python-time和datetime
在 Python 中,处理时间和日期是一个非常常见的任务。Python 提供了一些内置的模块专门用于处理时间和日期相关的操作,常用的时间相关模块包括:
- time 模块:处理时间的基本功能(如时间戳和简单的时间单位转换)。
- datetime 模块:高级时间与日期操作(如获取当前日期、时间差计算、格式化等)。
- calendar 模块:日历相关的操作,支持生成日历、判断闰年等功能。
- pytz 模块:处理时区(需单独安装)。
- dateutil 模块:扩展日期和时间操作(需单独安装)。
接下来,我们详细介绍time和datetime模块以及一些常见操作的代码示例。
一、time
time 模块主要用于处理时间戳(自1970年1月1日以来的秒数)、暂停程序运行、格式化时间等。在 Python 文档里,time是归类在Generic Operating System Services中,换句话说, 它提供的功能是更加接近于操作系统层面的。通读文档可知,time 模块是围绕着 Unix Timestamp 进行的。
1.1、时间格式
time模块中时间表现的格式主要有三种:
-
timestamp 时间戳: 时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。
-
struct_time 时间元组: 共有九个元素组。
gmtime(),localtime(),strptime()这三个函数会返回struct_time元组。属性 值 tm_year 年(2017) tm_mon 月(1-12) tm_mday 日(1-31) tm_hour 时(0-23) tm_min 分(0-59) tm_sec 秒(0-61) tm_wday 周几(0-6)0是周日 tm_yday 一年中的第几天 1 - 366 tm_isdst (是否是夏令时) 默认为-1 -
format time 格式化时间: 已格式化的结构使时间更具可读性。包括自定义格式和固定格式。‘2021-03-17 10:06:06’
格式 含义 示例 格式 描述 实例 %y 年 两位表示(00-99) %Y 年 四位表示(000-9999) %m 月 (数字01-12) %b 月 简称 %B 月 完整名称 %d 日 (数字0-31) %H 时 24小时制(0-23) %I 时 12小时制(01-12) %p AM/PM AM/PM %M 分 (00-59) %S 秒 (00-59) %f 微妙 (000000-999999) %a 星期名简称 (Wed) %A 星期名完整称 (Wednesday) %w 星期 (数字0-6),星期天为星期的开始 %W 周数,每周的第一天是周一 (00-53) %x 本地日期 (12/31/18) %X 本地时间 (17:41:00) %z UTC 偏移 %Z 时区 CST %c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示 Mon %j 年内的第几天 (001-366) %U 一年中的星期数 (00-53)星期天为星期的开始
1.2、time模块方法
-
time.time():返回当前时间的时间戳。
-
time.sleep(secs):线程推迟指定的时间运行。单位为秒。
-
time.localtime([secs]):将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。
-
time.gmtime([secs]):和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。
-
time.mktime(t):将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。
-
time.asctime([t]):把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:‘Sun Oct 1 12:04:38 2017’。如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。
-
time.ctime([secs]):把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。
-
time.strftime(format[, t]):把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。
-
time.strptime(string[, format]):把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。
-
import time# 返回当前时间的时间戳,输出为1760672018.8337336 print(time.time()) 1760673898.7117074# 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。 print(time.localtime()) print(time.localtime(1760671253.222)) time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=12, tm_min=4, tm_sec=58, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=290, tm_isdst=0) time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=11, tm_min=20, tm_sec=53, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=290, tm_isdst=0)# 将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time,用法与localtime一致 print(time.gmtime()) print(time.gmtime(1760671253.222)) time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=4, tm_min=4, tm_sec=58, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=290, tm_isdst=0) time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=3, tm_min=20, tm_sec=53, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=290, tm_isdst=0)# 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。 print(time.mktime(time.localtime())) print(time.mktime(time.gmtime())) print(time.mktime((2020, 12, 10, 8, 52, 30, 3, 345, 0))) 1760673898.0 1760645098.0 1607561550.0# 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time转换这种形式:‘Sun Oct 1 12:04:38 2017’。如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。 print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) print(time.asctime(time.gmtime())) Fri Oct 17 12:04:58 2025 Fri Oct 17 04:04:58 2025# 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转换这种形式:‘Sun Oct 1 12:04:38 2017’。如果参数未给或者为None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。 print(time.ctime()) print(time.ctime(1760671253.222)) Fri Oct 17 12:04:58 2025 Fri Oct 17 11:20:53 2025# 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", (2020, 12, 10, 8, 52, 30, 3, 345, 0))) print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime())) 2020-12-10 08:52:30 2025-10-17 12:04:58# 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作 print(time.strptime("2025-10-17 11:57:49", "%Y-%m-%d %X")) time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=11, tm_min=57, tm_sec=49, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=290, tm_isdst=-1)
1.3、时间模块转换
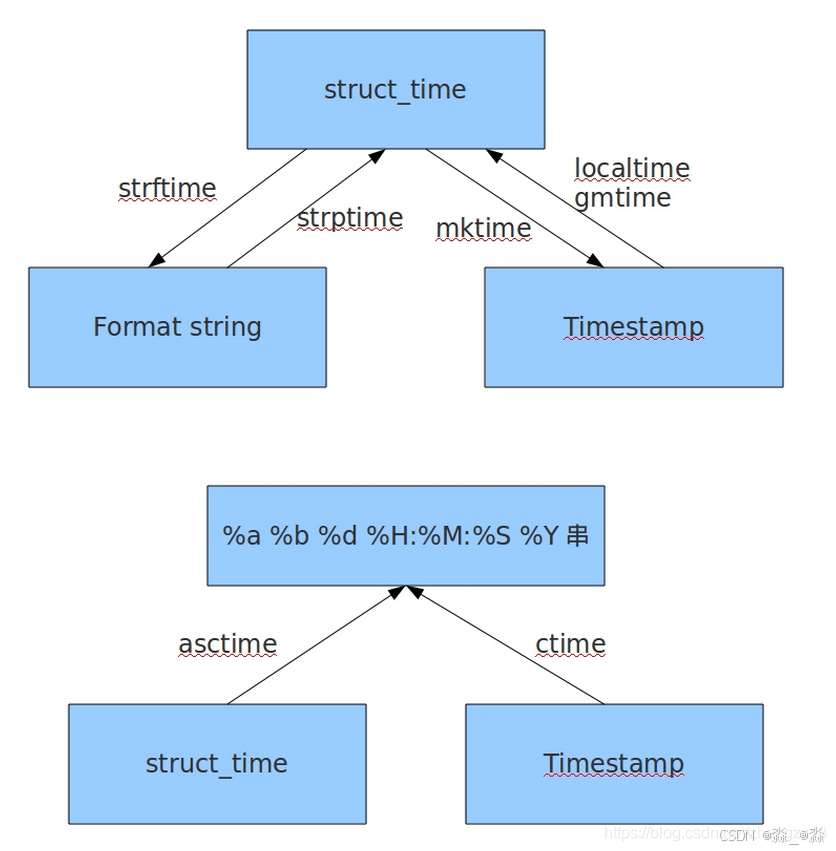
二、datetime
datatime 模块重新封装了 time 模块,提供了更多接口,变得更加直观和易于调用,提供了更多实用的函数,在实际实用中,用得比较多的是 datetime.datetime 和 datetime.timedelta。
- datetime.date:表示日期的类,主要用于处理年、月、日;
- datetime.time:表示时间的类,主要用于处理时、分、秒;
- datetime.datetime:表示日期时间的类,date类和time类的综合使用,可以处理年、月、日、时、分、秒;
- datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点的间隔,主要用于做时间加减的
- datetime.tzinfo:时区的相关信息。
2.1、datetime.datetime
datetime 包括了 date 与 time 的所有信息,格式为:datetime(year, month, day, hour=0,minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0, tzinfo=None, *, fold=0),参数范围值参考date 类与 time 类。
类方法和属性如下所示:
| 方法(属性) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| today() | 返回当地的当前时间 |
| now(tz=None) | 类似于 today(),可选参数 tz 可指定时区 |
| utcnow() | 类似于 now(),返回当前 UTC 时间 |
| fromtimestamp(时间戳) | 根据时间戳返回对应时间 |
| utcfromtimestamp(时间戳) | 根据时间戳返回对应 UTC 时间 |
| strptime(字符串,format) | 跟着字符串(对应的格式)返回时间 |
| combine(date, time) | 根据 date 和 time 返回对应时间 |
注意:now()的入参tz不能直接传入像 "Asia/Shanghai" 这样的字符串,而是要传入一个具体的时区对象,比如:
datetime.timezone.utcdatetime.timezone(timedelta(hours=8))zoneinfo.ZoneInfo("Asia/Shanghai")(Python 3.9+)pytz.timezone("Asia/Shanghai")(第三方库)
from datetime import datetime, date, time, timezone
import time as t # dateime和time都有time模块所以需要改名
import pytz# 返回当前系统时间,时区与系统一致
print(datetime.today())
2025-10-17 17:49:00.021914# 返回当前时间,可以指定时区。
print(datetime.now())
print(datetime.now(tz=pytz.timezone("Asia/Shanghai")))
print(datetime.now(tz=timezone.utc))
2025-10-17 17:49:00.021914
2025-10-17 17:49:00.845718+08:00
2025-10-17 09:49:00.845718+00:00# 返回当前 UTC 时间
print(datetime.utcnow())
2025-10-17 09:49:00.845718# 根据时间戳返回对应时间,入参必须是时间戳格式
print(datetime.fromtimestamp(t.time()))
2025-10-17 17:49:00.845719# 根据时间戳返回对应 UTC 时间,入参必须是时间戳格式
print(datetime.utcfromtimestamp(t.time()))
2025-10-17 09:49:00.845719# 根据提供的字符串(对应的格式)返回时间,返回时间格式为YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:dd
print(datetime.strptime("21/11/06 16:30", "%d/%m/%y %H:%M"))
2006-11-21 16:30:00# 根据 date 和 time 返回对应时间
print(datetime.combine(date(2222, 2, 2), time(2, 2, 2)))
2222-02-02 02:02:02
实例方法说明:
| 方法(属性) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| year | 年 |
| month | 月 |
| day | 日 |
| hour | 时 |
| minute | 分 |
| second | 秒 |
| microsecond | 微秒 |
| replace() | 生成一个新的日期对象,用参数指定的年,月,日,时,分,秒…代替原有对象中的属性 |
| timestamp() | datetime -> 时间戳 |
| strftime(format) | 返回自定义格式的字符串 |
a = datetime.now(tz=pytz.timezone("Asia/Shanghai"))
print(a.year)
print(a.month)
print(a.day)
print(a.hour)
print(a.minute)
print(a.second)
print(a.microsecond)
print(a.replace(second=57, day=20))
print(a.timestamp())
print(a.strftime("%Y%m%d %H:%M:%S"))2025
10
17
17
55
56
958712
2025-10-20 17:55:57.958712+08:00
1760694956.958712
20251017 17:55:56
2.2、datetime.timedelta
timedelta对象是用于表示两个日期或时间之间的差异。它通常用于日期和时间的计算和比较。格式:class datetime.timedelta(days=0, seconds=0, microseconds=0, milliseconds=0, hours=0, weeks=0)
print(timedelta(days=10,hours=5))
print(timedelta(days=10,hours=-5))#用timedelta加减时间时,dt必须是一个datetime.datetime格式的时间,不能是timestamp或者struct_time 时间元组,否则会报错
dt = datetime.utcnow()
delta = timedelta(hours=-5)
target = dt + delta
print(target)10 days, 5:00:00
9 days, 19:00:00
2025-10-17 06:13:37.125686
三、时间封装
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
__title__ = '操作时间的工具类'"""
import datetime
import time# ==========================
# ========== time ==========
# ==========================def getCurrentMilliSecondTime():"""description: 获取当前时间-毫秒级return: 1557730376981 -> str"""timestamps = str(round(time.time() * 1000))return timestampsdef getCurrentSecondTime():"""description: 获取当前时间-秒级return: 1557730377 -> str"""timestamps = str(round(time.time()))return timestampsdef getCurrentTimeTuple(times=time.time()):"""description: 接受秒级时间戳并返回时间元组(与mktime(tuple)相反)times: 默认当前时间 可传secondreturn: (tm_year=2019, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=13, tm_hour=10, tm_min=9, tm_sec=18, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=133, tm_isdst=0) -> tupletips: time.localtime() 不传参则取当前时间"""timestamps = time.localtime(times)return timestampsdef getTimeByTuple(tupleTime=time.localtime()):"""description: 接受时间元组并返回秒级时间戳(与localtime(sec)相反)tupleTime: 默认当前时间的元组 可通过time.localtime() or datetime.datetime.now().timetuple()获取return: 1557733061 -> str"""timestamps = str(round(time.mktime(tupleTime)))return timestampsdef getCurrentFormatTimeStr(times=time.time()):"""description: 将指定时间元组格式化为字符串times: 默认当前时间 可传secondreturn: 2019-05-13 15:00:47 -> strtips: %y 两位数的年份表示(00-99) %Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999) %m 月份(01-12) %d 月内中的一天(0-31)%H 24小时制小时数(0-23) %I 12小时制小时数(01-12) %M 分钟数(00=59) %S 秒(00-59) %w 星期(0-6)"""timestamps = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(times))return timestampsdef getCurrentTimeTupleByFormatStr(time_str=str(datetime.datetime.now()).split(".")[0], format_type="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"):"""description: 接受格式化字符串返回时间元组time_str: 格式化字符串 如:2019-05-13 15:00:47 默认当前时间format_type: 格式化规则 如:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S 默认%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%Sreturn: (tm_year=2019, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=13, tm_hour=10, tm_min=9, tm_sec=18, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=133, tm_isdst=0) -> tuple"""return time.strptime(time_str, format_type)def getCurrentTimeStr():"""description: 获取当前时间的可读形式字符串return: Mon May 13 11:27:42 2019 -> str"""return time.ctime()def getCurrentTimeStrByTuple(tupleTime=time.localtime()):"""description: 获取指定时间的可读形式字符串tupleTime: 时间元组 可通过time.localtime() or datetime.datetime.now().timetuple()获取 默认当前时间的元组return: Mon May 13 11:27:42 2019 -> str"""return time.asctime(tupleTime)def sleepTime():"""description: 推迟调用线程的运行"""for i in range(4):print(i)time.sleep(3)# ======================
# ====== datetime ======
# ======================def getNowDateTime():"""description: 获取当前日期&时间return: 2019-05-13 14:41:15 -> str"""timestamps = str(datetime.datetime.now()).split(".")[0]return timestampsdef getNowTime():"""description: 获取当前时间return: 14:41:15 -> str"""timestamps = str(datetime.datetime.now().time()).split(".")[0]return timestampsdef getTodayDate():"""description: 获取当前日期return: 2019-05-13 -> strtipe: datetime.datetime.now().date()有相同效果"""timestamps = str(datetime.date.today())return timestampsdef getTimeDate(times=time.time()):"""description: 获取指定时间戳的日期time: 秒 默认当前时间return: 2019-05-13 -> strtips: 一天86400秒"""timestamps = str(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(round(times)))return timestamps# 获取距离现在时间的任意时间的日期 正数 加,负数 减 return:2019-05-12
def getAnyDateTime(day, hour=0, min=0, sec=0):"""description: 获取距离现在时间的任意时间的日期&时间day: 天数 1代表当前时间+1天 -1代表当前时间-1天hour: 小时 2代表当前时间+2h -2代表当前时间-2h 默认=0min: 分钟 30代表当前时间+30min -30代表当前时间-30m 默认=0sec: 秒 120代表当前时间+120s -120代表当前时间-120s 默认=0return: 2019-05-15 15:37:41 -> str"""return str(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=day, hours=hour, minutes=min, seconds=sec)).split(".")[0]def getAnyDateSecondTime(day, hour=0, min=0, sec=0):"""description: 获取距离现在时间的任意时间的秒数day: 天数 1代表当前时间+1天 -1代表当前时间-1天hour: 小时 2代表当前时间+2h -2代表当前时间-2h 默认=0min: 分钟 30代表当前时间+30min -30代表当前时间-30m 默认=0sec: 秒 120代表当前时间+120s -120代表当前时间-120s 默认=0return: 1557902182 -> str"""anyDay = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=day, hours=hour, minutes=min, seconds=sec)return str(round(time.mktime(anyDay.timetuple())))def getTodayTime():"""description: 获取当天0点的时间戳return: 1557676800 -> str"""return str(round(time.mktime(datetime.date.today().timetuple())))def getCurrentWeekTime():"""description: 获取本周周一0点return: 1557676800 -> strtips: 可替换成: timestamps = time.mktime(time.strptime(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime(times)), "%Y-%m-%d"))"""week = int(time.strftime("%w", time.localtime()))times = round(time.time()) - (week - 1) * 86400timestamps = time.mktime(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(times).timetuple())return str(round(timestamps))def time_test():print(getCurrentMilliSecondTime())print(getCurrentSecondTime())print(getCurrentFormatTimeStr())print(getCurrentTimeTupleByFormatStr())print("=======")print(getCurrentTimeStr())print(getCurrentTimeStrByTuple(time.localtime()))print(getTimeByTuple(time.localtime()))print("=======")print(getNowDateTime())print(getNowTime())print(getNowDateTime())print(getTodayDate())print(getTimeDate(time.time() - 86400))print("=======")print(getAnyDateTime(2))print(getAnyDateSecondTime(2))print("=======")print(getTodayTime())print(getCurrentWeekTime())if __name__ == '__main__':print(time_test())
参考文档:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangzx18/article/details/113770877
https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/p/12208446.html
