Memblock-2
memblock是内核的第一个内存分配器,其主要应用在boot阶段。但是当memory hotplug功能启动时,其也可以运行在runtime阶段。memblock在linux v2.6.35 in 2010 引入内核,后逐步取代了bootmem分配器,成为了内核启动早期唯一的内存分配器。
It is also used to support hotplug memory and to switch to the buddy allocator after adding memory added at runtime using memblock.
Structure of Memblock
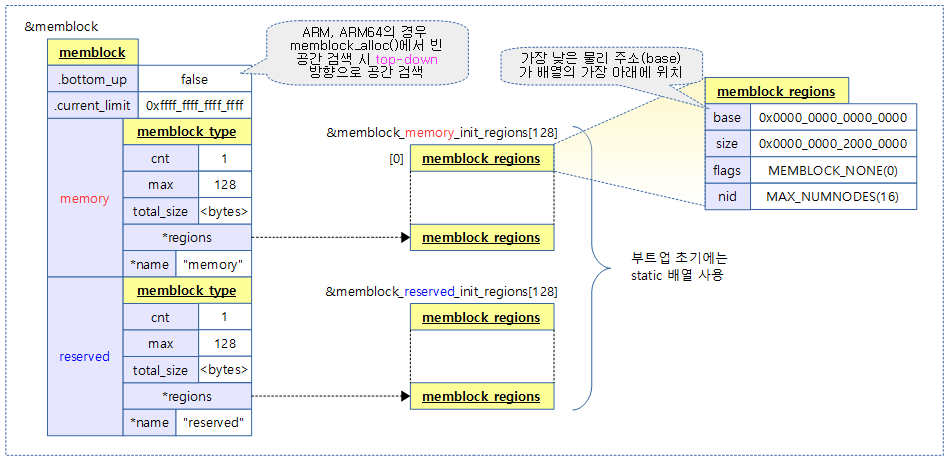
Memblock is managed by dividing it into two types as follows:
- memory type
- The memory type is used by registering the physical memory area to be used. It can be registered by limiting the use of only a part of the actual physical memory by kernel parameters. Initially, up to 128 areas can be used in the regions[ ] array, and it can be continuously expanded in units of 2 in the future.
- reserved type
- The reserved type is used by registering a physical memory area that is in use or will be used. Initially, up to 128 areas can be used in the regions[ ] array, and it can be continuously expanded in units of 2 in the future.
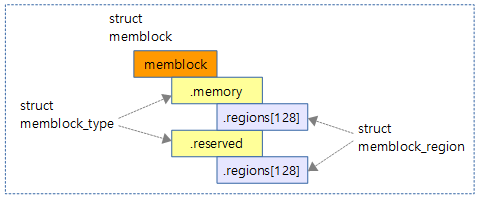
The following figure shows the relationship between the memblock, memblock_type, and memblock_regions structures.
API
memblock_add()
memblock_reserve()
memblock_add_range()
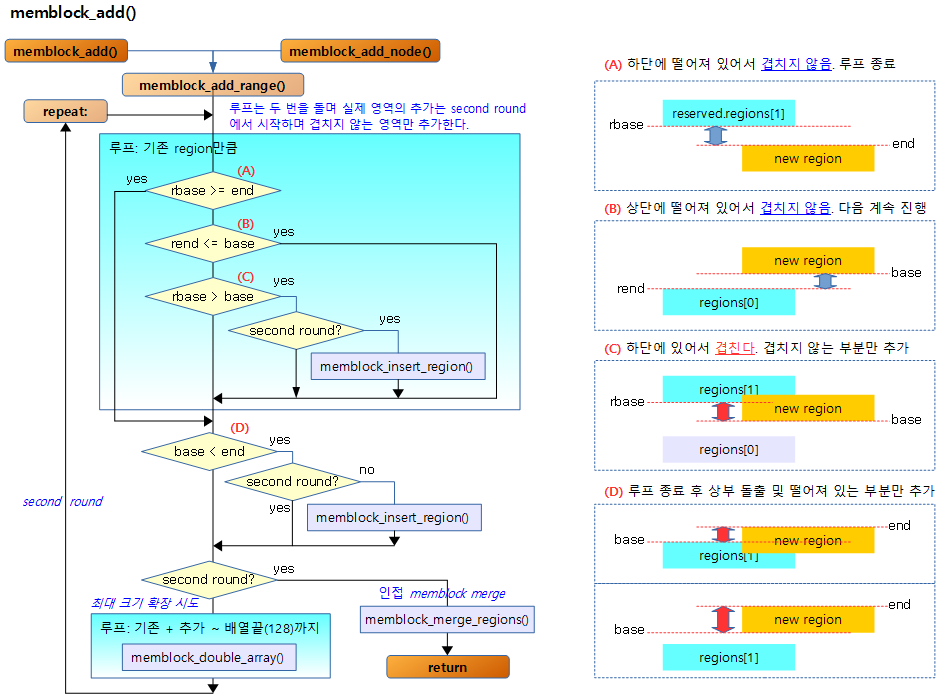
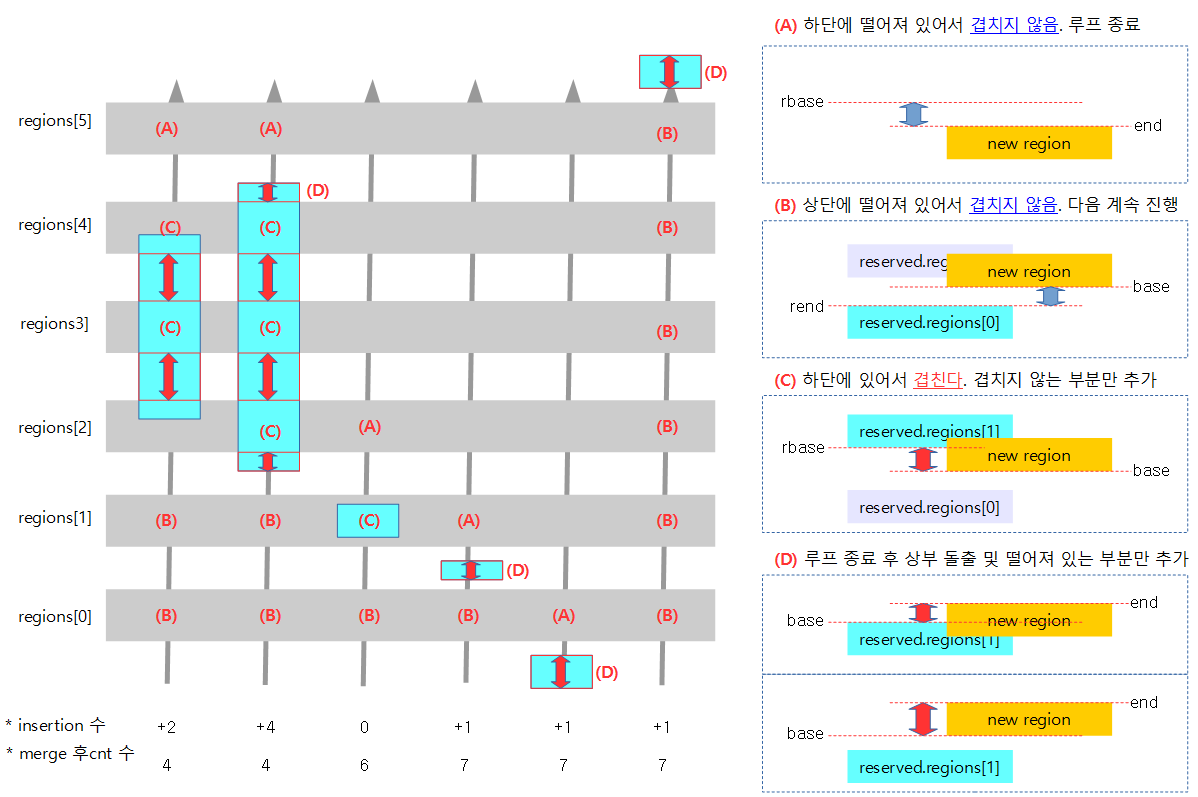
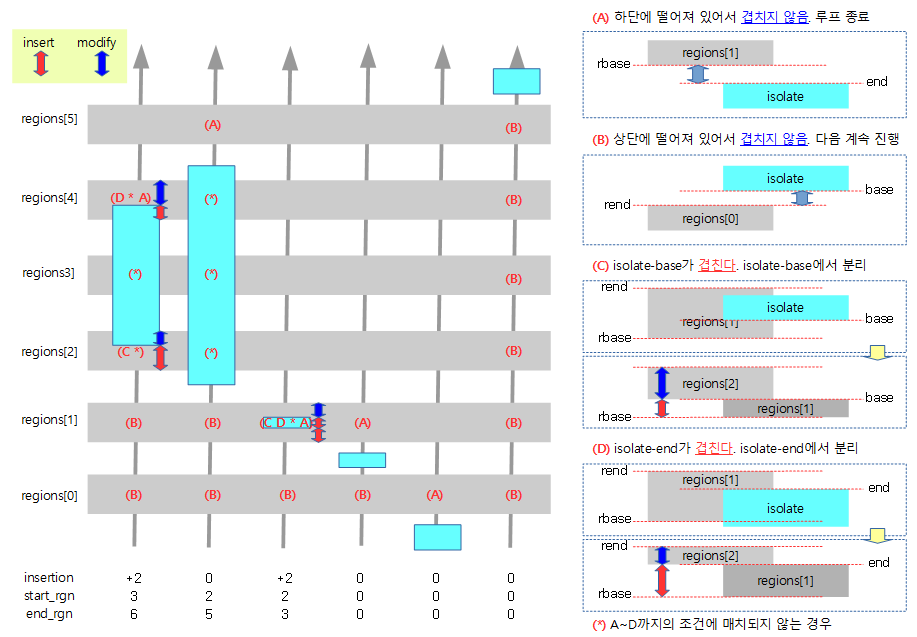
The figure below shows the six existing regions registered in gray, and the six cases in which a new memblock is added in sky blue, compared from region[0] in the direction of the arrow.
- If the area to be added overlaps with the existing memblock area, it is first split into non-overlapping areas and added, and then the adjacent blocks are finally merged.
- insertion number
- The number of actual insertions that occur when a memblock is added.
- Number of cnts after merge
- The number of memblocks that will ultimately remain after merging
memblock array expansion
memblock_double_array()
memblock merge
memblock_merge_regions()
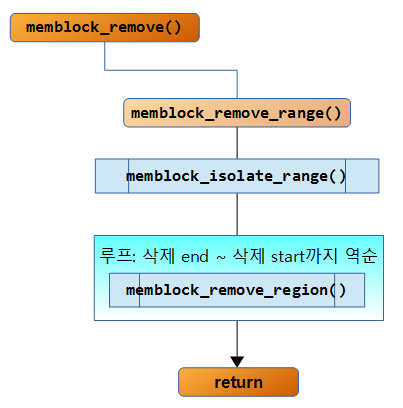
Delete memblock
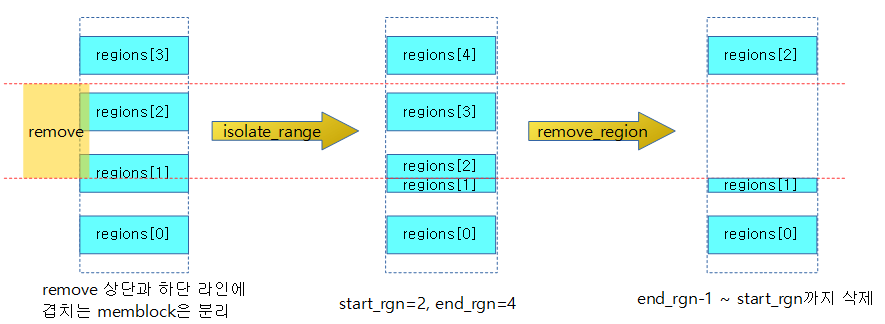
The following figure shows the memblock areas that change when the yellow remove range is deleted among the four memblock areas.
memblock separation
The following figure shows how the memblock_ioslate_range() function is processed.
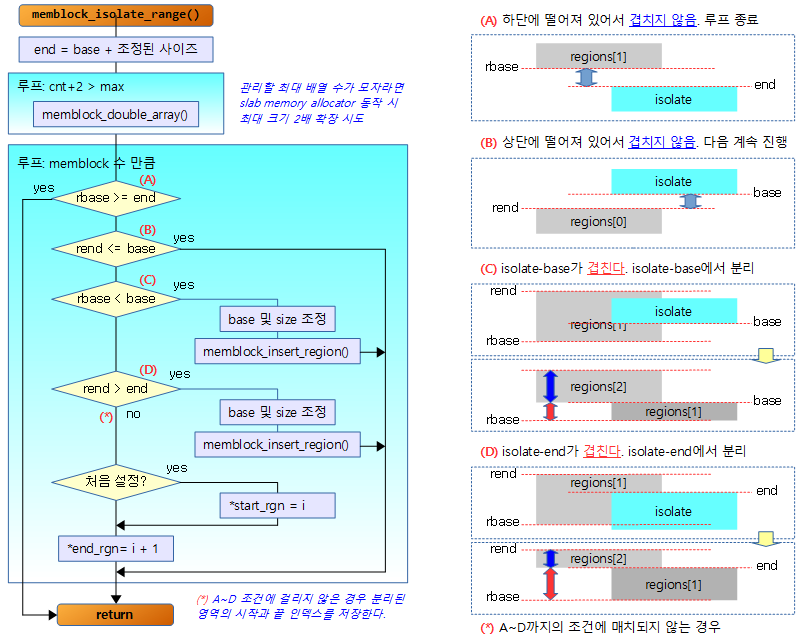
The following figure shows the comparison from region[0] in the direction of the arrow when each of the six memblock regions, marked in gray, is given a sky-blue isolation region.
- If the area to be separated overlaps with an existing memblock area, the overlapping part divides the memblock. And the part without a memblock is added.
- insertion
- The number of actual insertions that occur when a memblock is added is displayed.
- start_rgn
- Index number of an existing memblock area that overlaps the start of the isolation range
- end_rgn
- Index number of the existing memblock area that overlaps the end of the isolation range + 1
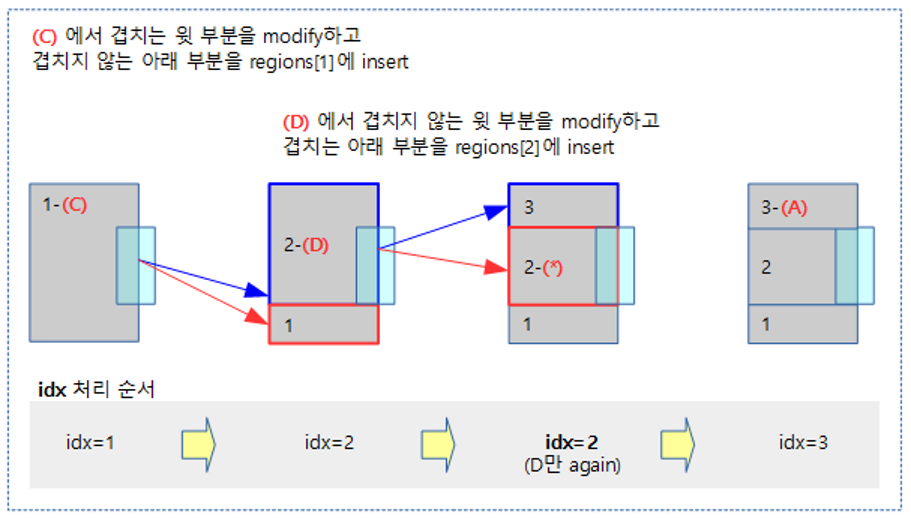
The following figure illustrates the first part of the six examples above in a little more detail.
- In the case of (C) and (D), when inserting, the idx area being processed is pushed up and added.
- (D) When proceeding with case, be careful to proceed with the area corresponding to idx once again.
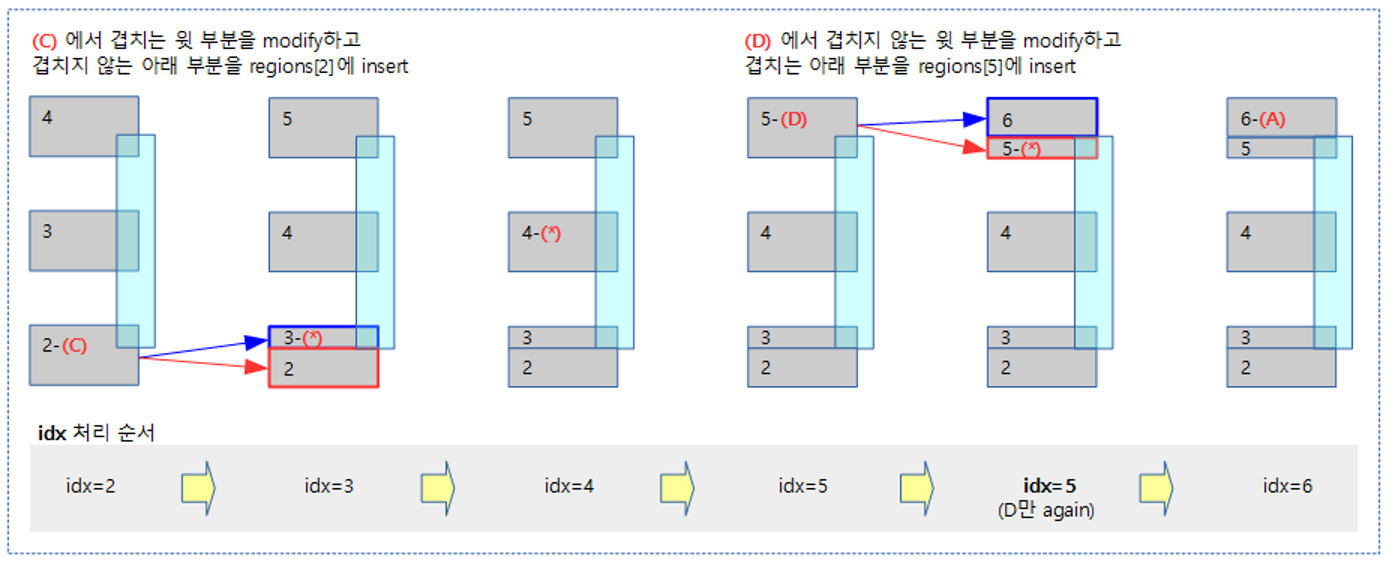
The following figure illustrates the third part of the six examples above in a bit more detail.