数据结构——二叉树的从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
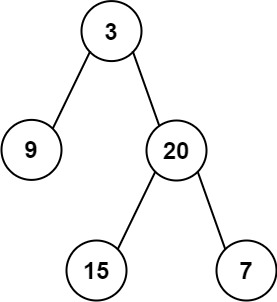
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
核心依据:两种遍历的特性
前序遍历:顺序为「根节点 → 左子树 → 右子树」,即第一个元素必然是当前子树的根节点。
中序遍历:顺序为「左子树 → 根节点 → 右子树」,即根节点左侧的元素都属于左子树,右侧的元素都属于右子树。
- 初始化与入口
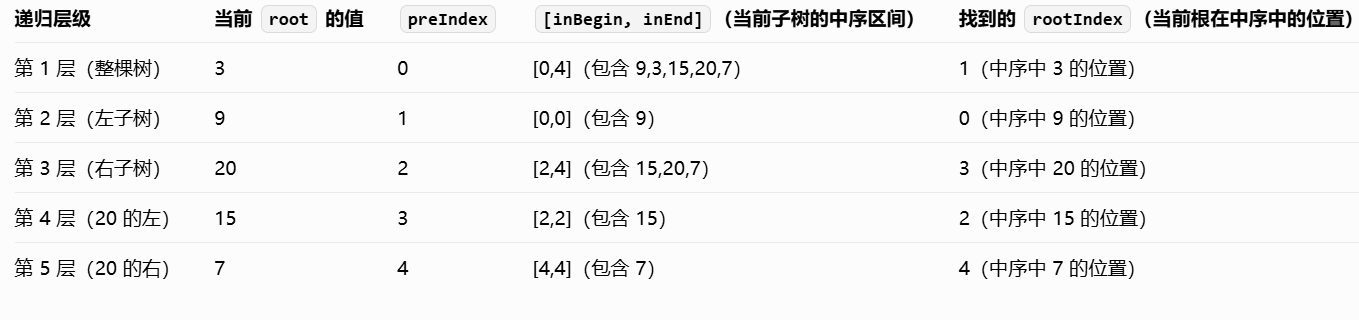
定义全局变量 preIndex,用于记录前序遍历中「当前根节点」的位置(从 0 开始)。
主方法 buildTree 调用辅助方法 buildTreeChild,并传入中序遍历的初始区间 [0, inorder.length-1](表示整棵树的中序范围)。 - 递归构建子树(buildTreeChild 方法)
该方法的作用是:根据当前子树的中序区间 [inBegin, inEnd],构建并返回当前子树的根节点。
① 终止条件
如果 inBegin > inEnd,说明当前区间内没有节点(子树为空),返回 null。
② 确定当前子树的根节点
从前序遍历的 preIndex 位置取元素,创建当前子树的根节点 root。
preIndex 自增(因为下一次递归需要处理前序遍历的下一个元素,即下一个子树的根)。
③ 定位根节点在中序中的位置
调用 findRootIndex 方法,在中序区间 [inBegin, inEnd] 内找到 root.val 对应的索引 rootIndex。这个索引是划分左、右子树的关键。
④ 递归构建左、右子树并挂载
左子树:中序区间为 [inBegin, rootIndex-1](根节点左侧的元素),递归调用 buildTreeChild 得到左子树的根,挂载到 root.left。
右子树:中序区间为 [rootIndex+1, inEnd](根节点右侧的元素),递归调用 buildTreeChild 得到右子树的根,挂载到 root.right。
⑤ 返回当前子树的根节点
将构建好的当前子树的根节点 root 返回,供上层递归挂载。 - 辅助方法:查找中序中根节点的位置(findRootIndex)
在中序数组的 [inBegin, inEnd] 区间内遍历,找到值为 key(当前根节点的值)的元素索引并返回。限定区间是为了避免找到其他子树的同名节点,确保准确性。
class Solution {
// 记录前序遍历的当前节点索引int preIndex = 0; public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {// 采用的递归的方法return buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);}public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {// 区间无效(无节点),返回null这时候说明二叉树已经创建好了递归可以结束了if (inBegin > inEnd) {return null;}// 前序的当前节点作为根节点TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);// 前序索引后移,指向下一个根节点preIndex++; // 在中序中找到根节点的位置int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder, root.val, inBegin, inEnd);// 递归构建左子树(中序左区间)和右子树(中序右区间)root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, inBegin, rootIndex - 1);
// 在每一个root变化的时候,子树的范围也在变化
//按着上面的图来说
/*假设前序遍历为 [1,2,3,4],中序遍历为 [2,1,3,4]:
第一层递归:
preIndex=0,root.val = preorder[0] = 1,此时 “根节点” 是整棵树的根(值为 1)。
在中序 [2,1,3,4] 中找 1 的位置,得到 rootIndex=1,划分左子树区间 [0,0](值 2)和右子树区间 [2,3](值 3,4)。
第二层递归(构建左子树):
preIndex=1(已递增),root.val = preorder[1] = 2,此时 “根节点” 是左子树的根(值为 2)。
在中序左区间 [0,0] 中找 2 的位置,得到 rootIndex=0,其左 / 右区间均无效(终止递归)。
第三层递归(构建右子树):
preIndex=2,root.val = preorder[2] = 3,此时 “根节点” 是右子树的根(值为 3)。
在中序右区间 [2,3] 中找 3 的位置,得到 rootIndex=2,划分右子树的右区间 [3,3](值 4)。
第四层递归(构建 3 的右子树):
preIndex=3,root.val = preorder[3] = 4,此时 “根节点” 是 3 的右子树的根(值为 4)。
在中序区间 [3,3] 中找 4 的位置,得到 rootIndex=3,递归终止。
*/root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
//二叉树创建完成就是比如说root = 3,那就是3.right = 9差不多就是这样子的return root;}// 在中序遍历的[inBegin, inEnd]区间内找根节点的索引//但是其实不加inBegin,inend也可以,但是可以避免全数组遍历导致错误。public int findRootIndex(int[] inorder, int key, int inBegin, int inEnd) {for (int i = inBegin; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (key == inorder[i]) {return i;}}return -1; }
}
假设前序遍历为 [1,2,3,4],中序遍历为 [2,1,3,4]:
第一层递归:
preIndex=0,root.val = preorder[0] = 1,此时 “根节点” 是整棵树的根(值为 1)。
在中序 [2,1,3,4] 中找 1 的位置,得到 rootIndex=1,划分左子树区间 [0,0](值 2)和右子树区间 [2,3](值 3,4)。
第二层递归(构建左子树):
preIndex=1(已递增),root.val = preorder[1] = 2,此时 “根节点” 是左子树的根(值为 2)。
在中序左区间 [0,0] 中找 2 的位置,得到 rootIndex=0,其左 / 右区间均无效(终止递归)。
第三层递归(构建右子树):
preIndex=2,root.val = preorder[2] = 3,此时 “根节点” 是右子树的根(值为 3)。
在中序右区间 [2,3] 中找 3 的位置,得到 rootIndex=2,划分右子树的右区间 [3,3](值 4)。
第四层递归(构建 3 的右子树):
preIndex=3,root.val = preorder[3] = 4,此时 “根节点” 是 3 的右子树的根(值为 4)。
在中序区间 [3,3] 中找 4 的位置,得到 rootIndex=3,递归终止。