JavaEE初级——Thread多线程
多线程
- 认识线程
- 线程的概念
- 创建线程
- Thread类
- Thread常见的构造函数
- Thread常见属性
- Thread中常用方法
- 线程的状态
认识线程
线程的概念
一个线程就是一个执行流,每一个线程都可以按照顺序执行自己代码,多个线程可以“同时”执行
多线程是并发编程的刚需
随着不断发展,单核CPU发展遇到了瓶颈,为了提高算力,就开始采用多核CPU,并发编程可以很好利用多核CPU
并且线程比进程更轻量,也程轻量级进程
创建 / 销毁 / 调度线程的效率多比进程快
创建线程
| 创建线程常用方法 |
|---|
| 继承 Thread, 重写 run |
| 实现 Runnable, 重写 run |
| 继承 Thread, 重写 run, 使用匿名内部类 |
| 实现 Runnable, 重写 run, 使用匿名内部类 |
| 使用 lambda 表达式 |
1.继承 Thread, 重写 run
class MyThread extends Thread{
//重写其Thread中的run方法@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("hello Thread");}
}
public class demo {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new MyThread();t.start();System.out.println("hello main");}
}2.实现 Runnable, 重写 run
class MyRunnalbe implements Runnable{//实现run方法@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("hello Thread");}
}
public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//传入Runnable对象MyRunnalbe myRunnalbe = new MyRunnalbe();Thread t = new Thread(myRunnalbe);t.start();System.out.println("hello main");}}3.继承 Thread, 重写 run, 使用匿名内部类
//使用匿名内部类实现
public class demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("hello Thread");}};t.start();System.out.println("hello main");}
}4.实现 Runnable, 重写 run, 使用匿名内部类
public class demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("hello Thread");}});t.start();System.out.println("hello main");}
}5.使用 lambda 表达式
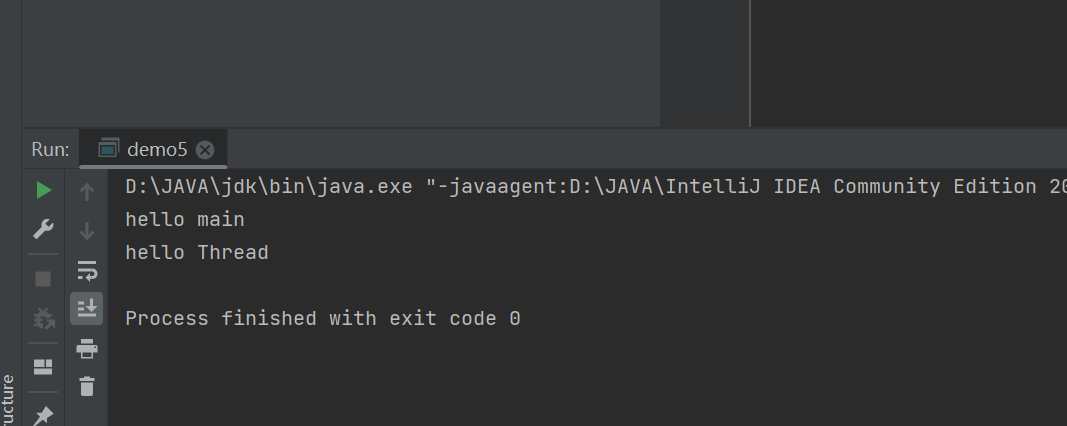
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(()->{System.out.println("hello Thread");});t.start();System.out.println("hello main");}
}
运行结果如下,但是其两个线程执行顺序是不确定的,所以结果有两种
一种先打印 hello main hello Thread,另一种就相反的顺序
t.start()是开启线程
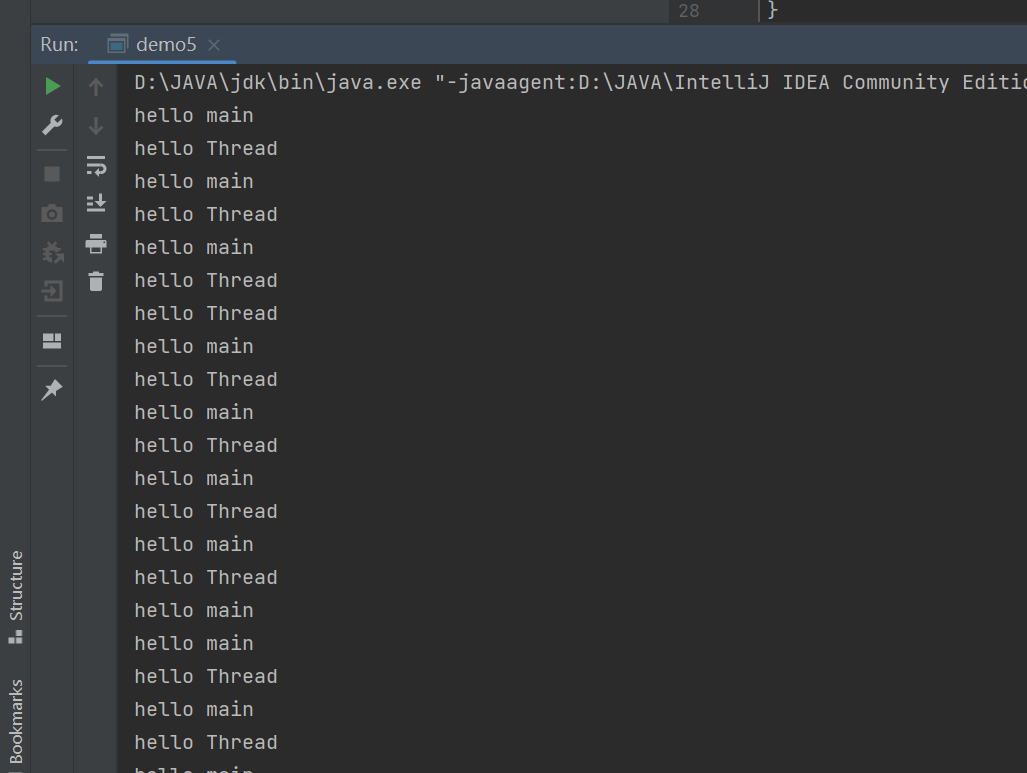
public class demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(()->{while (true){System.out.println("hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t.start();while (true){System.out.println("hello main");Thread.sleep(100);}}
}
上面这个代码是一直执行main和Thread这两个线程,并且执行顺序是不确定的,线程是和平常调用函数是不一样的,因为函数调用是会一直等函数执行完才可以执行下面的语句,因此如果这里是函数调用的话,只会出现一个值,要么一直打印hello Thread,要么是一直打印hello main
上面看似有5种,其实相当于三种,重写run方法,实现Runnable接口,使用lambda表达式
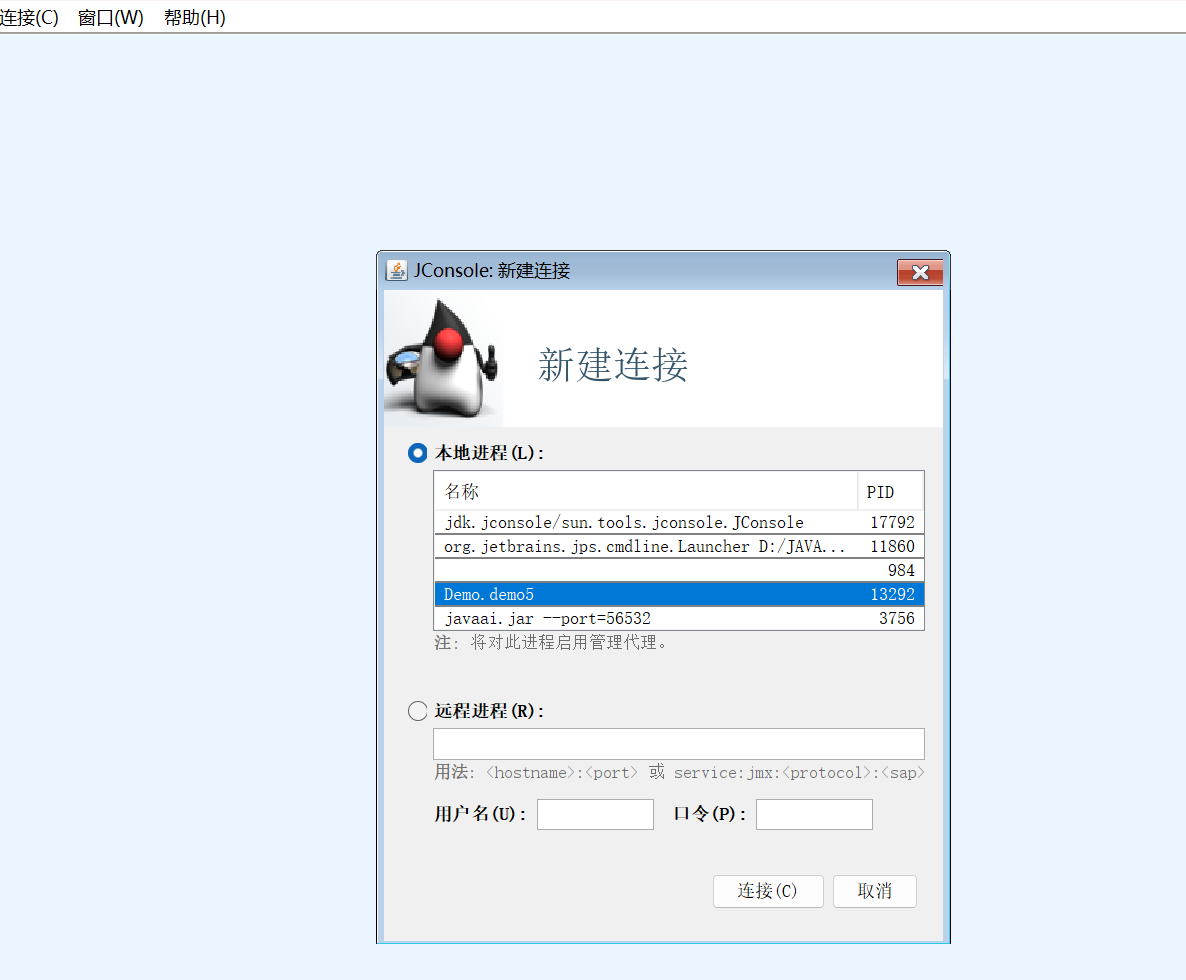
使用jdk目录下的bin目录中的的jconsole 来找出对应的线程文件,在这里面就可以找到我们创建的线程,此时main是线程,Thread-0也是我们创建的线程,由于我们创建的时候并没有给其命名,所以其系统自动命名为Thread - 数字
Thread类
Thread常见的构造函数
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Thread() | 创建线程对象 |
| Thread(Runnable target) | 使用Runnable对象创建线程对象 |
| public Thread(String name) | 创建线程对象,并命名 |
| public Thread(Runnable target, String name) | 使用Runnable对象创建线程对象,并命名 |
| public Thread(Runnable target, String name) | 线程分组管理 |
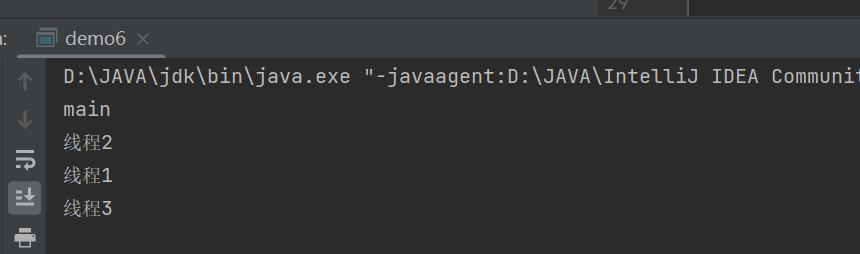
public class demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());},"线程1");Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());},"线程2");Thread t3 = new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());},"线程3");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();System.out.println("main");}
}运行结果如下,但是顺序是不确定的,可以看出给线程命名成功
这里的**Thread.currentThread()**是获取当前Thread线程对象,**getName()**是获取当前线程的名称
Thread常见属性
| 属性 | 获取方法 |
|---|---|
| ID | getId() |
| 名称 | getName() |
| 状态 | getState() |
| 优先级 | getPriority() |
| 是否后台线程 | isDaemon() |
| 是否存活 | isAlive() |
| 是否被中断 | isInterrupted() |
ID:是线程的唯一标识,不同线程不会重复
名称:就是线程的名字,这里可以自己命名,系统自动命名是Thread-数字
状态:表示线程的情况,这里可以简单认为阻塞和就绪,细说的话有好几种状态
优先级:我们可以给线程设置优先级,优先级高的先执行,但是对于像Windows、Lunix等高级系统,不能只看优先级,谁先执行决定权还是在操作系统
后台线程:也称守护线程,后台线程不会阻断整个线程结束,而前台线程会阻断整个线程结束,并且所有非后台进程结束,才算真的结束
存活:线程是否在执行,简单理解是run方法是否结束
中断:停止某一个线程运行
下面进行详细讲解
getName()获取线程名,默认为Thread - 数字
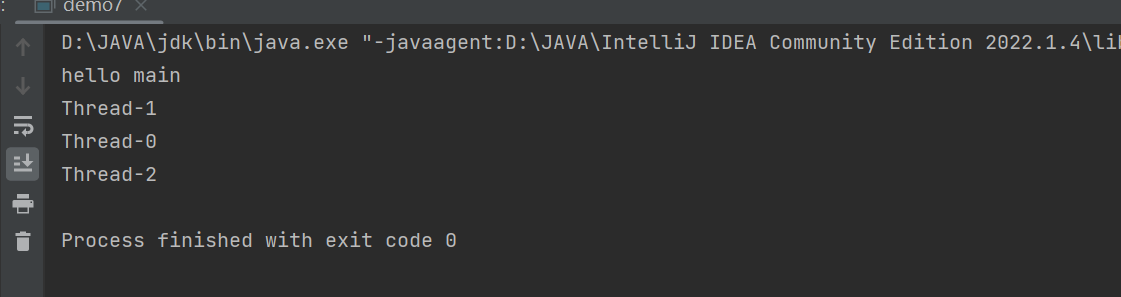
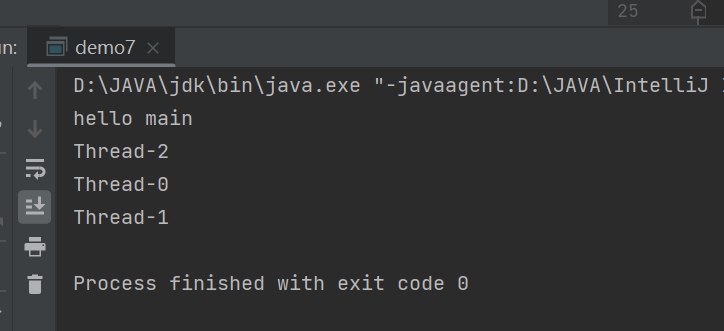
public class demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(()->{//获取线程名System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{//获取线程名System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());});Thread t3 = new Thread(()->{//获取线程名System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());});t.start();t2.start();t3.start();System.out.println("hello main");}
}
结果如下,其顺序是不确定的
isDaemon(),将一个线程设置为后台线程
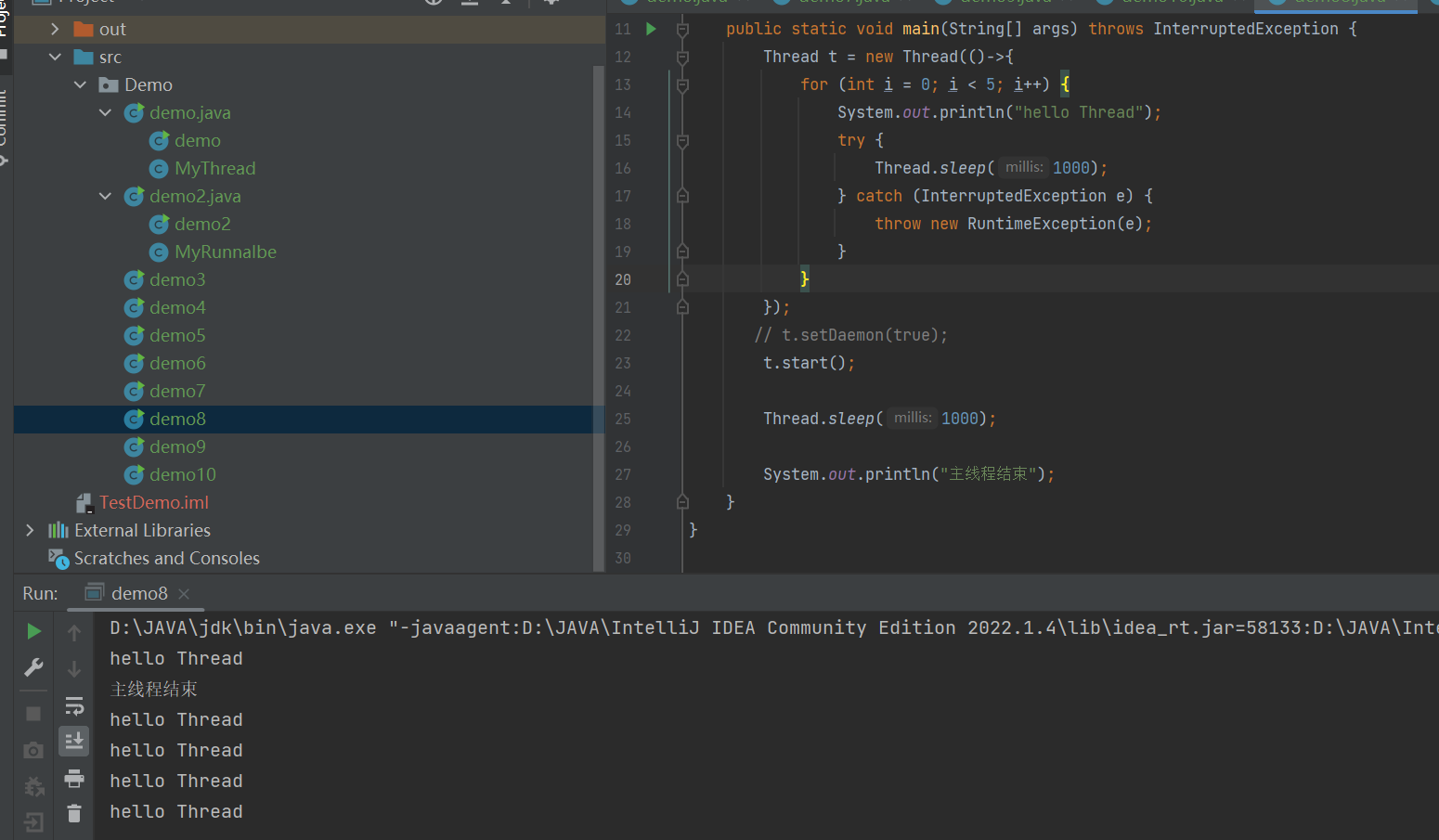
public class demo8 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});
//设置其为后端线程(守护线程)t.setDaemon(true);t.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("主线程结束");}
}
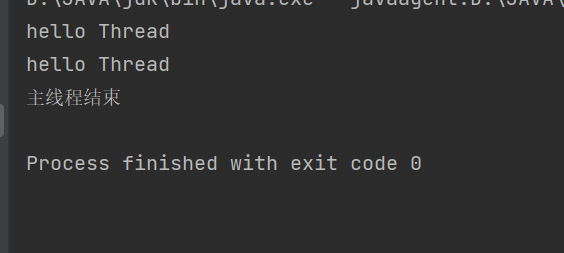
可以看出这里的后端线程没有执行完,但是前台线程执行完了,此时就结束了
如果不设置后端线程,其t线程和main线程都执行完才结束
Thread中常用方法
1.休眠当前线程 参数是休眠时间,一个是休眠当前线程millis毫秒,一个更精确
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static native void sleep(long millis) | 休眠当前线程millis毫秒 |
| public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos) | 同理,就是精度提高了 |
但是sleep(0)是特殊情况,属于线程主动放权,起到降低CPU的使用率,在资源紧张的时候,可能会进行一些合理的调整
中断一个线程
使用自己定义的一个标志位进行中断线程
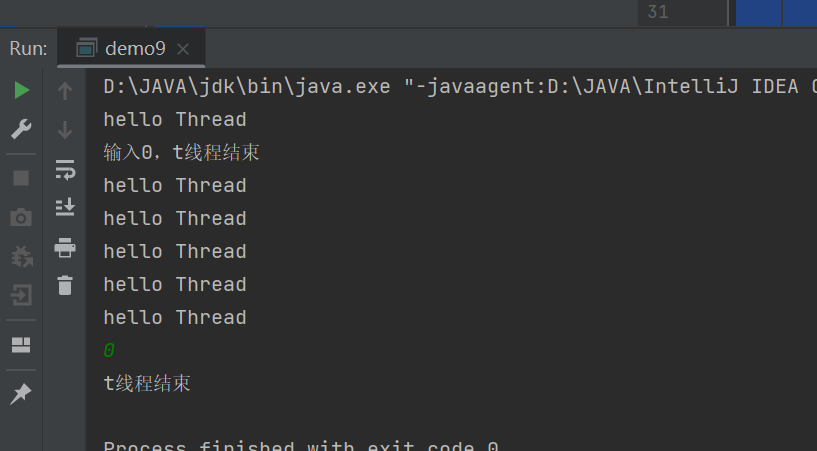
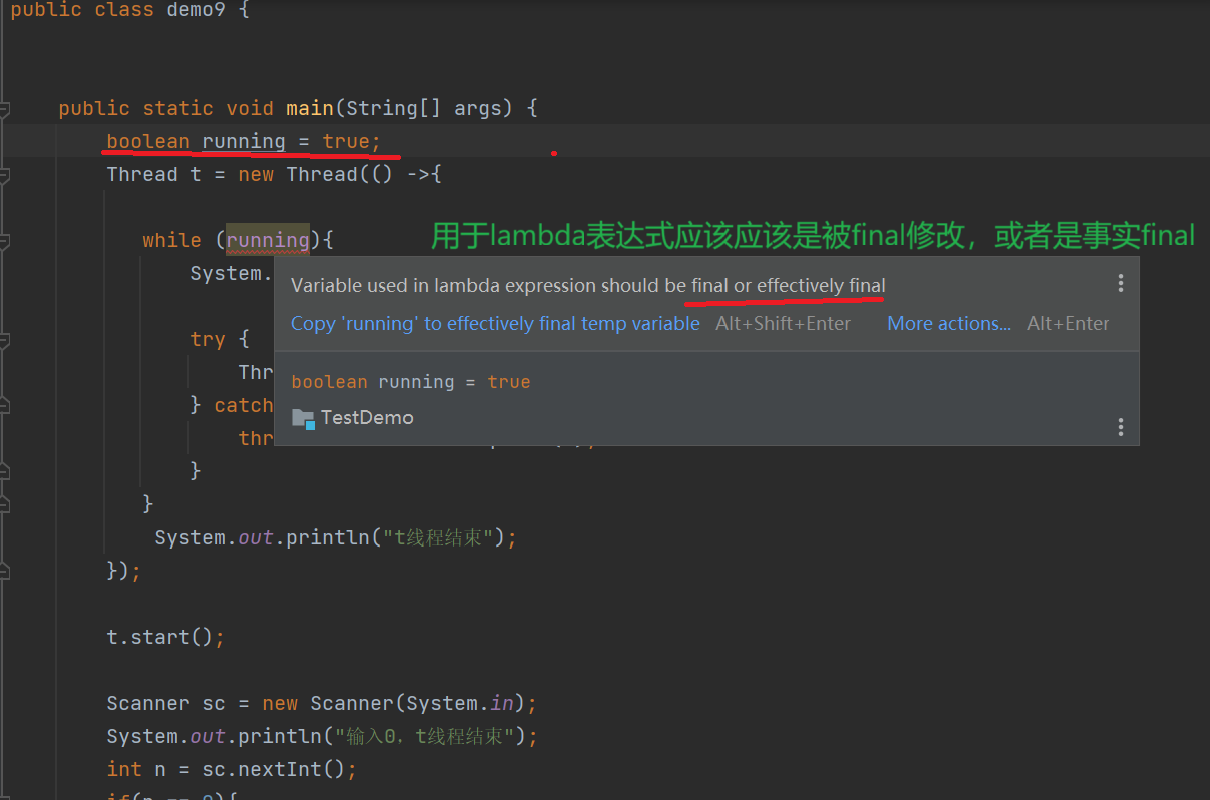
//中断一个线程
public class demo9 {private static boolean running = true;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(() ->{while (running){System.out.println("hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("t线程结束");});t.start();Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入0,t线程结束");int n = sc.nextInt();if(n == 0){running = false;}}
}运行结果如下
但是这个标识符要注意位置
像下面这样,将这个标识符放到main函数中,这样就会出现变量捕获
java中变量捕获,其实就是变量的一份拷贝,一旦拷贝了不一样可能会导致代码混乱,所以说java直接禁止了修改
但是可以像上面一样写成成员变量,这里就变成内部类访问外部类成员,这个是可以访问的
使用interrupted()和isInterrupted()来代替标志位
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void interrupt() | 中断其对象关联的线程,如果线程阻塞,以异常的方式,反之设置标志位 |
| public boolean isInterrupted() | 判断当前线程中断标志位是否设置,不清理中断标志位 |
| public static Thread currentThread() | 返回当前线程对象的引用 |
public class demo10 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t = new Thread(() -> {while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {System.out.println("hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});t.start();Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入0,阻断t线程");int n = sc.nextInt();if(n == 0){t.interrupt();}}
}
此时就会直接中断sleep
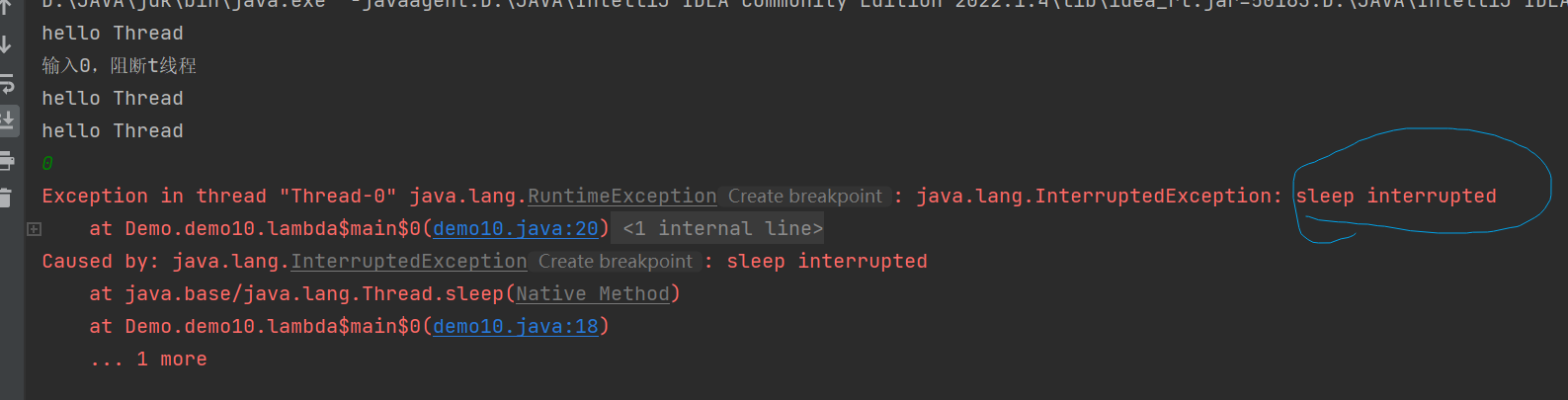
当线程因为wait/jioin/sleep方法引起阻塞,会以InterruptedException异常的形式通知,并中断标志,当然接不接书线程,主要还是取决于catch中是如何处理的
等待一个线程 join
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void join() | 等待线程结束 |
| public void join(long millis) | 等待线程结束,最多等millis毫秒 |
| public void join(long millis,int nanos | 和上面一样,但是时间的精度更高 |
有时候需要等待一个线程结束,才进行其他步骤
public class demo11 {private static int sum = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//创建一个线程,计算1 ~ 1000Thread t = new Thread(() ->{for(int i = 1;i <= 1000;i++){sum += i;}});t.start();//这里main线程要等到其t线程执行完才可以执行t.join();System.out.println(sum);}
}
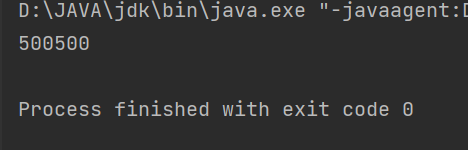
此时如果不等待t线程结束,拿此时main线程打印的sum值就不正确
线程的状态
| 状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NEW | 安排了,工作还没做 |
| RUNNABLE | 可工作的,又可以分为正在工作和准备开始工作 |
| TERMINATED | 工作完成了,线程已经销毁,但Thread对象还在 |
| WAITING | 标识在等待,死等状态 |
| TIMED_WAITING | 有时间限制的等待 |
| BLOCKED | 等待,特指由锁引起的等待 |
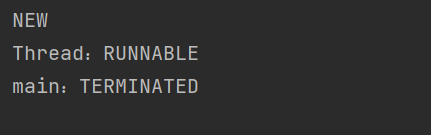
public class demo12 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(() ->{System.out.println("Thread:"+Thread.currentThread().getState());});System.out.println(t.getState());t.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("main:"+t.getState());}
}
此时先打印NEW,此时t线程都没有启动,t需要等到start才能执行
启动后 RUNNABLE 正在执行或准备执行,最后TERMINATED,说明已经执行完了
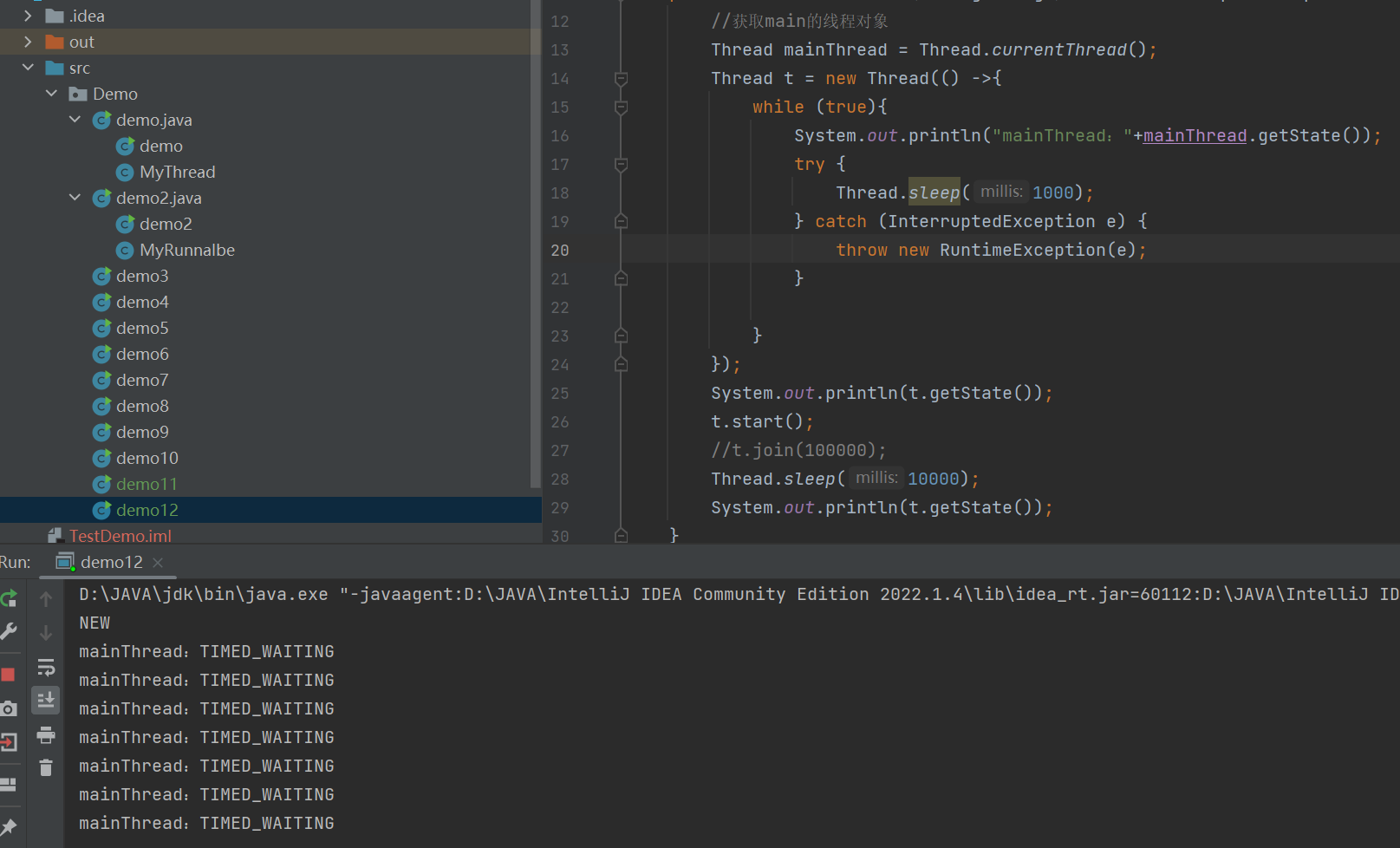
public class demo12 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//获取main的线程对象Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();Thread t = new Thread(() ->{while (true){System.out.println("mainThread:"+mainThread.getState());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});System.out.println(t.getState());t.start();t.join();System.out.println(t.getState());}
}
此时main线程要等待t线程执行完毕,并且这里是死等,因此t线程在执行时候,mainThread状态是 WAITING
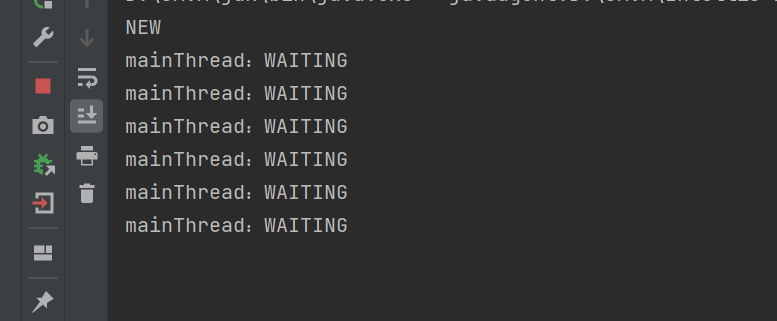
public class demo12 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//获取main的线程对象Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();Thread t = new Thread(() ->{while (true){System.out.println("mainThread:"+mainThread.getState());try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});System.out.println(t.getState());t.start();t.join(100000);System.out.println(t.getState());}
}
有时间限制的等待
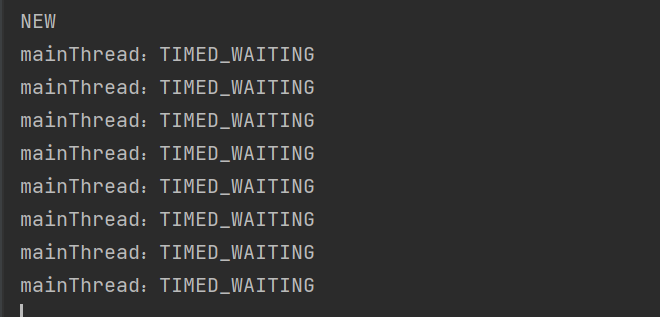
当然使用sleep也是同样的效果