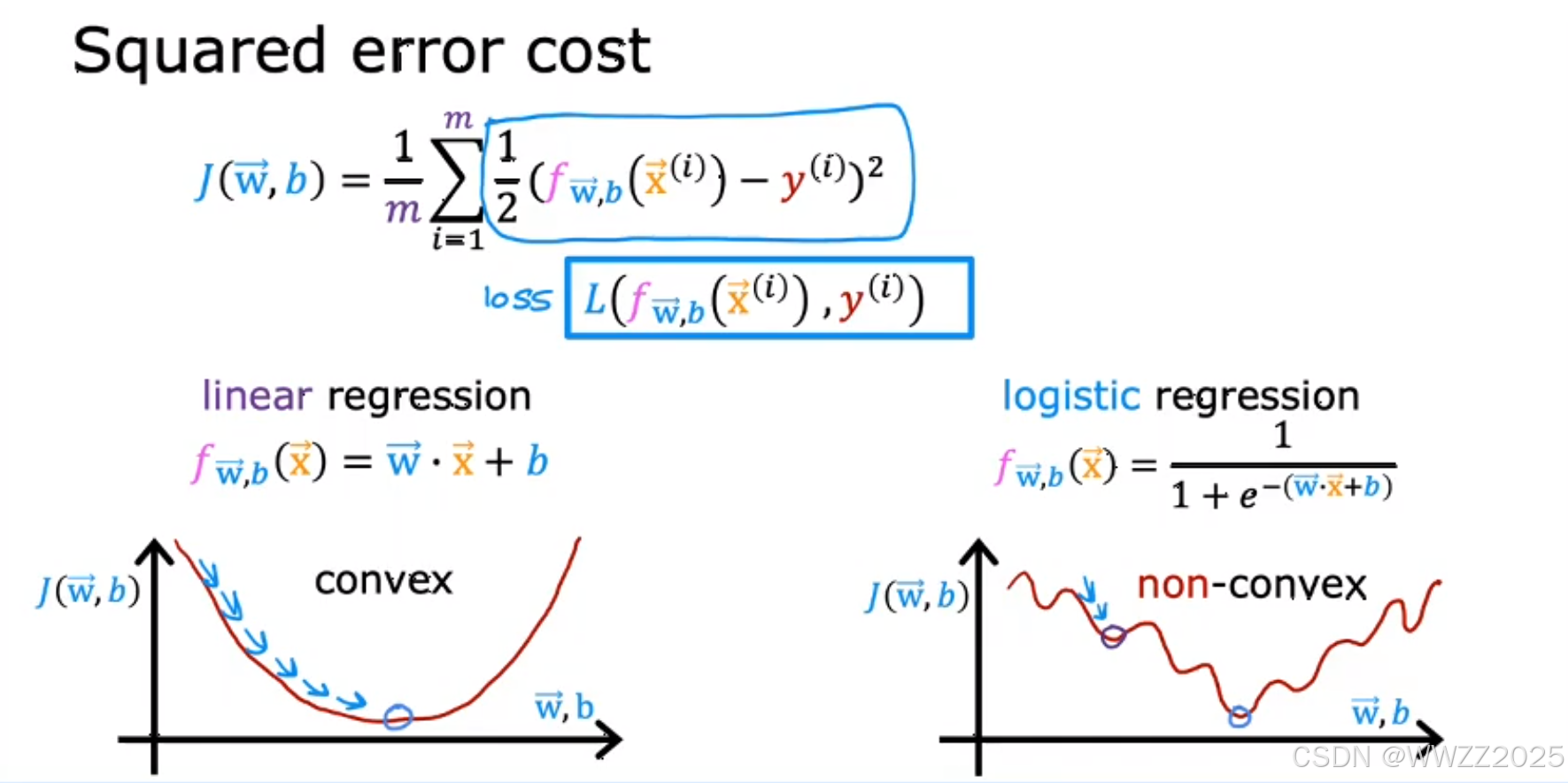
3.2 代价函数构建
逻辑回归的代价函数不用平方差误差函数,会出现如上右图所示非凸代价函数(non-convex),即多个局部最小值情况。
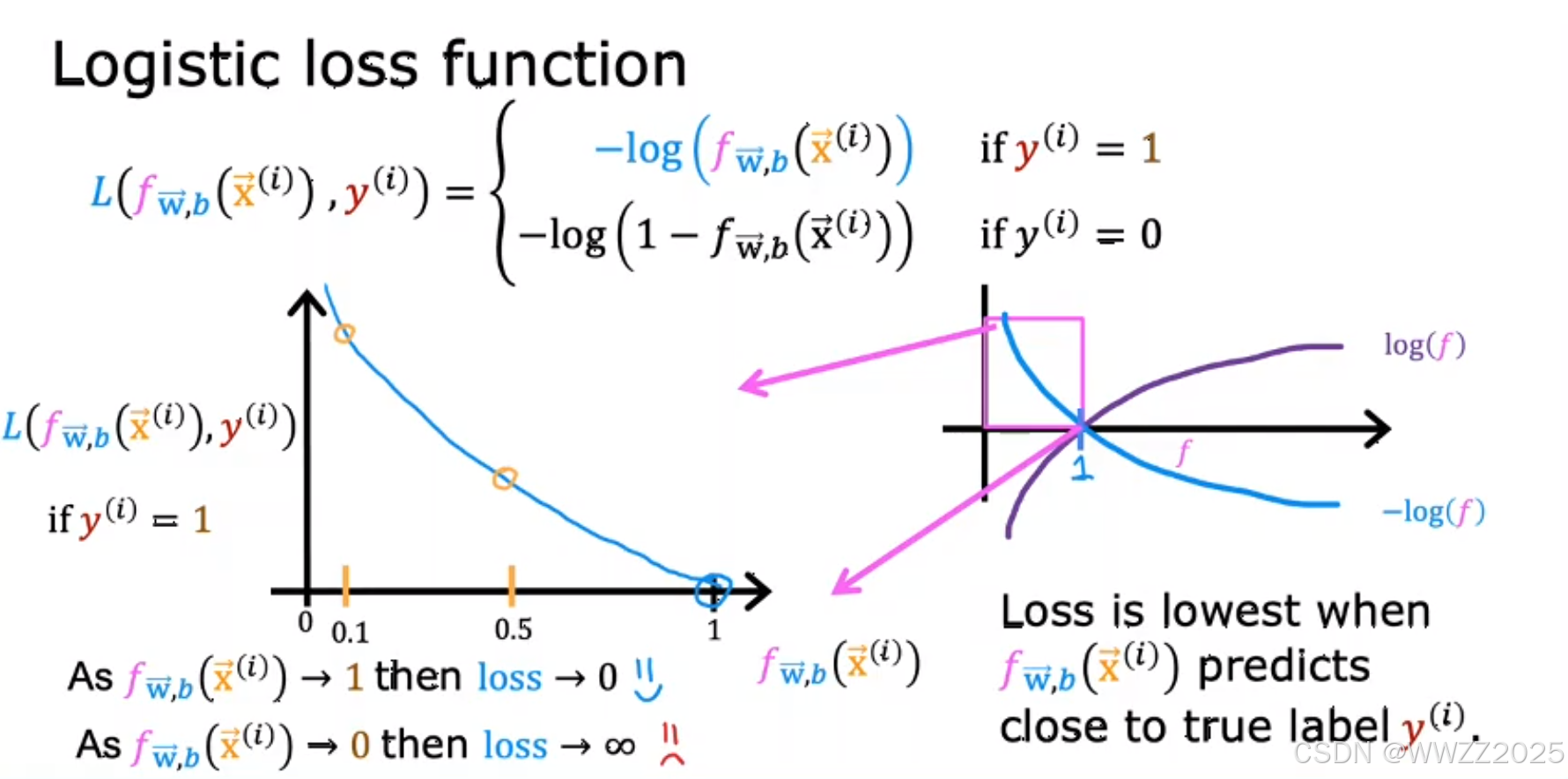
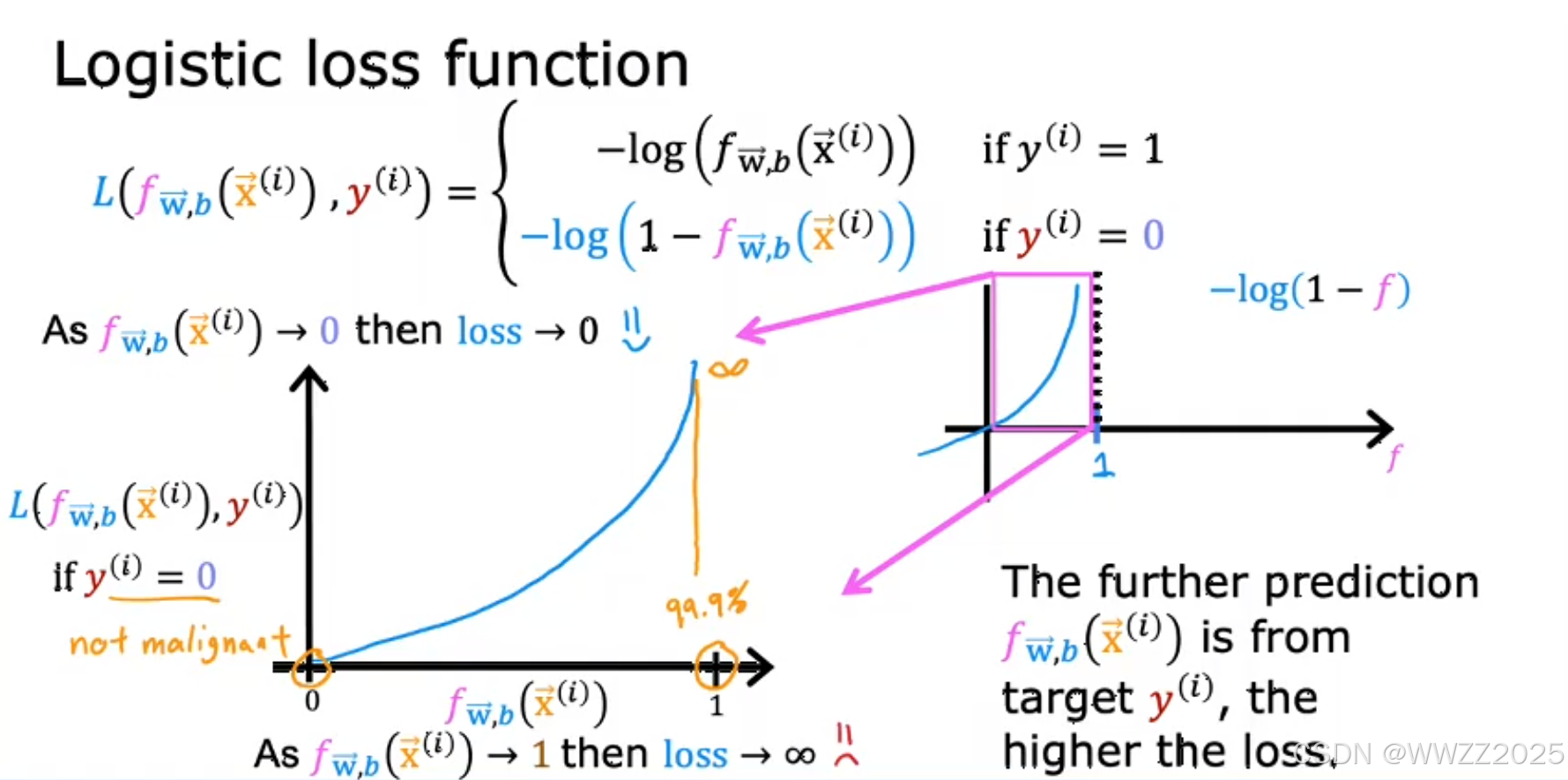
因此,另损失
,函数式如下:
当真实值为1,预测值越接近1,损失L就越小;
当真实值为0,预测值越接近0,损失L就越小。
3.3 简化代价函数
损失:
代价函数:
4 梯度下降
代价函数:
梯度下降: