Vue3的Pinia状态管理库【8】
Pinia状态管理库
- 1.概述:
- 2.核心内容:
- 1.Store(商店):数据共享仓库
- 1.什么是store:
- 2.状态(State):数据存储
- 3.操作(Actions):函数定义
- 4.获取器(Getters):类似于计算属性
- 3.pinia的优势:
- 4.使用:
- 1.下载pinia库:
- 2.配置main.ts:
- 3.创建store实例:
- 4.创建对应的组件:
- 5.将组件引入App.vue中:
- 5.测试结果展示:
- 5.store中数据的更新:
- 1.对sum进行累加和递减操作;
- 1.countStore补充调用的函数:
- 2.count组件内容补充:
- 3.测试:
- 2.对countStore中的三个数据都进行更新:
- 定义count组件功能按钮,及事件的回调函数
- 测试:
- 6.不同组件之间实现数据共享:
- 1.需求:
- 2.实现:
- 7.getters:
- 1.概述:
- 2.使用:
- 需求:
- 实现:
- 1.countStore中添加etters属性得内容:
- 2.count组件中展示上面getters中添加的两个计算属性数据:
- 3.测试结果展示:
- 8.storeToRefs:
- 1.概述:
- 2.使用:
- 3.测试:
- 9.store的组合式API写法:
- 1.概述:
- 2.实现:
- 3.测试:
- 10.$subscribe监听
- 1.概述:
- 2.案例分析:
1.概述:
Pinia 是 Vue.js 的一个状态管理库,用于在 Vue 应用程序中集中管理应用的状态。它被设计为 Vuex 的替代品,提供了一个更简单、更直观的 API,同时保持了类型安全并且在支持 Vue 3 的同时也兼容 Vue 2。
官方介绍文档:https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/
2.核心内容:
1.Store(商店):数据共享仓库
1.什么是store:
Store (如 Pinia) 是一个保存状态和业务逻辑的实体,它并不与你的组件树绑定。换句话说,它承载着全局状态。它有点像一个永远存在的组件,每个组件都可以读取和写入它。它有三个概念,[state](https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/core-concepts/state.html)、[getter](https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/core-concepts/getters.html) 和 [action](https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/core-concepts/actions.html),我们可以假设这些概念相当于组件中的 `data`、 `computed` 和 `methods`。
2.状态(State):数据存储
状态是商店中存储数据的部分;
3.操作(Actions):函数定义
操作是可以在商店中定义的函数,用于修改状态或者执行一些异步操作。它们可以包含复杂的业务逻辑,比如发送网络请求来更新状态。
4.获取器(Getters):类似于计算属性
获取器类似于 Vuex 中的计算属性,它们用于从状态中派生数据。
3.pinia的优势:
Pinia 是 Vue 的专属状态管理库,它允许你跨组件或页面共享状态。如果你熟悉组合式 API 的话,你可能会认为可以通过一行简单的 `export const state = reactive({})` 来共享一个全局状态。对于单页应用来说确实可以,但如果应用在服务器端渲染,这可能会使你的应用暴露出一些[安全漏洞](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/scaling-up/ssr#cross-request-state-pollution)。 而如果使用 Pinia,即使在小型单页应用中,你也可以获得如下功能:
- 测试工具集:
- 插件:可通过插件扩展 Pinia 功能;
- 为 JS 开发者提供适当的 TypeScript 支持以及自动补全功能;
- 支持服务端渲染;
- Devtools 支持:
- 追踪 actions、mutations 的时间线
- 在组件中展示它们所用到的 Store
- 让调试更容易的 Time travel
- 热更新:
- 不必重载页面即可修改 Store
- 开发时可保持当前的 State
4.使用:
1.下载pinia库:
npm install pinia
2.配置main.ts:
//导入createPinia函数
import {createPinia} from "pinia"; //创建pinia实例对象
const pinia=createPinia();//将pinia对象加载到vm中vm.use(pinia)
3.创建store实例:
在项目src目录下创建一个store文件夹,再在此文件夹下创建两个store(ts文件)
//导入defineStore函数
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
//通过此函数创建store实例
//此函数接收两个参数:参数1:表示此store的名字,参数2:表示此store实例中的三个核心actions:函数定义;state:数据;getters:类似计算属性
export const useCountStore=defineStore('countStore',{actions:{},state(){return{sum:1,school:'测试数据',address:'测试数据'}},getters:{}})
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
import {reactive} from "vue";
import axios from "axios";export const useJokeStore=defineStore('jokeStore',{actions:{//通过访问API获取笑话getJoke(){axios.get("https://api.vvhan.com/api/text/joke?type=json").then(res => {console.log(res.data.data)this.jokeList.unshift(res.data.data);}).catch(error => {console.log("请求失败")})}},state(){return{jokeList:[],}},getters:{}
})
4.创建对应的组件:
<template><div class="count">
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ countStore.school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ countStore.address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ countStore.sum }}</h2></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import {useCountStore} from "../store/CountStore.ts";//获取 store 实例 >>> proxy 不用.value
let countStore = useCountStore();</script><style scoped>.count {background-color: skyblue;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}select, button {margin: 0 5px;height: 25px;
}</style>
<template><div><button @click="getJoke">获取笑话</button><ul><li class="joke" v-for="(joke,index) in jokeList" :key="joke.id">{{ joke.title }}<br/>{{ joke.content }}</li></ul></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Joke">import {useJokeStore} from "../store/JokeStore";//导入对应store实例对象;const JokeStore=useJokeStore();//获取jokeList数据;const jokeList=JokeStore.jokeList;const getJoke=()=>{//调用getJoke()函数JokeStore.getJoke();};
</script><style scoped>
.joke {margin-top: 20px;background-color: orange;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}li {list-style: none;
}
button{margin-top: 10px;height: 36px;width: 360px;
}
</style>5.将组件引入App.vue中:
<template><count></count><joke></joke>
</template><script lang="ts" setup name="App">
import Count from "./components/count.vue";
import Joke from "./components/joke.vue";</script><style scoped>
</style>5.测试结果展示:
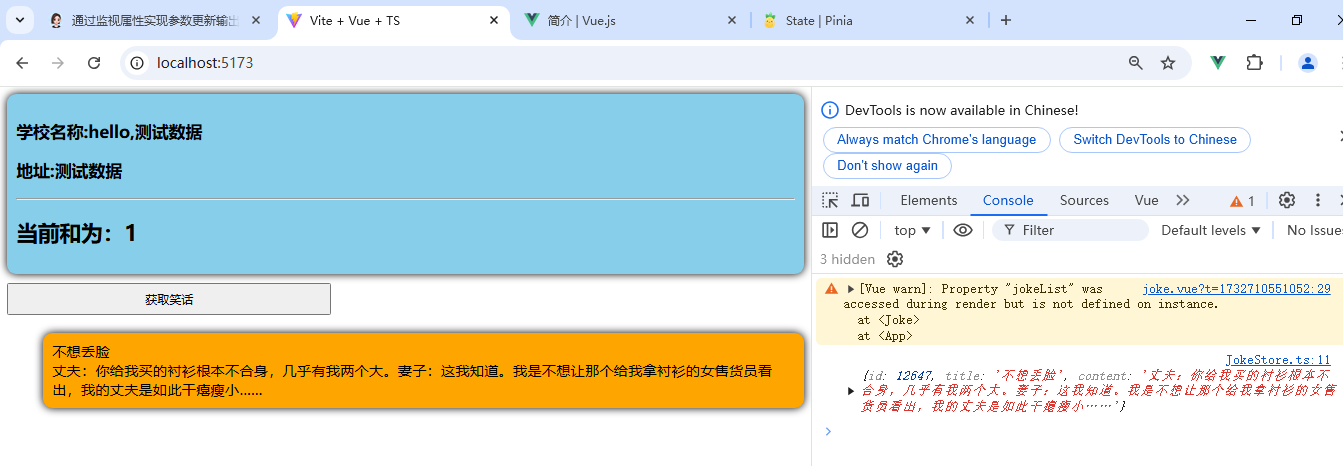
从测试结果可以看出,我们可以成功在页面上渲染出相关数据,而且重要的一点是,我们的数据或函数并没有直接定义在组件内部,而是将这些数据或参数定义在store中,再通过导入对应的store,获取相关的数据,或函数;这样做的优势是可以实现数据或函数的共享,即不同的组件可以获取相同的数据,只要在组件中导入对应的store即可;
5.store中数据的更新:
1.对sum进行累加和递减操作;
1.countStore补充调用的函数:
//导入defineStore函数
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
//通过此函数创建store实例
//此函数接收两个参数:参数1:表示此store的名字,参数2:表示此store实例中的三个核心actions:函数定义;state:数据;getters:类似计算属性
export const useCountStore=defineStore('countStore',{actions:{increment(value:number){if(this.sum<10){this.sum+=value;}},decrement(value:number){if(this.sum>1){this.sum-=value;}},},state(){return{sum:1,school:'测试数据',address:'测试数据'}},getters:{}})
2.count组件内容补充:
<template><div class="count">
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ countStore.school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ countStore.address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ countStore.sum }}</h2>//定义下拉选择框,并双向绑定数值n<select v-model.number="n"><option>1</option><option>2</option><option>3</option></select>//定义两个单击事件,用于实现递增和递减<button @click="add">加</button><button @click="minus">减</button><br/></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import {useCountStore} from "../store/CountStore.ts";//获取 store 实例 >>> proxy 不用.value
let countStore = useCountStore();
//定义用户选择的数据n
let n = ref(1); //用户选择的数值默认值为1;//定义单击事件的回调函数const add = () => {//注意n是通过ref函数创建的,因此操作时需要通过n.valuecountStore.increment(n.value);
}
const minus = () => {countStore.decrement(n.value);
}
</script><style scoped>.count {background-color: skyblue;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}select, button {margin: 0 5px;height: 25px;
}</style>
3.测试:
1.页面正常加载: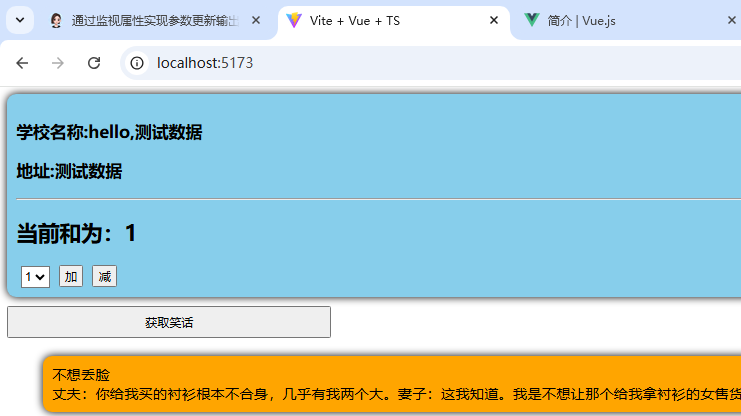
2.加2操作:
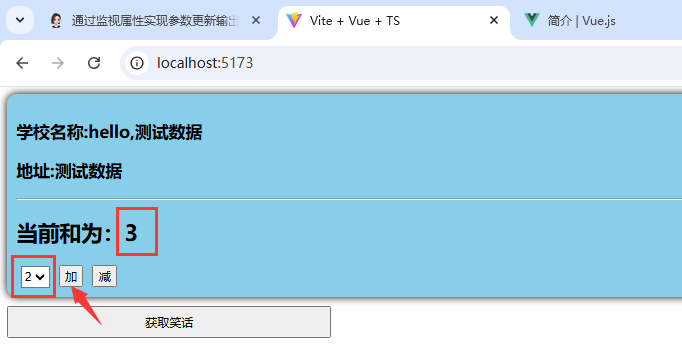
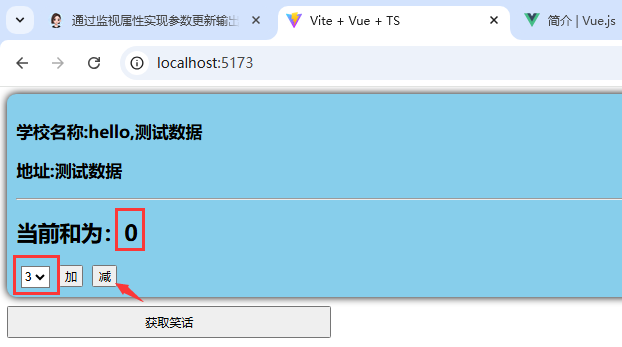
3.减3操作:
2.对countStore中的三个数据都进行更新:
定义count组件功能按钮,及事件的回调函数
<template><div class="count">
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ countStore.school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ countStore.address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ countStore.sum }}</h2>//定义下拉选择框,并双向绑定数值n<select v-model.number="n"><option>1</option><option>2</option><option>3</option></select>//定义两个单击事件,用于实现递增和递减<button @click="add">加</button><button @click="minus">减</button>//定义单击事件,用于更新school,address和sum<button @click="upData">修改数据</button><br/></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import {useCountStore} from "../store/CountStore.ts";//获取 store 实例 >>> proxy 不用.value
let countStore = useCountStore();
//定义用户选择的数据n
let n = ref(1); //用户选择的数值默认值为1;//定义递增或递减单击事件的回调函数const add = () => {//注意n是通过ref函数创建的,因此操作时需要通过n.valuecountStore.increment(n.value);
}
const minus = () => {countStore.decrement(n.value);
}
//定义三个数据都更新的回调函数://方式1:逐一更新
// const upData = () => {
// //方式一: 修改数据 三次
// // countStore.sum = 666;
// // countStore.school = "猿究院"
// // countStore.address = "北大街"//方式2:批量修改const upData = () => { countStore.$patch({sum: 666,school: "猿究院",address: "北大街"})}</script><style scoped>.count {background-color: skyblue;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}select, button {margin: 0 5px;height: 25px;
}</style>
测试:
页面正常加载:
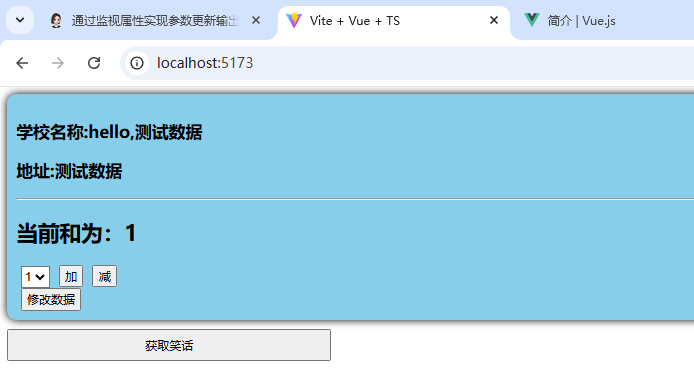
点击修改数据:
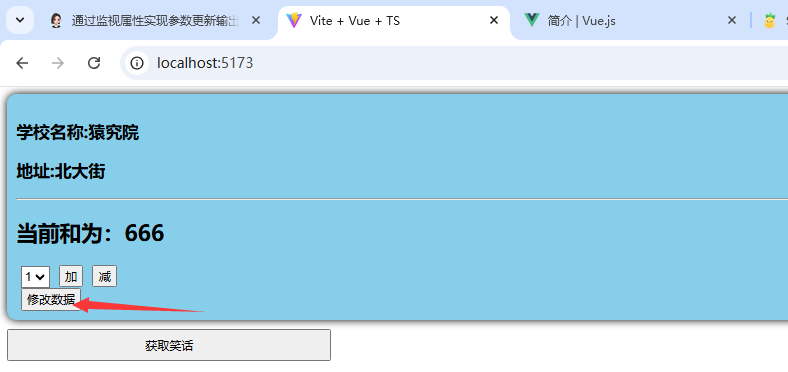
6.不同组件之间实现数据共享:
1.需求:
在上述案例中,实现在count组件中展示joke组件的数据;同时在joke组件中展示count组件的数据;
2.实现:
1.在count组件中引入jokeStore,并进行展示;
<template><div class="count"><!--获取jokestore的数据 --><h2>joke中有多少个笑话:{{ jokeStore.jokeList.length }}</h2>
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ countStore.school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ countStore.address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ countStore.sum }}</h2>//定义下拉选择框,并双向绑定数值n<select v-model.number="n"><option>1</option><option>2</option><option>3</option></select>//定义两个单击事件,用于实现递增和递减<button @click="add">加</button><button @click="minus">减</button>//定义单击事件,用于更新school,address和sum<button @click="upData">修改数据</button><br/></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import {useCountStore} from "../store/CountStore.ts";//获取 store 实例 >>> proxy 不用.value
let countStore = useCountStore();
//获取jokeStore实例
let jokeStore = useJokeStore();
//定义用户选择的数据n
let n = ref(1); //用户选择的数值默认值为1;//定义递增或递减单击事件的回调函数const add = () => {//注意n是通过ref函数创建的,因此操作时需要通过n.valuecountStore.increment(n.value);
}
const minus = () => {countStore.decrement(n.value);
}
//定义三个数据都更新的回调函数://方式1:逐一更新
// const upData = () => {
// //方式一: 修改数据 三次
// // countStore.sum = 666;
// // countStore.school = "猿究院"
// // countStore.address = "北大街"//方式2:批量修改const upData = () => { countStore.$patch({sum: 666,school: "猿究院",address: "北大街"})}</script><style scoped>.count {background-color: skyblue;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}select, button {margin: 0 5px;height: 25px;
}</style>
2.joke组件中引入countStore实例,并进行数据展示:
<template><div>//展示count组件的数据<h2>这是joke组件:{{CountStore.sum}}</h2><button @click="getJoke">获取笑话</button><ul><li class="joke" v-for="(joke,index) in jokeList" :key="joke.id">{{ joke.title }}<br/>{{ joke.content }}</li></ul></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Joke">import {useJokeStore} from "../store/JokeStore";//导入对应store实例对象;const JokeStore=useJokeStore();//导入CountStore实例对象const CountStore=useCountStore();//获取jokeList数据;const jokeList=JokeStore.jokeList;const getJoke=()=>{//调用getJoke()函数JokeStore.getJoke();};
</script><style scoped>
.joke {margin-top: 20px;background-color: orange;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}li {list-style: none;
}
button{margin-top: 10px;height: 36px;width: 360px;
}
</style>测试结果展示:
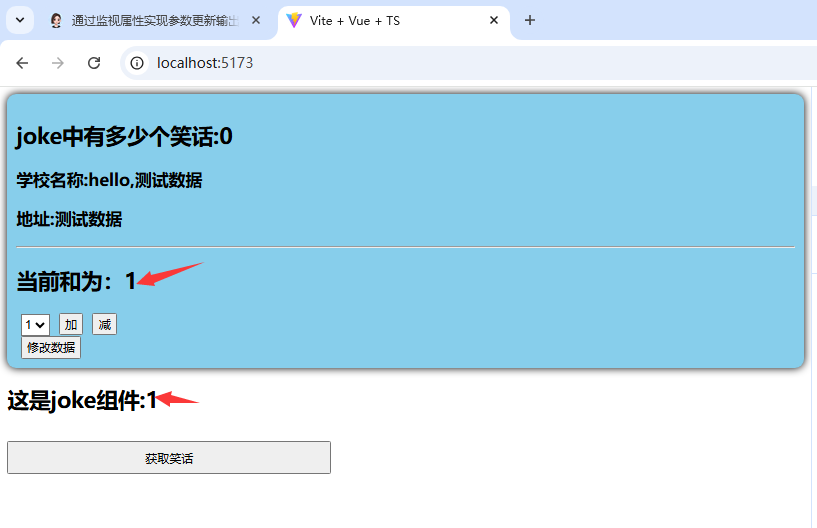
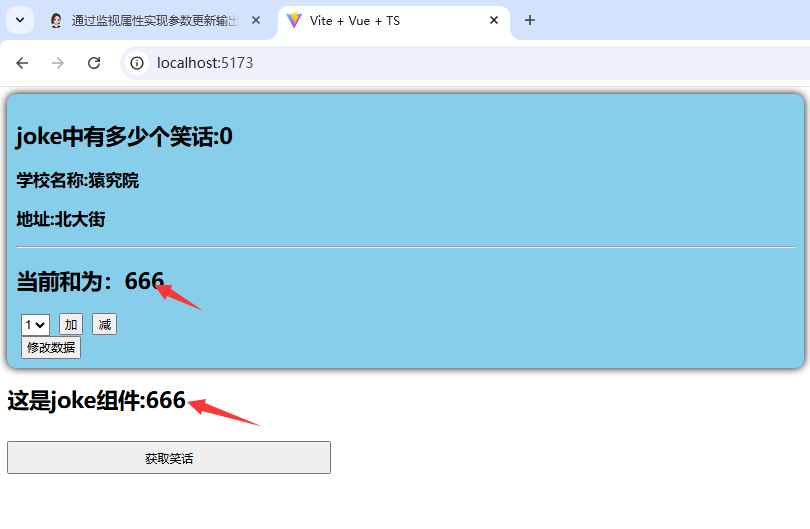
从测试结果可以看出,此时已经实现了多个组件之间的数据共享,而且在store中的数据都是响应式的,当该数据在某一组件中改变时,其他共享组件中的数据都会同时改变;
7.getters:
1.概述:
在上面我们说过getters属性类似于vue中的计算属性,可以通过已有数据计算得到没有的数据,所以本质上也可以作为store中的数据使用;
2.使用:
需求:
在countStore的getters中添加两个数据,该数据是由已有数据sum和school经过计算处理得来,最后再在count组件中展示这两个数据;
实现:
1.countStore中添加etters属性得内容:
getters:{bigSum:(state):number=>{return state.sum*10;},upperschool:(state):string=>{return state.school.toUpperCase();}}
说明:在getters中添加得计算属性都以一个回调函数,并且参数为state(存储已有数据的属性),然后在回调函数中对需要的数据进行计算处理并返回;
2.count组件中展示上面getters中添加的两个计算属性数据:
<template><div class="count"><!--获取jokestore的数据 --><h2>joke中有多少个笑话:{{ jokeStore.jokeList.length }}</h2>
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ countStore.school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ countStore.address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ countStore.sum }}</h2>//定义下拉选择框,并双向绑定数值n<select v-model.number="n"><option>1</option><option>2</option><option>3</option></select>//定义两个单击事件,用于实现递增和递减<button @click="add">加</button><button @click="minus">减</button>//定义单击事件,用于更新school,address和sum<button @click="upData">修改数据</button><br/>//展示getters中的内容<h4>sum扩大10倍:{{bigSum}}</h4><h4>学校大写:{{upperschool}}</h4></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts" name="Count">
import {useCountStore} from "../store/CountStore.ts";//获取 store 实例 >>> proxy 不用.value
let countStore = useCountStore();
//获取jokeStore实例
let jokeStore = useJokeStore();
//定义用户选择的数据n
let n = ref(1); //用户选择的数值默认值为1;//定义递增或递减单击事件的回调函数const add = () => {//注意n是通过ref函数创建的,因此操作时需要通过n.valuecountStore.increment(n.value);
}
const minus = () => {countStore.decrement(n.value);
}
//定义三个数据都更新的回调函数://方式1:逐一更新
// const upData = () => {
// //方式一: 修改数据 三次
// // countStore.sum = 666;
// // countStore.school = "猿究院"
// // countStore.address = "北大街"//方式2:批量修改const upData = () => { countStore.$patch({sum: 666,school: "猿究院",address: "北大街"})}</script><style scoped>.count {background-color: skyblue;padding: 10px;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
}select, button {margin: 0 5px;height: 25px;
}</style>
3.测试结果展示:
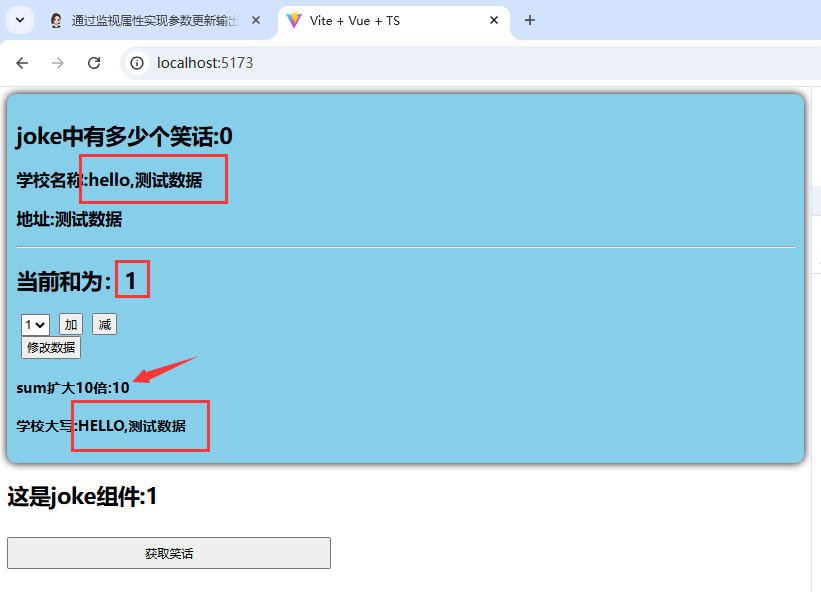
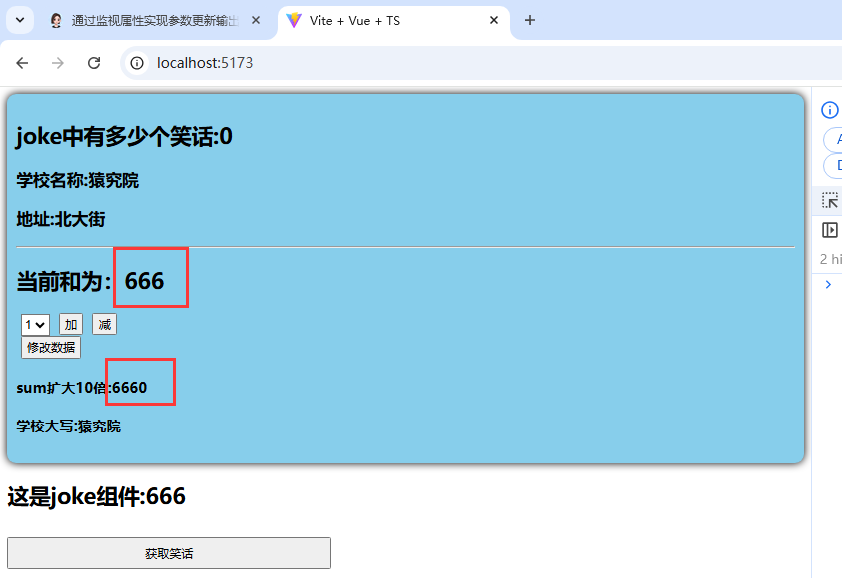
8.storeToRefs:
1.概述:
<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">storeToRefs</font> 是 <font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">Pinia</font> 库中的一个实用函数,主要用于从 <font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">Pinia</font> 商店(store)的状态(state)对象中创建响应式引用(reactive refs),以便在组件中更方便地使用商店中的数据。
2.使用:
在count组件和joke组件中引用store的数据:
//storeToRefs解构解析:只能解析出数据相关的内容,对于函数则无法解析;let{sum,school,address,bigSum,upperschool}=storeToRefs(countStore) let {jokeList}=storeToRefs(jokeStore)//解析后就可以在模板中直接使用了<template><div class="count"><!--获取jokestore的数据 --><h2>joke中有多少个笑话:{{ jokeList.length }}</h2>
<!--获取当前store的数据 --><h3>学校名称:{{ school }}</h3><h3>地址:{{ address }}</h3><hr/><h2>当前和为:{{ sum }}</h2><select v-model.number="n"><option>1</option><option>2</option><option>3</option></select><button @click="add">加</button><button @click="minus">减</button><br/><button @click="upData">修改数据</button><h4>sum扩大10倍:{{bigSum}}</h4><h4>学校大写:{{upperschool}}</h4></div></template>
3.测试:
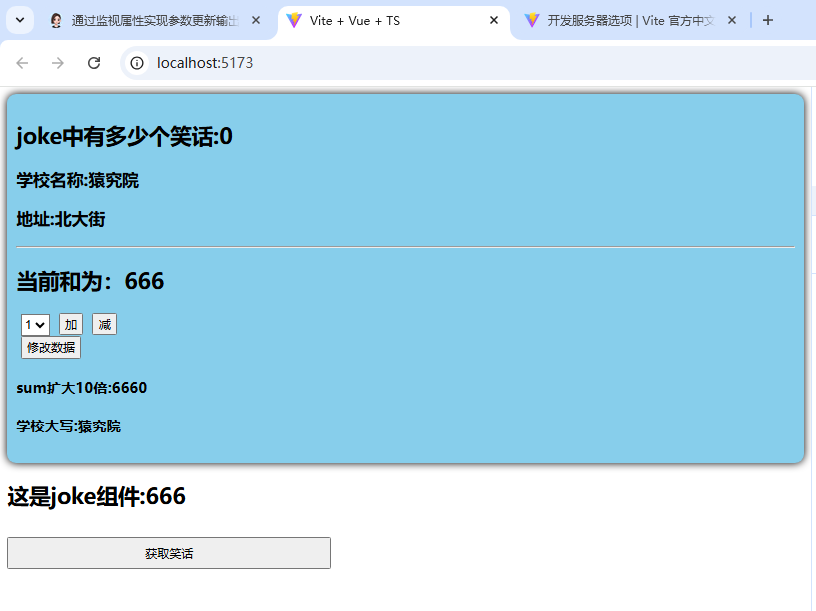
通过测试结果可以看出,此时仍可以正常展示数据;
9.store的组合式API写法:
1.概述:
上面案例中,我们再写store时,将数据,计算属性,函数分别写到了state,getters和actions属性中,而在组合式API写法中,则不再进行分开存储,而是将这些函数或数据定义在defineStore的第二个函数式参数中(上面的是对象式),最后通过return进行返回后就可以获取展示了;;
注意:**在组合式API写法中,不可以使用this,因为这个函数式参数类似于setup函数,其中的this为undefined;**
2.实现:
重新编写countStore.ts
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
import {computed, ref} from "vue";export const useCountStore = defineStore('countStore', () => {let sum = ref(1);let school = ref('hello,测试数据');let address = ref('测试数据');const increment = (value: number) => {if (sum < 10) {sum.value += value;}}const decrement = (value: number) => {if (sum > 1) {sum.value -= value;}}const bigSum = computed(()=>sum.value * 10);const upperschool =computed(()=>school.value.toUpperCase()) ;return {sum, school, address, increment, decrement, bigSum, upperschool}
})
3.测试:
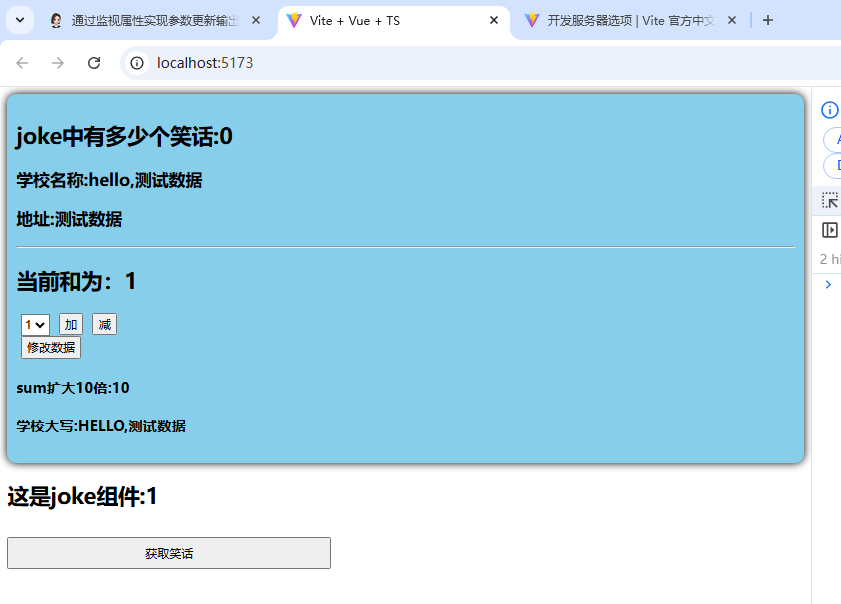
10.$subscribe监听
1.概述:
- 在 Pinia 中,
$subscribe是 store 实例的一个方法。它用于订阅整个 store 的状态变化。 - 每当 store 中的状态发生改变时,通过
$subscribe注册的回调函数就会被触发;
2.案例分析:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {state: () => ({count: 0}),actions: {increment () {this.count++}}
})
import { useCounterStore } from './store'const counterStore = useCounterStore()counterStore.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {console.log('store changed:', mutation)console.log('new state:', state)
})counterStore.increment()
说明:当调用increment方法改变count状态时,通过$subscribe注册的回调函数会被执行,在控制台打印出状态变化的相关信息和新的状态。
