python爬虫进阶版练习(只说重点,selenium)
目录
爬虫练习-电影数据
代码
批量数据的获取
多线程-爬虫练习
方法版
类版
爬虫之多进程-了解
multiprocessing模块
Manager类,实现数据共享
进程池的使用
多进程-爬虫练习
方法版
爬虫之协程
安装
常用方法
代码
协程-爬虫练习
代码
selenium介绍与安装
安装
selenium 控制浏览器
最大化窗口
设置宽与高
浏览器前进、后退
selenium元素定位
对象定位
操作元素
selenium 处理下拉框
selenium定位下拉菜单
选中元素
selenium 层级定位
窗口的定位
switch_to_frame()
selenium处理弹窗
代码
selenium拖拽元素
代码
selenium调用js方法
调用js的方法
JS代码功能
selenium 等待元素
强制等待
隐式等待
显示等待
selenium 参数使用
chrome59版本以后可以变成无头的浏览器,加以下参数
代理模式
防检测设置
Selenium 提升效率
提升效率方案
解析提速
通过参数
并发编程
爬虫练习-电影数据
要求获取电影信息:
- 名称
- 类型
- 所有演员
- 简介
代码
获取单个电影
import requests
from lxml import etree
# 地址
url = 'http://localhost:8000/playground/movies/2'
# 发送请求
resp = requests.get(url)
# 提取数据
e = etree.HTML(resp.text)
# 提取电影信息
# 名称
name = e.xpath('//h1/text()')
# 类型
_type = e.xpath('//div[@class="meta-item"][1]/span/text()')
# 演员
actors = e.xpath('//div[@class="actor-name"]/text()')
# 简介
intro = e.xpath('//p/text()')
print(name)
print(_type)
print(actors)
print(intro)
获取电影列表
import requests
from lxml import etree
url = 'http://localhost:8000/playground/7'
resp = requests.get(url)
e = etree.HTML(resp.text)
# 提取数据
# 获取电影的id
ids = e.xpath('//div[@class="movie-item"]/@data-movie-id')
for id in ids:# 拼写每部个电影的urlmovie_url = f'http://localhost:8000/playground/movies/{id}'movie_resp = requests.get(movie_url)# 进入了电影详情页et = etree.HTML(movie_resp.text)# 提取电影信息# 名称name = et.xpath('//h1/text()')# 类型_type = et.xpath('//div[@class="meta-item"][1]/span/text()')# 演员actors = et.xpath('//div[@class="actor-name"]/text()')# 简介intro = et.xpath('//p/text()')print(f'名称:{name[0]} 类型:{_type[0]} 演员:{actors} 简介:{intro[0]}')
获取分页数据:
- 获取总页码数量,生成所需要遍历的页码
- 获取下一页按钮,需要判断是否结束
import requests
from lxml import etree
def range_page():for i in range(1,43):url = f'http://localhost:8000/playground/7?page={i}'# 获取每一页的电影列表数据get_page(url)
def get_page(url):resp = requests.get(url)e = etree.HTML(resp.text)# 提取数据# 获取电影的idids = e.xpath('//div[@class="movie-item"]/@data-movie-id')# 遍历电影idfor id in ids:# 依次获取每部电影get_movie(id)
def get_movie(id):# 拼写每部个电影的urlmovie_url = f'http://localhost:8000/playground/movies/{id}'movie_resp = requests.get(movie_url)# 进入了电影详情页et = etree.HTML(movie_resp.text)# 提取电影信息# 名称name = et.xpath('//h1/text()')# 类型_type = et.xpath('//div[@class="meta-item"][1]/span/text()')# 演员actors = et.xpath('//div[@class="actor-name"]/text()')# 简介intro = et.xpath('//p/text()')print(f'名称:{name[0]} 类型:{_type[0]} 演员:{actors} 简介:{intro[0]}')
if __name__ == '__main__':range_page()
import requests
from lxml import etree
def start():url = 'http://localhost:8000/playground/7?page=41'while True:resp = requests.get(url)print(f'获取页面数据:{url}')e = etree.HTML(resp.text)# 获取电影的idids = e.xpath('//div[@class="movie-item"]/@data-movie-id')# 遍历电影idfor id in ids:# 依次获取每部电影get_movie(id)# pass# 获取下一页地址next_page = e.xpath('//div[@class="pagination"]/a[last()-1]/@href')[0]url = f'http://localhost:8000/playground/7{next_page}'# 获取下一页按钮的内容next_btn = e.xpath('//div[@class="pagination"]/a[last()-1]/text()')[0]if next_btn != '下一页':break
def get_movie(id):# 拼写每部个电影的urlmovie_url = f'http://localhost:8000/playground/movies/{id}'movie_resp = requests.get(movie_url)# 进入了电影详情页et = etree.HTML(movie_resp.text)# 提取电影信息# 名称name = et.xpath('//h1/text()')# 类型_type = et.xpath('//div[@class="meta-item"][1]/span/text()')# 演员actors = et.xpath('//div[@class="actor-name"]/text()')# 简介intro = et.xpath('//p/text()')print(f'名称:{name[0]} 类型:{_type[0]} 演员:{actors} 简介:{intro[0]}')
if __name__ == '__main__':start()
批量数据的获取
面对动态加载的数据获取,判断程序的结束条件
-
有没有总页数
-
如果没有,判断有没有总条数
- 总条数/每页个数
-
-
如果还没有,就自己手动测试结束的条件
- 到最后一页,不再响应数据
- 到最后一页,响应的数据是重复
import requests
for i in range(1,12):
# 获取数据地址url = f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page={i}&movie_type=&movie_time='# url = f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page=12&movie_type=&movie_time='# 发送请求resp = requests.get(url)# 获取数据,转成json格式data = resp.json()# 获取数据长度print(len(data.get('items')))print(data.get('items'))
# 面对动态加载的数据获取,判断程序的结束条件
# 1. 有不有总页数
# 2. 如果没有,判断有没有总条数 总条数/每页个数
# 3. 如果还没有,就自己手动测试结束的条件
# 3.1 到最后一页,不再响应数据
# 3.2 到最后一页,响应的数据是重复
多线程-爬虫练习
方法版
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queueimport requests
import re
def spider():# 只要是队列不为空就一直循环while not url_list.empty():# 获取数据url = url_list.get(timeout=1)page = re.findall('page=(\d+)',url)resp = requests.get(url)data = resp.json()print(f"第{page}页数据的总数为:{len(data.get('items'))}")if __name__ == '__main__':# 创建队列url_list = Queue()# 添加数据for i in range(1,12):url = f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page={i}&movie_type=&movie_time='url_list.put(url)for i in range(3):# 创建线程t = Thread(target=spider)# 开启线程t.start()
类版
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queueimport requests
import reclass MyThread(Thread):def run(self):# 只要是队列不为空就一直循环while not url_list.empty():# 获取数据url = url_list.get(timeout=1)page = re.findall('page=(\d+)',url)resp = requests.get(url)data = resp.json()print(f"第{page}页数据的总数为:{len(data.get('items'))}")if __name__ == '__main__':# 创建队列url_list = Queue()# 添加数据for i in range(1,12):url = f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page={i}&movie_type=&movie_time='url_list.put(url)for i in range(3):# 创建线程t = MyThread()# 开启线程t.start()
爬虫之多进程-了解

multiprocessing是python的多进程管理包,和threading.Thread类似
multiprocessing模块
multiprocessing模块可以让程序员在给定的机器上充分的利用CPU
在multiprocessing中,通过创建Process对象生成进程,然后调用它的start()方法
from multiprocessing import Processdef func(name):print('hello', name)if __name__ == "__main__":p = Process(target=func,args=('sxt',))p.start()p.join() # 等待进程执行完毕
Manager类,实现数据共享
在使用并发设计的时候最好尽可能的避免共享数据,尤其是在使用多进程的时候。 如果你真有需要 要共享数据,可以使用由Manager()返回的manager提供list, dict, Namespace, Lock, RLock, Semaphore, BoundedSemaphore, Condition, Event, Barrier, Queue, Value and Array类型的支持
from multiprocessing import Process,Manager,Lockdef print_num(info_queue,l,lo):with lo:for n in l:info_queue.put(n)def updata_num(info_queue,lo):with lo:while not info_queue.empty():print(info_queue.get())if __name__ == '__main__':manager = Manager()into_html = manager.Queue()lock = Lock()a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]b = [11, 12, 13, 14, 15]p1 = Process(target=print_num,args=(into_html,a,lock))p1.start()p2 = Process(target=print_num,args=(into_html,b,lock))p2.start()p3 = Process(target=updata_num,args=(into_html,lock))p3.start()p1.join()p2.join()p3.join()from multiprocessing import Process
from multiprocessing import Manager
import time
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
from time import sleepdef spider(url_queue):while not url_queue.empty():try:url = url_queue.get(timeout = 1)# headers = {'User-Agent':UserAgent().chrome}print(url)# resp = requests.get(url,headers = headers)# 处理响应结果# for d in resp.json().get('data'):# print(f'tid:{d.get("tid")} topic:{d.get("topicName")} content:{d.get("content")}')sleep(1)# if resp.status_code == 200:# print(f'成功获取第{i}页数据')except Exception as e:print(e)if __name__ == '__main__':url_queue = Manager().Queue()for i in range(1,11):url = f'https://www.hupu.com/home/v1/news?pageNo={i}&pageSize=50'url_queue.put(url)all_process = []for i in range(3):p1 = Process(target=spider,args=(url_queue,))p1.start()all_process.append(p1)[p.join() for p in all_process]
from multiprocessing import Process
from multiprocessing import Manager
import time
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
from time import sleepdef spider(url_queue):while not url_queue.empty():try:url = url_queue.get(timeout = 1)# headers = {'User-Agent':UserAgent().chrome}print(url)# resp = requests.get(url,headers = headers)# 处理响应结果# for d in resp.json().get('data'):# print(f'tid:{d.get("tid")} topic:{d.get("topicName")} content:{d.get("content")}')sleep(1)# if resp.status_code == 200:# print(f'成功获取第{i}页数据')except Exception as e:print(e)if __name__ == '__main__':url_queue = Manager().Queue()for i in range(1,11):url = f'https://www.hupu.com/home/v1/news?pageNo={i}&pageSize=50'url_queue.put(url)all_process = []for i in range(3):p1 = Process(target=spider,args=(url_queue,))p1.start()all_process.append(p1)[p.join() for p in all_process]
进程池的使用
-
进程池内部维护一个进程序列,当使用时,则去进程池中获取一个进程,如果进程池序列中没有可供使用的进进程,那么程序就会等待,直到进程池中有可用进程为止。
-
进程池中有两个方法:
-
apply同步执行-串行
-
apply_async异步执行-并行
-
from multiprocessing import Pool,Manager
def print_num(info_queue,l):for n in l:info_queue.put(n)def updata_num(info_queue):while not info_queue.empty():print(info_queue.get())if __name__ == '__main__':html_queue =Manager().Queue()a=[11,12,13,14,15]b=[1,2,3,4,5]pool = Pool(3)pool.apply_async(func=print_num,args=(html_queue,a))pool.apply_async(func=print_num,args=(html_queue,b))pool.apply_async(func=updata_num,args=(html_queue,))pool.close() #这里join一定是在close之后,且必须要加join,否则主进程不等待创建的子进程执行完毕pool.join() # 进程池中进程执行完毕后再关闭,如果注释,那么程序直接关闭
from multiprocessing import Pool,Manager
from time import sleepdef spider(url_queue):while not url_queue.empty():try:url = url_queue.get(timeout = 1)print(url)sleep(1)except Exception as e:print(e)if __name__ == '__main__':url_queue = Manager().Queue()for i in range(1,11):url = f'https://www.hupu.com/home/v1/news?pageNo={i}&pageSize=50'url_queue.put(url)pool = Pool(3)pool.apply_async(func=spider,args=(url_queue,))pool.apply_async(func=spider,args=(url_queue,))pool.apply_async(func=spider,args=(url_queue,))pool.close()pool.join()
多进程-爬虫练习

方法版
from multiprocessing import Manager,Processimport requests
import redef spider(url_list):while not url_list.empty():url = url_list.get()# 发送请求resp = requests.get(url)page = re.findall('page=(\d+)',url)# 提取数据data = resp.json()print(f"第{page}页数据的总数为:{len(data.get('items'))}")
if __name__ == '__main__':url_list = Manager().Queue()for i in range(1,11):url = f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page={i}&movie_type=&movie_time='url_list.put(url)# 创建一个进程列表all_process = []for i in range(3):# 创建进程p = Process(target=spider,args=(url_list,))# 开启进程p.start()# 将进程添加到列表中all_process.append(p)# for p in all_process:# # 等待进程运行结束# p.join()[p.join() for p in all_process]'''主进程默认不会等待子进程运行结束后,才结束。因此需要阻塞主主进程,等待子进程运行结束p.join()'''
爬虫之协程

网络爬虫速度效率慢,多部分在于阻塞IO这块(网络/磁盘)。在阻塞时,CPU的中内核是可以处理别的非IO操作。因此可以考虑使用协程来提升爬虫效率,这种操作的技术就是协程
协程一种轻量级线程,拥有自己的寄存器上下文和栈,本质是一个进程
相对于多进程,无需线程上下文切换的开销,无需原子操作锁定及同步的开销
简单的说就是让阻塞的子程序让出CPU给可以执行的子程序
一个进程包含多个线程,一个线程可以包含多个协程
多个线程相对独立,线程的切换受系统控制。 多个协程也相对独立,但是其切换由程序自己控制
安装
pip install aiohttp==3.11.6
官网 https://docs.aiohttp.org/en/stable/
常用方法
| 属性或方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| aiohttp.ClientSession() | 获取客户端函数 |
| session.get(url) | 发送get请求 |
| seesion.post(url) | 发送post请求 |
| resp.status | 获取响应状态码 |
| resp.url | 获取响应url地址 |
| resp.cookies | 获取响应cookie内容 |
| resp.headers | 获取响应头信息 |
| resp.read() | 获取响应bytes类型 |
| resp.text() | 获取响应文本内容 |
代码
import aiohttp
import asyncioasync def first():async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: # aiohttp.ClientSession() == import requests 模块async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get') as resp:rs = await resp.text()print(rs)headers = {'User-Agent':'aaaaaa123'}
async def test_header():async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers= headers) as session: # aiohttp.ClientSession() == import requests 模块async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get') as resp:rs = await resp.text()print(rs)async def test_params():async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers= headers) as session: # aiohttp.ClientSession() == import requests 模块async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get',params={'name':'bjsxt'}) as resp:rs = await resp.text()print(rs)async def test_cookie():async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers= headers,cookies={'token':'sxt123id'}) as session: # aiohttp.ClientSession() == import requests 模块async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get',params={'name':'bjsxt'}) as resp:rs = await resp.text()print(rs)async def test_proxy():async with aiohttp.ClientSession(headers= headers,cookies={'token':'sxt123id'}) as session: # aiohttp.ClientSession() == import requests 模块async with session.get('http://httpbin.org/get',params={'name':'bjsxt'},proxy = 'http://name:pwd@ip:port' ) as resp:rs = await resp.text()print(rs)if __name__ == '__main__':loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()loop.run_until_complete(test_cookie())
协程-爬虫练习
代码
import reimport aiohttp
import asyncioasync def spider(url,session):async with session.get(url) as resp:data = await resp.json()page = re.findall('page=(\d+)',url)print(f"第{page}页数据的总数为:{len(data.get('items'))}")
async def main():url_list = [f'http://localhost:8000/api/movies?page={i}&movie_type=&movie_time=' for i in range(1,11)]# 创建一个session,用于所有请求async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:# 创建所有的任务tasks = [spider(url,session) for url in url_list]# 并发执行所有任务await asyncio.gather(*tasks)if __name__ == '__main__':asyncio.run(main())
selenium介绍与安装

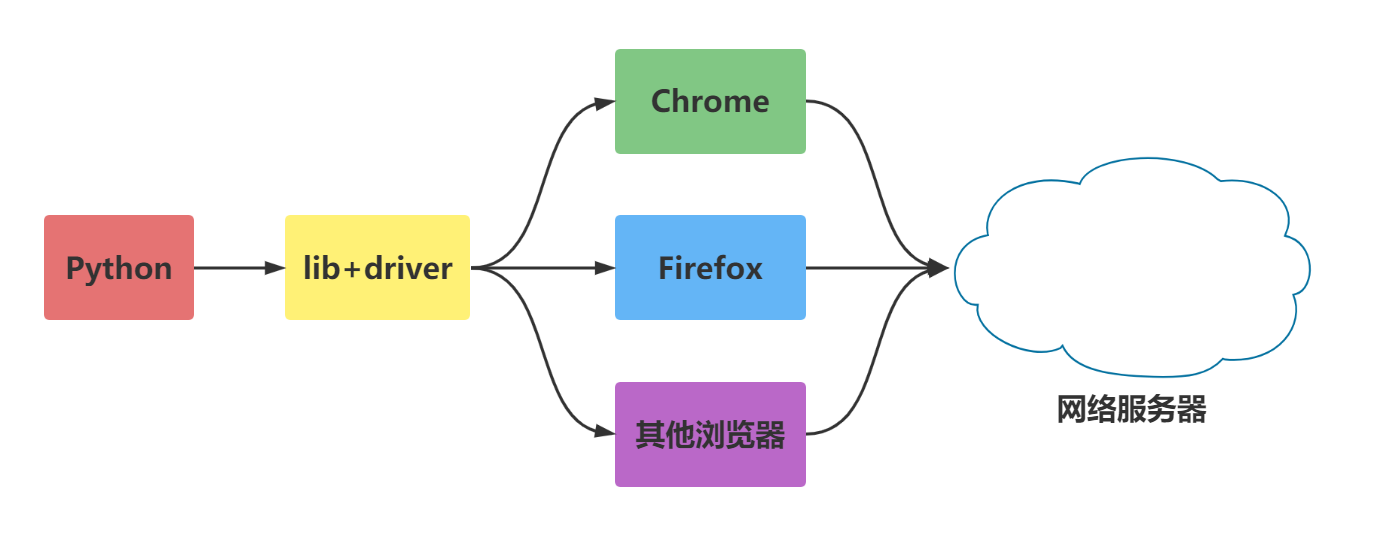
Selenium是一个Web的自动化测试工具,最初是为网站自动化测试而开发的,类型像我们玩游戏用的按键精灵,可以按指定的命令自动操作,不同是Selenium 可以直接运行在浏览器上,它支持所有主流的浏览器。
Selenium 可以根据我们的指令,让浏览器自动加载页面,获取需要的数据,甚至页面截屏,或者判断网站上某些动作是否发生。
Selenium 自己不带浏览器,不支持浏览器的功能,它需要与第三方浏览器结合在一起才能使用。
Selenium 官方参考文档:http://selenium-python.readthedocs.io/index.html
安装
pip install selenium==4.26.1
注意
selenium操作浏览器需要驱动(driver)
selenium版本是4.6.0以上,会自动下载
selenium版本是4.6.0以前,需要手动下载
测试代码
# pip install selenium
from selenium import webdriver# 创建一个浏览器
chrome = webdriver.Edge()
# 发送请求
chrome.get('http://localhost:8000/')
# 获取HTML
page = chrome.page_source
# 打印
print(page)
# 关闭浏览器
chrome.quit()
selenium 控制浏览器
最大化窗口
我们知道调用启动的浏览器不是全屏的,这样不会影响脚本的执行,但是有时候会影响我们“观看”脚本的执行。
browser = webdriver.Chrome()url= 'http://localhost:8000/'
browser.get(url)borwser.maximize_window()
设置宽与高
最大化还是不够灵活,能不能随意的设置浏览的宽、高显示?当然是可以的。
browser = webdriver.Chrome()url= 'http://localhost:8000/'
browser.get(url)borwser.set_window_size(500,600)
浏览器前进、后退
浏览器上有一个后退、前进按钮,对于浏览网页的人是比较方便的;对于做web自动化测试的同学来说应该算是一个比较难模拟的问题
其实很简单,下面看看python的实现方式
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
first_url= 'http://localhost:8000/'
browser.get(first_url)
time.sleep(2)
second_url='http://localhost:8000/playground'
browser.get(second_url)
time.sleep(2)
browser.back()
time.sleep(1)
browser.forward()
time.sleep(2)
browser.quit()
selenium元素定位

对象的定位应该是自动化的核心,要想操作一个对象,首先应该识别这个对象。 一个对象就是一个人一样,他会有各种的特征(属性),如比我们可以通过一个人的身份证号,姓名,或者他住在哪个街道、楼层、门牌找到这个人。
对象定位
webdriver提供了对象定位方法
-
find_element(type,value)
-
find_elements(type,value)
利用 By 类来确定哪种选择方式
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
chrome.find_element(by=By.ID,value='su')
By 类的一些属性如下
-
ID = "id"
-
NAME = "name"
-
XPATH = "xpath"
-
LINK_TEXT = "link text"
-
PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT = "partial link text"
-
TAG_NAME = "tag name"
-
CLASS_NAME = "class name"
-
CSS_SELECTOR = "css selector"
操作元素
前面讲到了不少知识都是定位元素,定位只是第一步,定位之后需要对这个原素进行操作。
鼠标点击呢还是键盘输入,这要取决于我们定位的是按钮还输入框。
一般来说,webdriver中比较常用的操作对象的方法有下面几个
-
click 点击对象
-
send_keys 在对象上模拟按键输入
-
clear 清除对象的内容,如果可以的话
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By# 打开一个浏览器
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# 访问链接
browser.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/4')
# 获取内容-表单上面的
p = browser.find_element(By.XPATH,'//p')
print(p.text)
# p2 = browser.find_element_by_id('//p') # 旧版本的selenium有,新的没有# 获取用户名输入框
user_input = browser.find_element(By.ID,'name')
# 在输入框输入内容
user_input.send_keys('鸣人')
# 获取出处输入框
book_input = browser.find_element(By.ID,'book')
book_input.send_keys('火影')
# 获取提交按钮
submit_btn = browser.find_element(By.XPATH,'//form/button')
# 点击提交按钮
submit_btn.click()# 关闭浏览器
browser.quit()
selenium 处理下拉框

在爬取数据时,有时数据太多,而官网提供了筛选功能select标签,像这样的数据,我们只需要定位元素,点击即可
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from time import sleepdef test_select():driver = webdriver.Chrome()driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/11')# 获取第一个菜单按钮并点击driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//select[@id="MovieTime"]/option[@value="28"]').click()sleep(1)driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//select[@id="SeatType"]/option[@value="25"]').click()total = driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//div[@class="result-info"][3]/span[@class="price-tag"]')print(total.text)# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':test_select()
selenium定位下拉菜单

选中元素
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from time import sleepdef test_dropdowns():driver = webdriver.Chrome()driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/10')sleep(1)driver.find_element(By.ID,'dropdownMenu1').click()sleep(1)action2 = driver.find_element(By.ID,'action2')print(f'点击{action2.text}按钮')action2.click()sleep(6)driver.quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':test_dropdowns()
selenium 层级定位

窗口的定位
对于一个现代的web应用,经常会出现框架(frame) 或窗口(window)的应用,这也就给我们的定位带来了一个难题。
有时候我们定位一个元素,定位器没有问题,但一直定位不了,这时候就要检查这个元素是否在一个frame中,seelnium webdriver 提供了一个switch_to_frame方法,可以很轻松的来解决这个问题
多层框架或窗口的定位:
-
driver.switch_to.frame()
switch_to_frame()
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef select_frame():# 创建浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 打开网页driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/12')# 切换iframedriver.switch_to.frame('f1')# 定位元素div = driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME, 'stat-number')print(div.text)driver.quit()if __name__ =='__main__':select_frame()
selenium处理弹窗

有时,页面可能要弹窗口。只需要去定位弹窗上的“确定”按钮即可
-
switch_to
焦点集中到页面上的一个警告(提示)
-
accept( )
确认弹出窗
-
dismiss( )
取消弹出窗
切换至弹窗
chrome.switch_to
代码
####
from time import sleepfrom selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_alert():# 创建一个浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 访问页面driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/13')sleep(2)# 处理弹窗alert = driver.switch_to.alert# 获取弹窗的内容print(f'页面加载弹窗内容为:{alert.text}')# 点击确定alert.accept()# 获取按钮btns = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, 'popup-btn')# 点击第2个按钮btns[1].click()confirm = driver.switch_to.alertprint(f'弹窗内容为:{confirm.text}')# 点击取消confirm.dismiss()# 点击第3个按钮 弹出输入框btns[2].click()prompt = driver.switch_to.alertprint(f'输入框内容为:{prompt.text}')prompt.send_keys('hello')prompt.accept()# 点击第4个按钮 弹出模态框btns[3].click()# 获取模态框确认按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//div[@id="customModal"]/div/button')btn.click()# 点击第6个按钮 弹出多个弹窗btns[5].click()# 消掉第1个弹窗driver.switch_to.alert.accept()# 消掉第2个弹窗driver.switch_to.alert.accept()# 在第3个窗口中输入内容driver.switch_to.alert.send_keys("你好")# 消掉第3个弹窗driver.switch_to.alert.accept()# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':test_alert()
selenium拖拽元素

要完成元素的拖拽,首先需要指定被拖动的元素和拖动目标元素,然后利用 ActionChains 类来实现,ActionChains用于定制动作。通过ActionChains对象中的perform()执行动作
代码
from time import sleepfrom selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_drop():# 创建一个浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 访问页面driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/14')# 获取元素draggable = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'draggable')draggable2 = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'draggable2')draggable3 = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'draggable3')# 拖拽元素-1次到位actions = webdriver.ActionChains(driver).drag_and_drop(draggable, draggable2)actions.perform()# 拖拽元素-慢慢拖动for i in range(10):webdriver.ActionChains(driver).drag_and_drop_by_offset(draggable3, 10,0).perform()sleep(0.5)sleep(2)driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':test_drop()
selenium调用js方法

有时候我们需要控制页面滚动条上的滚动条,但滚动条并非页面上的元素,这个时候就需要借助js是来进行操作
一般用到操作滚动条的会两个场景:
-
要操作的页面元素不在当前页面范围,无法进行操作,需要拖动滚动条
-
注册时的法律条文需要阅读,判断用户是否阅读的标准是:滚动条是否拉到最下方
调用js的方法
execute_script(script, *args)
JS代码功能
// 拉动滚动条
document.元素.scrollTop=高度
document.元素.scrollTo(宽度,高度)
window.scrollTo(宽度,高度)// 获取页面高度
document.body.scrollHeight
// 获取元素高度
document.getElementById('scrollContent').scrollHeight
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_js():# 创建一个浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 访问地址driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/15')# 拉动正页面滚动条js = 'document.documentElement.scrollTop=10000'js2 = 'document.getElementById("scrollContent").scrollTop=100'js3 ='window.scrollTo(0,1000)'js4= '''const bar = document.getElementById('progressBar');let width = 0;clearInterval(progressInterval);progressInterval = setInterval(() => {if (width >= 100) {clearInterval(progressInterval);updateStatus('进度完成');return;}width++;bar.style.width = width + '%';updateStatus(`进度: ${width}%`);}, 50);'''driver.execute_script(js2)# 关闭浏览器sleep(2)driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':test_js()
selenium 等待元素

-
网速慢
-
AJAX请求数据
-
调试
强制等待
使用 time.sleep
作用:当代码运行到强制等待这一行的时候,无论出于什么原因,都强制等待指定的时间,需要通过time模块实现
优点:简单
缺点:无法做有效的判断,会浪费时间
import timefrom selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_with_sleep():''' 使用 sleep 进行测试 '''print("=== 使用 sleep 测试 ===")# 记录开始时间start_time = time.time()# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")time.sleep(1)# 定位元素# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'loadContentBtn')# 模拟点击btn.click()time.sleep(5)# 获取延迟加载的数据div = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'delayedContent')# 打印数据print(div.text)# 获取结束时间end_time = time.time()print(f'用时:{end_time - start_time}')# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':test_with_sleep()
隐式等待
chrome.implicitly_wait(time_num)
到了一定的时间发现元素还没有加载,则继续等待我们指定的时间,如果超过了我们指定的时间还没有加载就会抛出异常,如果没有需要等待的时候就已经加载完毕就会立即执行
优点: 设置一次即可
缺点:必须等待加载完成才能到后续的操作,或者等待超时才能进入后续的操作
注意:只能等待元素出现在 DOM 中
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_with_implicit_wait1():''' 使用隐式等待进行测试 这个案例不行,因为文档已经加载了,所以隐示不等'''print("=== 使用隐式等待测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 设置隐式等待时间driver.implicitly_wait(5)# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadContentBtn")btn.click()# 获取延迟加载的数据div = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'delayedContent')# 打印数据print(div.text)# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()def test_with_implicit_wait2():''' 使用隐式等待进行测试 '''print("=== 使用隐式等待测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 设置隐式等待时间driver.implicitly_wait(10)# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "gridBtn")btn.click()# 获取延迟加载的数据div = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//div[@class="grid-item visible"][5]')# 打印数据print(div.text)# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()from time import sleep
def test_with_implicit_wait3():''' 使用隐式等待进行测试 '''print("=== 使用隐式等待测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()# 设置隐式等待时间driver.implicitly_wait(10)# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadElementsBtn")btn.click()# 获取延迟加载的数据div = driver.find_element(By.ID, 'element-3')sleep(0.2)# 打印数据print(div.text)# 关闭浏览器driver.quit()
if __name__ =='__main__':# test_with_implicit_wait1()# test_with_implicit_wait2()test_with_implicit_wait3()
显示等待
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
指定一个等待条件,并且指定一个最长等待时间,会在这个时间内进行判断是否满足等待条件,如果成立就会立即返回,如果不成立,就会一直等待,直到等待你指定的最长等待时间,如果还是不满足,就会抛出异常,如果满足了就会正常返回
优点:专门用于对指定一个元素等待,加载完即可运行后续代码
缺点:多个元素都需要要单独设置等待
常见的等待条件
-
EC.presence_of_element_located() 元素存在
-
EC.visibility_of_element_located() 元素可见
-
EC.element_to_be_clickable() 元素可点击
-
EC.presence_of_all_elements_located() 所有元素存在
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECdef test_presence_of_element_located():''' 使用 WebDriverWait 进行测试 '''print("=== 使用 WebDriverWait 测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadContentBtn")btn.click()# 2. 等待延迟内容元素在DOM中存在div = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "delayedContent")))print(f"元素标签名: {div.tag_name}")print(f"元素文本: {div.text}")
def test_visibility_of_element_located():''' 使用 WebDriverWait 进行测试 '''print("=== 使用 WebDriverWait 测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadContentBtn")btn.click()# 2. 等待延迟内容元素在DOM中存在div = wait.until(EC.visibility_of_element_located((By.ID, "delayedContent")))print(f"元素标签名: {div.tag_name}")print(f"元素文本: {div.text}") def test_presence_of_all_elements_located1():"""测试所有元素存在 - EC.presence_of_all_elements_located()这个条件用于等待多个元素都在DOM中出现"""# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 1. 点击加载网格元素按钮grid_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "gridBtn")grid_button.click()# 2. 等待所有网格元素加载完成grid_items = wait.until(EC.presence_of_all_elements_located((By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")))print(f"加载的元素总数: {len(grid_items)}")def test_presence_of_all_elements_located2():"""测试所有元素存在 - EC.presence_of_all_elements_located()这个条件用于等待多个元素都在DOM中出现"""# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 1. 点击加载网格元素按钮grid_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "gridBtn")grid_button.click()# 2. 等待所有网格元素加载完成wait.until(element_loads)items = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")print(f"加载的元素总数: {len(items)}")def element_loads(driver):items = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")return True if len(items) ==6 else Falseif __name__ == "__main__":test_presence_of_element_located()# test_visibility_of_element_located()# test_presence_of_all_elements_located1()# test_presence_of_all_elements_located2()
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECdef test_presence_of_element_located():''' 使用 WebDriverWait 进行测试 '''print("=== 使用 WebDriverWait 测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadContentBtn")btn.click()# 2. 等待延迟内容元素在DOM中存在div = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "delayedContent")))print(f"元素标签名: {div.tag_name}")print(f"元素文本: {div.text}")
def test_visibility_of_element_located():''' 使用 WebDriverWait 进行测试 '''print("=== 使用 WebDriverWait 测试 ===")# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 定位按钮btn = driver.find_element(By.ID, "loadContentBtn")btn.click()# 2. 等待延迟内容元素在DOM中存在div = wait.until(EC.visibility_of_element_located((By.ID, "delayedContent")))print(f"元素标签名: {div.tag_name}")print(f"元素文本: {div.text}") def test_presence_of_all_elements_located1():"""测试所有元素存在 - EC.presence_of_all_elements_located()这个条件用于等待多个元素都在DOM中出现"""# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 1. 点击加载网格元素按钮grid_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "gridBtn")grid_button.click()# 2. 等待所有网格元素加载完成grid_items = wait.until(EC.presence_of_all_elements_located((By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")))print(f"加载的元素总数: {len(grid_items)}")def test_presence_of_all_elements_located2():"""测试所有元素存在 - EC.presence_of_all_elements_located()这个条件用于等待多个元素都在DOM中出现"""# 打开浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome()wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) # 设置显式等待时间为10秒# 访问页面driver.get("http://localhost:8000/playground/16")# 1. 点击加载网格元素按钮grid_button = driver.find_element(By.ID, "gridBtn")grid_button.click()# 2. 等待所有网格元素加载完成wait.until(element_loads)items = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")print(f"加载的元素总数: {len(items)}")def element_loads(driver):items = driver.find_elements(By.CLASS_NAME, "grid-item")return True if len(items) ==6 else Falseif __name__ == "__main__":test_presence_of_element_located()# test_visibility_of_element_located()# test_presence_of_all_elements_located1()# test_presence_of_all_elements_located2()
selenium 参数使用

chrome59版本以后可以变成无头的浏览器,加以下参数
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import Bydef test_headless():"""使用无头模式进行测试"""print("=== 使用无头模式测试 ===")# 创建参数对象options = Options()options.add_argument('--headless')# options.add_argument('--headless=new') # 需要 Chrome 109 或更高版本# 创建一个浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)# 访问页面driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/17')# 获取元素div = driver.find_element(By.TAG_NAME, 'h3')print(div.text)driver.quit()
代理模式
def test_proxy():"""使用代理进行测试"""print("=== 使用代理测试 ===")options = Options()options.add_argument('--proxy-server=http://127.0.0.1:7890')driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)driver.get('http://localhost:8000/tool/request_content')proxy =driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//div[@class="info-card"][1]/div[@class="data-row"][2]/div[@class="data-value"]')print(proxy.text)driver.quit()
防检测设置
def test_check():# 创建参数对象options = Options()# 禁用自动化控制检测options.add_argument('--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled')# 禁用网页安全策略# options.add_argument('--disable-web-security')# 排除自动化开关# options.add_experimental_option('excludeSwitches', ['enable-automation'])# 禁用自动化扩展# options.add_experimental_option('useAutomationExtension', False)# 创建一个浏览器driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)driver.execute_cdp_cmd("Page.addScriptToEvaluateOnNewDocument", {"source": "Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {get: () => false})"})# 访问页面driver.get('http://localhost:8000/playground/17')# 获取有有没有自动化print(driver.execute_script("return window.navigator.webdriver"))driver.quit()
使用 window.navigator.webdriver 检测
Selenium 提升效率

提升效率方案
-
解析方面
-
参数设置
-
并发编程
解析提速
selenium本身提取数据,会比使用XPath、BS4、re这种提取方式要慢。因为每一个selenium的操作,都需要和浏览器通信
# 先用Selenium获取动态内容
driver.get(url)# 然后用XPath解析,这样更快
e = etree.HTML(driver.page_source)
data = e.xpath('//div')
通过参数
-
开启无头
-
关闭图片
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Optionschrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument('--headless') # 无头模式
chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-images') # 禁用图片
chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-javascript') # 如果不需要JS
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
并发编程
-
使用多进程
from multiprocessing import Pooldef scrape_url(url):driver = setup_driver() # 每个进程创建独立的driver# 爬取逻辑driver.quit()if __name__ == '__main__':urls = ['url1', 'url2', 'url3']with Pool(processes=4) as pool:results = pool.map(scrape_url, urls)
使用协程
注意:
Selenium本身支持异步操作,但实现方式比较特殊。它使用了一种特殊的机制来模拟同步操作,但实际上在底层是异步执行的
在JavaScript中使用Selenium时,所有的WebDriver操作都会返回Promise,这使得可以使用async/await来处理异步操作
然而,这种异步机制并不是真正意义上的异步并发,如果需要真正的异步并发爬虫,建议使用:
Playwright
Pyppeteer
aiohttp
# 安装
pip install playwright==1.49.0
代码案例
import asyncio
from playwright.async_api import async_playwrightasync def scrape_url(url):async with async_playwright() as p:browser = await p.chromium.launch()page = await browser.new_page()await page.goto(url)# 爬取逻辑await browser.close()async def main():urls = ['url1', 'url2', 'url3']tasks = [scrape_url(url) for url in urls]await asyncio.gather(*tasks)asyncio.run(main())
