数据结构(顺序表和链表)
数据结构(题)
一、顺序表
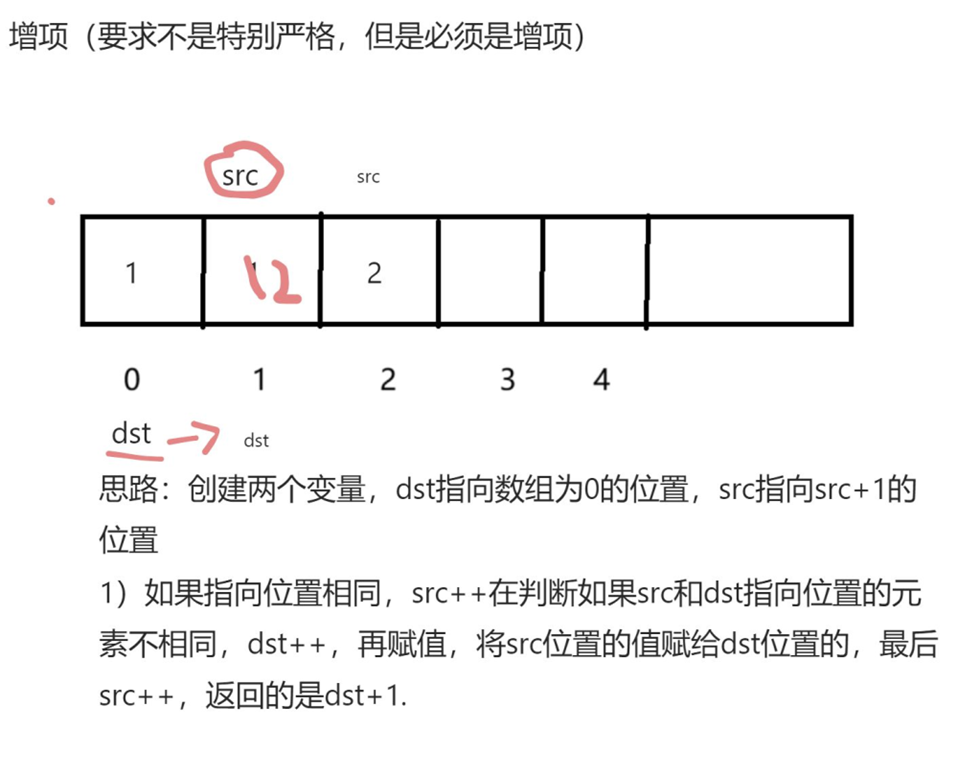
1、移除元素
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {int dst = 0;int src = 0;while(src<numsSize){if(nums[src]!=val){nums[dst]=nums[src];dst++;}src++;}return dst;
}2、删除有序数组中的重复项


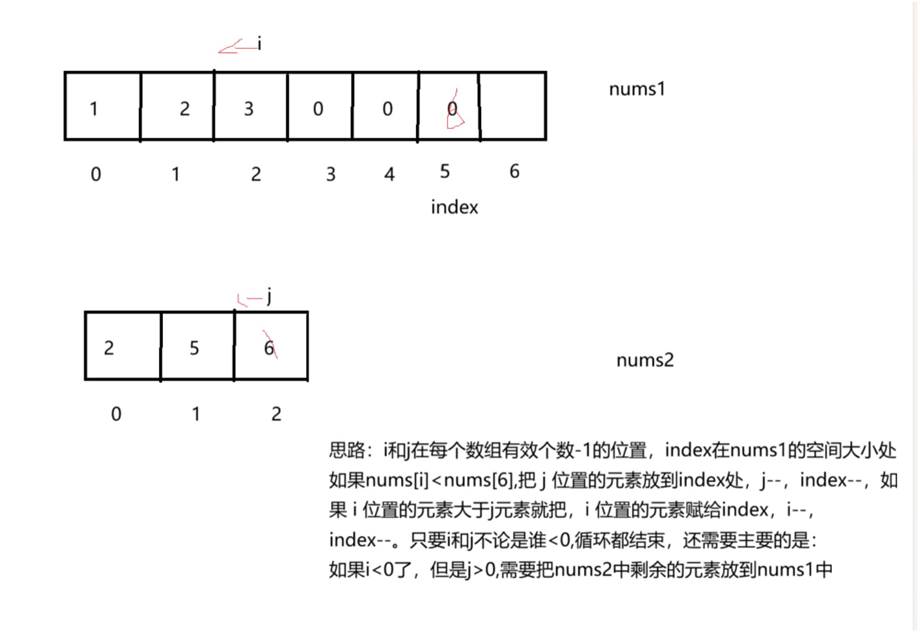
3、合并两个有序数组

void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {int i=m-1;int j=n-1;int index=m+n-1;while(i>=0&&j>=0){if(nums2[j]>nums1[i]){nums1[index]=nums2[j];j--;index--;}else{nums1[index]=nums1[i];i--;index--;}}while(j>=0){nums1[index--]=nums2[j--];}
}
二、链表
1、移除链表元素
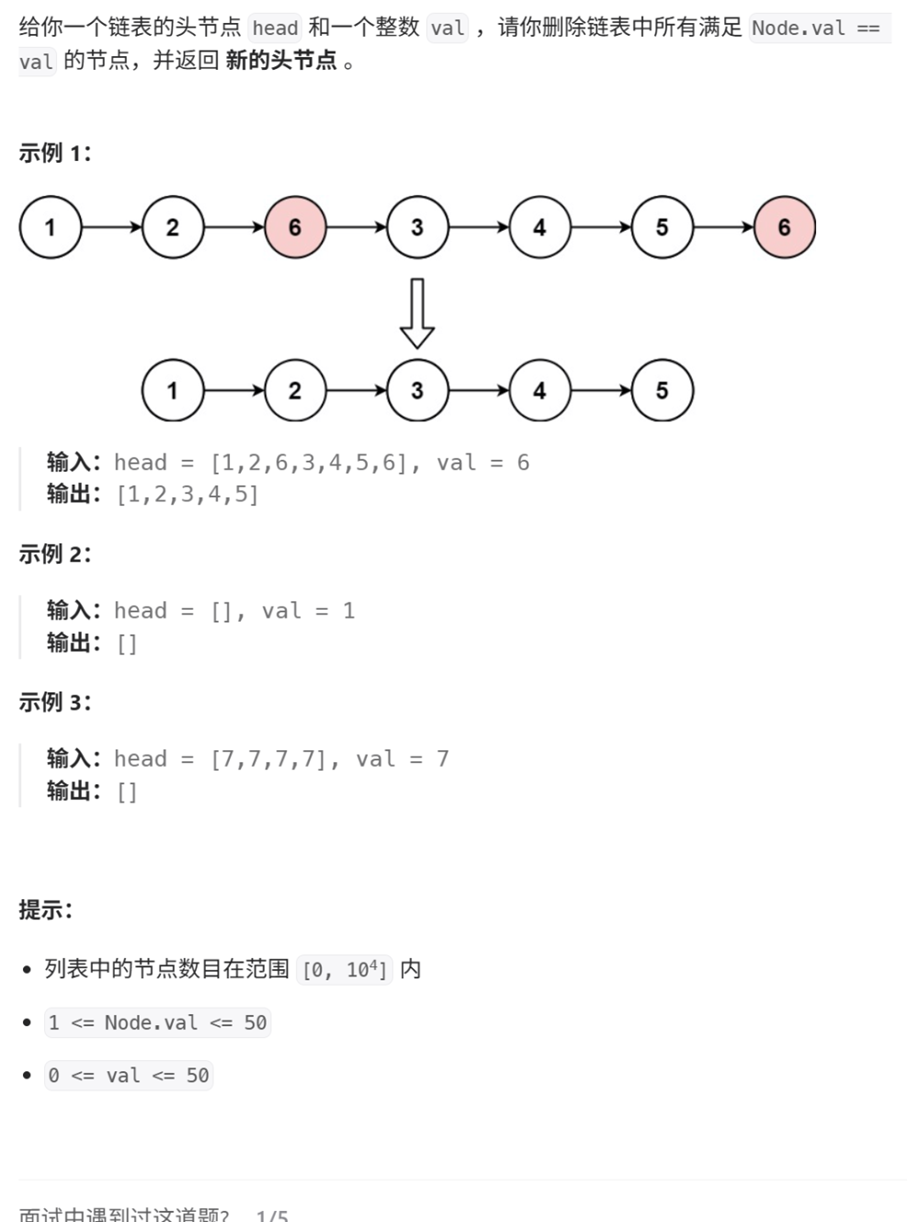
思路1:遍历、查找、删除
思路2:再创建一个新的链表,把节点不为val的节点放入新链表
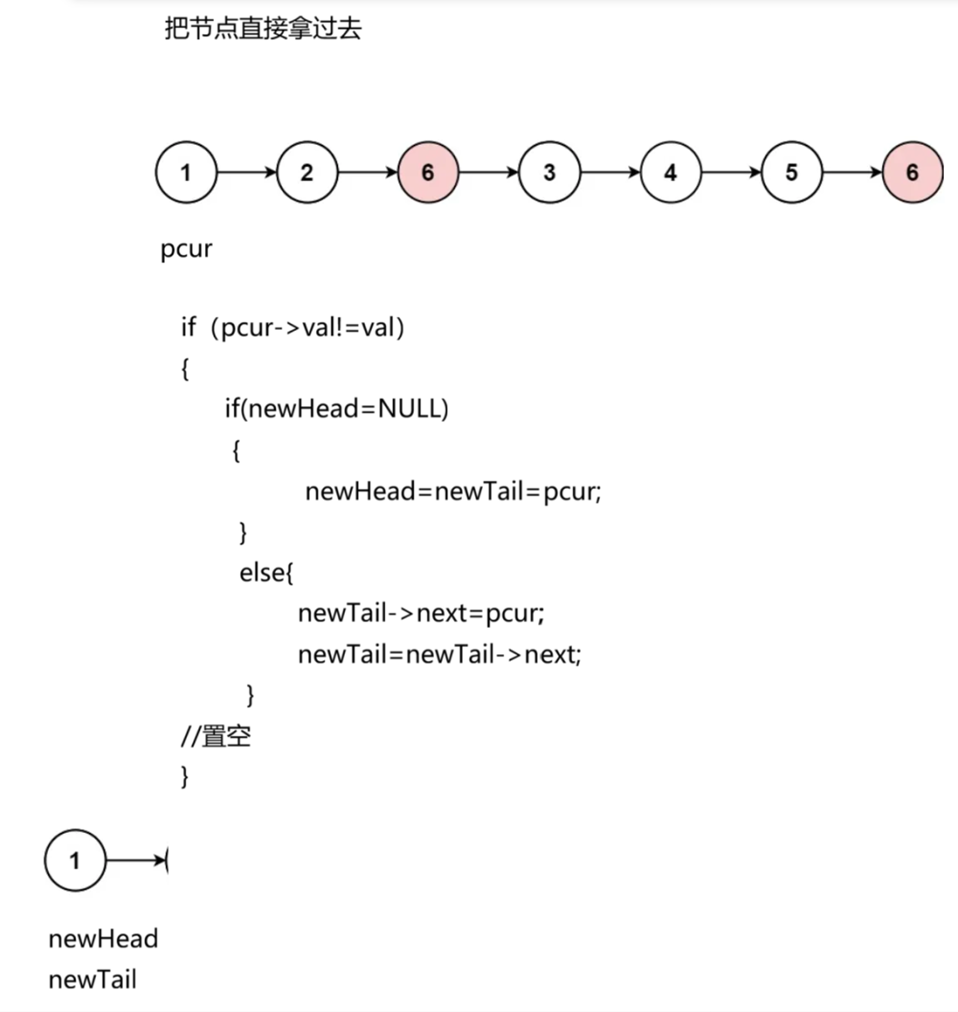
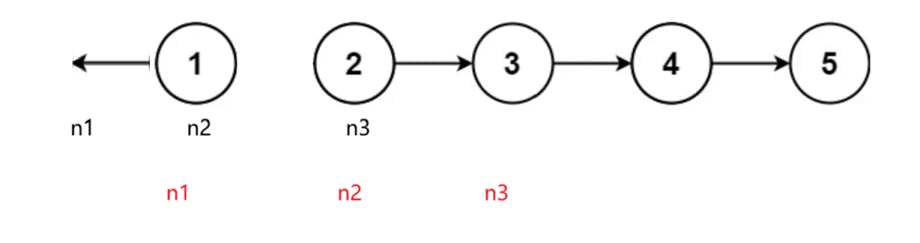
2、反转链表
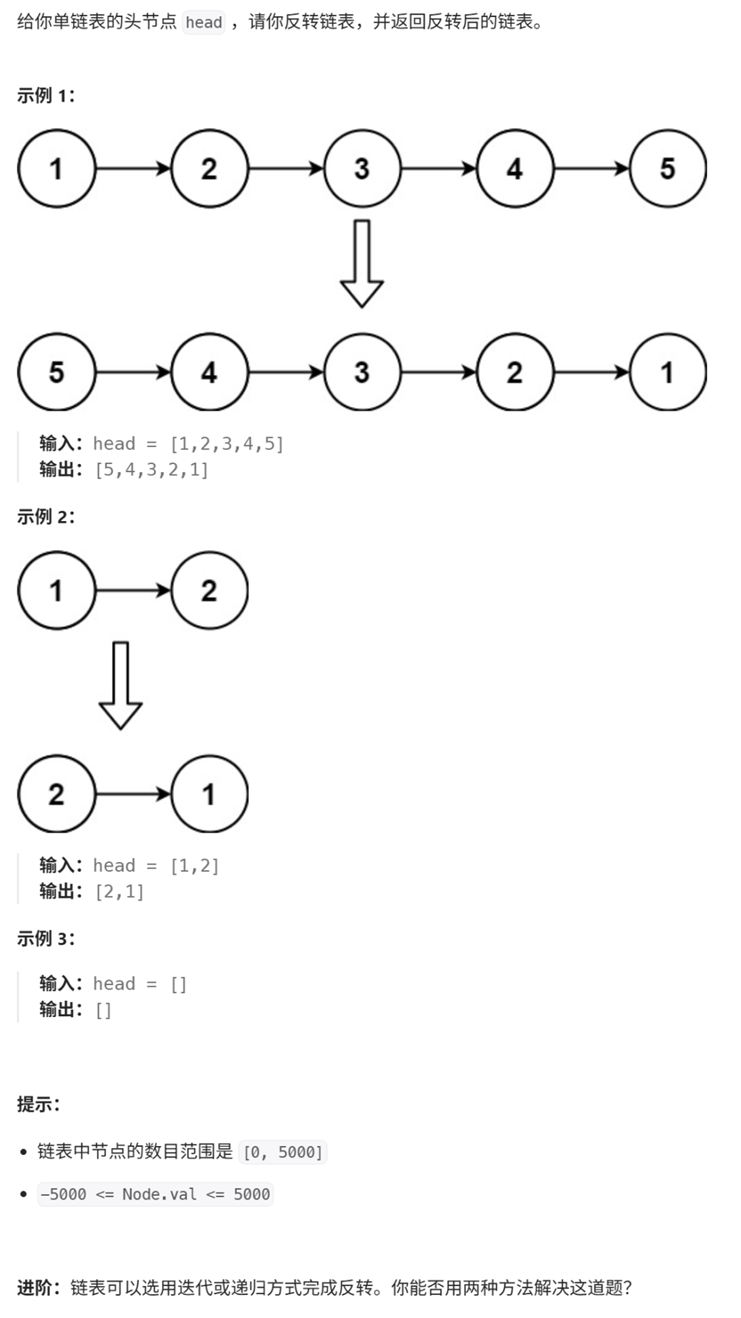
思路1:新建一个链表,将原链表中的节点插入新的链表中
思路2:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if(head==NULL){return head;}ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;n1=NULL;n2=head;n3=n2->next;while(n2){n2->next=n1;n1=n2;n2=n3;if(n3)n3=n3->next;}return n1;
}
3、链表的中间结点
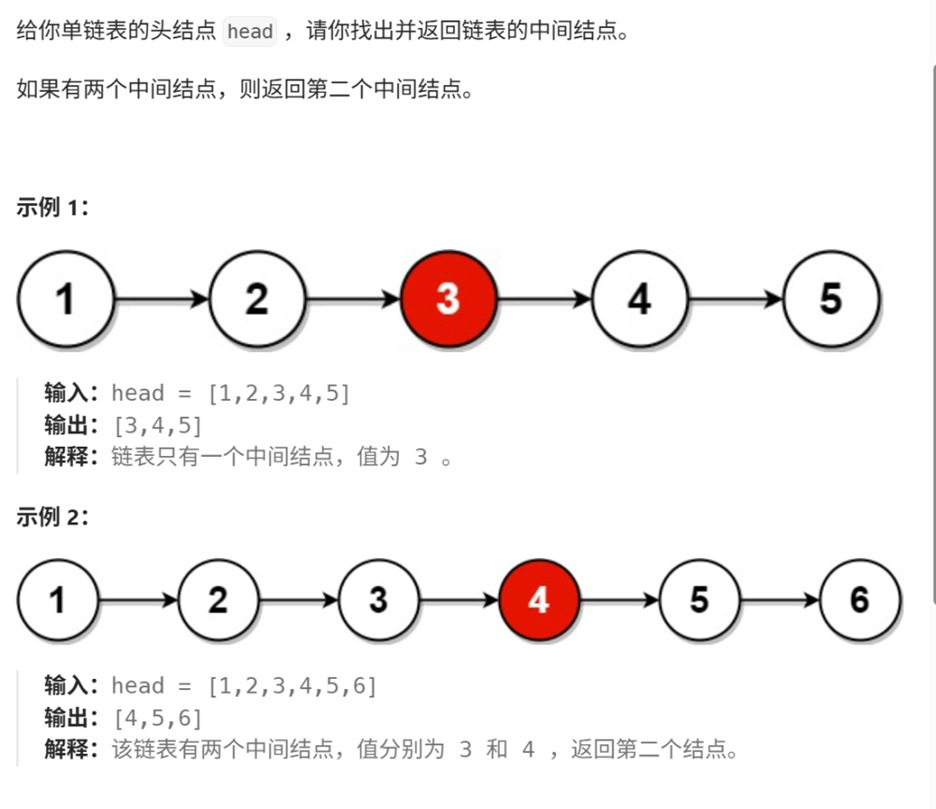
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow=head;ListNode* fast=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;}return slow;
}4、合并两个有序链表
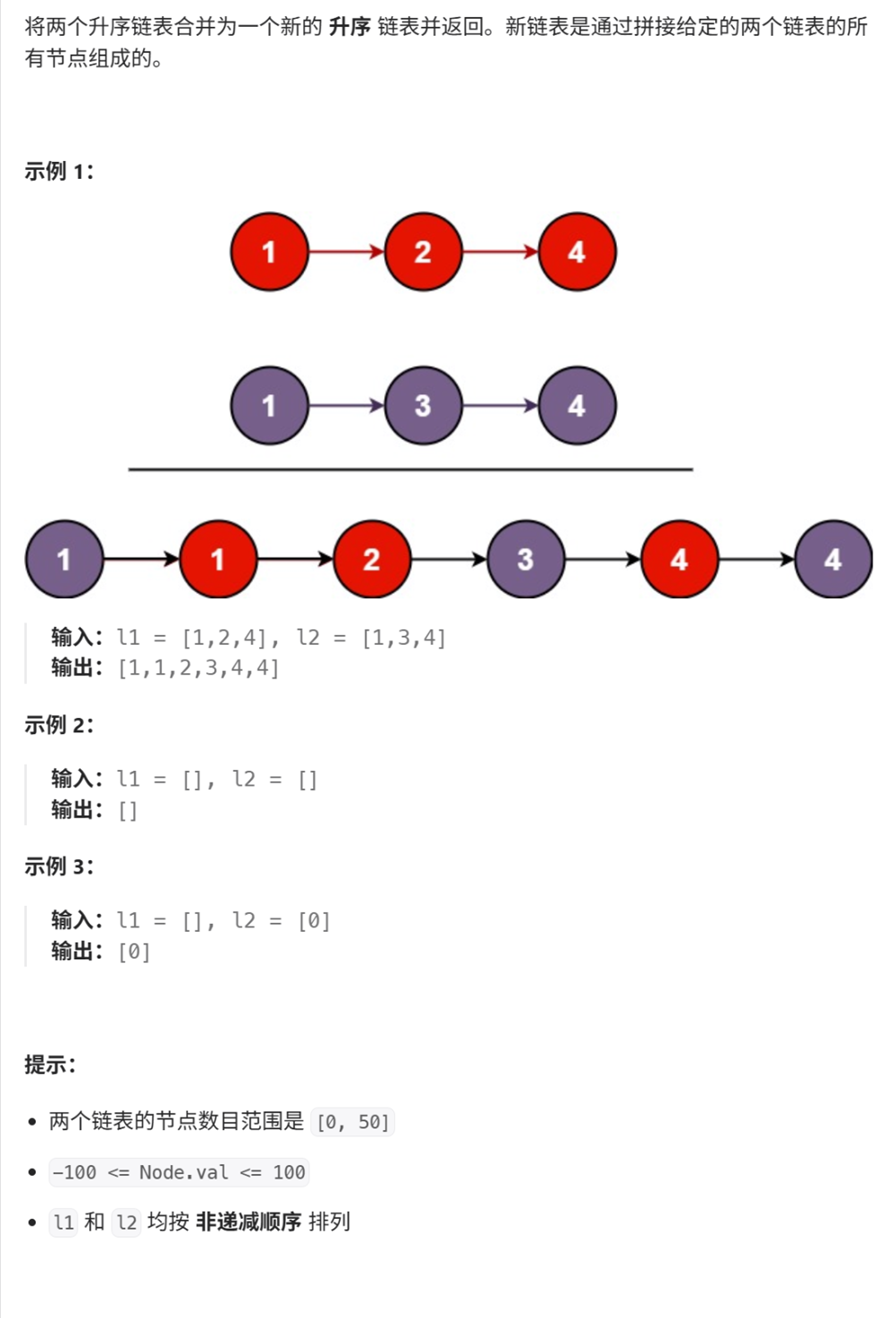
思路1:比较两个链表,哪个小把哪个放入新的链表中
需要注意的两点是:① l1和l2是否为空②新链表是否为空
思路2:
申请一个哨兵位(占位子)
可以优化代码(一直要判断链表是否为空)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {ListNode* newHead,*newTail;newHead=newTail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* l1=list1;ListNode* l2=list2;if(l1==NULL){return list2;}if(l2==NULL){return list1;}while(l1&&l2){if(l1->val<l2->val){newTail->next=l1;newTail=newTail->next;l1=l1->next;}else{newTail->next=l2;newTail=newTail->next;l2=l2->next;}}//l1走到空和l2走到空if(l1){newTail->next=l1;}if(l2){newTail->next=l2;}ListNode* pcur=newHead->next;free(newHead);newHead=NULL;return pcur;
}
5、链表分割

/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {ListNode* lessHed,*lessTail;lessHed=lessTail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* GreateHead,*GreatTail;GreateHead=GreatTail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* pcur = pHead;while(pcur){if(pcur->val<x){lessTail->next=pcur;lessTail=lessTail->next;}else{GreatTail->next=pcur;GreatTail=GreatTail->next;}pcur=pcur->next;}GreatTail->next=NULL;//将大小链表首尾相连lessTail->next=GreateHead->next;ListNode* retHead=lessHed->next;free(lessHed);free(GreateHead);lessHed=GreateHead=NULL;return retHead;}
};
6、链表的回文结构
思路1:创建新的链表,将原链表反转的结果保存在新链表中,遍历新旧链表比较
思路2:创建新数组,保存链表中所有节点的值,判断数组是否为回文结构
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {int arr[900]={0};int i=0;ListNode* pcur=A;while(pcur){arr[i++]=pcur->val;pcur=pcur->next;}int left =0;int right=i-1;while(left<right){if(arr[left]!=arr[right]){return false;;}left++;right--;}return true;}
};
上述解法只能适用于给定长度的链表题中!!!
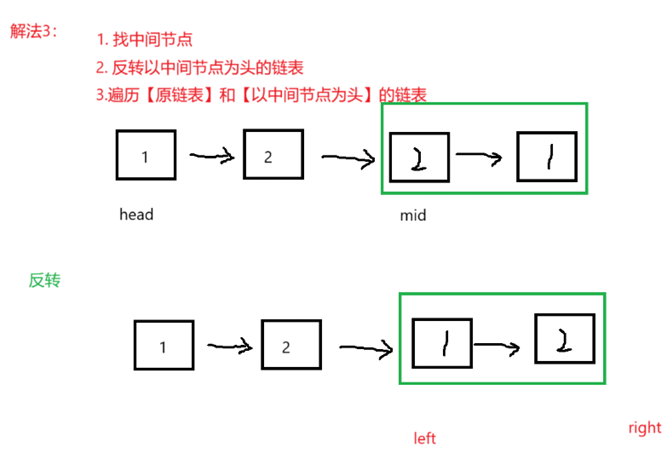
思路3:
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {public:struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if (head == NULL) {return head;}ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3;n1 = NULL;n2 = head;n3 = n2->next;while (n2) {n2->next = n1;n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if (n3)n3 = n3->next;}return n1;}bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {ListNode* mid=middleNode(A);ListNode* right=reverseList(mid);ListNode* left =A;while(right){if(left->val!=right->val){return false;}left=left->next;right=right->next;}return true;}
};
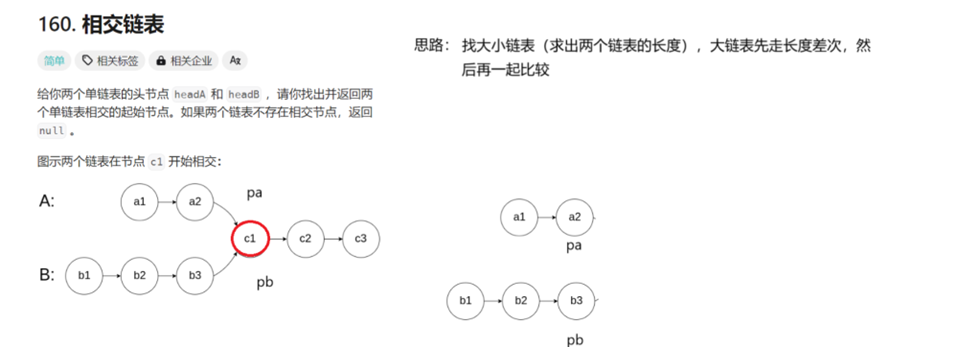
7、相交链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {ListNode* pa=headA;ListNode* pb=headB;int SizeA=0;int SizeB=0;//统计两个链表的大小while(pa){SizeA++;pa=pa->next;}while(pb){SizeB++;pb=pb->next;}int gap=abs(SizeA-SizeB);//绝对值,差值//让长链表先走gap步ListNode* longSize=headB;ListNode* shortSize=headA;if(SizeA>SizeB){longSize =headA;shortSize=headB;}while(gap--){longSize=longSize->next;}//找相等的节点while(shortSize){if(longSize==shortSize)//相等的话这个节点已经是相交的节点了{return shortSize;}shortSize=shortSize->next;longSize=longSize->next;}return NULL;
}
8、环形链表
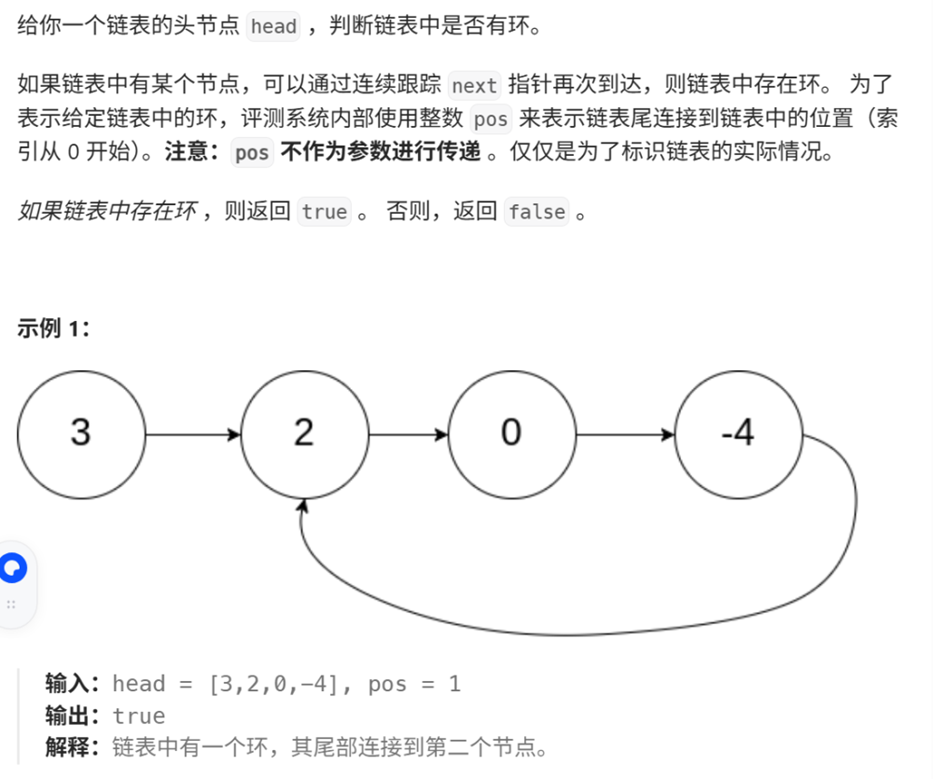
快慢指针,如果slow和fast最开始都指向head,slow走一步,fast走两步,如果slow和fast有相交则有环。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow=head;ListNode* fast=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(fast==slow)return true;}return false;
}
9、环形链表(2)
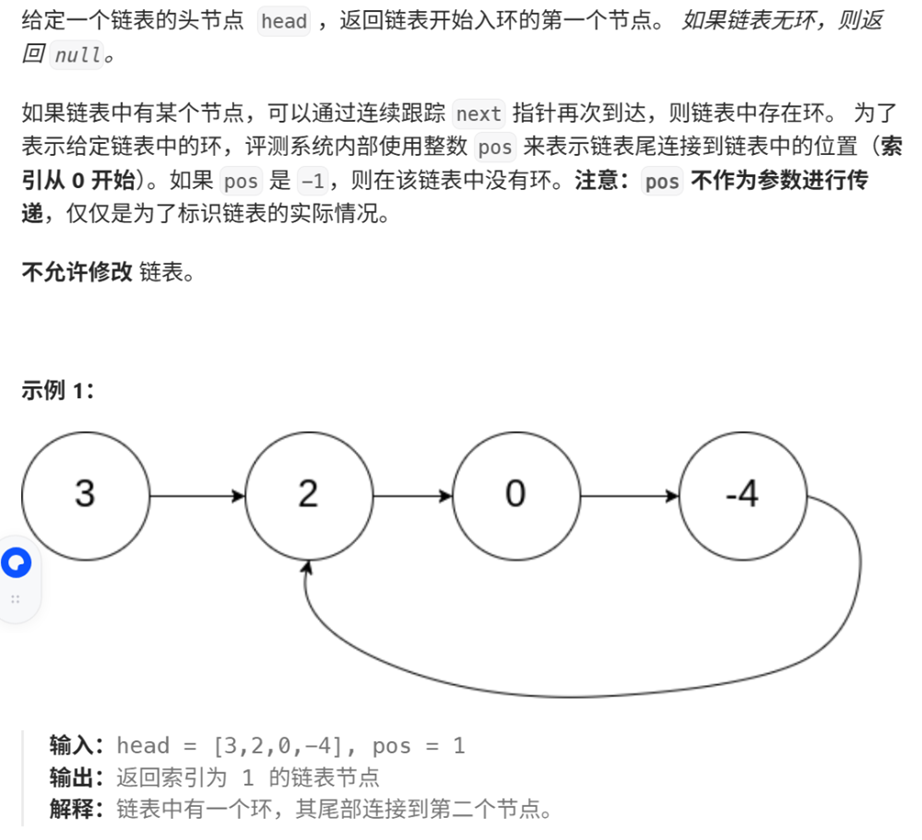
目标:找出入环的第一个节点
快慢指针:相遇点到入环起始节点的距离==链表头节点到入环起点的距离。
①循环找到slow和fast的相遇点
②再创建一个节点,从head开始,pcur和slow指针一起遍历,如果相同,则找到入环第一个节点。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode* fast = head;ListNode* slow = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {ListNode* pcur = head;while (pcur != slow) {slow = slow->next;pcur = pcur->next;}return pcur;}}return NULL;
}
10、随即表的复制
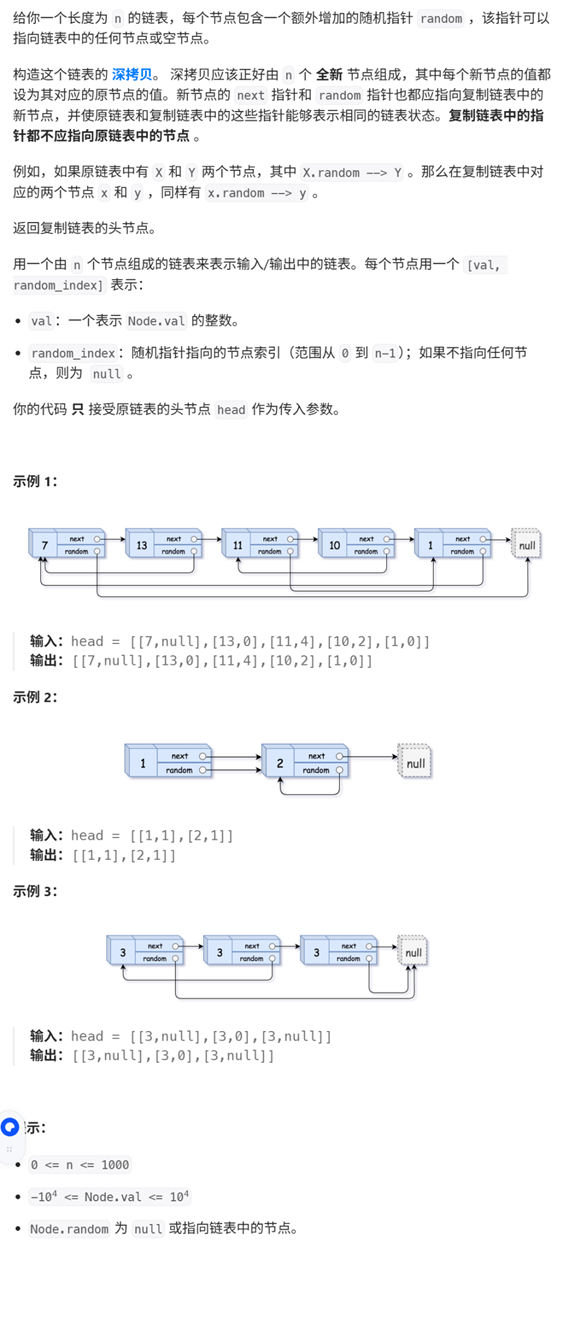
目标:复制原链表的指针,但都不指向原链表,如下例子,要得到的链表:
![]()
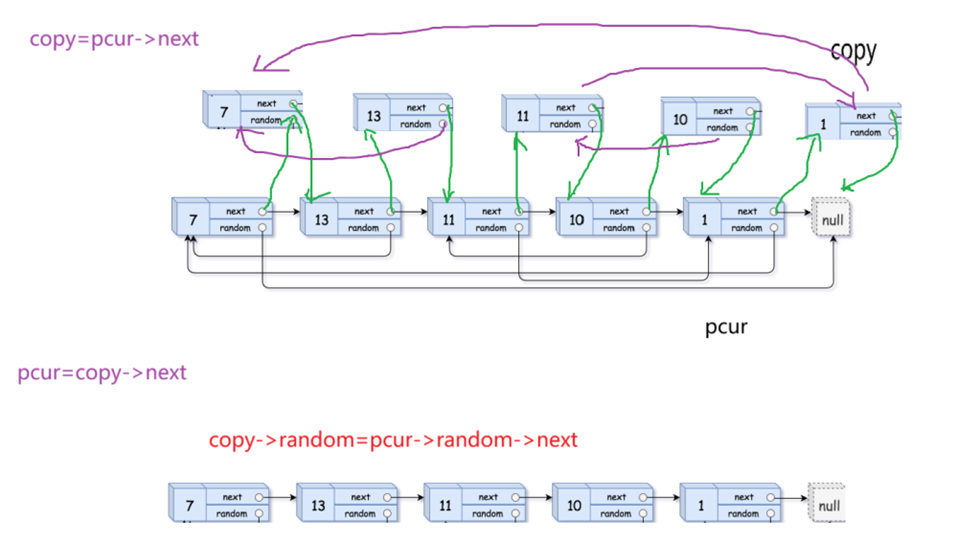
思路:
①拷贝节点
②重置random指针
copy->random=pcur->random->next
③断开新旧链表
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/
typedef struct Node Node;
Node* buyNode(int x) {Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));node->val = x;node->next = node->random = NULL;return node;
}
void AddNode(Node* head) {Node* pcur = head;while (pcur) {Node* next = pcur->next;Node* newnode = buyNode(pcur->val);newnode->next = next;pcur->next = newnode;pcur = next;}
}
void setRandom(Node* head) {Node* pcur = head;while (pcur) {Node* copy = pcur->next;if (pcur->random)copy->random = pcur->random->next;pcur = copy->next;}
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {if (head == NULL) {return head;}AddNode(head);setRandom(head);Node* pcur = head;Node *newHead, *newTail;newHead = newTail = pcur->next;while (newTail->next) {pcur = newTail->next;newTail->next = pcur->next;newTail = newTail->next;}return newHead;
}