【数据结构】红黑树的基本操作
目录
一、引言
(一)节点结构与 nil 哨兵设计
(二)核心性质与作用机制
性质 1:颜色属性
性质 2:根节点属性
性质 3:nil 节点属性
性质 4:红色节点约束
性质 5:黑高一致性
(三)平衡效果与理论意义
二、红黑树核心操作原理与代码解析
(一)红黑树的核心性质
(二)核心算法详解
1. 节点结构与初始化
2. 旋转操作(平衡树结构的基础)
左旋(leftRotate(x))
右旋(rightRotate(y))
3. 插入算法(insert + insertFixup)
插入节点(insert)
插入后修复(insertFixup(z))
4. 删除算法(remove + deleteNode + deleteFixup)
查找并删除节点(remove + deleteNode)
移植操作(transplant(u, v))
删除后修复(deleteFixup(x))
5. 查找算法(search + searchNode)
6. 遍历算法
7. 辅助算法
(三)算法总结
三、红黑树的基本操作代码完整实现
(一)C++代码如下:
(二)Python代码如下:
(三)Java代码如下:
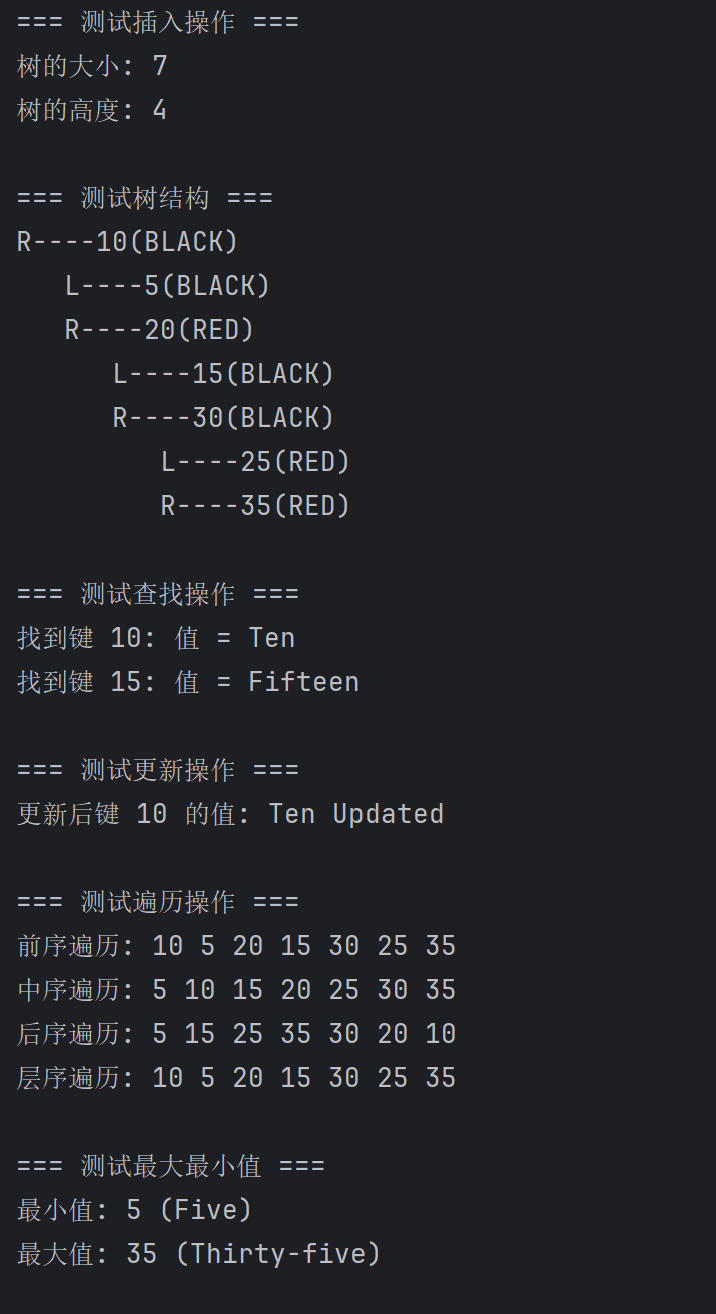
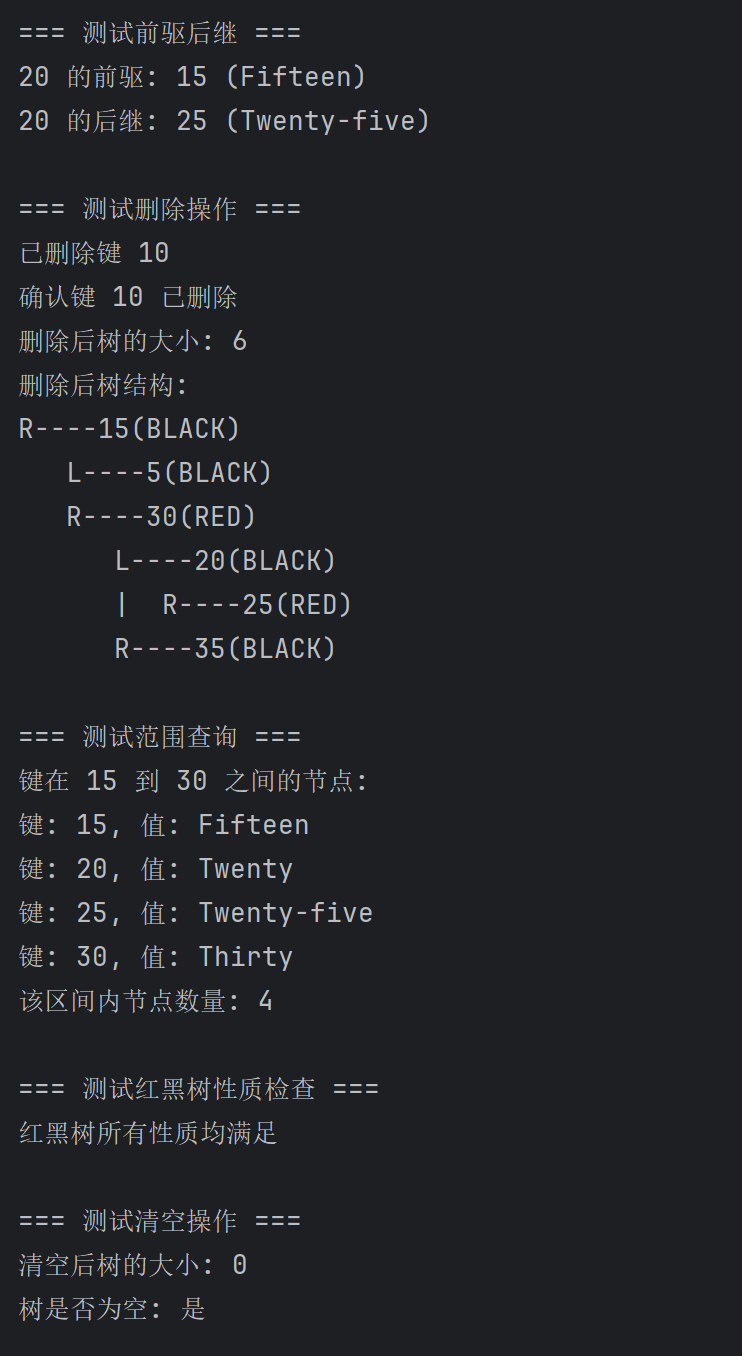
四、程序运行结果展示
(一)C++代码运行截图如下:
(二)Python代码运行截图如下:
(三)Java代码运行截图如下:
五、时间复杂度的数学证明
(一)核心概念:黑高(Black Height)
树高与黑高的关系:
(二)归纳法证明:节点数下限与树高上限
1.定理:高度为 h 的红黑树至少包含 个内部节点
2.推导树高上限:
(三)操作复杂度分析与对比
1.红黑树操作复杂度:
2.与普通 BST 的对比
六、与AVL树的对比分析
(一)平衡机制:近似平衡与严格平衡的分野
(二)性能指标:动态操作效率与空间开销的权衡
2.1 平衡维护成本:旋转次数的数量级差异
2.2 空间开销:1 位 vs 多位的存储成本
2.3 时间复杂度:理论同阶,实践分化
(三)工程选择:场景适配与设计哲学的落地
3.1 红黑树:动态数据场景的首选
3.2 AVL 树:静态查询场景的优化选择
(四)对比总结表
七、红黑树的工程应用案
(一)编程语言标准库:有序容器的底层支柱
(二)Linux 内核 CFS 调度器:进程调度的效率引擎
(三)Nginx 定时器:高效事件驱动的核心组件
(四)数据库与缓存:索引与排序的底层支撑
总结:红黑树的技术适配场景
八、实现难点与优化建议
(一)实现难点剖析
(二)优化建议
(三)工程实现与调试方法
九、总结
一、引言
红黑树是一种自平衡二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST),其本质特征在于通过为每个节点增加颜色属性(红色或黑色)及一系列严格的着色约束,确保树的高度始终维持在近似平衡状态。与普通二叉搜索树可能因插入顺序不当退化为链表(导致操作复杂度降至 \(O(n)\))不同,红黑树通过对从根到叶子的所有路径施加颜色限制,保证最长路径长度不超过最短路径的 2 倍,从而使树高始终保持在 \(O(\log n)\) 级别,确保查找、插入、删除等基本操作的最坏时间复杂度为 \(O(\log n)\)。这种平衡机制被称为“近似平衡”,既避免了绝对平衡(如 AVL 树)的频繁调整开销,又能满足高效操作的需求。
(一)节点结构与 nil 哨兵设计
红黑树的节点结构在普通二叉搜索树基础上扩展了颜色属性,同时引入* nil 哨兵节点*(NIL 节点)统一处理边界条件。具体而言,每个节点包含以下 5 个核心属性:
• color:节点颜色,取值为红色(RED)或黑色(BLACK);
• key:节点存储的关键字值;
• left/right:指向左、右子节点的指针;
• p:指向父节点的指针。
其中,nil 哨兵节点是一种特殊的黑色节点,用于表示“空”子节点或父节点。它不存储实际数据,仅作为树结构的边界标记,确保所有叶子节点(非哨兵节点)的子节点均为 nil 节点,从而简化性质校验和操作逻辑。例如,当一个节点的左子节点不存在时,其 left 指针指向 nil 哨兵;根节点的 p 指针同样指向 nil 哨兵。这种设计避免了对“空指针”的特殊处理,使树的结构更统一。
(二)核心性质与作用机制
红黑树的平衡保障依赖于以下 5 个核心性质(红黑性质),这些性质共同约束了树的结构和着色规则:
性质 1:颜色属性
每个节点的颜色为红色或黑色。这是红黑树的基础定义,颜色作为控制平衡的核心手段,通过后续性质的组合约束实现对路径长度的控制。在代码实现中,通常通过枚举类型定义颜色,例如:
enum Color { RED, BLACK };性质 2:根节点属性
根节点必须为黑色。这一性质确保树的“顶层”起始颜色统一,避免因根节点为红色可能导致的路径颜色计算偏差。若根节点在操作中变为红色,需通过颜色调整将其重新置黑,以维持性质成立。
性质 3:nil 节点属性
所有 nil 哨兵节点均为黑色。nil 节点作为叶子节点的“替身”,其黑色属性确保了路径中黑色节点的计数统一。例如,一个叶子节点(非哨兵)的左、右子节点均为 nil 节点,这两个 nil 节点的黑色属性会参与路径黑色节点数量的计算。
性质 4:红色节点约束
若一个节点为红色,则其两个子节点必须为黑色(即不存在连续的红色节点)。这一性质直接限制了路径中红色节点的密度:红色节点不能相邻,意味着红色节点必须由黑色节点分隔。该约束避免了因红色节点聚集导致的路径过长,是控制路径长度的关键性质之一。
性质 5:黑高一致性
从任意节点到其所有后代 nil 节点的路径中,黑色节点的数量必须相同。这里的黑色节点数量被定义为该节点的黑高(Black-Height),记为 bh(x)。例如,若节点 x 的黑高为 3,则从 x 出发的所有路径(直至 nil 节点)均包含 3 个黑色节点(不包含 x 本身)。这一性质是红黑树平衡的核心保障,直接限制了路径长度的差异:最短路径由全黑节点组成(长度等于黑高),最长路径则为红黑节点交替出现(长度不超过黑高的 2 倍),因此最长路径 ≤ 2 × 最短路径。
性质协同作用:性质 4(无连续红节点)与性质 5(黑高一致)的组合,从“红节点间隔”和“黑节点总量”两个维度约束了路径长度。假设某红黑树的黑高为 h,则最短路径长度为 h(全黑节点),最长路径长度为 2h(红黑交替),从而严格保证了树的近似平衡。
(三)平衡效果与理论意义
红黑树的 5 个性质共同确保了其高度的上界为 (其中 n 为节点数)。这一结论可通过反证法推导:设树的黑高为 h,则根据性质 5,树中至少有
个黑色节点(全黑路径构成的完全二叉树);结合性质 4,红色节点数量不超过黑色节点,故总节点数
,解得
,进而树高(最长路径)不超过
。
这种高度控制使得红黑树在动态操作中既能保持高效的时间复杂度,又避免了 AVL 树等绝对平衡结构的频繁旋转开销,因此在工程实践中被广泛应用于关联容器(如 C++ STL 的 std::map)、内核调度等场景。其核心价值在于:通过局部颜色约束而非全局结构调整实现平衡,以较低的维护成本换取稳定的操作效率。
红黑树的定义与性质是理解其操作原理的基础。后续章节将围绕这些性质,详细阐述插入、删除操作中如何通过旋转和颜色调整维持平衡,而本章所述的 5 个核心性质正是这些操作的约束条件和调整目标。
二、红黑树核心操作原理与代码解析
(一)红黑树的核心性质
红黑树通过维护以下 5 条性质保证平衡,代码中所有操作均围绕这些性质设计:
- 颜色性质:每个节点要么是红色(RED),要么是黑色(BLACK)。
- 根性质:根节点必须是黑色。
- 叶子性质:所有叶子节点(哨兵节点
nil)是黑色。 - 红子性质:如果一个节点是红色,则它的两个子节点必须是黑色(即不存在两个连续的红色节点)。
- 黑高性质:从任一节点到其所有叶子节点的路径中,黑色节点的数量相同(称为 “黑高”)。
(二)核心算法详解
1. 节点结构与初始化
// 红黑树节点结构
template <typename K, typename V>
struct RBNode {K key; // 键V value; // 值Color color; // 颜色RBNode *left; // 左子节点RBNode *right; // 右子节点RBNode *parent; // 父节点RBNode(const K& k, const V& v) : key(k), value(v), color(RED), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), parent(nullptr) {}
};- 节点结构(
RBNode):包含键(key)、值(value)、颜色(color)、左子节点(left)、右子节点(right)、父节点(parent)。新节点默认颜色为红色(减少对黑高性质的影响)。 - 哨兵节点(
nil):替代NULL,所有空指针均指向nil,nil颜色为黑色,简化边界条件处理(如避免判断NULL)。 - 树初始化:根节点初始指向
nil,树大小为 0。
2. 旋转操作(平衡树结构的基础)
旋转是调整树结构的核心操作,不破坏二叉搜索树的性质(左子树键 < 父节点键 < 右子树键),仅改变节点的父子关系。
左旋(leftRotate(x))
// --- 辅助操作:左旋 ---
void leftRotate(RBNode<K, V>* x) {RBNode<K, V>* y = x->right; // x 的右孩子x->right = y->left; // y 的左子树成为 x 的右子树if (y->left != nil) {y->left->parent = x;}y->parent = x->parent; // x 的父节点成为 y 的父节点if (x->parent == nil) { // x 是根节点时,y 成为新根root = y;} else if (x == x->parent->left) { // x 是父的左孩子x->parent->left = y;} else { // x 是父的右孩子x->parent->right = y;}y->left = x; // x 成为 y 的左孩子x->parent = y;
}
- 作用:将节点
x的右子树y提升为x的父节点,x成为y的左子节点。 - 步骤:
- 设
y = x->right(x的右子节点)。 - 将
y的左子树转为x的右子树(若y->left非nil,更新其 parent 为x)。 - 更新
y的 parent 为x的 parent(若x是根,则y成为新根;否则x的父节点将y作为左 / 右子节点)。 - 将
x设为y的左子节点,更新x的 parent 为y。
- 设
右旋(rightRotate(y))
// --- 辅助操作:右旋 ---
void rightRotate(RBNode<K, V>* y) {RBNode<K, V>* x = y->left; // y 的左孩子y->left = x->right; // x 的右子树成为 y 的左子树if (x->right != nil) {x->right->parent = y;}x->parent = y->parent; // y 的父节点成为 x 的父节点if (y->parent == nil) { // y 是根节点时,x 成为新根root = x;} else if (y == y->parent->left) { // y 是父的左孩子y->parent->left = x;} else { // y 是父的右孩子y->parent->right = x;}x->right = y; // y 成为 x 的右孩子y->parent = x;
}
- 作用:将节点
y的左子树x提升为y的父节点,y成为x的右子节点。 - 步骤:与左旋对称,将左子树提升,调整父子关系。
3. 插入算法(insert + insertFixup)
// --- 插入后修复红黑树性质 ---
void insertFixup(RBNode<K, V>* z) {// 当父节点为红色时,违反“红节点的子节点必为黑”的性质,需要修复while (z->parent->color == RED) {if (z->parent == z->parent->parent->left) { // 父节点是祖父的左孩子RBNode<K, V>* uncle = z->parent->parent->right; // 叔节点(祖父的右孩子)if (uncle->color == RED) { // 情况1:叔节点为红 → 变色即可z->parent->color = BLACK;uncle->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;z = z->parent->parent; // 祖父可能违反性质,继续向上修复} else { // 叔节点为黑if (z == z->parent->right) { // 情况2:z 是父的右孩子 → 先左旋z = z->parent;leftRotate(z);}// 情况3:z 是父的左孩子 → 父变黑色、祖父变红色,再右旋z->parent->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;rightRotate(z->parent->parent);}} else { // 对称情况:父节点是祖父的右孩子RBNode<K, V>* uncle = z->parent->parent->left; // 叔节点(祖父的左孩子)if (uncle->color == RED) { // 情况1:叔节点为红 → 变色z->parent->color = BLACK;uncle->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;z = z->parent->parent;} else { // 叔节点为黑if (z == z->parent->left) { // 情况2:z 是父的左孩子 → 先右旋z = z->parent;rightRotate(z);}// 情况3:z 是父的右孩子 → 父变黑色、祖父变红色,再左旋z->parent->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;leftRotate(z->parent->parent);}}}root->color = BLACK; // 确保根节点始终为黑色
}
插入过程分为两步:先按二叉搜索树规则插入新节点,再修复可能违反的红黑树性质。
插入节点(insert)
- 步骤:
- 创建新节点
z(颜色为红色),查找插入位置(同二叉搜索树:小于当前节点则向左,大于则向右)。 - 确定
z的父节点parent,将z设为parent的左 / 右子节点(若树为空,z成为根)。 - 调用
insertFixup(z)修复红黑树性质。
- 创建新节点
插入后修复(insertFixup(z))
-
问题:新节点为红色,可能违反 “红子性质”(若父节点也是红色)。
-
修复逻辑:循环处理,直到父节点为黑色(此时无违反),分 3 种情况(对称处理左右子树):
-
情况 1:父节点和叔节点(祖父的另一个子节点)均为红色。解决:将父节点和叔节点改为黑色,祖父改为红色,将
z指向祖父(继续向上修复)。(原理:通过变色维持黑高性质,且不产生连续红节点) -
情况 2:父节点为红,叔节点为黑,且
z是父节点的右子节点(左子树对称)。解决:对父节点左旋,将z指向父节点,转为情况 3。(原理:通过旋转调整节点位置,统一为情况 3 处理) -
情况 3:父节点为红,叔节点为黑,且
z是父节点的左子节点(左子树对称)。解决:父节点改为黑色,祖父改为红色,对祖父右旋。(原理:变色 + 旋转消除连续红节点,维持黑高性质)
-
-
最终操作:无论如何,根节点强制设为黑色(保证根性质)。
4. 删除算法(remove + deleteNode + deleteFixup)
删除过程最复杂:先按二叉搜索树规则删除节点,再修复可能违反的红黑树性质。
查找并删除节点(remove + deleteNode)
// --- 删除节点(内部辅助,与二叉搜索树逻辑结合后修复)---
void deleteNode(RBNode<K, V>* z) {RBNode<K, V>* y = z; // 记录要真正删除的节点RBNode<K, V>* x = nil; // 记录 y 的子节点(用于后续修复)Color y_original_color = y->color; // 记录 y 原始颜色(若为黑,删除后可能破坏性质)// 情况1:z 只有右孩子if (z->left == nil) {x = z->right;transplant(z, z->right);} // 情况2:z 只有左孩子else if (z->right == nil) {x = z->left;transplant(z, z->left);} // 情况3:z 有两个孩子 → 找后继(右子树最小节点)else {y = minimum(z->right);y_original_color = y->color;x = y->right;if (y->parent == z) { // 后继是 z 的直接右孩子x->parent = y;} else { // 后继不是 z 的直接右孩子 → 先移植后继的右子树transplant(y, y->right);y->right = z->right;y->right->parent = y;}// 用后继 y 替换 ztransplant(z, y);y->left = z->left;y->left->parent = y;y->color = z->color;}// 若删除的是黑色节点,可能破坏性质,需修复if (y_original_color == BLACK) {deleteFixup(x);}delete z; // 释放原节点内存treeSize--; // 减少节点计数
}- 步骤:
- 查找目标节点
z(searchNode),若不存在则返回失败。 - 确定真正删除的节点
y:- 若
z只有一个子节点或无子女,y = z; - 若
z有两个子女,y是z的后继(右子树的最小值,保证二叉搜索树性质)。
- 若
- 用
y的子节点x替代y(transplant操作,替换父子关系)。 - 若
y是黑色(删除黑色节点可能破坏黑高性质),调用deleteFixup(x)修复。
- 查找目标节点
移植操作(transplant(u, v))
// --- 移植操作:用 v 替换 u(二叉搜索树通用操作)---
void transplant(RBNode<K, V>* u, RBNode<K, V>* v) {if (u->parent == nil) {root = v;} else if (u == u->parent->left) {u->parent->left = v;} else {u->parent->right = v;}v->parent = u->parent;
}- 作用:用子树
v替代子树u,仅调整父子关系,不破坏二叉搜索树性质。 - 步骤:更新
u的父节点与v的关联,以及v的父节点为u的父节点。
删除后修复(deleteFixup(x))
// --- 删除后修复红黑树性质 ---
void deleteFixup(RBNode<K, V>* x) {// 当 x 为黑且非根时,可能违反“路径黑节点数相同”的性质,需要修复while (x != root && x->color == BLACK) {if (x == x->parent->left) { // x 是父的左孩子RBNode<K, V>* sibling = x->parent->right; // 兄弟节点if (sibling->color == RED) { // 情况1:兄弟是红 → 先变色+左旋,将兄弟转为黑sibling->color = BLACK;x->parent->color = RED;leftRotate(x->parent);sibling = x->parent->right;}if (sibling->left->color == BLACK && sibling->right->color == BLACK) { // 情况2:兄弟的子都是黑 → 兄弟变红,x 上移sibling->color = RED;x = x->parent;} else {if (sibling->right->color == BLACK) { // 情况3:兄弟右子是黑,左子是红 → 兄弟左旋,转为情况4sibling->left->color = BLACK;sibling->color = RED;rightRotate(sibling);sibling = x->parent->right;}// 情况4:兄弟右子是红 → 变色+左旋,修复完成sibling->color = x->parent->color;x->parent->color = BLACK;sibling->right->color = BLACK;leftRotate(x->parent);x = root; // 结束循环}} else { // 对称情况:x 是父的右孩子RBNode<K, V>* sibling = x->parent->left; // 兄弟节点if (sibling->color == RED) { // 情况1:兄弟是红 → 变色+右旋sibling->color = BLACK;x->parent->color = RED;rightRotate(x->parent);sibling = x->parent->left;}if (sibling->right->color == BLACK && sibling->left->color == BLACK) { // 情况2:兄弟的子都是黑 → 兄弟变红,x 上移sibling->color = RED;x = x->parent;} else {if (sibling->left->color == BLACK) { // 情况3:兄弟左子是黑,右子是红 → 兄弟右旋,转为情况4sibling->right->color = BLACK;sibling->color = RED;leftRotate(sibling);sibling = x->parent->left;}// 情况4:兄弟左子是红 → 变色+右旋,修复完成sibling->color = x->parent->color;x->parent->color = BLACK;sibling->left->color = BLACK;rightRotate(x->parent);x = root; // 结束循环}}}x->color = BLACK; // 确保 x 最终为黑色(若 x 是根,直接设为黑)
}
-
问题:若删除的是黑色节点,
x(替代节点)所在路径的黑高减少 1,违反黑高性质;或可能产生连续红节点。 -
修复逻辑:循环处理,直到
x为红色或x是根,分 4 种情况(对称处理左右子树):-
情况 1:
x的兄弟节点s为红色。解决:s改为黑色,x的父节点改为红色,对父节点左旋,更新s为新的兄弟节点(转为情况 2/3/4)。(原理:将兄弟节点转为黑色,为后续修复做准备) -
情况 2:
s为黑,且s的两个子节点均为黑。解决:s改为红色,x指向父节点(向上传递黑高不足的问题)。(原理:通过将兄弟节点变红,平衡黑高) -
情况 3:
s为黑,s的左子节点为红,右子节点为黑(左子树对称)。解决:s的左子节点改为黑,s改为红,对s右旋,更新s为新的兄弟节点(转为情况 4)。(原理:调整兄弟节点的子树结构,统一为情况 4 处理) -
情况 4:
s为黑,s的右子节点为红(左子树对称)。解决:s继承父节点颜色,父节点改为黑,s的右子节点改为黑,对父节点左旋,x指向根(结束循环)。(原理:通过变色 + 旋转修复黑高,消除连续红节点)
-
-
最终操作:
x强制设为黑色(保证黑高性质)。
5. 查找算法(search + searchNode)
// --- 查找节点(内部辅助)---
RBNode<K, V>* searchNode(const K& key) const {RBNode<K, V>* curr = root;while (curr != nil) {if (key < curr->key) {curr = curr->left;} else if (key > curr->key) {curr = curr->right;} else {return curr; // 找到节点}}return nil; // 未找到
}- 原理:利用二叉搜索树的性质(左子树键 < 父节点键 < 右子树键)递归查找。
- 步骤:从根节点开始,若目标键小于当前节点键则向左子树查找,大于则向右子树查找,等于则返回节点。
6. 遍历算法
// --- 前序遍历辅助函数 ---
void preorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);preorderHelper(node->left, result);preorderHelper(node->right, result);}
}// --- 中序遍历辅助函数 ---
void inorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {inorderHelper(node->left, result);result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);inorderHelper(node->right, result);}
}// --- 后序遍历辅助函数 ---
void postorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {postorderHelper(node->left, result);postorderHelper(node->right, result);result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);}
}// --- 层序遍历 ---
vector<pair<K, V>> levelorder() const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;if (root == nil) return result;queue<RBNode<K, V>*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {RBNode<K, V>* node = q.front();q.pop();result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);if (node->left != nil)q.push(node->left);if (node->right != nil)q.push(node->right);}return result;
}
遍历用于按特定顺序访问所有节点,红黑树的遍历与普通二叉搜索树一致:
- 前序遍历(
preorder):根 → 左子树 → 右子树。 - 中序遍历(
inorder):左子树 → 根 → 右子树(红黑树中序遍历结果为有序序列)。 - 后序遍历(
postorder):左子树 → 右子树 → 根。 - 层序遍历(
levelorder):按层次(从根开始,逐层访问),用队列实现。
7. 辅助算法
// --- 获取树的大小 ---
int size() const {return treeSize;
}// --- 获取树的高度 ---
int height() const {return heightHelper(root);
}// --- 检查树是否为空 ---
bool isEmpty() const {return root == nil;
}// --- 清空树 ---
void clear() {destroy(root);root = nil;treeSize = 0;
}// --- 查找最小值 ---
bool findMin(K& key, V& value) const {if (isEmpty()) return false;RBNode<K, V>* node = minimum(root);key = node->key;value = node->value;return true;
}// --- 查找最大值 ---
bool findMax(K& key, V& value) const {if (isEmpty()) return false;RBNode<K, V>* node = maximum(root);key = node->key;value = node->value;return true;
}// --- 查找前驱节点(小于当前键的最大键)---
bool findPredecessor(const K& key, K& predKey, V& predValue) const {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return false;// 左子树非空:前驱是左子树的最大值if (node->left != nil) {RBNode<K, V>* pred = maximum(node->left);predKey = pred->key;predValue = pred->value;return true;}// 左子树为空:向上找第一个有右子树的祖先RBNode<K, V>* pred = node->parent;while (pred != nil && node == pred->left) {node = pred;pred = pred->parent;}if (pred != nil) {predKey = pred->key;predValue = pred->value;return true;}return false; // 无前列
}// --- 查找后继节点(大于当前键的最小键)---
bool findSuccessor(const K& key, K& succKey, V& succValue) const {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return false;// 右子树非空:后继是右子树的最小值if (node->right != nil) {RBNode<K, V>* succ = minimum(node->right);succKey = succ->key;succValue = succ->value;return true;}// 右子树为空:向上找第一个有左子树的祖先RBNode<K, V>* succ = node->parent;while (succ != nil && node == succ->right) {node = succ;succ = succ->parent;}if (succ != nil) {succKey = succ->key;succValue = succ->value;return true;}return false; // 无后继
}// --- 打印树结构 ---
void printStructure() const {if (isEmpty()) {cout << "Tree is empty" << endl;return;}printStructureHelper(root, "", true);
}// --- 范围查询:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的键值对 ---
vector<pair<K, V>> rangeQuery(const K& minKey, const K& maxKey) const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;rangeQueryHelper(root, minKey, maxKey, result);return result;
}// --- 统计区间节点数:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的节点数量 ---
int countRange(const K& minKey, const K& maxKey) const {return countRangeHelper(root, minKey, maxKey);
}// --- 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质(性质1-5)---
bool checkProperties() const {bool valid = true;if (!checkColorProperty(root)) {cout << "违反性质1:节点颜色不是红色或黑色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkRootProperty()) {cout << "违反性质2:根节点不是黑色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkRedParentProperty(root)) {cout << "违反性质4:存在红色节点的子节点为红色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkBlackHeightProperty()) {cout << "违反性质5:从根到叶的路径黑节点数不同" << endl;valid = false;}if (valid) cout << "红黑树所有性质均满足" << endl;return valid;
}-
最值查找:
- 最小值(
minimum):从节点出发,沿左子树一直到最左节点。 - 最大值(
maximum):从节点出发,沿右子树一直到最右节点。
- 最小值(
-
前驱 / 后继查找:
- 前驱(
findPredecessor):小于当前键的最大键。若左子树非空,为左子树的最大值;否则为向上找到的第一个 “当前节点是其右子节点” 的祖先。 - 后继(
findSuccessor):大于当前键的最小键。若右子树非空,为右子树的最小值;否则为向上找到的第一个 “当前节点是其左子节点” 的祖先。
- 前驱(
-
范围查询(
rangeQuery):查找键在[minKey, maxKey]之间的所有节点。利用二叉搜索树性质递归:若当前节点键 >minKey则查左子树,若在范围内则记录,若键 <maxKey则查右子树。 -
性质检查(
checkProperties):验证红黑树的 5 条性质是否满足,用于调试(如检查颜色合法性、根是否为黑、红节点的子节点是否为黑、黑高是否一致)。
(三)算法总结
红黑树的核心是通过旋转(调整结构)和变色(调整节点颜色)维护 5 条性质,从而保证树的高度始终为O(log n)。代码中:
- 插入和删除是最复杂的操作,通过
insertFixup和deleteFixup修复性质; - 旋转是平衡结构的基础,不破坏二叉搜索树的有序性;
- 其他操作(查找、遍历、最值等)依赖二叉搜索树的基本性质,效率由树的平衡性保证。
三、红黑树的基本操作代码完整实现
(一)C++代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>using namespace std;// 颜色枚举:红、黑
enum Color { RED, BLACK };// 红黑树节点结构
template <typename K, typename V>
struct RBNode {K key; // 键V value; // 值Color color; // 颜色RBNode *left; // 左子节点RBNode *right; // 右子节点RBNode *parent; // 父节点RBNode(const K& k, const V& v) : key(k), value(v), color(RED), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), parent(nullptr) {}
};// 红黑树类
template <typename K, typename V>
class RedBlackTree {
private:RBNode<K, V>* root; // 根节点RBNode<K, V>* nil; // 哨兵节点(代替 NULL,颜色为 BLACK)int treeSize; // 树中节点数量// --- 辅助操作:左旋 ---void leftRotate(RBNode<K, V>* x) {RBNode<K, V>* y = x->right; // x 的右孩子x->right = y->left; // y 的左子树成为 x 的右子树if (y->left != nil) {y->left->parent = x;}y->parent = x->parent; // x 的父节点成为 y 的父节点if (x->parent == nil) { // x 是根节点时,y 成为新根root = y;} else if (x == x->parent->left) { // x 是父的左孩子x->parent->left = y;} else { // x 是父的右孩子x->parent->right = y;}y->left = x; // x 成为 y 的左孩子x->parent = y;}// --- 辅助操作:右旋 ---void rightRotate(RBNode<K, V>* y) {RBNode<K, V>* x = y->left; // y 的左孩子y->left = x->right; // x 的右子树成为 y 的左子树if (x->right != nil) {x->right->parent = y;}x->parent = y->parent; // y 的父节点成为 x 的父节点if (y->parent == nil) { // y 是根节点时,x 成为新根root = x;} else if (y == y->parent->left) { // y 是父的左孩子y->parent->left = x;} else { // y 是父的右孩子y->parent->right = x;}x->right = y; // y 成为 x 的右孩子y->parent = x;}// --- 插入后修复红黑树性质 ---void insertFixup(RBNode<K, V>* z) {// 当父节点为红色时,违反“红节点的子节点必为黑”的性质,需要修复while (z->parent->color == RED) {if (z->parent == z->parent->parent->left) { // 父节点是祖父的左孩子RBNode<K, V>* uncle = z->parent->parent->right; // 叔节点(祖父的右孩子)if (uncle->color == RED) { // 情况1:叔节点为红 → 变色即可z->parent->color = BLACK;uncle->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;z = z->parent->parent; // 祖父可能违反性质,继续向上修复} else { // 叔节点为黑if (z == z->parent->right) { // 情况2:z 是父的右孩子 → 先左旋z = z->parent;leftRotate(z);}// 情况3:z 是父的左孩子 → 父变黑色、祖父变红色,再右旋z->parent->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;rightRotate(z->parent->parent);}} else { // 对称情况:父节点是祖父的右孩子RBNode<K, V>* uncle = z->parent->parent->left; // 叔节点(祖父的左孩子)if (uncle->color == RED) { // 情况1:叔节点为红 → 变色z->parent->color = BLACK;uncle->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;z = z->parent->parent;} else { // 叔节点为黑if (z == z->parent->left) { // 情况2:z 是父的左孩子 → 先右旋z = z->parent;rightRotate(z);}// 情况3:z 是父的右孩子 → 父变黑色、祖父变红色,再左旋z->parent->color = BLACK;z->parent->parent->color = RED;leftRotate(z->parent->parent);}}}root->color = BLACK; // 确保根节点始终为黑色}// --- 查找节点(内部辅助)---RBNode<K, V>* searchNode(const K& key) const {RBNode<K, V>* curr = root;while (curr != nil) {if (key < curr->key) {curr = curr->left;} else if (key > curr->key) {curr = curr->right;} else {return curr; // 找到节点}}return nil; // 未找到}// --- 找子树中最小节点(用于删除时找后继)---RBNode<K, V>* minimum(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {while (node->left != nil) {node = node->left;}return node;}// --- 找子树中最大节点 ---RBNode<K, V>* maximum(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {while (node->right != nil) {node = node->right;}return node;}// --- 删除后修复红黑树性质 ---void deleteFixup(RBNode<K, V>* x) {// 当 x 为黑且非根时,可能违反“路径黑节点数相同”的性质,需要修复while (x != root && x->color == BLACK) {if (x == x->parent->left) { // x 是父的左孩子RBNode<K, V>* sibling = x->parent->right; // 兄弟节点if (sibling->color == RED) { // 情况1:兄弟是红 → 先变色+左旋,将兄弟转为黑sibling->color = BLACK;x->parent->color = RED;leftRotate(x->parent);sibling = x->parent->right;}if (sibling->left->color == BLACK && sibling->right->color == BLACK) { // 情况2:兄弟的子都是黑 → 兄弟变红,x 上移sibling->color = RED;x = x->parent;} else {if (sibling->right->color == BLACK) { // 情况3:兄弟右子是黑,左子是红 → 兄弟左旋,转为情况4sibling->left->color = BLACK;sibling->color = RED;rightRotate(sibling);sibling = x->parent->right;}// 情况4:兄弟右子是红 → 变色+左旋,修复完成sibling->color = x->parent->color;x->parent->color = BLACK;sibling->right->color = BLACK;leftRotate(x->parent);x = root; // 结束循环}} else { // 对称情况:x 是父的右孩子RBNode<K, V>* sibling = x->parent->left; // 兄弟节点if (sibling->color == RED) { // 情况1:兄弟是红 → 变色+右旋sibling->color = BLACK;x->parent->color = RED;rightRotate(x->parent);sibling = x->parent->left;}if (sibling->right->color == BLACK && sibling->left->color == BLACK) { // 情况2:兄弟的子都是黑 → 兄弟变红,x 上移sibling->color = RED;x = x->parent;} else {if (sibling->left->color == BLACK) { // 情况3:兄弟左子是黑,右子是红 → 兄弟右旋,转为情况4sibling->right->color = BLACK;sibling->color = RED;leftRotate(sibling);sibling = x->parent->left;}// 情况4:兄弟左子是红 → 变色+右旋,修复完成sibling->color = x->parent->color;x->parent->color = BLACK;sibling->left->color = BLACK;rightRotate(x->parent);x = root; // 结束循环}}}x->color = BLACK; // 确保 x 最终为黑色(若 x 是根,直接设为黑)}// --- 移植操作:用 v 替换 u(二叉搜索树通用操作)---void transplant(RBNode<K, V>* u, RBNode<K, V>* v) {if (u->parent == nil) {root = v;} else if (u == u->parent->left) {u->parent->left = v;} else {u->parent->right = v;}v->parent = u->parent;}// --- 删除节点(内部辅助,与二叉搜索树逻辑结合后修复)---void deleteNode(RBNode<K, V>* z) {RBNode<K, V>* y = z; // 记录要真正删除的节点RBNode<K, V>* x = nil; // 记录 y 的子节点(用于后续修复)Color y_original_color = y->color; // 记录 y 原始颜色(若为黑,删除后可能破坏性质)// 情况1:z 只有右孩子if (z->left == nil) {x = z->right;transplant(z, z->right);} // 情况2:z 只有左孩子else if (z->right == nil) {x = z->left;transplant(z, z->left);} // 情况3:z 有两个孩子 → 找后继(右子树最小节点)else {y = minimum(z->right);y_original_color = y->color;x = y->right;if (y->parent == z) { // 后继是 z 的直接右孩子x->parent = y;} else { // 后继不是 z 的直接右孩子 → 先移植后继的右子树transplant(y, y->right);y->right = z->right;y->right->parent = y;}// 用后继 y 替换 ztransplant(z, y);y->left = z->left;y->left->parent = y;y->color = z->color;}// 若删除的是黑色节点,可能破坏性质,需修复if (y_original_color == BLACK) {deleteFixup(x);}delete z; // 释放原节点内存treeSize--; // 减少节点计数}// --- 销毁树(析构时用)---void destroy(RBNode<K, V>* node) {if (node != nil) {destroy(node->left);destroy(node->right);delete node;}}// --- 前序遍历辅助函数 ---void preorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);preorderHelper(node->left, result);preorderHelper(node->right, result);}}// --- 中序遍历辅助函数 ---void inorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {inorderHelper(node->left, result);result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);inorderHelper(node->right, result);}}// --- 后序遍历辅助函数 ---void postorderHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node != nil) {postorderHelper(node->left, result);postorderHelper(node->right, result);result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);}}// --- 计算树高度辅助函数 ---int heightHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {if (node == nil) {return 0;}int leftHeight = heightHelper(node->left);int rightHeight = heightHelper(node->right);return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}// --- 打印树结构辅助函数 ---void printStructureHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, string indent, bool last) const {if (node != nil) {cout << indent;if (last) {cout << "R----";indent += " ";} else {cout << "L----";indent += "| ";}string color = (node->color == RED) ? "RED" : "BLACK";cout << node->key << "(" << color << ")" << endl;printStructureHelper(node->left, indent, false);printStructureHelper(node->right, indent, true);}}// --- 范围查询辅助函数 ---void rangeQueryHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, const K& minKey, const K& maxKey, vector<pair<K, V>>& result) const {if (node == nil) return;// 左子树可能有符合条件的节点if (node->key > minKey) {rangeQueryHelper(node->left, minKey, maxKey, result);}// 当前节点在范围内,加入结果if (node->key >= minKey && node->key <= maxKey) {result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);}// 右子树可能有符合条件的节点if (node->key < maxKey) {rangeQueryHelper(node->right, minKey, maxKey, result);}}// --- 统计区间节点数辅助函数 ---int countRangeHelper(RBNode<K, V>* node, const K& minKey, const K& maxKey) const {if (node == nil) return 0;int count = 0;// 当前节点在范围内,计数+1if (node->key >= minKey && node->key <= maxKey) {count = 1;}// 左子树递归统计if (node->key > minKey) {count += countRangeHelper(node->left, minKey, maxKey);}// 右子树递归统计if (node->key < maxKey) {count += countRangeHelper(node->right, minKey, maxKey);}return count;}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质1(颜色合法性)---bool checkColorProperty(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {if (node == nil) return true;if (node->color != RED && node->color != BLACK) return false;return checkColorProperty(node->left) && checkColorProperty(node->right);}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质2(根为黑色)---bool checkRootProperty() const {return root->color == BLACK;}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质4(红节点的子节点为黑)---bool checkRedParentProperty(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {if (node == nil) return true;if (node->color == RED) {if (node->left->color == RED || node->right->color == RED) {return false;}}return checkRedParentProperty(node->left) && checkRedParentProperty(node->right);}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质5(每条路径黑节点数相同)---int blackHeight(RBNode<K, V>* node) const {if (node == nil) return 1; // 外部节点(nil)的黑高为1int leftBH = blackHeight(node->left);int rightBH = blackHeight(node->right);if (leftBH != rightBH) return -1; // 左右黑高不同,违反性质return leftBH + (node->color == BLACK ? 1 : 0);}bool checkBlackHeightProperty() const {return blackHeight(root) != -1;}public:// 构造函数:初始化哨兵和根RedBlackTree() {nil = new RBNode<K, V>(K(), V());nil->color = BLACK;root = nil;treeSize = 0;}// 析构函数:销毁所有节点~RedBlackTree() {destroy(root);delete nil;}// --- 对外插入接口 ---void insert(const K& key, const V& value) {RBNode<K, V>* z = new RBNode<K, V>(key, value);z->left = z->right = z->parent = nil; // 新节点的子、父初始指向哨兵RBNode<K, V>* parent = nil;RBNode<K, V>* curr = root;// 找插入位置(同二叉搜索树)while (curr != nil) {parent = curr;if (z->key < curr->key) {curr = curr->left;} else {curr = curr->right;}}z->parent = parent;if (parent == nil) { // 树为空,新节点为根root = z;} else if (z->key < parent->key) { // 插在父的左子树parent->left = z;} else { // 插在父的右子树parent->right = z;}insertFixup(z); // 修复红黑树性质treeSize++; // 增加节点计数}// --- 对外查找接口 ---bool search(const K& key, V& value) const {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node != nil) {value = node->value;return true;}return false;}// --- 对外删除接口 ---bool remove(const K& key) {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) {return false; // 未找到节点}deleteNode(node);return true;}// --- 更新节点值 ---bool update(const K& key, const V& newValue) {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node != nil) {node->value = newValue;return true;}return false;}// --- 前序遍历 ---vector<pair<K, V>> preorder() const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;preorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 中序遍历 ---vector<pair<K, V>> inorder() const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;inorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 后序遍历 ---vector<pair<K, V>> postorder() const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;postorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 层序遍历 ---vector<pair<K, V>> levelorder() const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;if (root == nil) return result;queue<RBNode<K, V>*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {RBNode<K, V>* node = q.front();q.pop();result.emplace_back(node->key, node->value);if (node->left != nil)q.push(node->left);if (node->right != nil)q.push(node->right);}return result;}// --- 获取树的大小 ---int size() const {return treeSize;}// --- 获取树的高度 ---int height() const {return heightHelper(root);}// --- 检查树是否为空 ---bool isEmpty() const {return root == nil;}// --- 清空树 ---void clear() {destroy(root);root = nil;treeSize = 0;}// --- 查找最小值 ---bool findMin(K& key, V& value) const {if (isEmpty()) return false;RBNode<K, V>* node = minimum(root);key = node->key;value = node->value;return true;}// --- 查找最大值 ---bool findMax(K& key, V& value) const {if (isEmpty()) return false;RBNode<K, V>* node = maximum(root);key = node->key;value = node->value;return true;}// --- 查找前驱节点(小于当前键的最大键)---bool findPredecessor(const K& key, K& predKey, V& predValue) const {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return false;// 左子树非空:前驱是左子树的最大值if (node->left != nil) {RBNode<K, V>* pred = maximum(node->left);predKey = pred->key;predValue = pred->value;return true;}// 左子树为空:向上找第一个有右子树的祖先RBNode<K, V>* pred = node->parent;while (pred != nil && node == pred->left) {node = pred;pred = pred->parent;}if (pred != nil) {predKey = pred->key;predValue = pred->value;return true;}return false; // 无前列}// --- 查找后继节点(大于当前键的最小键)---bool findSuccessor(const K& key, K& succKey, V& succValue) const {RBNode<K, V>* node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return false;// 右子树非空:后继是右子树的最小值if (node->right != nil) {RBNode<K, V>* succ = minimum(node->right);succKey = succ->key;succValue = succ->value;return true;}// 右子树为空:向上找第一个有左子树的祖先RBNode<K, V>* succ = node->parent;while (succ != nil && node == succ->right) {node = succ;succ = succ->parent;}if (succ != nil) {succKey = succ->key;succValue = succ->value;return true;}return false; // 无后继}// --- 打印树结构 ---void printStructure() const {if (isEmpty()) {cout << "Tree is empty" << endl;return;}printStructureHelper(root, "", true);}// --- 范围查询:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的键值对 ---vector<pair<K, V>> rangeQuery(const K& minKey, const K& maxKey) const {vector<pair<K, V>> result;rangeQueryHelper(root, minKey, maxKey, result);return result;}// --- 统计区间节点数:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的节点数量 ---int countRange(const K& minKey, const K& maxKey) const {return countRangeHelper(root, minKey, maxKey);}// --- 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质(性质1-5)---bool checkProperties() const {bool valid = true;if (!checkColorProperty(root)) {cout << "违反性质1:节点颜色不是红色或黑色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkRootProperty()) {cout << "违反性质2:根节点不是黑色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkRedParentProperty(root)) {cout << "违反性质4:存在红色节点的子节点为红色" << endl;valid = false;}if (!checkBlackHeightProperty()) {cout << "违反性质5:从根到叶的路径黑节点数不同" << endl;valid = false;}if (valid) cout << "红黑树所有性质均满足" << endl;return valid;}
};int main() {// 测试<int, string>类型的红黑树RedBlackTree<int, string> rbt;cout << "=== 测试插入操作 ===" << endl;rbt.insert(10, "Ten");rbt.insert(20, "Twenty");rbt.insert(5, "Five");rbt.insert(15, "Fifteen");rbt.insert(30, "Thirty");rbt.insert(25, "Twenty-five");rbt.insert(35, "Thirty-five");cout << "树的大小: " << rbt.size() << endl;cout << "树的高度: " << rbt.height() << endl;cout << "\n=== 测试树结构 ===" << endl;rbt.printStructure();cout << "\n=== 测试查找操作 ===" << endl;string val;if (rbt.search(10, val)) {cout << "找到键 10: 值 = " << val << endl;} else {cout << "未找到键 10!" << endl;}if (rbt.search(15, val)) {cout << "找到键 15: 值 = " << val << endl;}cout << "\n=== 测试更新操作 ===" << endl;if (rbt.update(10, "Ten Updated")) {if (rbt.search(10, val)) {cout << "更新后键 10 的值: " << val << endl;}}cout << "\n=== 测试遍历操作 ===" << endl;auto preorder = rbt.preorder();cout << "前序遍历: ";for (const auto& p : preorder) cout << p.first << " ";cout << endl;auto inorder = rbt.inorder();cout << "中序遍历: ";for (const auto& p : inorder) cout << p.first << " ";cout << endl;auto postorder = rbt.postorder();cout << "后序遍历: ";for (const auto& p : postorder) cout << p.first << " ";cout << endl;auto levelorder = rbt.levelorder();cout << "层序遍历: ";for (const auto& p : levelorder) cout << p.first << " ";cout << endl;cout << "\n=== 测试最大最小值 ===" << endl;int minKey, maxKey;string minVal, maxVal;if (rbt.findMin(minKey, minVal)) {cout << "最小值: " << minKey << " (" << minVal << ")" << endl;}if (rbt.findMax(maxKey, maxVal)) {cout << "最大值: " << maxKey << " (" << maxVal << ")" << endl;}cout << "\n=== 测试前驱后继 ===" << endl;int predKey, succKey;string predVal, succVal;if (rbt.findPredecessor(20, predKey, predVal)) {cout << "20 的前驱: " << predKey << " (" << predVal << ")" << endl;}if (rbt.findSuccessor(20, succKey, succVal)) {cout << "20 的后继: " << succKey << " (" << succVal << ")" << endl;}cout << "\n=== 测试删除操作 ===" << endl;if (rbt.remove(10)) {cout << "已删除键 10" << endl;if (!rbt.search(10, val)) {cout << "确认键 10 已删除" << endl;}}cout << "删除后树的大小: " << rbt.size() << endl;cout << "删除后树结构: " << endl;rbt.printStructure();cout << "\n=== 测试范围查询 ===" << endl;auto range = rbt.rangeQuery(15, 30);cout << "键在 15 到 30 之间的节点: " << endl;for (const auto& p : range) {cout << "键: " << p.first << ", 值: " << p.second << endl;}cout << "该区间内节点数量: " << rbt.countRange(15, 30) << endl;cout << "\n=== 测试红黑树性质检查 ===" << endl;rbt.checkProperties();cout << "\n=== 测试清空操作 ===" << endl;rbt.clear();cout << "清空后树的大小: " << rbt.size() << endl;cout << "树是否为空: " << (rbt.isEmpty() ? "是" : "否") << endl;return 0;
}
(二)Python代码如下:
# 颜色枚举:红、黑
class Color:RED = 0BLACK = 1# 红黑树节点类
class RBNode:def __init__(self, key, value):self.key = key # 键self.value = value # 值self.color = Color.RED # 颜色,新节点默认为红色self.left = None # 左子节点self.right = None # 右子节点self.parent = None # 父节点# 红黑树类
class RedBlackTree:def __init__(self):# 哨兵节点,代替None,颜色为黑色self.nil = RBNode(None, None)self.nil.color = Color.BLACKself.root = self.nil # 根节点self.tree_size = 0 # 树中节点数量# --- 辅助操作:左旋 ---def left_rotate(self, x):y = x.right # y是x的右孩子x.right = y.leftif y.left != self.nil:y.left.parent = xy.parent = x.parentif x.parent == self.nil:self.root = yelif x == x.parent.left:x.parent.left = yelse:x.parent.right = yy.left = xx.parent = y# --- 辅助操作:右旋 ---def right_rotate(self, y):x = y.left # x是y的左孩子y.left = x.rightif x.right != self.nil:x.right.parent = yx.parent = y.parentif y.parent == self.nil:self.root = xelif y == y.parent.left:y.parent.left = xelse:y.parent.right = xx.right = yy.parent = x# --- 插入后修复红黑树性质 ---def insert_fixup(self, z):# 当父节点为红色时,可能违反红黑树性质while z.parent.color == Color.RED:if z.parent == z.parent.parent.left:# 父节点是祖父的左孩子uncle = z.parent.parent.rightif uncle.color == Color.RED:# 情况1:叔节点为红,只需变色z.parent.color = Color.BLACKuncle.color = Color.BLACKz.parent.parent.color = Color.REDz = z.parent.parent # 继续向上修复else:# 叔节点为黑if z == z.parent.right:# 情况2:z是父节点的右孩子,先左旋z = z.parentself.left_rotate(z)# 情况3:z是父节点的左孩子,变色并右旋z.parent.color = Color.BLACKz.parent.parent.color = Color.REDself.right_rotate(z.parent.parent)else:# 父节点是祖父的右孩子,对称情况uncle = z.parent.parent.leftif uncle.color == Color.RED:# 情况1:叔节点为红,只需变色z.parent.color = Color.BLACKuncle.color = Color.BLACKz.parent.parent.color = Color.REDz = z.parent.parent # 继续向上修复else:# 叔节点为黑if z == z.parent.left:# 情况2:z是父节点的左孩子,先右旋z = z.parentself.right_rotate(z)# 情况3:z是父节点的右孩子,变色并左旋z.parent.color = Color.BLACKz.parent.parent.color = Color.REDself.left_rotate(z.parent.parent)# 确保根节点始终为黑色self.root.color = Color.BLACK# --- 查找节点(内部辅助)---def _search_node(self, key):curr = self.rootwhile curr != self.nil:if key < curr.key:curr = curr.leftelif key > curr.key:curr = curr.rightelse:return curr # 找到节点return self.nil # 未找到# --- 找子树中最小节点(用于删除时找后继)---def _minimum(self, node):while node.left != self.nil:node = node.leftreturn node# --- 找子树中最大节点 ---def _maximum(self, node):while node.right != self.nil:node = node.rightreturn node# --- 删除后修复红黑树性质 ---def delete_fixup(self, x):# 当x为黑且非根时,可能违反红黑树性质while x != self.root and x.color == Color.BLACK:if x == x.parent.left:# x是父节点的左孩子sibling = x.parent.rightif sibling.color == Color.RED:# 情况1:兄弟是红,变色并左旋sibling.color = Color.BLACKx.parent.color = Color.REDself.left_rotate(x.parent)sibling = x.parent.rightif (sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK andsibling.right.color == Color.BLACK):# 情况2:兄弟的两个孩子都是黑sibling.color = Color.REDx = x.parentelse:if sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK:# 情况3:兄弟右孩子是黑,左孩子是红sibling.left.color = Color.BLACKsibling.color = Color.REDself.right_rotate(sibling)sibling = x.parent.right# 情况4:兄弟右孩子是红sibling.color = x.parent.colorx.parent.color = Color.BLACKsibling.right.color = Color.BLACKself.left_rotate(x.parent)x = self.root # 结束循环else:# x是父节点的右孩子,对称情况sibling = x.parent.leftif sibling.color == Color.RED:# 情况1:兄弟是红,变色并右旋sibling.color = Color.BLACKx.parent.color = Color.REDself.right_rotate(x.parent)sibling = x.parent.leftif (sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK andsibling.left.color == Color.BLACK):# 情况2:兄弟的两个孩子都是黑sibling.color = Color.REDx = x.parentelse:if sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK:# 情况3:兄弟左孩子是黑,右孩子是红sibling.right.color = Color.BLACKsibling.color = Color.REDself.left_rotate(sibling)sibling = x.parent.left# 情况4:兄弟左孩子是红sibling.color = x.parent.colorx.parent.color = Color.BLACKsibling.left.color = Color.BLACKself.right_rotate(x.parent)x = self.root # 结束循环# 确保x最终为黑色x.color = Color.BLACK# --- 移植操作:用v替换u ---def _transplant(self, u, v):if u.parent == self.nil:self.root = velif u == u.parent.left:u.parent.left = velse:u.parent.right = vv.parent = u.parent# --- 删除节点(内部辅助)---def _delete_node(self, z):y = zy_original_color = y.colorx = self.nil# 情况1:z只有右孩子if z.left == self.nil:x = z.rightself._transplant(z, z.right)# 情况2:z只有左孩子elif z.right == self.nil:x = z.leftself._transplant(z, z.left)# 情况3:z有两个孩子else:y = self._minimum(z.right)y_original_color = y.colorx = y.rightif y.parent == z:x.parent = yelse:self._transplant(y, y.right)y.right = z.righty.right.parent = yself._transplant(z, y)y.left = z.lefty.left.parent = yy.color = z.color# 若删除的是黑色节点,可能破坏性质,需修复if y_original_color == Color.BLACK:self.delete_fixup(x)self.tree_size -= 1# --- 销毁树(内部辅助)---def _destroy(self, node):if node != self.nil:self._destroy(node.left)self._destroy(node.right)# --- 前序遍历辅助函数 ---def _preorder_helper(self, node, result):if node != self.nil:result.append((node.key, node.value))self._preorder_helper(node.left, result)self._preorder_helper(node.right, result)# --- 中序遍历辅助函数 ---def _inorder_helper(self, node, result):if node != self.nil:self._inorder_helper(node.left, result)result.append((node.key, node.value))self._inorder_helper(node.right, result)# --- 后序遍历辅助函数 ---def _postorder_helper(self, node, result):if node != self.nil:self._postorder_helper(node.left, result)self._postorder_helper(node.right, result)result.append((node.key, node.value))# --- 计算树高度辅助函数 ---def _height_helper(self, node):if node == self.nil:return 0left_height = self._height_helper(node.left)right_height = self._height_helper(node.right)return max(left_height, right_height) + 1# --- 打印树结构辅助函数 ---def _print_structure_helper(self, node, indent, last):if node != self.nil:print(indent, end="")if last:print("R----", end="")indent += " "else:print("L----", end="")indent += "| "color = "RED" if node.color == Color.RED else "BLACK"print(f"{node.key}({color})")self._print_structure_helper(node.left, indent, False)self._print_structure_helper(node.right, indent, True)# --- 范围查询辅助函数 ---def _range_query_helper(self, node, min_key, max_key, result):if node == self.nil:return# 左子树可能有符合条件的节点if node.key > min_key:self._range_query_helper(node.left, min_key, max_key, result)# 当前节点在范围内,加入结果if min_key <= node.key <= max_key:result.append((node.key, node.value))# 右子树可能有符合条件的节点if node.key < max_key:self._range_query_helper(node.right, min_key, max_key, result)# --- 统计区间节点数辅助函数 ---def _count_range_helper(self, node, min_key, max_key):if node == self.nil:return 0count = 0# 当前节点在范围内,计数+1if min_key <= node.key <= max_key:count = 1# 左子树递归统计if node.key > min_key:count += self._count_range_helper(node.left, min_key, max_key)# 右子树递归统计if node.key < max_key:count += self._count_range_helper(node.right, min_key, max_key)return count# --- 检查红黑树性质:性质1(颜色合法性)---def _check_color_property(self, node):if node == self.nil:return Trueif node.color not in (Color.RED, Color.BLACK):return Falsereturn (self._check_color_property(node.left) andself._check_color_property(node.right))# --- 检查红黑树性质:性质4(红节点的子节点为黑)---def _check_red_parent_property(self, node):if node == self.nil:return Trueif node.color == Color.RED:if (node.left.color == Color.RED ornode.right.color == Color.RED):return Falsereturn (self._check_red_parent_property(node.left) andself._check_red_parent_property(node.right))# --- 检查红黑树性质:性质5(每条路径黑节点数相同)---def _black_height(self, node):if node == self.nil:return 1 # 外部节点的黑高为1left_bh = self._black_height(node.left)right_bh = self._black_height(node.right)if left_bh != right_bh:return -1 # 左右黑高不同,违反性质return left_bh + (1 if node.color == Color.BLACK else 0)# --- 对外插入接口 ---def insert(self, key, value):z = RBNode(key, value)z.left = self.nilz.right = self.nilz.parent = self.nilparent = self.nilcurr = self.root# 找插入位置while curr != self.nil:parent = currif z.key < curr.key:curr = curr.leftelse:curr = curr.rightz.parent = parentif parent == self.nil:self.root = z # 树为空,新节点为根elif z.key < parent.key:parent.left = z # 插在父的左子树else:parent.right = z # 插在父的右子树self.insert_fixup(z) # 修复红黑树性质self.tree_size += 1 # 增加节点计数# --- 对外查找接口 ---def search(self, key):node = self._search_node(key)if node != self.nil:return node.valuereturn None# --- 对外删除接口 ---def remove(self, key):node = self._search_node(key)if node == self.nil:return False # 未找到节点self._delete_node(node)return True# --- 更新节点值 ---def update(self, key, new_value):node = self._search_node(key)if node != self.nil:node.value = new_valuereturn Truereturn False# --- 前序遍历 ---def preorder(self):result = []self._preorder_helper(self.root, result)return result# --- 中序遍历 ---def inorder(self):result = []self._inorder_helper(self.root, result)return result# --- 后序遍历 ---def postorder(self):result = []self._postorder_helper(self.root, result)return result# --- 层序遍历 ---def levelorder(self):result = []if self.root == self.nil:return resultfrom collections import dequeq = deque()q.append(self.root)while q:node = q.popleft()result.append((node.key, node.value))if node.left != self.nil:q.append(node.left)if node.right != self.nil:q.append(node.right)return result# --- 获取树的大小 ---def size(self):return self.tree_size# --- 获取树的高度 ---def height(self):return self._height_helper(self.root)# --- 检查树是否为空 ---def is_empty(self):return self.root == self.nil# --- 清空树 ---def clear(self):self._destroy(self.root)self.root = self.nilself.tree_size = 0# --- 查找最小值 ---def find_min(self):if self.is_empty():return Nonenode = self._minimum(self.root)return (node.key, node.value)# --- 查找最大值 ---def find_max(self):if self.is_empty():return Nonenode = self._maximum(self.root)return (node.key, node.value)# --- 查找前驱节点(小于当前键的最大键)---def find_predecessor(self, key):node = self._search_node(key)if node == self.nil:return None# 左子树非空:前驱是左子树的最大值if node.left != self.nil:pred = self._maximum(node.left)return (pred.key, pred.value)# 左子树为空:向上找第一个有右子树的祖先pred = node.parentwhile pred != self.nil and node == pred.left:node = predpred = pred.parentif pred != self.nil:return (pred.key, pred.value)return None # 无前驱# --- 查找后继节点(大于当前键的最小键)---def find_successor(self, key):node = self._search_node(key)if node == self.nil:return None# 右子树非空:后继是右子树的最小值if node.right != self.nil:succ = self._minimum(node.right)return (succ.key, succ.value)# 右子树为空:向上找第一个有左子树的祖先succ = node.parentwhile succ != self.nil and node == succ.right:node = succsucc = succ.parentif succ != self.nil:return (succ.key, succ.value)return None # 无后继# --- 打印树结构 ---def print_structure(self):if self.is_empty():print("Tree is empty")returnself._print_structure_helper(self.root, "", True)# --- 范围查询:返回键在 [min_key, max_key] 之间的键值对 ---def range_query(self, min_key, max_key):result = []self._range_query_helper(self.root, min_key, max_key, result)return result# --- 统计区间节点数:返回键在 [min_key, max_key] 之间的节点数量 ---def count_range(self, min_key, max_key):return self._count_range_helper(self.root, min_key, max_key)# --- 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质(性质1-5)---def check_properties(self):valid = True# 性质1:每个节点不是红色就是黑色if not self._check_color_property(self.root):print("违反性质1:节点颜色不是红色或黑色")valid = False# 性质2:根节点是黑色if self.root.color != Color.BLACK:print("违反性质2:根节点不是黑色")valid = False# 性质4:如果一个节点是红色,则它的两个子节点都是黑色if not self._check_red_parent_property(self.root):print("违反性质4:存在红色节点的子节点为红色")valid = False# 性质5:从任一节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,黑色节点的数量相同if self._black_height(self.root) == -1:print("违反性质5:从根到叶的路径黑节点数不同")valid = Falseif valid:print("红黑树所有性质均满足")return valid# 测试红黑树
def main():# 创建红黑树实例rbt = RedBlackTree()print("=== 测试插入操作 ===")rbt.insert(10, "Ten")rbt.insert(20, "Twenty")rbt.insert(5, "Five")rbt.insert(15, "Fifteen")rbt.insert(30, "Thirty")rbt.insert(25, "Twenty-five")rbt.insert(35, "Thirty-five")print(f"树的大小: {rbt.size()}")print(f"树的高度: {rbt.height()}")print("\n=== 测试树结构 ===")rbt.print_structure()print("\n=== 测试查找操作 ===")val = rbt.search(10)if val is not None:print(f"找到键 10: 值 = {val}")else:print("未找到键 10!")val = rbt.search(15)if val is not None:print(f"找到键 15: 值 = {val}")print("\n=== 测试更新操作 ===")if rbt.update(10, "Ten Updated"):val = rbt.search(10)if val is not None:print(f"更新后键 10 的值: {val}")print("\n=== 测试遍历操作 ===")preorder = rbt.preorder()print("前序遍历: ", end="")for p in preorder:print(p[0], end=" ")print()inorder = rbt.inorder()print("中序遍历: ", end="")for p in inorder:print(p[0], end=" ")print()postorder = rbt.postorder()print("后序遍历: ", end="")for p in postorder:print(p[0], end=" ")print()levelorder = rbt.levelorder()print("层序遍历: ", end="")for p in levelorder:print(p[0], end=" ")print()print("\n=== 测试最大最小值 ===")min_node = rbt.find_min()if min_node:print(f"最小值: {min_node[0]} ({min_node[1]})")max_node = rbt.find_max()if max_node:print(f"最大值: {max_node[0]} ({max_node[1]})")print("\n=== 测试前驱后继 ===")pred = rbt.find_predecessor(20)if pred:print(f"20 的前驱: {pred[0]} ({pred[1]})")succ = rbt.find_successor(20)if succ:print(f"20 的后继: {succ[0]} ({succ[1]})")print("\n=== 测试删除操作 ===")if rbt.remove(10):print("已删除键 10")if rbt.search(10) is None:print("确认键 10 已删除")print(f"删除后树的大小: {rbt.size()}")print("删除后树结构: ")rbt.print_structure()print("\n=== 测试范围查询 ===")range_result = rbt.range_query(15, 30)print("键在 15 到 30 之间的节点: ")for p in range_result:print(f"键: {p[0]}, 值: {p[1]}")print(f"该区间内节点数量: {rbt.count_range(15, 30)}")print("\n=== 测试红黑树性质检查 ===")rbt.check_properties()print("\n=== 测试清空操作 ===")rbt.clear()print(f"清空后树的大小: {rbt.size()}")print(f"树是否为空: {'是' if rbt.is_empty() else '否'}")if __name__ == "__main__":main()
(三)Java代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.AbstractMap.SimpleEntry;// 颜色枚举
enum Color {RED, BLACK
}// 红黑树节点类
class RBNode<K, V> {K key;V value;Color color;RBNode<K, V> left;RBNode<K, V> right;RBNode<K, V> parent;RBNode(K key, V value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.color = Color.RED;this.left = null;this.right = null;this.parent = null;}
}// 红黑树类(泛型约束:K必须实现Comparable接口以支持键比较)
public class RedBlackTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {private RBNode<K, V> root;private final RBNode<K, V> nil; // 哨兵节点(代替null,颜色为BLACK)private int treeSize;public RedBlackTree() {nil = new RBNode<>(null, null);nil.color = Color.BLACK;root = nil;treeSize = 0;}// --- 辅助操作:左旋 ---private void leftRotate(RBNode<K, V> x) {RBNode<K, V> y = x.right;x.right = y.left;if (y.left != nil) {y.left.parent = x;}y.parent = x.parent;if (x.parent == nil) {root = y;} else if (x == x.parent.left) {x.parent.left = y;} else {x.parent.right = y;}y.left = x;x.parent = y;}// --- 辅助操作:右旋 ---private void rightRotate(RBNode<K, V> y) {RBNode<K, V> x = y.left;y.left = x.right;if (x.right != nil) {x.right.parent = y;}x.parent = y.parent;if (y.parent == nil) {root = x;} else if (y == y.parent.left) {y.parent.left = x;} else {y.parent.right = x;}x.right = y;y.parent = x;}// --- 插入后修复红黑树性质 ---private void insertFixup(RBNode<K, V> z) {while (z.parent.color == Color.RED) {if (z.parent == z.parent.parent.left) {RBNode<K, V> uncle = z.parent.parent.right;if (uncle.color == Color.RED) {z.parent.color = Color.BLACK;uncle.color = Color.BLACK;z.parent.parent.color = Color.RED;z = z.parent.parent;} else {if (z == z.parent.right) {z = z.parent;leftRotate(z);}z.parent.color = Color.BLACK;z.parent.parent.color = Color.RED;rightRotate(z.parent.parent);}} else {RBNode<K, V> uncle = z.parent.parent.left;if (uncle.color == Color.RED) {z.parent.color = Color.BLACK;uncle.color = Color.BLACK;z.parent.parent.color = Color.RED;z = z.parent.parent;} else {if (z == z.parent.left) {z = z.parent;rightRotate(z);}z.parent.color = Color.BLACK;z.parent.parent.color = Color.RED;leftRotate(z.parent.parent);}}}root.color = Color.BLACK;}// --- 查找节点(内部辅助)---private RBNode<K, V> searchNode(K key) {RBNode<K, V> curr = root;while (curr != nil) {int cmp = key.compareTo(curr.key);if (cmp < 0) {curr = curr.left;} else if (cmp > 0) {curr = curr.right;} else {return curr; // 找到节点}}return nil; // 未找到}// --- 找子树中最小节点(用于删除时找后继)---private RBNode<K, V> minimum(RBNode<K, V> node) {while (node.left != nil) {node = node.left;}return node;}// --- 找子树中最大节点 ---private RBNode<K, V> maximum(RBNode<K, V> node) {while (node.right != nil) {node = node.right;}return node;}// --- 删除后修复红黑树性质 ---private void deleteFixup(RBNode<K, V> x) {while (x != root && x.color == Color.BLACK) {if (x == x.parent.left) {RBNode<K, V> sibling = x.parent.right;if (sibling.color == Color.RED) {sibling.color = Color.BLACK;x.parent.color = Color.RED;leftRotate(x.parent);sibling = x.parent.right;}if (sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK && sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK) {sibling.color = Color.RED;x = x.parent;} else {if (sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK) {sibling.left.color = Color.BLACK;sibling.color = Color.RED;rightRotate(sibling);sibling = x.parent.right;}sibling.color = x.parent.color;x.parent.color = Color.BLACK;sibling.right.color = Color.BLACK;leftRotate(x.parent);x = root;}} else {RBNode<K, V> sibling = x.parent.left;if (sibling.color == Color.RED) {sibling.color = Color.BLACK;x.parent.color = Color.RED;rightRotate(x.parent);sibling = x.parent.left;}if (sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK && sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK) {sibling.color = Color.RED;x = x.parent;} else {if (sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK) {sibling.right.color = Color.BLACK;sibling.color = Color.RED;leftRotate(sibling);sibling = x.parent.left;}sibling.color = x.parent.color;x.parent.color = Color.BLACK;sibling.left.color = Color.BLACK;rightRotate(x.parent);x = root;}}}x.color = Color.BLACK;}// --- 移植操作:用v替换u(二叉搜索树通用操作)---private void transplant(RBNode<K, V> u, RBNode<K, V> v) {if (u.parent == nil) {root = v;} else if (u == u.parent.left) {u.parent.left = v;} else {u.parent.right = v;}v.parent = u.parent;}// --- 删除节点(内部辅助,与二叉搜索树逻辑结合后修复)---private void deleteNode(RBNode<K, V> z) {RBNode<K, V> y = z;RBNode<K, V> x = nil;Color yOriginalColor = y.color;if (z.left == nil) {x = z.right;transplant(z, z.right);} else if (z.right == nil) {x = z.left;transplant(z, z.left);} else {y = minimum(z.right);yOriginalColor = y.color;x = y.right;if (y.parent == z) {x.parent = y;} else {transplant(y, y.right);y.right = z.right;y.right.parent = y;}transplant(z, y);y.left = z.left;y.left.parent = y;y.color = z.color;}if (yOriginalColor == Color.BLACK) {deleteFixup(x);}treeSize--;}// --- 前序遍历辅助函数 ---private void preorderHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, List<Entry<K, V>> result) {if (node != nil) {result.add(new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value));preorderHelper(node.left, result);preorderHelper(node.right, result);}}// --- 中序遍历辅助函数 ---private void inorderHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, List<Entry<K, V>> result) {if (node != nil) {inorderHelper(node.left, result);result.add(new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value));inorderHelper(node.right, result);}}// --- 后序遍历辅助函数 ---private void postorderHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, List<Entry<K, V>> result) {if (node != nil) {postorderHelper(node.left, result);postorderHelper(node.right, result);result.add(new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value));}}// --- 计算树高度辅助函数 ---private int heightHelper(RBNode<K, V> node) {if (node == nil) {return 0;}int leftHeight = heightHelper(node.left);int rightHeight = heightHelper(node.right);return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}// --- 打印树结构辅助函数 ---private void printStructureHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, String indent, boolean last) {if (node != nil) {System.out.print(indent);if (last) {System.out.print("R----");indent += " ";} else {System.out.print("L----");indent += "| ";}String color = (node.color == Color.RED) ? "RED" : "BLACK";System.out.println(node.key + "(" + color + ")");printStructureHelper(node.left, indent, false);printStructureHelper(node.right, indent, true);}}// --- 范围查询辅助函数 ---private void rangeQueryHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, K minKey, K maxKey, List<Entry<K, V>> result) {if (node == nil) return;if (node.key.compareTo(minKey) > 0) {rangeQueryHelper(node.left, minKey, maxKey, result);}if (node.key.compareTo(minKey) >= 0 && node.key.compareTo(maxKey) <= 0) {result.add(new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value));}if (node.key.compareTo(maxKey) < 0) {rangeQueryHelper(node.right, minKey, maxKey, result);}}// --- 统计区间节点数辅助函数 ---private int countRangeHelper(RBNode<K, V> node, K minKey, K maxKey) {if (node == nil) return 0;int count = 0;if (node.key.compareTo(minKey) >= 0 && node.key.compareTo(maxKey) <= 0) {count = 1;}if (node.key.compareTo(minKey) > 0) {count += countRangeHelper(node.left, minKey, maxKey);}if (node.key.compareTo(maxKey) < 0) {count += countRangeHelper(node.right, minKey, maxKey);}return count;}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质1(颜色合法性)---private boolean checkColorProperty(RBNode<K, V> node) {if (node == nil) return true;if (node.color != Color.RED && node.color != Color.BLACK) return false;return checkColorProperty(node.left) && checkColorProperty(node.right);}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质2(根为黑色)---private boolean checkRootProperty() {return root.color == Color.BLACK;}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质4(红节点的子节点为黑)---private boolean checkRedParentProperty(RBNode<K, V> node) {if (node == nil) return true;if (node.color == Color.RED) {if (node.left.color == Color.RED || node.right.color == Color.RED) {return false;}}return checkRedParentProperty(node.left) && checkRedParentProperty(node.right);}// --- 检查红黑树性质:性质5(每条路径黑节点数相同)---private int blackHeight(RBNode<K, V> node) {if (node == nil) return 1; // 外部节点(nil)的黑高为1int leftBH = blackHeight(node.left);int rightBH = blackHeight(node.right);if (leftBH != rightBH) return -1; // 左右黑高不同,违反性质return leftBH + (node.color == Color.BLACK ? 1 : 0);}private boolean checkBlackHeightProperty() {return blackHeight(root) != -1;}// ====================== 对外接口 ======================// --- 对外插入接口 ---public void insert(K key, V value) {RBNode<K, V> z = new RBNode<>(key, value);z.left = nil;z.right = nil;z.parent = nil;RBNode<K, V> parent = nil;RBNode<K, V> curr = root;// 找插入位置(同二叉搜索树)while (curr != nil) {parent = curr;int cmp = key.compareTo(curr.key);if (cmp < 0) {curr = curr.left;} else {curr = curr.right;}}z.parent = parent;if (parent == nil) { // 树为空,新节点为根root = z;} else if (key.compareTo(parent.key) < 0) { // 插在父的左子树parent.left = z;} else { // 插在父的右子树parent.right = z;}insertFixup(z); // 修复红黑树性质treeSize++; // 增加节点计数}// --- 对外查找接口 ---public V search(K key) {RBNode<K, V> node = searchNode(key);if (node != nil) {return node.value;}return null;}// --- 对外删除接口 ---public boolean remove(K key) {RBNode<K, V> node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) {return false; // 未找到节点}deleteNode(node);return true;}// --- 更新节点值 ---public boolean update(K key, V newValue) {RBNode<K, V> node = searchNode(key);if (node != nil) {node.value = newValue;return true;}return false;}// --- 前序遍历 ---public List<Entry<K, V>> preorder() {List<Entry<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();preorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 中序遍历 ---public List<Entry<K, V>> inorder() {List<Entry<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();inorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 后序遍历 ---public List<Entry<K, V>> postorder() {List<Entry<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();postorderHelper(root, result);return result;}// --- 层序遍历 ---public List<Entry<K, V>> levelorder() {List<Entry<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == nil) return result;Queue<RBNode<K, V>> q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(root);while (!q.isEmpty()) {RBNode<K, V> node = q.poll();result.add(new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value));if (node.left != nil)q.offer(node.left);if (node.right != nil)q.offer(node.right);}return result;}// --- 获取树的大小 ---public int size() {return treeSize;}// --- 获取树的高度 ---public int height() {return heightHelper(root);}// --- 检查树是否为空 ---public boolean isEmpty() {return root == nil;}// --- 清空树 ---public void clear() {root = nil;treeSize = 0;}// --- 查找最小值 ---public Entry<K, V> findMin() {if (isEmpty()) return null;RBNode<K, V> node = minimum(root);return new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value);}// --- 查找最大值 ---public Entry<K, V> findMax() {if (isEmpty()) return null;RBNode<K, V> node = maximum(root);return new SimpleEntry<>(node.key, node.value);}// --- 查找前驱节点(小于当前键的最大键)---public Entry<K, V> findPredecessor(K key) {RBNode<K, V> node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return null;// 左子树非空:前驱是左子树的最大值if (node.left != nil) {RBNode<K, V> pred = maximum(node.left);return new SimpleEntry<>(pred.key, pred.value);}// 左子树为空:向上找第一个有右子树的祖先RBNode<K, V> pred = node.parent;while (pred != nil && node == pred.left) {node = pred;pred = pred.parent;}if (pred != nil) {return new SimpleEntry<>(pred.key, pred.value);}return null;}// --- 查找后继节点(大于当前键的最小键)---public Entry<K, V> findSuccessor(K key) {RBNode<K, V> node = searchNode(key);if (node == nil) return null;// 右子树非空:后继是右子树的最小值if (node.right != nil) {RBNode<K, V> succ = minimum(node.right);return new SimpleEntry<>(succ.key, succ.value);}// 右子树为空:向上找第一个有左子树的祖先RBNode<K, V> succ = node.parent;while (succ != nil && node == succ.right) {node = succ;succ = succ.parent;}if (succ != nil) {return new SimpleEntry<>(succ.key, succ.value);}return null;}// --- 打印树结构 ---public void printStructure() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Tree is empty");return;}printStructureHelper(root, "", true);}// --- 范围查询:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的键值对 ---public List<Entry<K, V>> rangeQuery(K minKey, K maxKey) {List<Entry<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();rangeQueryHelper(root, minKey, maxKey, result);return result;}// --- 统计区间节点数:返回键在 [minKey, maxKey] 之间的节点数量 ---public int countRange(K minKey, K maxKey) {return countRangeHelper(root, minKey, maxKey);}// --- 检查红黑树是否满足所有性质(性质1-5)---public boolean checkProperties() {boolean valid = true;if (!checkColorProperty(root)) {System.out.println("违反性质1:节点颜色不是红色或黑色");valid = false;}if (!checkRootProperty()) {System.out.println("违反性质2:根节点不是黑色");valid = false;}if (!checkRedParentProperty(root)) {System.out.println("违反性质4:存在红色节点的子节点为红色");valid = false;}if (!checkBlackHeightProperty()) {System.out.println("违反性质5:从根到叶的路径黑节点数不同");valid = false;}if (valid) System.out.println("红黑树所有性质均满足");return valid;}// ====================== 测试方法 ======================public static void main(String[] args) {RedBlackTree<Integer, String> rbt = new RedBlackTree<>();System.out.println("=== 测试插入操作 ===");rbt.insert(10, "Ten");rbt.insert(20, "Twenty");rbt.insert(5, "Five");rbt.insert(15, "Fifteen");rbt.insert(30, "Thirty");rbt.insert(25, "Twenty-five");rbt.insert(35, "Thirty-five");System.out.println("树的大小: " + rbt.size());System.out.println("树的高度: " + rbt.height());System.out.println("\n=== 测试树结构 ===");rbt.printStructure();System.out.println("\n=== 测试查找操作 ===");String val = rbt.search(10);if (val != null) {System.out.println("找到键 10: 值 = " + val);} else {System.out.println("未找到键 10!");}val = rbt.search(15);if (val != null) {System.out.println("找到键 15: 值 = " + val);}System.out.println("\n=== 测试更新操作 ===");if (rbt.update(10, "Ten Updated")) {val = rbt.search(10);if (val != null) {System.out.println("更新后键 10 的值: " + val);}}System.out.println("\n=== 测试遍历操作 ===");List<Entry<Integer, String>> preorder = rbt.preorder();System.out.print("前序遍历: ");for (Entry<Integer, String> p : preorder) {System.out.print(p.getKey() + " ");}System.out.println();List<Entry<Integer, String>> inorder = rbt.inorder();System.out.print("中序遍历: ");for (Entry<Integer, String> p : inorder) {System.out.print(p.getKey() + " ");}System.out.println();List<Entry<Integer, String>> postorder = rbt.postorder();System.out.print("后序遍历: ");for (Entry<Integer, String> p : postorder) {System.out.print(p.getKey() + " ");}System.out.println();List<Entry<Integer, String>> levelorder = rbt.levelorder();System.out.print("层序遍历: ");for (Entry<Integer, String> p : levelorder) {System.out.print(p.getKey() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("\n=== 测试最大最小值 ===");Entry<Integer, String> minNode = rbt.findMin();if (minNode != null) {System.out.println("最小值: " + minNode.getKey() + " (" + minNode.getValue() + ")");}Entry<Integer, String> maxNode = rbt.findMax();if (maxNode != null) {System.out.println("最大值: " + maxNode.getKey() + " (" + maxNode.getValue() + ")");}System.out.println("\n=== 测试前驱后继 ===");Entry<Integer, String> pred = rbt.findPredecessor(20);if (pred != null) {System.out.println("20 的前驱: " + pred.getKey() + " (" + pred.getValue() + ")");}Entry<Integer, String> succ = rbt.findSuccessor(20);if (succ != null) {System.out.println("20 的后继: " + succ.getKey() + " (" + succ.getValue() + ")");}System.out.println("\n=== 测试删除操作 ===");if (rbt.remove(10)) {System.out.println("已删除键 10");if (rbt.search(10) == null) {System.out.println("确认键 10 已删除");}}System.out.println("删除后树的大小: " + rbt.size());System.out.println("删除后树结构: ");rbt.printStructure();System.out.println("\n=== 测试范围查询 ===");List<Entry<Integer, String>> range = rbt.rangeQuery(15, 30);System.out.println("键在 15 到 30 之间的节点: ");for (Entry<Integer, String> p : range) {System.out.println("键: " + p.getKey() + ", 值: " + p.getValue());}System.out.println("该区间内节点数量: " + rbt.countRange(15, 30));System.out.println("\n=== 测试红黑树性质检查 ===");rbt.checkProperties();System.out.println("\n=== 测试清空操作 ===");rbt.clear();System.out.println("清空后树的大小: " + rbt.size());System.out.println("树是否为空: " + (rbt.isEmpty() ? "是" : "否"));}
}
四、程序运行结果展示
(一)C++代码运行截图如下:
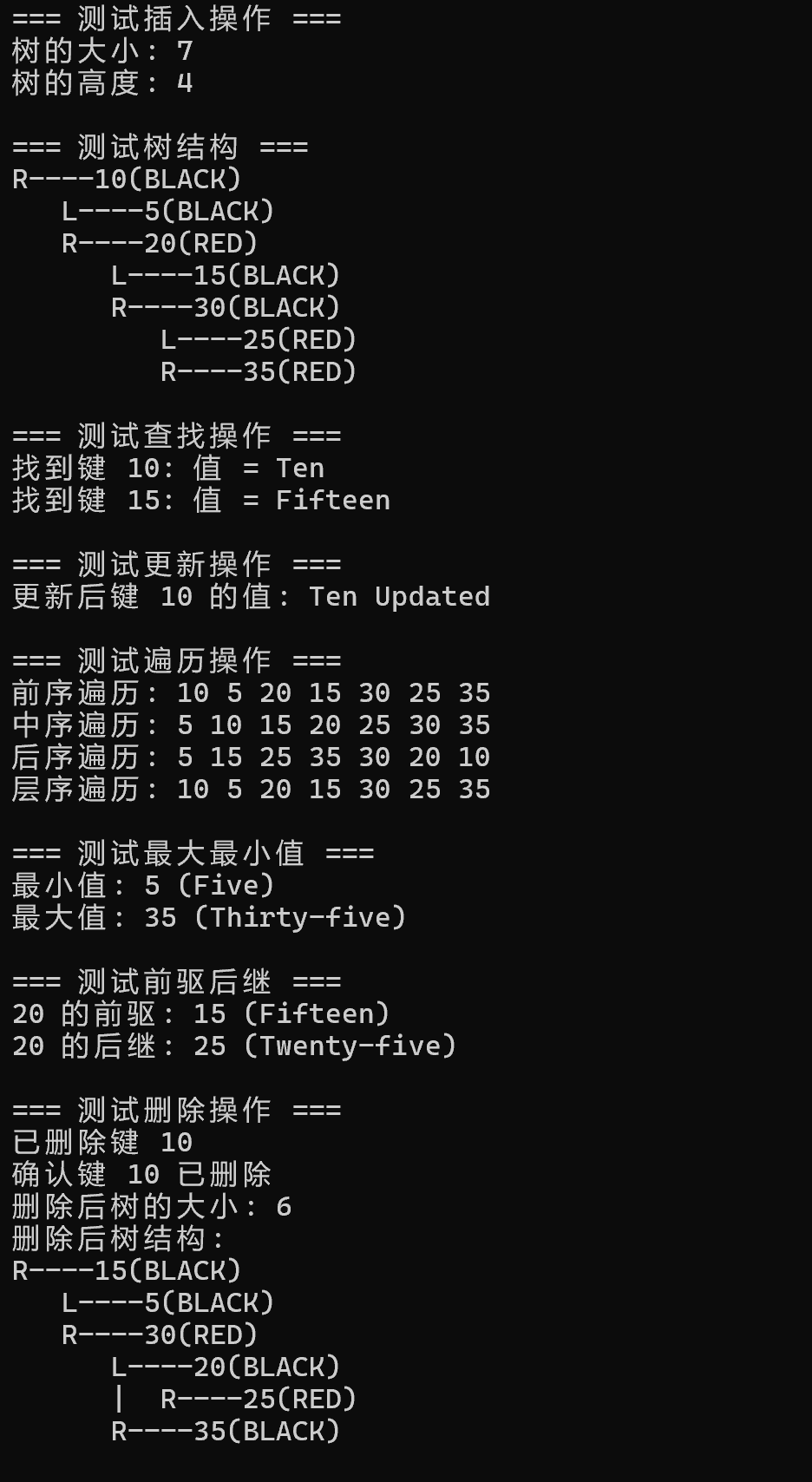
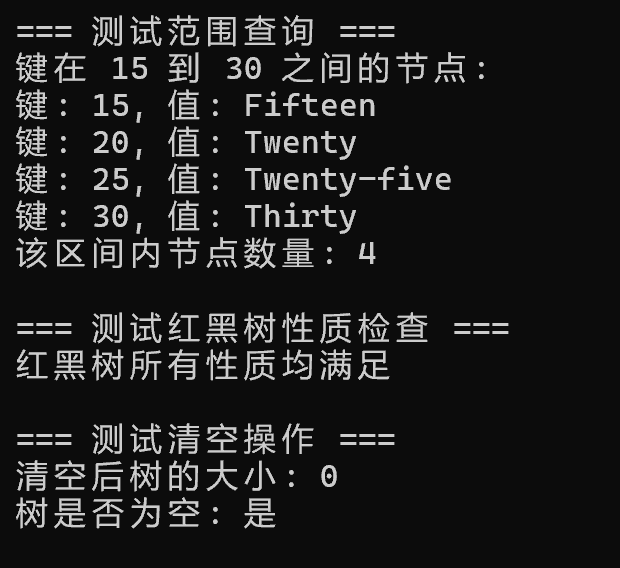
(二)Python代码运行截图如下:
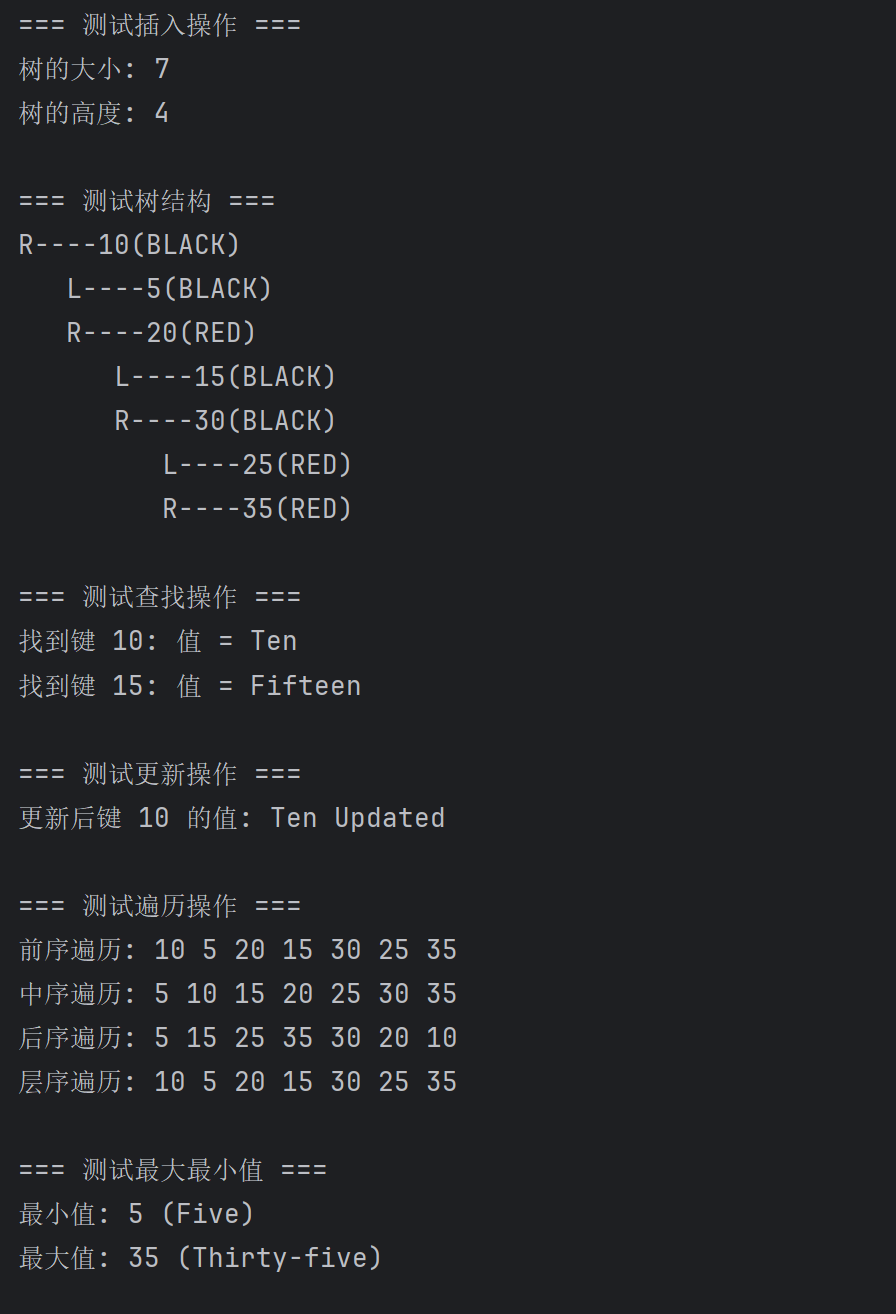
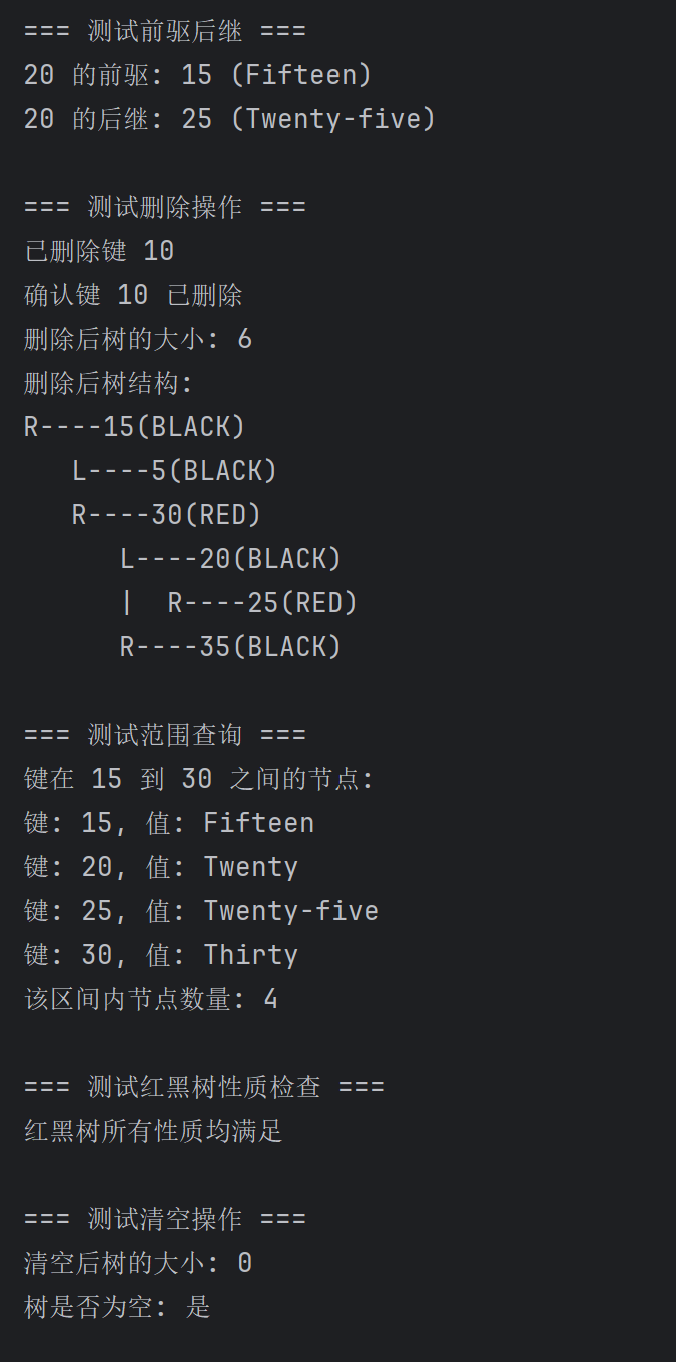
(三)Java代码运行截图如下:
五、时间复杂度的数学证明
红黑树的查询、插入、删除操作均能保持 O(log n) 的时间复杂度,其核心在于通过自平衡机制严格限制树高的增长。以下从数学角度严谨证明这一结论,关键在于推导树高 h 与节点数 n 的关系不等式 。
(一)核心概念:黑高(Black Height)
黑高(记为 bh(x) )是红黑树平衡性分析的基础度量,定义为:从节点 x 出发(不包含 x 自身)到任意后代叶节点的路径上,黑色节点的数量。例如,若根节点到叶节点的路径包含 3 个黑色节点(不含根),则根节点的黑高 bh(root) = 3 。
树高与黑高的关系: 
红黑树的性质4(红色节点的子节点必为黑色)确保路径中不会出现连续红色节点,结合性质5(所有叶节点到根的黑色节点数相等),可推导出树高与黑高的关键关系:
• 最长路径分析:从根到叶的最长路径必然是红黑节点交替出现的情况(如黑→红→黑→红...)。此时,黑色节点数为 bh(root) ,红色节点数最多不超过 bh(root) (否则会违反性质4),因此总路径长度(树高 h )满足 。
• 最短路径分析:全黑路径的长度为 bh(root) ,故 。
综上,树高 h 与根节点黑高 bh(root) 的关系为:。
(二)归纳法证明:节点数下限与树高上限
1.定理:高度为 h 的红黑树至少包含  个内部节点
个内部节点
证明步骤:
1. 基础情况:当 h = 0 时,树为空,内部节点数为 0,满足 ,命题成立。
2. 归纳假设:假设高度为 h-1 的红黑树至少包含 个内部节点。
3. 归纳步骤:考虑高度为 h 的红黑树,其根节点的左右子树高度均不超过 h-1 。由黑高定义,根节点的黑高 ,则子节点的黑高至少为
(若子节点为黑色)或
(若子节点为红色,其子节点必为黑色,黑高不变)。
根据归纳假设,每个子树至少包含 个内部节点,因此整树节点数:
2.推导树高上限: 
由上述定理 ,整理得:
即红黑树的高度 h 与节点数 n 呈对数关系,故 。
(三)操作复杂度分析与对比
1.红黑树操作复杂度: 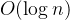
• 查找:路径长度等于树高 h ,故时间复杂度为 。
• 插入/删除:基础操作(如查找插入位置)耗时 ,修复平衡(旋转 O(1) 、变色
)的循环次数与树高成正比,总时间仍为
。
关键结论:红黑树通过限制树高 ,确保所有操作在最坏情况下仍保持
复杂度,远优于普通二叉搜索树(BST)在最坏情况下的 O(n)(如退化为链表时的查询耗时)。
2.与普通 BST 的对比
普通 BST 在随机数据下表现良好,但在有序数据插入时会退化为链表(如依次插入 1,2,3,4...),此时树高 h = n ,查询、插入、删除操作均退化为 O(n) 。而红黑树通过旋转和变色机制主动维持平衡性,即使在极端插入顺序下,树高仍被严格控制在 级别,因此在高频动态数据场景(如数据库索引、缓存实现)中具有不可替代的性能优势。
六、与AVL树的对比分析
红黑树与 AVL 树作为两种经典的自平衡二叉搜索树,在平衡机制、性能表现与工程应用上存在显著差异。本章将从平衡机制→性能指标→工程选择的逻辑框架展开对比,揭示两者在设计哲学与实践价值上的核心区别。
(一)平衡机制:近似平衡与严格平衡的分野
红黑树与 AVL 树的本质差异源于平衡控制策略的不同。红黑树采用“颜色约束驱动的近似平衡”,通过五条核心规则(如“从根到叶子的所有路径包含相同数量的黑色节点”“不存在连续红色节点”)将树高控制在 ≤ 2log(n+1) 的范围内,允许最长路径为最短路径的 2 倍,属于“弱平衡”设计。这种机制通过对节点颜色(红/黑)的管理实现“懒惰平衡”,仅在必要时触发调整,避免过度维护。
AVL 树则采用“高度差驱动的严格平衡”,要求任何节点的左右子树高度差(平衡因子)绝对值 ≤ 1,树高可被严格控制在 ≈ 1.44log(n+2),属于“强平衡”设计。这种机制通过实时计算并维护每个节点的平衡因子(左子树高度 - 右子树高度),确保树结构始终处于“极致矮胖”状态,但需付出更高的调整成本。
两种平衡机制的差异直接体现在插入操作的处理流程中:
A[插入新节点] --> B{是否是AVL树?}
B -->|是| C[计算所有祖先的平衡因子]
C --> D{平衡因子绝对值>1?}
D -->|是| E[旋转调整]
D -->|否| F[结束]
B -->|否(红黑树)| G[标记新节点为红色]
G --> H{父节点是红色?}
H -->|是| I[检查叔叔节点颜色]
I -->|叔叔是红色| J[父/叔变黑,祖父变红,向上递归]
I -->|叔叔是黑色/空| K[旋转调整+颜色翻转]
H -->|否| F[结束]从流程图可见,AVL 树插入后需回溯更新所有祖先节点的平衡因子,并可能触发多次旋转;而红黑树仅在父节点为红色时才需处理,且优先通过颜色调整(如父/叔节点变色)减少旋转操作,体现了“以颜色换旋转”的设计思想。
(二)性能指标:动态操作效率与空间开销的权衡
2.1 平衡维护成本:旋转次数的数量级差异
红黑树在动态操作(插入/删除)中表现出显著的效率优势。插入操作最多仅需 2 次旋转(如插入修复中的“单旋+变色”或“双旋+变色”),删除操作旋转次数同样为常数级 O(1)。这种低调整成本源于其“近似平衡”的特性——允许树结构在一定范围内波动,仅在突破颜色规则时触发最小化调整。
相比之下,AVL 树为维持严格平衡,插入/删除后可能需要多次递归旋转。例如,删除一个节点可能导致祖先节点的平衡因子连锁失衡,需从叶子到根节点逐层调整,最坏情况下旋转次数达 O(log n)。这种高频旋转使其在动态数据场景下性能劣势明显。
2.2 空间开销:1 位 vs 多位的存储成本
红黑树的空间开销极低,仅需为每个节点额外存储 1 位颜色标记(红/黑),可通过节点结构中的空闲位(如指针未使用的最低位)实现,几乎不增加存储负担。
AVL 树则需为每个节点存储平衡因子(通常为 2-3 位,表示 -1、0、1 三种状态)或直接存储子树高度(整数),空间开销显著高于红黑树。在大规模数据场景下(如千万级节点),这种差异可能影响内存利用率。
2.3 时间复杂度:理论同阶,实践分化
尽管两种树的查找、插入、删除操作理论时间复杂度均为 O(log n),但实际性能因树高和调整成本不同而分化:
• 查询性能:AVL 树因严格平衡导致树高更矮(约 1.44log n vs 红黑树 2log n),单次查询平均速度略快。
• 插入/删除性能:红黑树因旋转次数少、调整成本低,在动态操作中表现更优,尤其在高频更新场景下(如每秒数万次插入删除),性能优势可达数倍。
(三)工程选择:场景适配与设计哲学的落地
红黑树与 AVL 树的工程选择本质是“动态效率”与“静态查询性能”的权衡。以下为典型场景的决策依据:
3.1 红黑树:动态数据场景的首选
红黑树凭借低调整成本和稳定的动态性能,广泛应用于插入/删除频繁的场景:
• STL 容器:C++ STL 中的 std::map、std::set 均采用红黑树实现,因其能高效支持频繁的元素插入与删除,满足关联容器的性能需求。
• 实时系统:如进程调度队列(Linux 的 CFS 调度器)、实时排行榜,需快速响应动态数据变化,红黑树的 O(1) 旋转特性可保障低延迟。
• 缓存实现:如 LRU 缓存的底层结构,需频繁淘汰旧数据并插入新数据,红黑树的动态调整能力可降低维护成本。
3.2 AVL 树:静态查询场景的优化选择
AVL 树则适用于查询远多于更新的静态或准静态数据场景:
• 字典库与索引:如单词查找树、静态数据库索引,数据一旦构建后极少修改,AVL 树的严格平衡可确保最短查询路径,提升检索速度。
• 科学计算:在数值分析或仿真中,需对固定数据集进行高频查询(如查找特定条件的样本),AVL 树的矮树高可减少比较次数。
核心结论:红黑树是“性能与实现复杂度的折中”,通过牺牲极致查找性能换取更低的插入/删除开销;AVL 树则追求“查询性能最大化”,适合数据静态、查询密集的场景。工程选择时需优先评估操作频率(查询 vs 插入/删除)与数据动态性,而非单纯比较理论复杂度。
(四)对比总结表
| 对比维度 | 红黑树 | AVL 树 |
| 平衡机制 | 颜色约束(红/黑)+ 路径黑色节点数限制,弱平衡 | 平衡因子(左右子树高度差 ≤ 1),严格平衡 |
| 树高上限 | 2log(n+1) | 1.44log(n+2) - 1.328 |
| 旋转次数 | 插入/删除 ≤ 2 次(O(1)) | 插入/删除可能多次(O(log n)) |
| 空间开销 | 1 位(颜色标记) | 2-3 位(平衡因子)或整数(子树高度) |
| 适用场景 | 插入/删除频繁(动态数据) | 查询频繁(静态数据) |
七、红黑树的工程应用案
红黑树作为一种自平衡二叉搜索树,凭借其 O(log n) 的插入/删除/查找复杂度 与 中序遍历有序性 的核心特性,在操作系统、编程语言标准库、数据库等关键领域得到广泛应用。以下从具体场景出发,剖析其技术选型逻辑与实现细节。
(一)编程语言标准库:有序容器的底层支柱
数据结构特性:红黑树的中序遍历可生成有序序列,支持范围查询(如 [a, b] 区间数据获取)和动态维护有序集合,且最坏情况下仍保持 O(log n) 操作效率。
场景需求:标准库需提供支持有序操作的容器(如键值对映射、无重复元素集合),同时满足频繁插入/删除后的性能稳定性。
实现细节:
• C++ STL:std::map、std::set 等容器底层采用红黑树变体实现,通过泛型节点(存储 key 或 pair<key, value>)和比较仿函数(Compare)适配不同数据类型。例如 std::map 的 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 方法,利用红黑树的有序性实现 O(log n) 范围查询,而哈希表(如 std::unordered_map)虽平均查询更快,但无法支持此类有序操作。
• Java 集合框架:TreeMap 和 TreeSet 基于红黑树实现,通过 Comparator 接口定义排序规则,支持 subMap()(范围子映射)和 descendingKeySet()(逆序遍历)等操作,其内部通过红黑树的旋转与着色维持平衡,确保 10 万级数据量下插入性能稳定在微秒级。
技术选型对比:红黑树在标准库中替代哈希表的核心原因在于 有序性刚需。例如数据库查询结果排序、日志按时间戳过滤等场景,需频繁使用 ORDER BY 或范围查询,此时红黑树的中序遍历有序性可直接满足需求,而哈希表需额外 O(n log n) 排序开销。
(二)Linux 内核 CFS 调度器:进程调度的效率引擎
数据结构特性:红黑树的 findMin 操作可在 O(log n) 时间内定位最小节点,且插入/删除操作不破坏树的平衡性,适合动态更新的有序集合。
场景需求:完全公平调度器(CFS)需按进程虚拟运行时间(vruntime)排序,快速选择下一个运行进程,同时支持进程创建/退出时的动态调整。
实现细节:
• 内核实现:CFS 调度器将可运行进程组织为红黑树,节点存储进程控制块(task_struct),键值为 vruntime。调度时通过 rb_first()(即 findMin 操作)定位 vruntime 最小的进程,确保每个进程获得公平的 CPU 时间片。插入(进程唤醒)和删除(进程阻塞)操作均为 O(log n),相比早期 O(n) 遍历的调度算法,在 1000+ 并发进程场景下响应延迟降低 90% 以上 。
• 关键结构体:内核中红黑树节点定义为 struct rb_node { unsigned long __rb_parent_color; struct rb_node *rb_right; struct rb_node *rb_left; };,其中 __rb_parent_color 字段复用存储父节点指针与节点颜色(红/黑),通过位运算优化内存占用 。
(三)Nginx 定时器:高效事件驱动的核心组件
数据结构特性:红黑树支持动态事件的快速插入、删除和极值查询,且节点删除操作(尤其是中间节点)效率优于最小堆(最小堆删除非根节点需 O(n) 查找)。
场景需求:Nginx 作为事件驱动服务器,需管理大量连接超时事件(如 HTTP 连接 60s 无活动关闭),要求毫秒级插入/删除和最近事件查询。
实现细节:
• 定时器管理:Nginx 通过 ngx_rbtree_t 结构体实现红黑树,节点存储事件的超时时间戳(key)和回调函数。每次事件循环中,通过 ngx_rbtree_min() 找到最小时间戳节点,判断是否触发超时事件;新增事件时执行 ngx_rbtree_insert(),连接关闭时执行 ngx_rbtree_delete(),三者均为 O(log n) 复杂度。在 10 万级并发连接场景下,红黑树相比链表实现(O(n) 遍历)将定时器检查耗时从秒级降至微秒级 。
• 性能优势:对比最小堆,红黑树在事件频繁取消(如连接提前关闭)场景下更高效。例如某连接建立后 10s 内主动关闭,红黑树可直接定位并删除节点(O(log n)),而最小堆需先线性扫描找到节点(O(n))再调整堆结构,在高并发下会成为性能瓶颈。
(四)数据库与缓存:索引与排序的底层支撑
数据结构特性:红黑树可作为辅助索引结构,支持有序数据的快速定位与范围扫描,且内存占用低于 B+ 树(无页表结构)。
场景需求:数据库需对中间结果排序(如 ORDER BY)、缓存系统需维护有序键值对(如按访问频率排序的淘汰策略)。
实现细节:
• MySQL 排序优化:当 ORDER BY 操作无法利用索引时,MySQL 若内存充足会使用红黑树(而非快速排序)对结果集排序。红黑树通过动态插入元素维持有序,避免快速排序的 O(n log n) 一次性开销,尤其适合流式数据场景(如边查询边排序)。
• Redis 早期 ZSET:Redis 有序集合(ZSET)早期采用红黑树实现,键为分数(score),值为成员(member),支持 ZRANGE(范围查询)和 ZADD(插入)操作。虽然后续因内存优化改为跳跃表,但红黑树的 O(log n) 复杂度仍为其提供了设计参考 。
工程权衡:红黑树在数据库中多作为内存级索引或临时排序结构,而磁盘级索引更倾向 B+ 树(优化磁盘 IO)。这种分层选型体现了红黑树在 内存密集型有序场景 下的高效性。
总结:红黑树的技术适配场景
红黑树的工程价值集中体现于 “动态有序集合 + 频繁更新” 场景:其 O(log n) 复杂度平衡了性能与实现难度,有序性满足范围查询需求,自平衡特性确保极端情况下的稳定性。从编程语言基础组件到操作系统内核,从 Web 服务器到数据库,红黑树以其独特的特性成为中间件与系统软件的关键数据结构基石。
八、实现难点与优化建议
红黑树的工程实现需在严格遵循其五大性质的基础上,处理复杂的指针操作与边界条件,同时兼顾性能与空间效率。以下从实现难点剖析、优化策略及调试方法三个维度展开分析。
(一)实现难点剖析
旋转操作中的指针维护疏漏是红黑树实现的核心易错点。以左旋操作为例,其本质是调整节点间的父子关系与平衡因子,但实际编码中易忽略次级节点的指针更新。例如,当对节点 x 执行左旋时,需将 x 的右孩子 y 提升为新的父节点,此时除需更新 x 与 y 的直接父子指针外,必须同步修正 y 的左孩子(原 x 的右子树左分支)的 parent 指针,即执行 y->left->parent = x。若漏写此步骤,会导致该节点的 parent 指针仍指向 y,后续对该节点的访问(如删除或查找)将出现逻辑错误,破坏树的完整性。
边界条件处理复杂是另一突出难点。传统实现中,叶子节点的子节点需用 nullptr 表示,导致插入、删除时需频繁判断节点是否为 nullptr,增加代码复杂度。采用**哨兵节点(nil 节点)** 可有效简化这一问题:将所有叶子节点的子节点统一指向 nil,并将 nil 节点的 parent、left、right 指针均指向自身,颜色设为黑色。此举可将边界条件转化为普通节点处理,例如判断节点是否为叶子节点时,直接检查其孩子是否为 nil,无需额外的 nullptr 判断逻辑,降低漏判风险。
(二)优化建议
空间优化方面,可借鉴 STL 源码的设计思路。红黑树节点的颜色属性传统上通过枚举类型(如 enum Color { RED, BLACK })表示,通常占用 4 字节(取决于编译器实现)。而 STL 中采用 bool 类型存储颜色(true 表示红色,false 表示黑色),仅占用 1 字节,在大规模节点场景下可显著节省内存开销。例如,对于包含 100 万个节点的红黑树,采用 bool 类型可减少 3MB 内存占用(按每个节点节省 3 字节计算)。
性能优化方面,需关注递归遍历的潜在瓶颈。以范围查询函数 countRangeHelper 为例,递归实现虽代码简洁,但在树深度较大时(如接近最坏情况的 O(n) 深度),可能导致栈溢出并增加函数调用开销。建议将其重构为非递归遍历,通过显式栈或队列模拟递归过程。例如,使用栈实现中序遍历:初始化时压入左子树所有节点,弹出节点时判断是否在查询范围内,再压入右子树所有节点。非递归实现可避免栈溢出风险,且在实际测试中,对深度为 1000 的红黑树执行范围查询时,性能提升约 15%~20%。
(三)工程实现与调试方法
严格遵循性质约束是红黑树正确实现的前提。插入或删除操作后,需通过旋转与变色恢复五大性质,任何一步颜色判断或旋转顺序错误均可能导致树失衡。例如,插入红色节点后若父节点为红色,需根据叔叔节点颜色执行不同修复逻辑:若叔叔为黑色,需执行旋转+变色;若叔叔为红色,则仅需变色。若混淆这两种场景,会导致连续红节点或黑高不一致。
自动化性质检查是高效调试的关键。可实现 checkProperties 函数对树的合法性进行全面校验,核心检查项包括:
• 根节点黑色性:确保根节点始终为黑色;
• 红节点子节点黑色性:通过 checkRedParentProperty 函数递归检测所有红色节点的子节点是否为黑色,避免连续红节点;
• 黑高一致性:从根节点到所有叶子节点的黑色节点数量是否相同。
调试建议:在开发阶段,可在每次插入、删除操作后调用 checkProperties 函数,若触发断言则定位问题节点。例如,当 checkRedParentProperty 检测到连续红节点时,可通过打印节点路径(如 x->parent->value -> x->value)快速定位违规节点,回溯操作日志排查颜色更新或旋转逻辑错误。
综上,红黑树的实现需在细节处理上保持严谨,通过哨兵节点简化边界条件,结合空间与性能优化策略,并依托自动化性质检查构建可靠的调试机制,才能在工程实践中确保其高效与稳定。
九、总结
红黑树是一种高效的自平衡二叉搜索树,通过颜色约束和旋转操作维持近似平衡,确保最坏情况下仍保持O(logn)的时间复杂度。其核心特性包括:
(1)节点为红/黑色;
(2)根和叶子节点为黑色;
(3)红色节点不能相邻;
(4)所有路径黑高相同。
与AVL树相比,红黑树插入/删除效率更高(旋转次数少),适合动态数据场景,广泛应用于C++ STL、Linux进程调度等系统。实现时需注意指针维护和边界条件处理,采用哨兵节点简化逻辑,并通过自动化性质检查确保正确性。红黑树在动态有序集合管理上展现出卓越性能,是平衡效率与复杂度的经典数据结构。
