区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(6)

Conference:International World Wide Web Conference (WWW)
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:交叉/综合/新兴
Year:2025
Conference time:Sydney, Australia April - 2 May 2025
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(1)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(2)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(3)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(4)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(5)
21
Title:
Serial Scammers and Attack of the Clones: How Scammers Coordinate Multiple Rug Pulls on Decentralized Exchanges
连环诈骗和克隆的进攻:诈骗者如何协调对去中心化交易所的多次诈骗
Authors:

Key words:
Cryptocurrency, Scam, Rug Pull, Honeypot, Ethereum, BSC
加密货币、骗局、地毯拉扯、蜜罐、以太坊、BSC
Abstract:
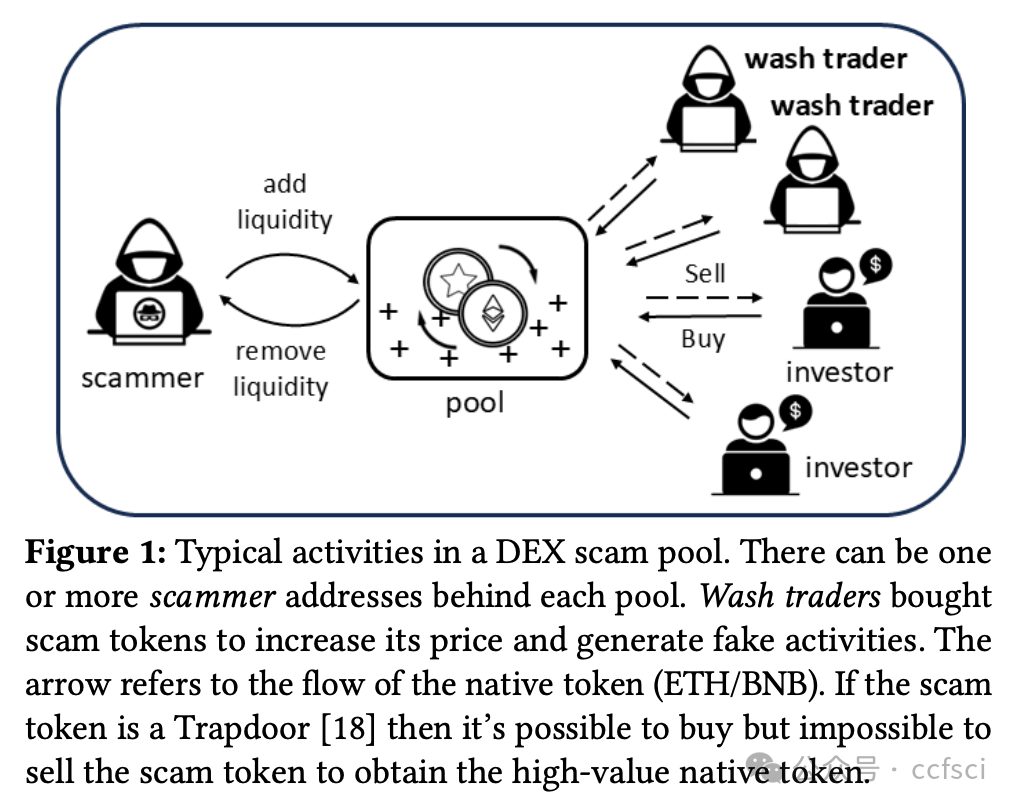
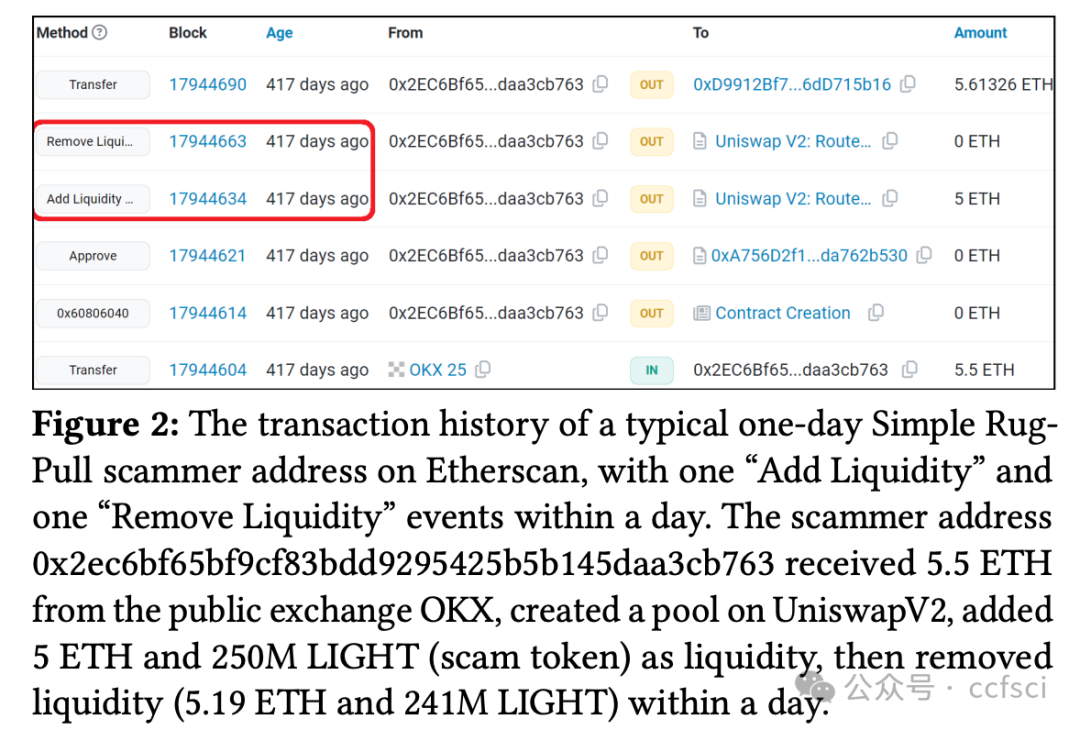
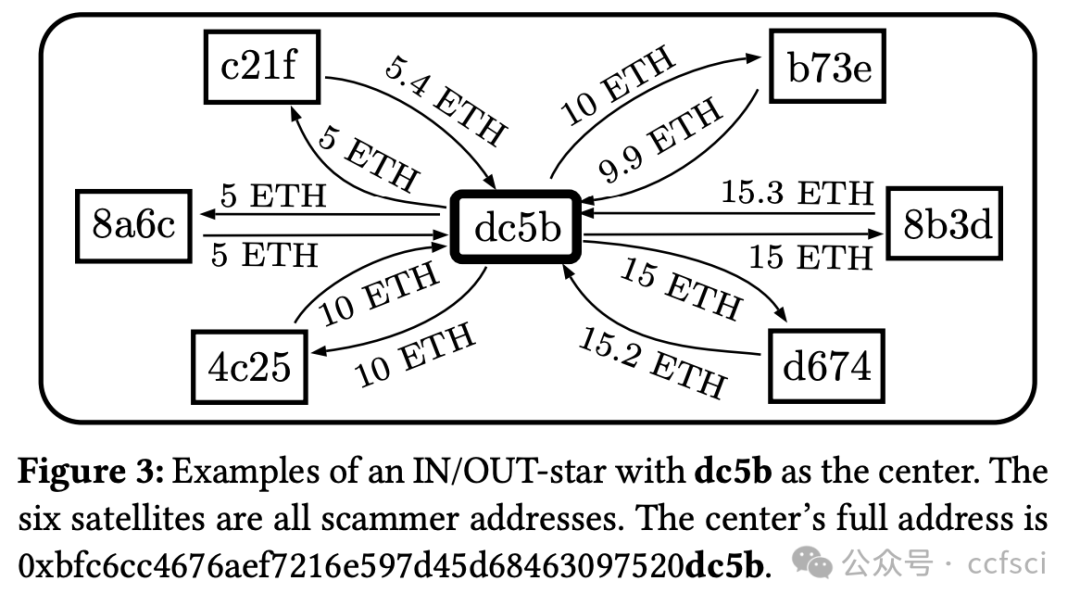
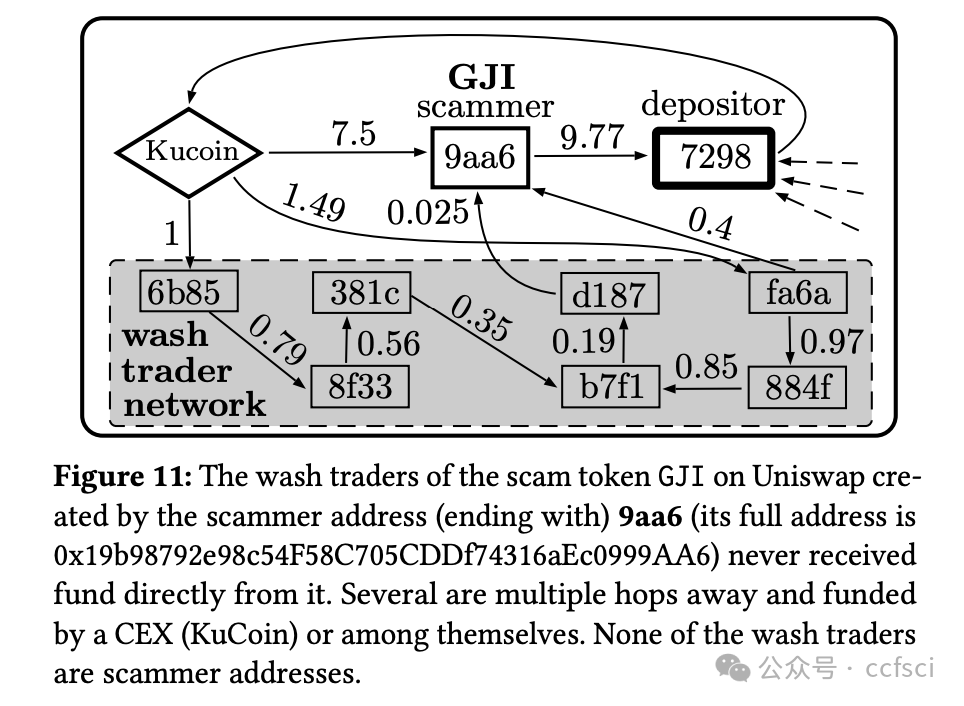
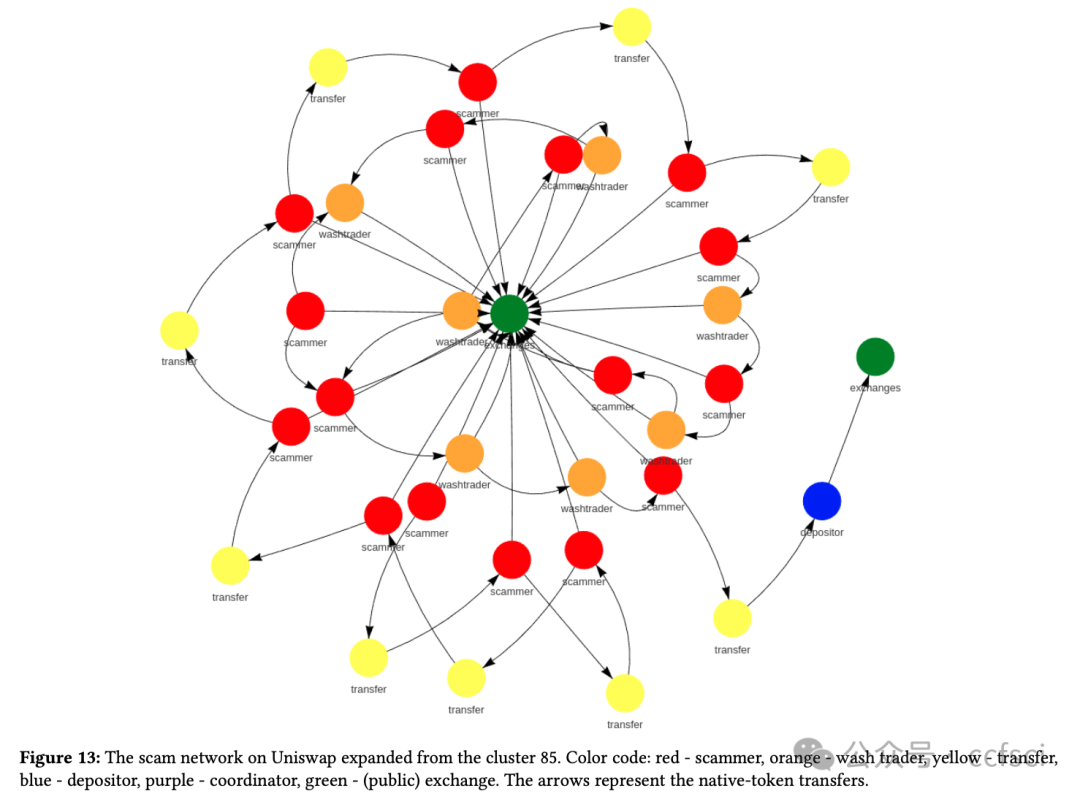
We explored the ubiquitous phenomenon of serial scammers, each of whom deployed dozens to thousands of addresses to conduct a series of similar Rug Pulls on popular decentralized exchanges. We first constructed two datasets of around 384,000 scammer addresses behind all one-day Simple Rug Pulls on Uniswap (Ethereum) and Pancakeswap (BSC), and identified distinctive scam patterns including star, chain, and major (scam-funding) flow. These patterns, which collectively cover about 40% of all scammer addresses in our datasets, reveal typical ways scammers run multiple Rug Pulls and organize the money flow among different addresses. We then studied the more general concept of scam cluster, which comprises scammer addresses linked together via direct ETH/BNB transfers or behind the same scam pools. We found that scam token contracts are highly similar within each cluster (average similarities >70%) and dissimilar across different clusters (average similarities <30%), corroborating our view that each cluster belongs to the same scammer/scam organization. Lastly, we analyze the scam profit of individual scam pools and clusters, employing a novel cluster-aware profit formula that takes into account the important role of wash traders. The analysis shows that the existing formula inflates the profit by at least 35% on Uniswap and 24% on Pancakeswap.a
我们探究了普遍存在的连环诈骗现象,每个诈骗者都会部署数十到数千个地址,在热门的去中心化交易所进行一系列类似的 Rug Pull 操作。我们首先构建了两个数据集,其中包含 Uniswap(以太坊)和 Pancakeswap(BSC)上所有单日 Simple Rug Pull 背后的约 384,000 个诈骗者地址,并识别出独特的诈骗模式,包括星型、链型和主要(诈骗资金)流。这些模式总共涵盖了我们数据集中约 40% 的诈骗者地址,揭示了诈骗者运行多个 Rug Pull 并在不同地址之间组织资金流动的典型方式。随后,我们研究了更通用的诈骗集群概念,该概念由通过直接 ETH/BNB 转账或同一诈骗池背后的诈骗者地址链接在一起组成。我们发现,每个集群内的诈骗代币合约高度相似(平均相似度 >70%),而不同集群之间的相似度则较低(平均相似度 <30%),这证实了我们的观点,即每个集群都属于同一个诈骗者/诈骗组织。最后,我们分析了各个诈骗池和集群的诈骗利润,并采用了一种新的集群感知利润公式,该公式考虑了刷量交易者的重要作用。分析表明,现有公式在 Uniswap 上至少夸大了 35% 的利润,在 Pancakeswap 上至少夸大了 24% 的利润。
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3696410.3714919
22
Title:
Centralization in the Decentralized Web: Challenges and Opportunities in IPFS Data Management
去中心化网络中的中心化:IPFS 数据管理的挑战与机遇
Authors:

Key words:
IPFS, Deduplication, Network Measurement
IPFS、重复数据删除、网络测量
Abstract:
The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a pioneering effort for Web 3.0, well-known for its decentralized infrastructure. However, some recent studies have shown that IPFS exhibits a high degree of centralization and has integrated centralized components for improved performance. While this change contradicts the core decentralized ethos of IPFS and introduces risks of hurting the data replication level and thus availability, it also opens some opportunities for better data management and cost savings through deduplication.
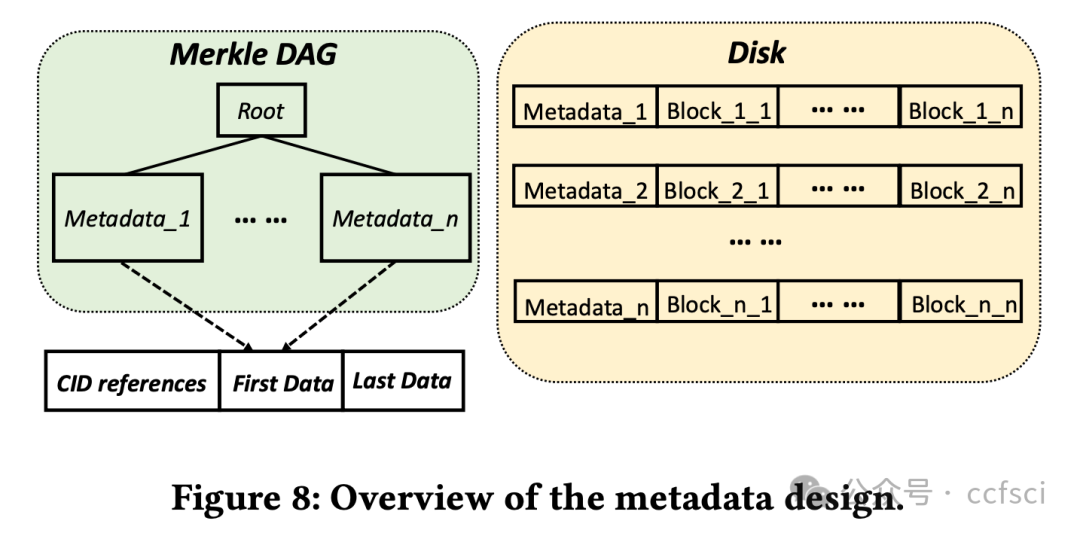
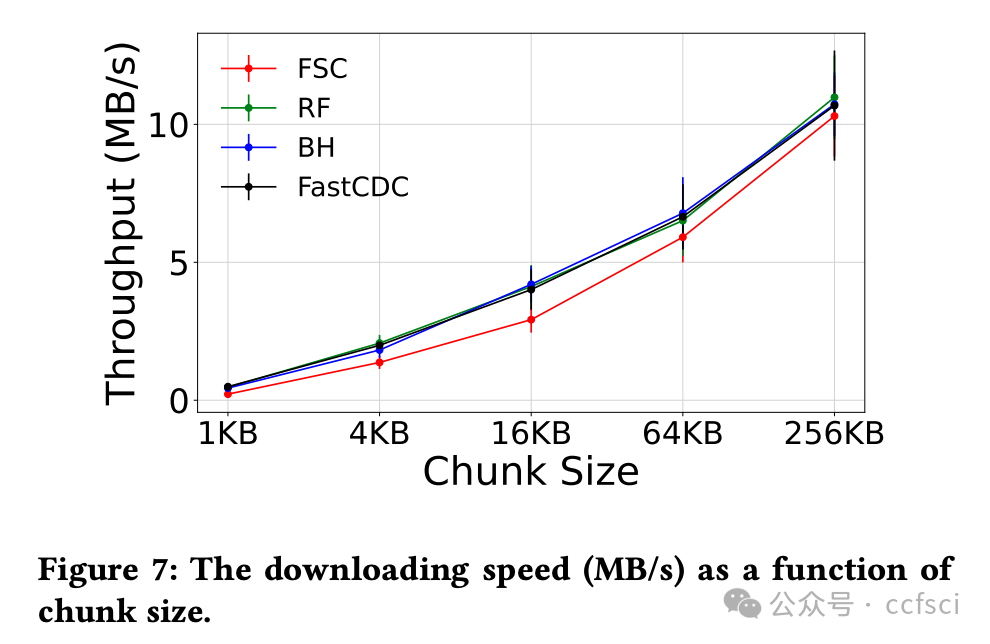
To explore these challenges and opportunities, we start by collecting an extensive dataset of IPFS internal traffic spanning the last three years with 20+ billion messages. By analyzing this long-term trace, we obtain a more complete and accurate view of how the status of centralization evolves over an extended period. In particular, our study reveals that (1) IPFS shows a low replication level, with only 2.71% of data files replicated more than 5 times. While increasing replication enhances lookup performance and data availability, it adversely affects downloading throughput due to the overhead involved in managing peer connections, (2) there is a clear growing trend in centralization within IPFS in the last 3 years, with just 5% of peers now hosting over 80% of the content, significantly decreasing from 21.38% 3 years ago, which is largely driven by the increase of cloud nodes, (3) the default deduplication strategy of IPFS using Fixed-Size Chunking (FSC) is largely inefficient, especially with the default 256KB chunk size, showing near-zero duplication being detected. Although Content-Defined Chunking (CDC) with smaller chunks could save ~1.8 petabytes (PB) storage space, it could impact user performance negatively. We thus design and evaluate a new metadata format that optimizes deduplication without compromising performance.
星际文件系统 (IPFS) 是 Web 3.0 的开创性成果,以其去中心化的基础架构而闻名。然而,最近的一些研究表明,IPFS 表现出高度的中心化,并集成了中心化组件以提升性能。虽然这种变化违背了 IPFS 的核心去中心化理念,并带来了损害数据复制水平和可用性的风险,但它也为通过重复数据删除来改善数据管理和节省成本创造了一些机会。
为了探索这些挑战和机遇,我们首先收集了过去三年 IPFS 内部流量的大量数据集,其中包含超过 200 亿条消息。通过分析这些长期追踪数据,我们可以更全面、更准确地了解中心化状态在长期内的演变情况。具体而言,我们的研究表明:(1) IPFS 的复制水平较低,只有 2.71% 的数据文件复制超过 5 次。虽然增加复制可以提高查找性能和数据可用性,但由于管理对等连接所涉及的开销,它会对下载吞吐量产生不利影响;(2)过去 3 年,IPFS 内部的中心化趋势明显增长,目前只有 5% 的对等方托管了 80% 以上的内容,与 3 年前的 21.38% 相比大幅下降,这主要是由于云节点的增加所致;(3)IPFS 使用固定大小分块 (FSC) 的默认重复数据删除策略效率很低,尤其是默认的 256KB 块大小,几乎检测不到重复。虽然具有较小块的内容定义分块 (CDC) 可以节省约 1.8 PB 的存储空间,但它可能会对用户性能产生负面影响。因此,我们设计并评估了一种新的元数据格式,该格式可在不影响性能的情况下优化重复数据删除。
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3696410.3714627
23
Title:
Gamblers or Delegatees: Identifying Hidden Participant Roles in Crypto Casinos
赌徒还是代表:识别加密货币赌场中隐藏的参与者角色
Authors:

Key words:
Crypto gambling, Anonymity, Security, Delegatees, Role identification, Graph Neural Networks, Structural Entropy
加密赌博、匿名性、安全性、代表、角色识别、图神经网络、结构熵
Abstract:
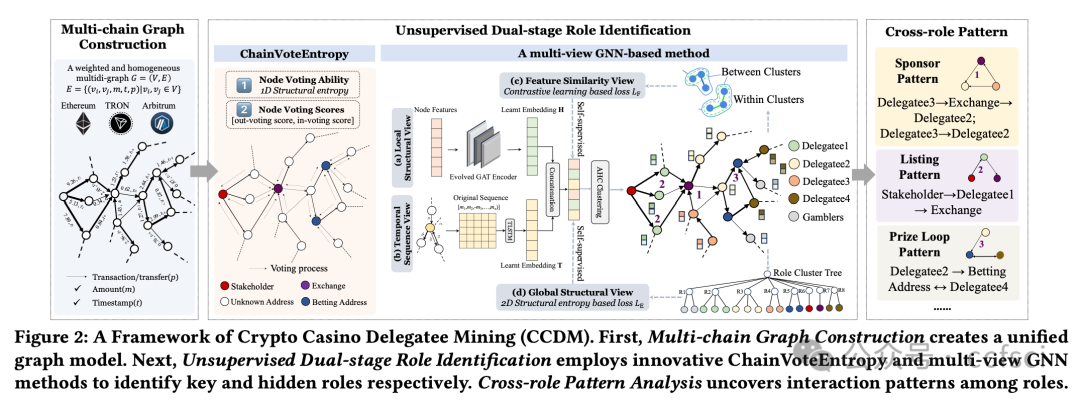
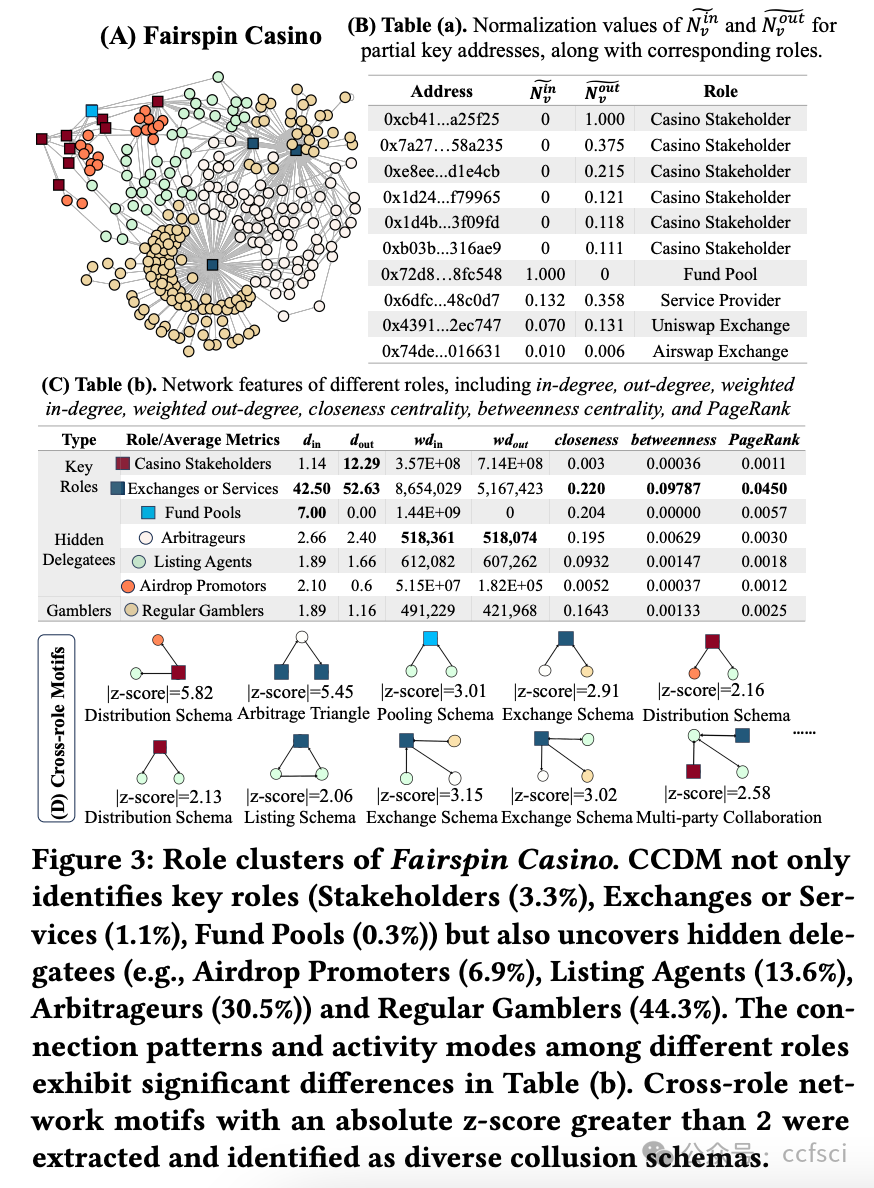
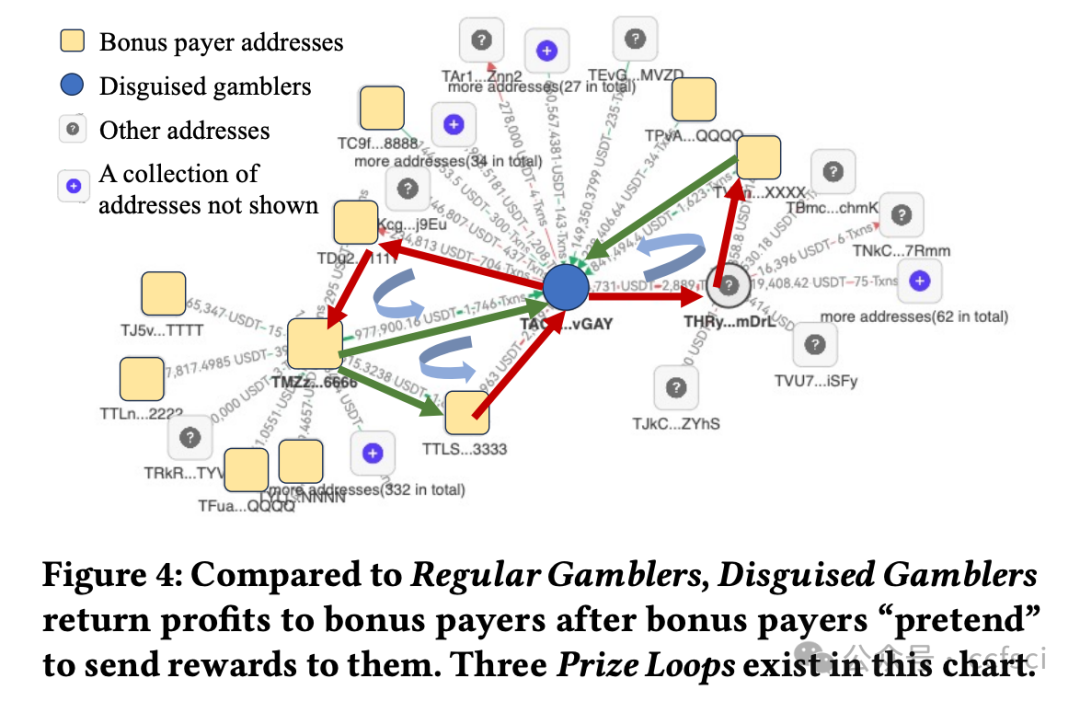
With the development of blockchain technology, crypto gambling has gained popularity due to its high level of anonymity. However, similar to traditional casinos, crypto casinos are controlled by a few internal Delegatees, making it impossible for them to achieve complete transparency and fairness. These delegatees are hidden among gamblers and are difficult to identify and distinguish in anonymous and large-scale blockchain transaction networks. This paper proposes an unsupervised dual-stage role identification method to adaptively identify key roles and hidden delegatees in label-sparse crypto casinos. Specifically, inspired by voting-style transaction patterns, we propose a novel voting influence metric for key node identification. This metric is based on one-dimensional structural entropy to capture global dissemination capability. Subsequently, we develop a multi-view graph neural network framework enhanced with two-dimensional global structural entropy minimization and self-supervised contrastive learning to improve the robustness and interpretability of hidden role partitioning. Experiments on real-world cases of the most mainstream blockchains-Ethereum, TRON, and Arbitrum-demonstrate that our proposed method effectively reveals distinct role compositions and collusion patterns, distinguishing between gamblers and delegatees. Our results achieve a higher match with identities confirmed by judicial authorities than existing methods, indicating the effectiveness and generalizability of our approach in enhancing security and regulation oversight.
随着区块链技术的发展,加密博彩因其高度匿名性而广受欢迎。然而,与传统赌场类似,加密赌场由少数内部代表控制,无法实现完全的透明和公平。这些代表隐藏在赌徒之中,在匿名且大规模的区块链交易网络中难以识别和区分。本文提出了一种无监督双阶段角色识别方法,用于自适应地识别标签稀疏的加密赌场中的关键角色和隐藏代表。具体而言,受投票式交易模式的启发,我们提出了一种用于关键节点识别的新型投票影响力指标。该指标基于一维结构熵来捕捉全局传播能力。随后,我们开发了一个多视图图神经网络框架,该框架通过二维全局结构熵最小化和自监督对比学习进行增强,以提高隐藏角色划分的鲁棒性和可解释性。在以太坊、波场TRON和Arbitrum等主流区块链的真实案例上进行的实验表明,我们提出的方法能够有效揭示不同的角色构成和共谋模式,区分赌徒和受托人。与现有方法相比,我们的结果与司法机关确认的身份匹配度更高,表明我们的方法在增强安全性和监管监督方面的有效性和普适性。

Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3696410.3714689
