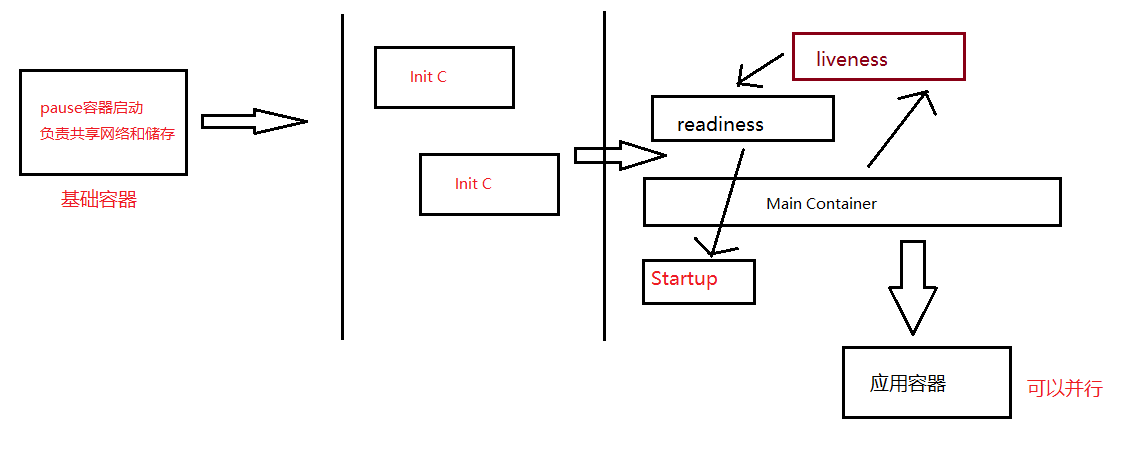
Pod的进阶
Pod 资源限制
在 Kubernetes 中,为了合理管理集群中的资源,容器的 CPU 和内存资源都可以设置请求值(requests)和限制值(limits)。这些设置确保了容器的资源分配和限制,避免资源争用和过度使用。
资源请求与限制(Request & Limit)
请求(request):当容器启动时,Kubernetes 会根据容器的资源请求来决定容器应该调度到哪个节点上。这个值表示容器在运行时最少需要的资源。
限制(limit):容器在运行时可以使用的最大资源量。如果容器超过了这个限制,Kubernetes 会采取措施来控制容器的资源使用,防止过度消耗。
官网示例:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-compute-resources-container/
//Pod 和 容器 的资源请求和限制:
spec.containers[].resources.requests.cpu //定义创建容器时预分配的CPU资源
spec.containers[].resources.requests.memory //定义创建容器时预分配的内存资源
spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpu //定义 cpu 的资源上限
spec.containers[].resources.limits.memory //定义内存的资源上限
vim resource.ymalapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata: # 也可以理解为标签name: frontend
spec:containers:- name: webimage: nginxenv:- name: WEB_ROOT_PASSWORDvalue: "password"resources:requests:memory: "64Mi" # 最少 64Mi 内存cpu: "250m" # 最少 0.25 CPUlimits:memory: "128Mi" # 最大 128Mi 内存cpu: "500m" # 最大 0.5 CPU- name: dbimage: mysqlenv:- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDvalue: "abc123"resources:requests:memory: "512Mi" # 最少 512Mi 内存cpu: "0.5" # 最少 0.5 CPUlimits:memory: "1Gi" # 最大 1Gi 内存cpu: "1" # 最大 1 CPU# 启动
kubectl apply -f resource.yaml查看节点
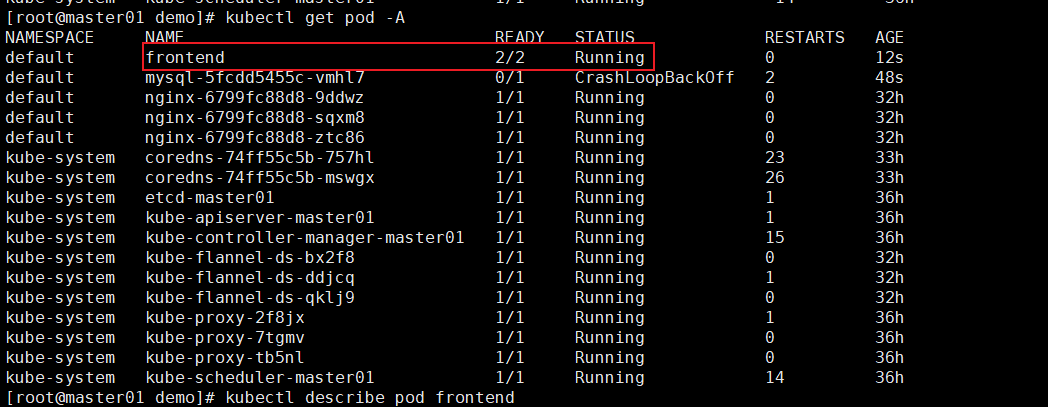
查看信息
# 详细信息
kubectl describe pod frontend# 查看pod资源分配情况
kubectl get pods -o wide# 查看节点资源
kubectl describe nodes node02
节点资源的信息(部分)
CPU 与内存资源分配的实际情况
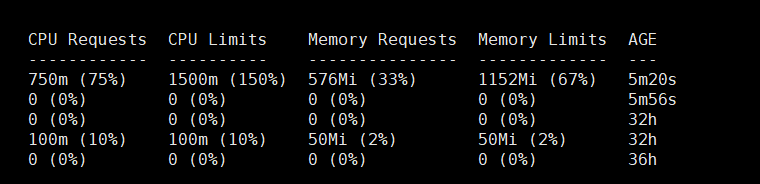
总结
资源请求与限制:
requests是容器启动时最少需要的资源,调度器依据该值选择节点。limits是容器能够使用的最大资源值,超出该值的资源请求会被限制。
自动匹配:
如果未设置
requests,Kubernetes 会自动将其设置为与limits相同。
资源的分配:
Pod 中多个容器的资源请求与限制会被加总,以便监控和调整节点的资源分配。
资源单位:
CPU 使用
m(毫核)表示,例如:500m表示 0.5 个 CPU。内存 使用标准的字节单位表示,通常推荐使用基于 2 的指数单位,如
Gi,Mi等。
探针的三种规则
| 探针类型 | 作用说明 | 探测失败时行为 | 默认状态 | 特殊说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| livenessProbe | 判断容器是否正在运行(存活) | kubelet 杀死容器 → 按 Pod 的 restartPolicy 决定是否重启 | Success | 随容器生命周期持续探测 |
| readinessProbe | 判断容器是否准备好接受请求(就绪) | 将该 Pod IP 从对应 Service 的 Endpoints 中剔除 | Success | 在首次探测成功前,Pod 处于 NotReady;只有 Success 后才会变为 Ready |
| startupProbe | 判断容器内的应用是否已启动(针对启动慢或启动时间不确定的应用) v1.17 引入 | 失败:kubelet 杀死容器 → 按 restartPolicy 重启; 成功前,其他探针均不生效 | Success | 成功前,livenessProbe/readinessProbe 被禁用;成功后交由其他探针接管探测 |
Probe支持三种检查方法
| 探测方式 | 工作原理 | 成功条件 | 典型使用场景示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| exec | 在容器内执行指定命令 | 命令退出返回码为 0 | 运行自定义脚本、检查本地文件/进程等 |
| tcpSocket | 对容器 IP 的指定端口做 TCP 三次握手检测 | 端口可建立 TCP 连接(打开) | 数据库、缓存等非 HTTP 服务的端口监听检测 |
| httpGet | 对容器 IP 的指定端口和路径发起 HTTP GET 请求 | 响应状态码 ≥200 且 <400 | Web 服务的健康检查接口 |
liveness-exec
vim exec.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: liveness-execnamespace: default
spec:containers:- name: liveness-exec-containerimage: busyboximagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentcommand: ["/bin/sh","-c","touch /tmp/live ; sleep 30; rm -rf /tmp/live; sleep 60"] # livenessProbe:exec:command: ["test","-e","/tmp/live"]initialDelaySeconds: 1periodSeconds: 3# 运行
kubectl create -f exec.yaml描述节点信息
kubectl describe pods liveness-exec截取部分
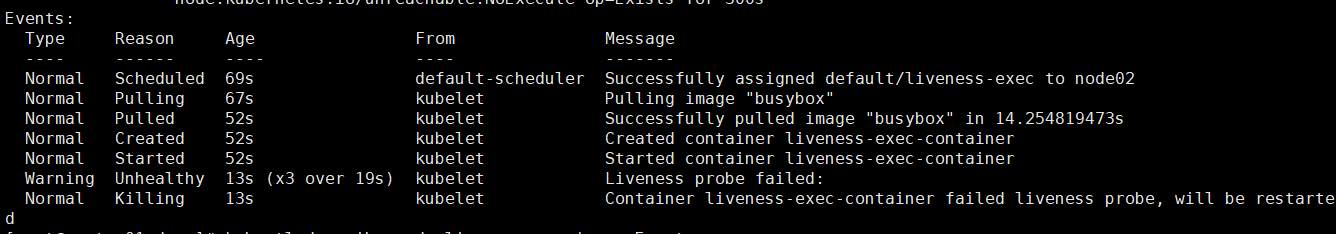
实时监控
kubectl get pod -w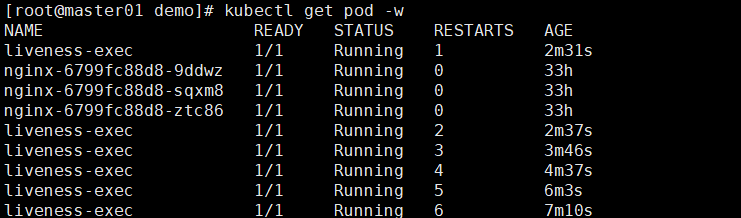
httpget
vim httpget.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: liveness-httpgetnamespace: default
spec:containers:- name: liveness-httpget-containerimage: nginximagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80livenessProbe:httpGet:port: http # 80端口path: /index.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 1periodSeconds: 3timeoutSeconds: 10
验证是否创建成功
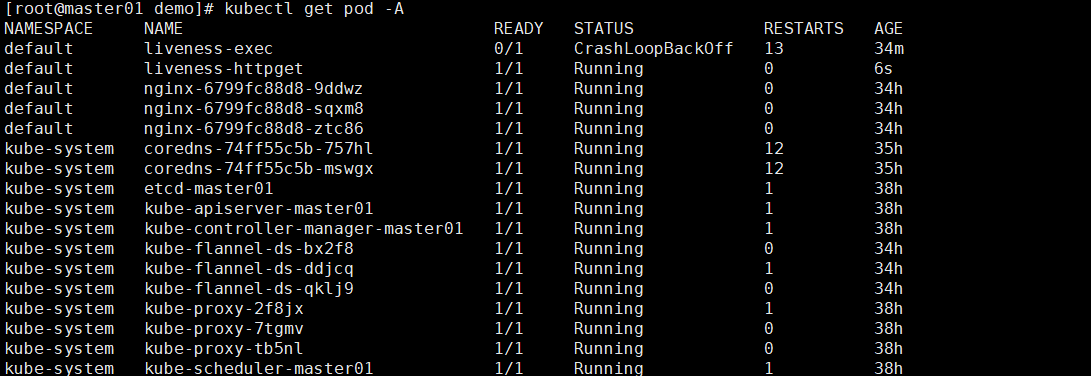
删除容器里面的html文件
kubectl exec -it liveness-httpget -- rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html判断容器被是或否被杀死,然后重启
kubectl describe pod liveness-httpget | grep -E 'Killing|Started|Liveness'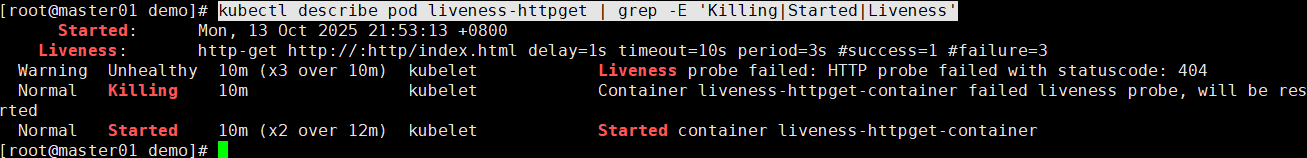
也可以通过节点查看
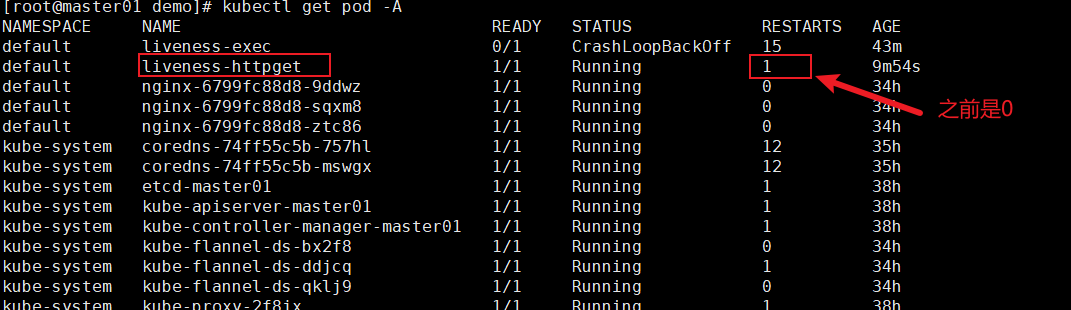
tcpsocket
vim tcpsocket.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: probe-tcp
spec:containers:- name: nginximage: soscscs/myapp:v1livenessProbe:initialDelaySeconds: 5timeoutSeconds: 1tcpSocket:port: 8080periodSeconds: 10failureThreshold: 2kubectl create -f tcpsocket.yaml
kubectl get pods -w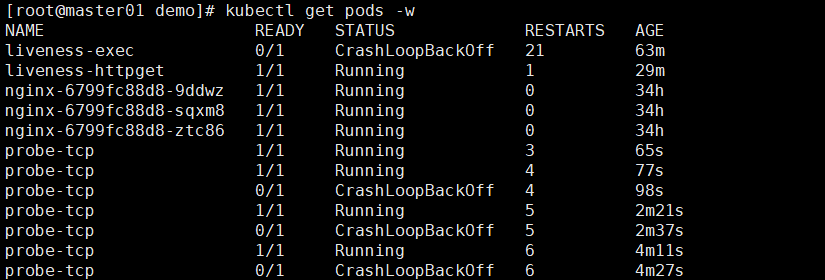
这里因为没有监测到8080端口,所以它一直崩溃
准备就绪
vim readiness-httpget.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: readiness-httpgetnamespace: default
spec:containers:- name: readiness-httpget-containerimage: soscscs/myapp:v1imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80readinessProbe:httpGet:port: 80path: /index1.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 1periodSeconds: 3livenessProbe:httpGet:port: httppath: /index.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 1periodSeconds: 3timeoutSeconds: 10kubectl create -f readiness-httpget.yamlkubectl exec -it readiness-httpget sh
cd /usr/share/nginx/html/
ls
50x.html index.html
echo 123 > index1.html
exitkubectl get pods 此时节点的状态
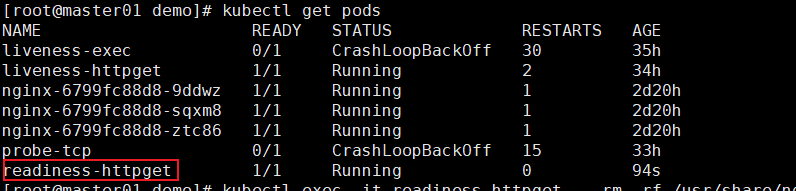
删除index.html
kubectl exec -it readiness-httpget -- rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/index.htmlkubectl get pods -w监测状态
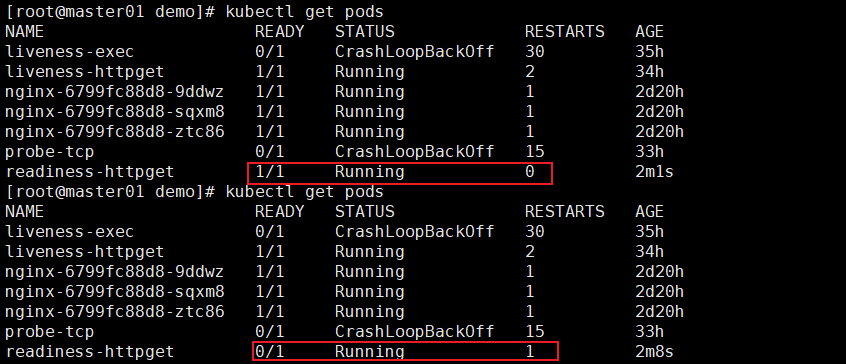
就绪监测2
vim readiness-myapp.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: myapp1labels:app: myapp
spec:containers:- name: myappimage: soscscs/myapp:v1ports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80readinessProbe:httpGet:port: 80path: /index.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 5periodSeconds: 5timeoutSeconds: 10
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: myapp2labels:app: myapp
spec:containers:- name: myappimage: soscscs/myapp:v1ports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80readinessProbe:httpGet:port: 80path: /index.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 5periodSeconds: 5timeoutSeconds: 10
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: myapp3labels:app: myapp
spec:containers:- name: myappimage: soscscs/myapp:v1ports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80readinessProbe:httpGet:port: 80path: /index.htmlinitialDelaySeconds: 5periodSeconds: 5timeoutSeconds: 10
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: myapp
spec:selector:app: myapptype: ClusterIPports:- name: httpport: 80targetPort: 80kubectl create -f readiness-myapp.yaml
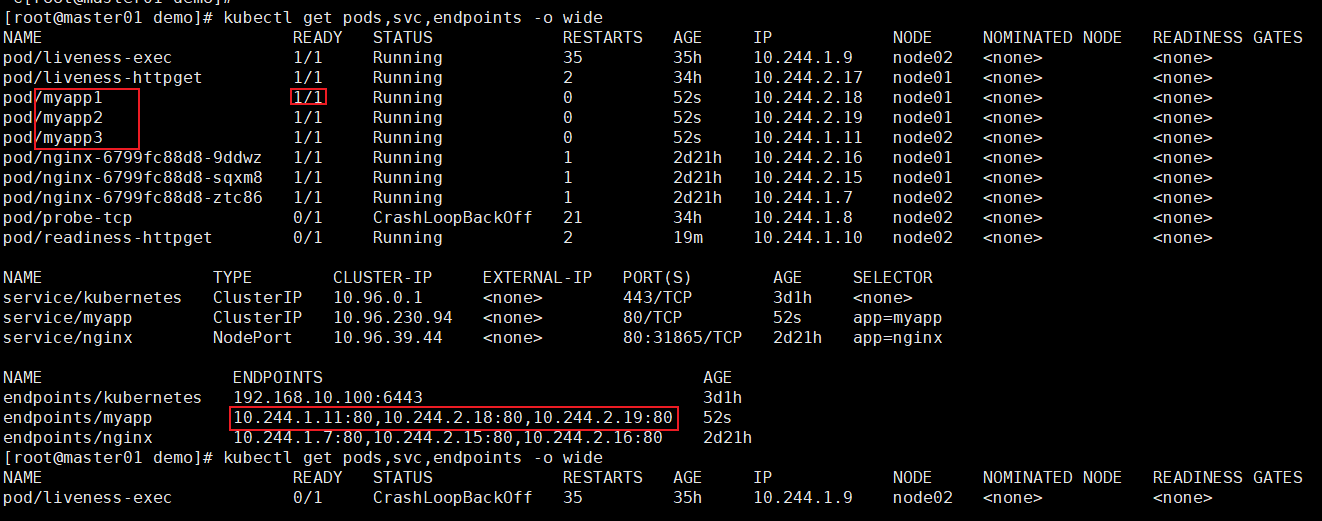
删除index.html
kubectl exec -it pod/myapp1 -- rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html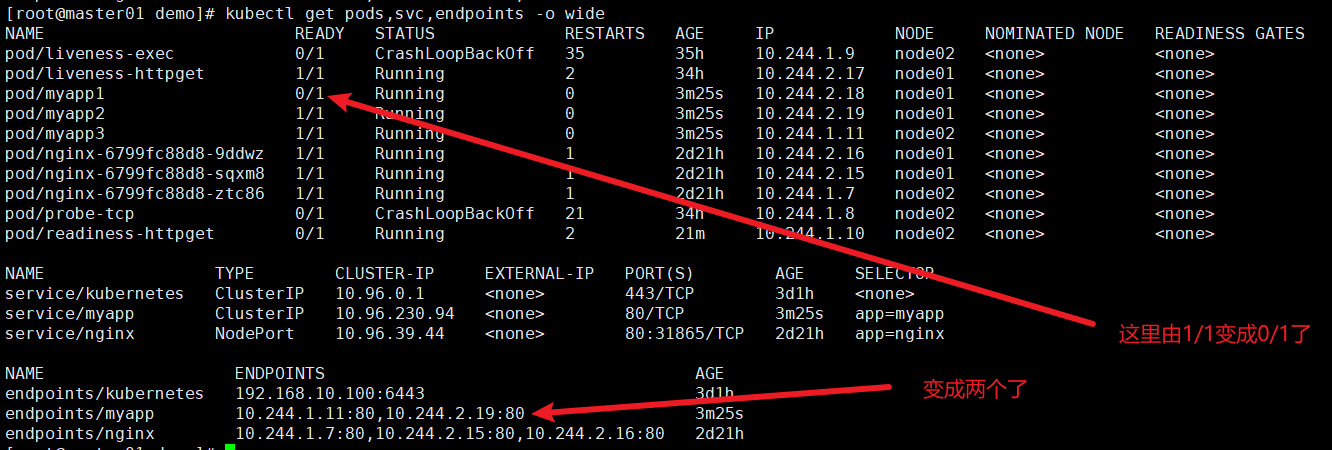
pod的生命周期