memcpy 简单实现
今天我们来看一下memcpy的实现,虽然看起来很简单,但是要考虑两个坑,大家查缺补漏一下,当然在arm上可以借助neon simd之类的加速,但是我们这波先不考虑
简单实现
搞清楚了了入参和返回参类型,直接使用unsigned char* 开启while循环搬运完成
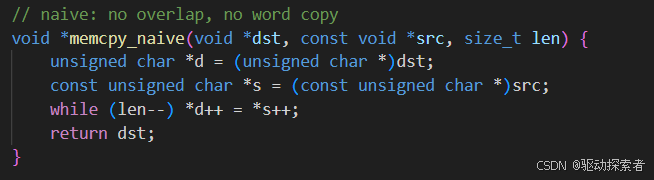
考虑重叠问题
当src dst buf出现重叠区域的时候会发现src buf在搬运的过程中,未搬运部分有可能被提前写入,导致src数据丢失,需要分类讨论,从左往右或者从右往左搬运
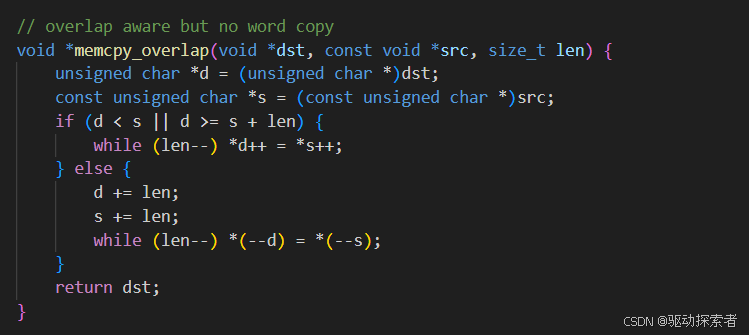
考虑效率问题
但是每次搬运一个char也太慢了,所以能每次可以搬运一个unsigned int肯定比char效率高,但是涉及到dst src len三个参数的align,看来很多实现,好像对dst和src的align考虑不是特别严格,只用管len的align,所以代码如下
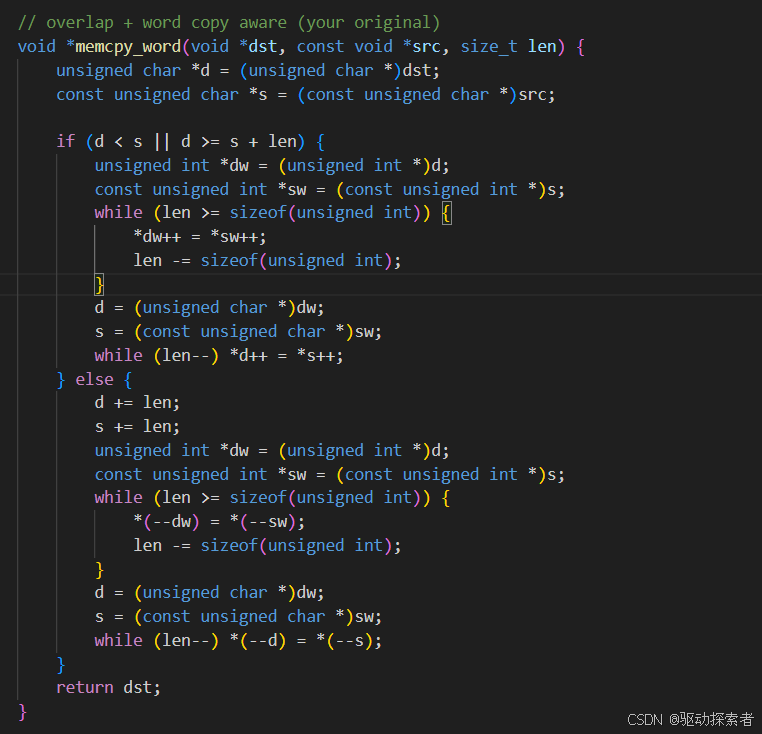
测试程序
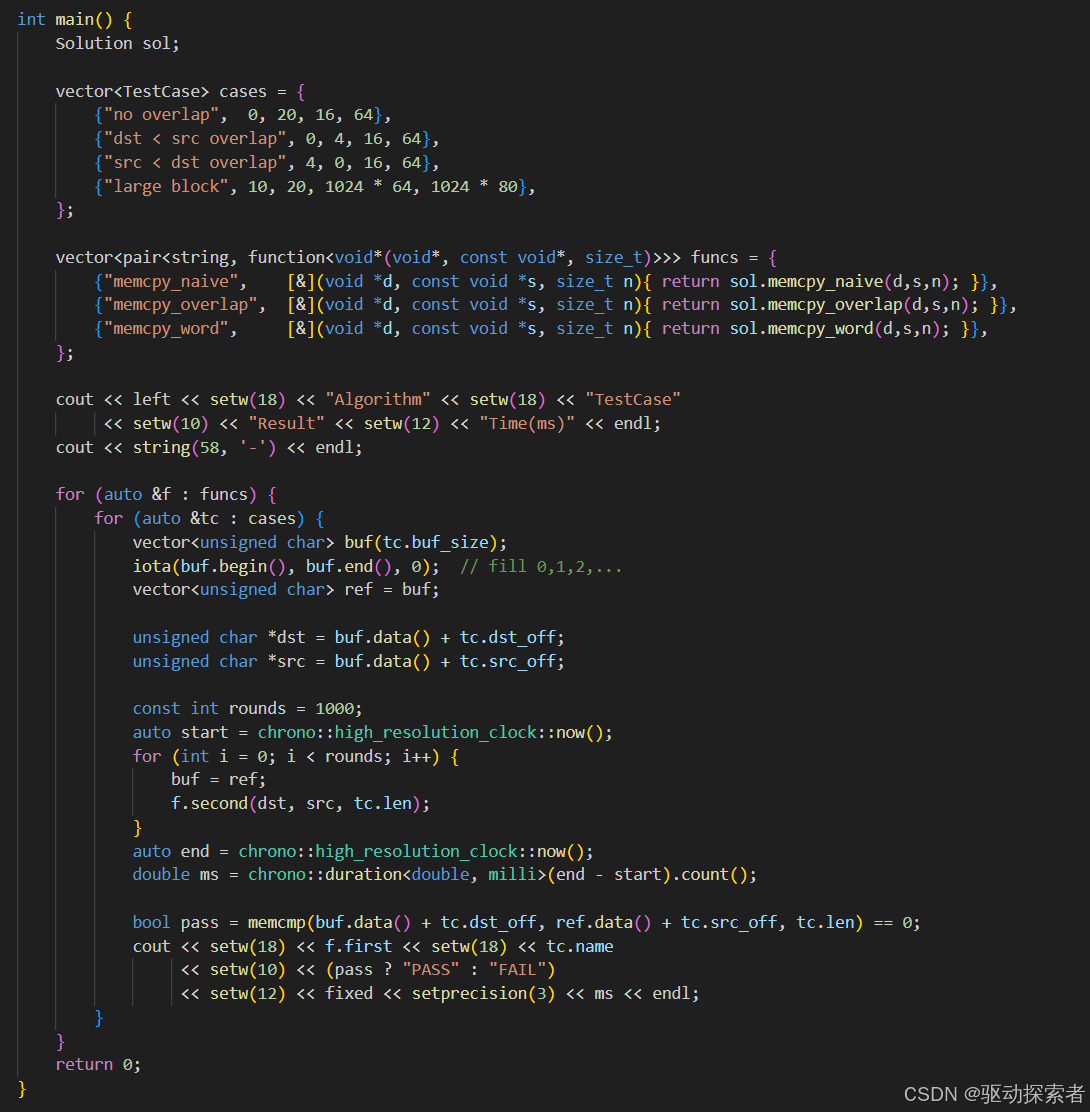
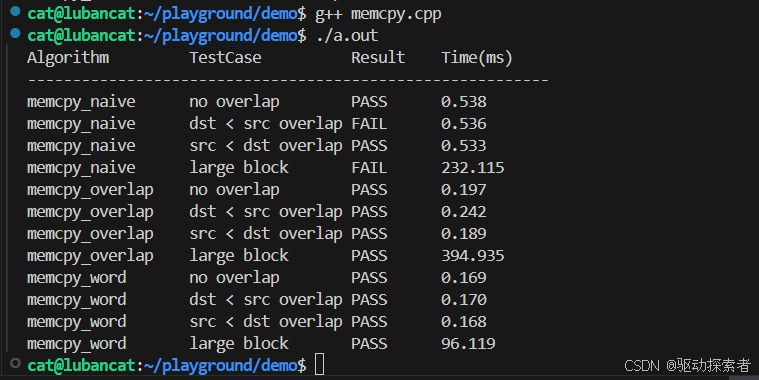
可以看到方法三是正确率和效率都比较ok的
整体代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:// naive: no overlap, no word copyvoid *memcpy_naive(void *dst, const void *src, size_t len) {unsigned char *d = (unsigned char *)dst;const unsigned char *s = (const unsigned char *)src;while (len--) *d++ = *s++;return dst;}// overlap aware but no word copyvoid *memcpy_overlap(void *dst, const void *src, size_t len) {unsigned char *d = (unsigned char *)dst;const unsigned char *s = (const unsigned char *)src;if (d < s || d >= s + len) {while (len--) *d++ = *s++;} else {d += len;s += len;while (len--) *(--d) = *(--s);}return dst;}// overlap + word copy aware (your original)void *memcpy_word(void *dst, const void *src, size_t len) {unsigned char *d = (unsigned char *)dst;const unsigned char *s = (const unsigned char *)src;if (d < s || d >= s + len) {unsigned int *dw = (unsigned int *)d;const unsigned int *sw = (const unsigned int *)s;while (len >= sizeof(unsigned int)) {*dw++ = *sw++;len -= sizeof(unsigned int);}d = (unsigned char *)dw;s = (const unsigned char *)sw;while (len--) *d++ = *s++;} else {d += len;s += len;unsigned int *dw = (unsigned int *)d;const unsigned int *sw = (const unsigned int *)s;while (len >= sizeof(unsigned int)) {*(--dw) = *(--sw);len -= sizeof(unsigned int);}d = (unsigned char *)dw;s = (const unsigned char *)sw;while (len--) *(--d) = *(--s);}return dst;}
};struct TestCase {string name;size_t src_off;size_t dst_off;size_t len;size_t buf_size;
};int main() {Solution sol;vector<TestCase> cases = {{"no overlap", 0, 20, 16, 64},{"dst < src overlap", 0, 4, 16, 64},{"src < dst overlap", 4, 0, 16, 64},{"large block", 10, 20, 1024 * 64, 1024 * 80},};vector<pair<string, function<void*(void*, const void*, size_t)>>> funcs = {{"memcpy_naive", [&](void *d, const void *s, size_t n){ return sol.memcpy_naive(d,s,n); }},{"memcpy_overlap", [&](void *d, const void *s, size_t n){ return sol.memcpy_overlap(d,s,n); }},{"memcpy_word", [&](void *d, const void *s, size_t n){ return sol.memcpy_word(d,s,n); }},};cout << left << setw(18) << "Algorithm" << setw(18) << "TestCase"<< setw(10) << "Result" << setw(12) << "Time(ms)" << endl;cout << string(58, '-') << endl;for (auto &f : funcs) {for (auto &tc : cases) {vector<unsigned char> buf(tc.buf_size);iota(buf.begin(), buf.end(), 0); // fill 0,1,2,...vector<unsigned char> ref = buf;unsigned char *dst = buf.data() + tc.dst_off;unsigned char *src = buf.data() + tc.src_off;const int rounds = 1000;auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();for (int i = 0; i < rounds; i++) {buf = ref;f.second(dst, src, tc.len);}auto end = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();double ms = chrono::duration<double, milli>(end - start).count();bool pass = memcmp(buf.data() + tc.dst_off, ref.data() + tc.src_off, tc.len) == 0;cout << setw(18) << f.first << setw(18) << tc.name<< setw(10) << (pass ? "PASS" : "FAIL")<< setw(12) << fixed << setprecision(3) << ms << endl;}}return 0;
}
