java-IO流-字节流
认识IO流
I指input,称为输入流,负责把数据读到内存中
O指output,称为输出流,负责写数据出去
io流分类
- 按流的方向:
输入流,输出流 - 按流的内容:
字节流(适合操作所有类型的文件:音视频、图片、文本文件的复制、转移)
字符流(只适合操作纯文本文件:读写txt、java文件)
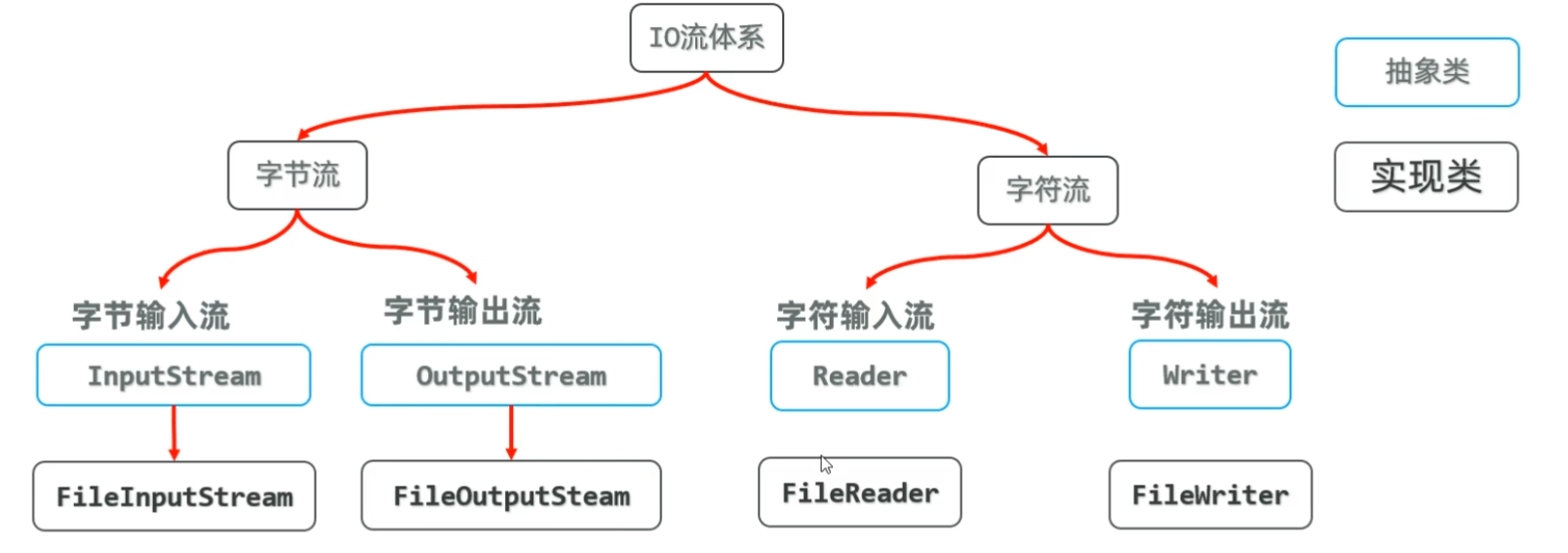
io流体系
- 字节输入流InputStream
- 字节输出流OutputStream
- 字符输入流Reader
- 字符输出流Writer
字节流
FileInputStream(文件字节输入流)
以内存为基准,可把磁盘文件中的数据以字节的形式读入内存

public class FileInputStreamDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//文件字节输入流读取文件中的字节数组到内存中//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道和文件接通//InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt"));InputStream is = new FileInputStream("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt");//简化写法//2、读取文件中的字节并输出:每次读一个字节//定义一个变量记住每次读取的一个字节(垃圾)int b;while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) b);}//每次读取一个字节的问题:性能较差,读取汉字输出会乱码}
}
public class FileInputStreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//文件字节输入流读取文件中的字节数组到内存中//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道和文件接通//InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt"));InputStream is = new FileInputStream("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt");//简化写法//2、读取文件中的字节并输出:每次读多个字节//定义一个字节数组,每次读取多个字节byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//定义一个变量记住每次读取的字节个数int len;while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {String s = new String(buffer, 0, len);System.out.print(s);}//拓展:每次读取多个字节,性能得到提升,因为一次读取多个字节,减少硬盘和内存的交互次数,提升性能//仍无法避免汉字乱码,存在截断汉字字节的可能性}
}
一次读完全部字节

读取文本适合用字符流;字节流适合做数据的转移,如:文件复制
public class FileInputStreamDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//文件字节输入流读取文件中的字节数组到内存中//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道和文件接通//InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt"));InputStream is = new FileInputStream("product\\src\\guzhenren.txt");//简化写法//2、一次性读完文件中的所有字节:可以避免读取汉字输出乱码byte[] bytes = is.readAllBytes();String rs = new String(bytes);System.out.println(rs);is.close();}
}
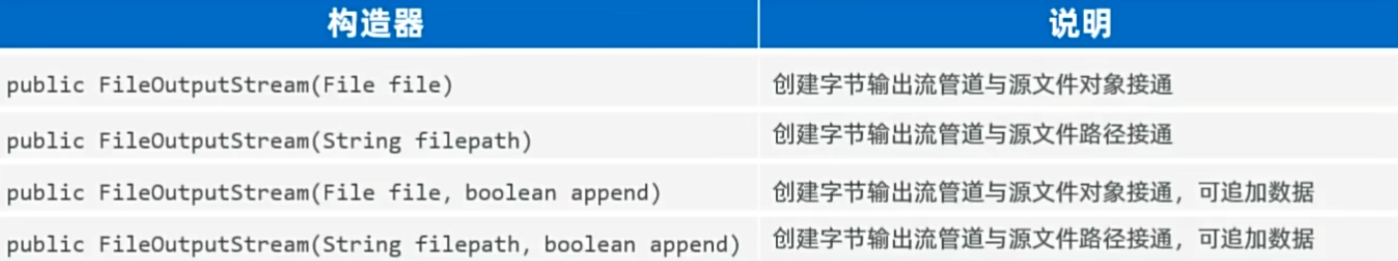
FileOutputStream(文件字节输出流)
以内存为基准,可把内存中的数据以字节的形式写出到文件中
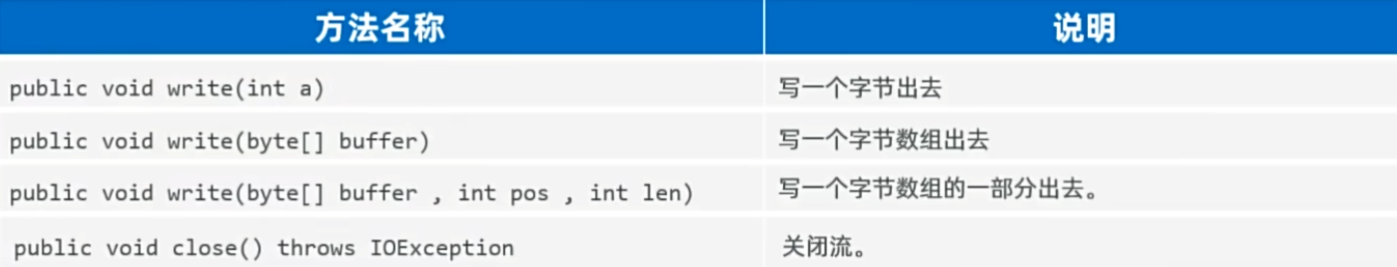
public class FileOutputStreamDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//文件字节输出流//1、创建文件字节输出流管道与目标文件接通//OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("product\\src\\wenzhenren.txt");//覆盖管道OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("product\\src\\wenzhenren.txt", true);//追加管道//2、写入数据//public void write(int b)os.write(97);os.write('a');//os.write('文');//会乱码os.write("\r\n".getBytes());//换行//3、写一个字节数组//public void write(byte[] buffer)byte[] buffer = "人是万物之灵,文乃天地真精".getBytes();os.write(buffer);os.write("\r\n".getBytes());//4、写一个字节数组的一部分出去//public void write(byte[] buffer, int pos, int len)os.write(buffer, 0, 3);os.write(buffer, 15, 3);os.write("\r\n".getBytes());os.close();//关闭管道}
}
文件复制
public class CopyDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//字节流完成文件的复制操作//源文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\pixiv\saber.jpg//目标文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\图片\saber_copy.jpg(复制过去时必须带文件名,无法自动生成文件名)try {copyFile("C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\pixiv\\saber.jpg", "C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\图片\\saber_copy.jpg");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//复制文件public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) throws Exception {//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道与源文件接通FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcPath);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destPath);//2、定义一个字节数组,每次读取多个字节byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {//3、把读取到的字节写入到文件中fos.write(buffer, 0, len);//读取多少个字节,写入多少个字节}System.out.println("复制完毕!");}
}
资源释放方案
try-catch-finally
finally代码区特点:无论try中程序正常执行还是出现异常,最后一定执行finally区,除非JVM终止
作用:一般用于程序执行完成后进行资源的释放操作
public class CopyDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//字节流完成文件的复制操作//源文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\pixiv\saber.jpg//目标文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\图片\saber_copy.jpg(复制过去时必须带文件名,无法自动生成文件名)copyFile("C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\pixiv\\saber.jpg", "C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\图片\\saber_copy.jpg");}//复制文件public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath){FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos = null;try {//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道与源文件接通fis = new FileInputStream(srcPath);fos = new FileOutputStream(destPath);//2、定义一个字节数组,每次读取多个字节byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {//3、把读取到的字节写入到文件中fos.write(buffer, 0, len);//读取多少个字节,写入多少个字节}System.out.println("复制完毕!");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//最后一定执行一次,即使程序出现异常try {if(fos != null) fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if(fis != null) fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
代码太臃肿
try-with-resource

资源使用完毕后 自动调用其close方法,完成对资源的释放
- ()中只能放资源,否则报错
- 什么是资源?
资源一般指最终实现了AutoCloseable接口

public class CopyDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//资源释放新方式:try-with-resource//源文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\pixiv\saber.jpg//目标文件:C:\Users\hanyue\Pictures\图片\saber_copy.jpg(复制过去时必须带文件名,无法自动生成文件名)copyFile("C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\pixiv\\saber.jpg", "C:\\Users\\hanyue\\Pictures\\图片\\saber_copy.jpg");}//复制文件public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath){//1、创建一个文件字节输入流管道与源文件接通try( //只能放资源对象,用完后会自动调用close方法自动关闭FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcPath);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destPath);) {//2、定义一个字节数组,每次读取多个字节byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {//3、把读取到的字节写入到文件中fos.write(buffer, 0, len);//读取多少个字节,写入多少个字节}System.out.println("复制完毕!");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
