《Muduo网络库:实现Channel通道以及Poller抽象基类》
实现了日志功能之后,再来封装一下socket地址类型。
实现InetAddress类
InetAddress.h
#pragma once#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <string>// 封装socket地址类型(sockaddr_in结构)
class InetAddress
{
public:explicit InetAddress(uint16_t port, std::string ip = "127.0.0.1");explicit InetAddress(const struct sockaddr_in &addr): addr_(addr){}// 获取IPstd::string toIp() const;// 获取IP:端口 std::string toIpPort() const;// 获取端口uint16_t toPort() const;// 获取sockaddr_in结构const sockaddr_in *getSockAddr() const{return &addr_;}private:sockaddr_in addr_;
};InetAddress.cc
#include "InetAddress.h"#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>InetAddress::InetAddress(uint16_t port, std::string ip)
{bzero(&addr_, 0);addr_.sin_family = AF_INET;addr_.sin_port = htons(port);addr_.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
}// 获取IP
std::string InetAddress::toIp() const
{char buf[64] = {0};inet_ntop(AF_INET, &addr_.sin_addr, buf, sizeof buf);return buf;
}
// 获取IP:端口
std::string InetAddress::toIpPort() const
{// 格式ip:portchar buf[64] = {0};inet_ntop(AF_INET, &addr_.sin_addr, buf, sizeof buf);size_t iplen = strlen(buf);uint16_t port = ntohs(addr_.sin_port);sprintf(buf + iplen, ":%u", port);return buf;
}
// 获取端口
uint16_t InetAddress::toPort() const
{return ntohs(addr_.sin_port);
}// 可以测试功能代码是否编写正确
// #include <iostream>
// int main()
// {
// InetAddress addr(8080);
// std::cout << addr.toIpPort() << std::endl;
// return 0;
// }封装好了socket地址类型,下面就开始着手编写TcpServer类了。
当我们使用过Muduo网络库服务器编程就知道TcpServer相当于是Muduo库给用户提供的编写服务器的入口的一个类,把Muduo库所有的有关服务器编程相关的东西都打包到一起了,包括反应堆、事件分发器、事件回调等。
我们看以下Muduo的源码也可以看到。
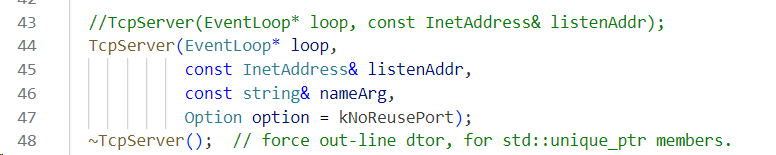
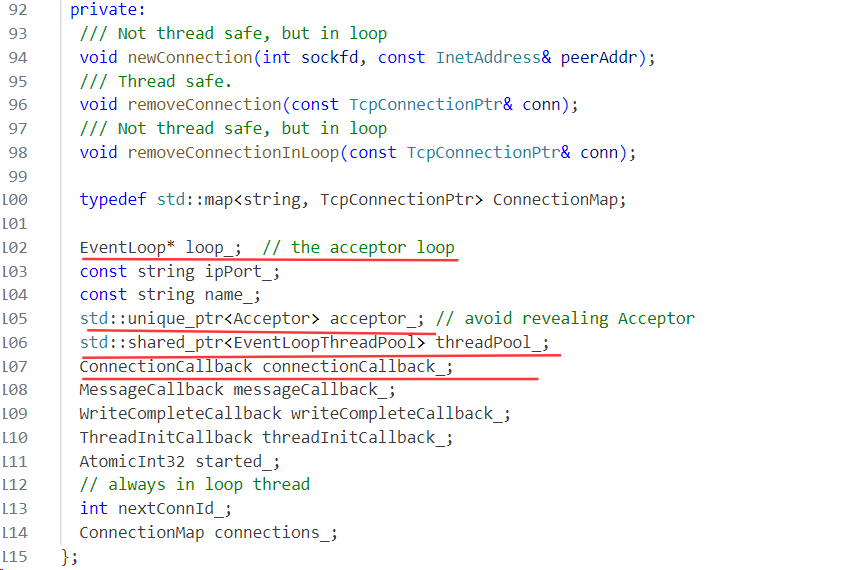
TcpServer类就是打包所有资源的一个“盒子”,那我们一步一步来剖析。
EventLoop,就是Reactor模型里面最重要的事件循环了,可以想象成epoll。
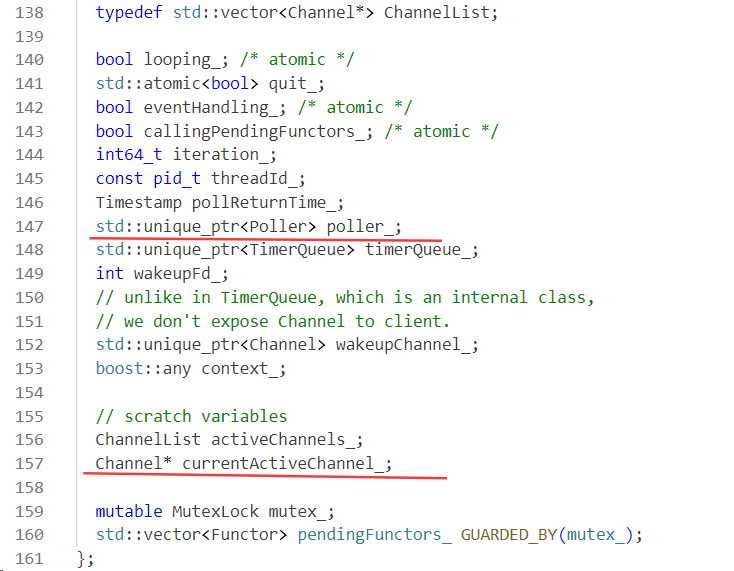
EventLoop事件循环有两个重要的成员:
- Poller抽象基类:由EpollPoller(基于epoll)和PollPoller(基于poll)继承,它关注的是poll和epoll感兴趣的事件。
- Channel通道:它所关注的是fd和它感兴趣的事件以及实际Poller返回的fd上发生的事件。
简单理解,EventLoop就是事件循环,最重要的两个东西,一个是epoll,一个是epoll所监听的fd以及它所感兴趣的事件和最终epoll_wait通知的发生的事件。
下面我们先将Channel和Poller实现,进而来实现EventLoop。
EventLoop.h
#pragma once// 事件循环类 主要包含了两个大模块 Channel Poller(epoll的抽象)
class EventLoop
{
public:
private:
};EventLoop.cc
#include "EventLoop.h"实现Channel通道
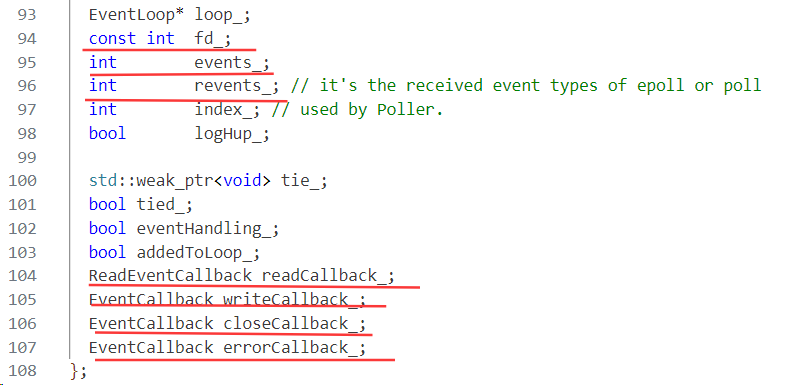
sockfd以及感兴趣的事件和发生的事件、事件相应的回调操作都在Channel通道里。
Channel.h
#pragma once#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"#include <functional>
#include <memory>class EventLoop;/*** 理清楚 EventLoop、Channel、Poller之间的关系。在Reactor模型上对应多路事件分发器* Channel 理解为通道 封装了sockfd和其感兴趣的事件event,比如EPOLLIN、EPOLLOUT* 还绑定了Poller返回的具体事件,Poller返回通知Channel发生的事件后,Channel调用相应的事件回调操作*/class Channel : noncopyable
{
public:using EventCallback = std::function<void()>; // 事件回调using ReadEventCallback = std::function<void(Timestamp)>; // 只读事件回调Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd);~Channel();// 得到poller通知的发生的事件以后,处理事件的void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);// 设置回调函数对象void setReadCallback(ReadEventCallback cb) { readCallback_ = std::move(cb); }void setWriteCallback(EventCallback cb) { writeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }void setCloseCallback(EventCallback cb) { closeCallback_ = std::move(cb); }void setErrorCallback(EventCallback cb) { errorCallback_ = std::move(cb); }// 防止当channel被手动remove掉,channel还在执行回调操作void tie(const std::shared_ptr<void>&);int fd() const { return fd_; } // 获取当前channel的fd_int events() const { return events_; } // 获取当前channel的感兴趣的事件events_void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by poller// 设置fd相应的事件状态void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); }void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }// 返回channel fd当前的事件状态bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }bool isReading() const { return events_ & kReadEvent; }int index() { return index_; } // 获取当前channel的状态index_void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; } // 设置channel当前的状态 used by poller// 返回当前channel属于哪一个EventLoop// one loop per threadEventLoop* ownerLoop() { return loop_; }// 在Poller中移除Channelvoid remove();private:// 在Poller中更新Channelvoid update();void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);// channel感兴趣的事件的状态static const int kNoneEvent; // 对任何事件不感兴趣static const int kReadEvent; // 可读事件static const int kWriteEvent; // 可写事件EventLoop *loop_; // 定义Channel所属的事件循环EventLoopint fd_; // fd, poller监听的对象int events_; // 注册fd感兴趣的事件int revents_; // poller返回的具体发生的事件int index_; // channel的初始状态std::weak_ptr<void> tie_;bool tied_;// 因为Channel通道能获知fd最终发生的具体事件revents,所以它负责调用具体事件的回调操作,根据事件的类型调用相应事件的回调ReadEventCallback readCallback_;EventCallback writeCallback_;EventCallback closeCallback_;EventCallback errorCallback_;
};Channel.cc
#include "Channel.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "Logger.h"#include <sys/epoll.h>const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0;
const int Channel::kReadEvent = EPOLLIN | EPOLLPRI;
const int Channel::kWriteEvent = EPOLLOUT;// EventLoop: ChannelList Poller
Channel::Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd): loop_(loop), fd_(fd), events_(0), revents_(0), index_(-1), tied_(false)
{
}
Channel::~Channel()
{
}// channel的tie方法什么时候调用过?
void Channel::tie(const std::shared_ptr<void> &obj)
{tie_ = obj;tied_ = true;
}/*** 当改变channel所表示fd的events事件状态后,update负责在poller里面更改fd相应的事件(也就是epoll_ctl操作)* EventLoop:ChannelList、Poller。一个EventLoop有一个poller和多个channel* channel和poller是两个不同的模块,channel无法直接操作poller,但是他们都属于一个EventLoop。*/
// 在channel所属的EventLoop中,更新Poller中当前的channel
void Channel::update()
{// 通过channel所属的EventLoop,调用poller的相应方法,更新fd的events事件// add code...// loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
// 在channel所属的EventLoop中,把Poller中当前的channel删掉
void Channel::remove()
{// add code...// loop_->removeChannel(this);
}// fd得到poller通知以后,处理事件的
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{if (tied_){std::shared_ptr<void> guard = tie_.lock();if (guard){handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);}}else{handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);}
}// 根据poller通知channel发生的具体事件,由channel负责调用具体的事件回调操作
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{LOG_INFO("channel handleEvent revents:%d\n", revents_);if ((revents_ & EPOLLHUP) && !(revents_ & EPOLLIN)){if (closeCallback_){closeCallback_();}}if (revents_ & EPOLLERR){if (errorCallback_){errorCallback_();}}if (revents_ & (EPOLLIN | EPOLLPRI)){if (readCallback_){readCallback_(receiveTime);}}if (revents_ & EPOLLOUT){if (writeCallback_){writeCallback_();}}
}也就是说Channel向Poller中注册fd及其感兴趣的事件,Poller未来通过epoll_wait监听到fd上发生的事件后,通知返回给Channel,Channel得到fd发生的事件之后调用我们预先设定好的相应事件的回调操作处理事件。
实现Poller抽象基类
Muduo并没有直接使用epoll或poll,而是使用了一个Poller抽象类,通过引用不同的派生类对象,调用他们的同名覆盖方法,就可以非常方便的去扩展不同的IO复用能力。
Poller.h
#pragma once#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>class Channel;
class EventLoop;/*** muduo库中多路事件分发器的核心IO复用模块* 理清楚EventLoop、Channel、Poller三者之间的关系*/
class Poller : noncopyable
{
public:using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel *>;Poller(EventLoop *loop);virtual ~Poller() = default;// 给所有IO复用保留统一的接口virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) = 0;virtual void updateChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;virtual void removeChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;// 判断参数channel是否在当前Poller当中bool hasChannel(Channel *channel) const;// EventLoop可以通过该接口获取默认的IO复用的具体实现static Poller *newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop);protected:// unordered_map的key表示sockfd,value表示sockfd所属的channel通道using ChannelMap = std::unordered_map<int, Channel *>;ChannelMap channels_;private:EventLoop *ownerloop_; // 定义Poller所属的EventLoop事件循环
};Poller.cc
#include "Poller.h"
#include "Channel.h"Poller::Poller(EventLoop *loop): ownerloop_(loop)
{
}bool Poller::hasChannel(Channel *channel) const
{auto it = channels_.find(channel->fd());return it != channels_.end() && it->second == channel;
}一、
Poller通过unordered_map定义了一个ChannelMap,保存(以fd映射channel*的方式)了所有要监听的channel通道。当Channel向Poller注册一个channel通道时,Poller就会调用相应的方法将该channel通道保存到ChannelMap中,当Channel要删除一个通道时,Poller也会将其从ChannelMap中删除。
同时定义了一个ChannelList,未来EpollPoller通过epoll_wait检测到某channel有事件发生时,就将该channel添加到ChannelList中,EventLoop就拿到了Poller返回的channel列表了。
二、
Poller是一个抽象类基类,EpollPoller(基于epoll)或PollPoller(基于poll)要继承这个基类,如果在Poller.cc中实现static Poller *newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop),这个函数是用来获取一个具体的IO复用方式的,也就是poll或epoll,Poller抽象基类与具体的实现方式耦合性高,基类不应该知道其派生类的存在。
所以获取具体的IO复用方式的实现,在单独的公共的源文件中实现。通过一个公共的文件,分解了Poller与具体的IO复用方式强耦合。
DefaultPoller.cc
#include "Poller.h"
#include <stdlib.h>Poller *Poller::newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop)
{if (getenv("MUDUO_USE_POLL")){return nullptr; // 生成poll的实例,这里目前还没有实现poll}else{return nullptr; // 生成epoll的实例,这里目前还没有实现epoll}
}实现EpollPoller类
Muduo库源码中实现了EpollPoller(基于epoll)和PollPoller(基于poll),我们只实现EpollPoller。EpollPoller继承Poller抽象基类,重写Poller的抽象方法。
要理清EventLoop、Channel、Poller三者之间的关系。
Muduo库采用one loop per thread,一个线程一个事件循环,这是现在高性能服务器设计普遍采用的一种模式。基于充分利用多核CPU性能,线程数肯定不只一个,也就是可以有多个事件循环。一个线程对应一个EventLoop,一个EventLoop对应一个Poller,一个Poller可以监听多个Channel(多路)。
EpollPoller.h
#pragma once#include "Poller.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"#include <vector>
#include "sys/epoll.h"class EventLoop;
class Channel;/** * epoll的使用* epoll_create* epoll_ctl* epoll_wait*/
class EpollPoller : public Poller
{
public:EpollPoller(EventLoop *loop);~EpollPoller() override;// 重写基类Poller的抽象方法Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) override;void updateChannel(Channel *channel) override;void removeChannel(Channel *channel) override;private:static const int kInitEventListSize = 16;// 填写活跃的连接void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const;// 更新channel通道void update(int operation, Channel *channel);using EventList = std::vector<struct epoll_event>;int epollfd_;EventList events_; // 存放epoll_wait返回的发生的事件的数组
};EpollPoller.cc
#include "EpollPoller.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Channel.h"#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>// 表示channel通道的状态
const int kNew = -1; // channel未添加到Poller中 channel的成员index=-1
const int kAdded = 1; // channel已添加到Poller中
const int kDeleted = 2; // channel从Poller中删除EpollPoller::EpollPoller(EventLoop *loop): Poller(loop), epollfd_(epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC)), events_(kInitEventListSize)
{if (epollfd_ < 0){LOG_FATAL("epoll_create error:%d\n", errno)}
}
EpollPoller::~EpollPoller()
{close(epollfd_);
}Timestamp EpollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels)
{// 实际用LOG_DEBUG输出日志更合理LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd total count:%d \n", __FUNCTION__, channels_.size());int numEvents = epoll_wait(epollfd_, &*events_.begin(), static_cast<int>(events_.size()), timeoutMs);int saveErrno = errno;Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());if (numEvents > 0){LOG_INFO("%d events happened \n", numEvents);fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);if (numEvents == events_.size()){events_.resize(events_.size() * 2);}}else if (numEvents == 0) // 超时{LOG_DEBUG("%s timeout! \n", __FUNCTION__);}else // 错误{if (saveErrno != EINTR){errno = saveErrno;LOG_ERROR("EPollPoller::poll() err!");}}return now;
}// 填写活跃的连接
void EpollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const
{for (int i = 0; i < numEvents; i++){Channel *channel = static_cast<Channel *>(events_[i].data.ptr);channel->set_revents(events_[i].events);activeChannels->push_back(channel); // EventLoop就拿到了它的Poller给它返回的所有发生事件的channel列表了}
}/*** Channel update remove => EventLoop updateChannel removeChannel => Poller updateChannel removeChannel* EventLoop => 未来通过Poller.poll获取就绪的channel* ChannelList Poller* ChannelMap <fd,channel*>* 当一个channel注册到Poller中,Poller就将该channel添加ChannelMap中* 当一个channel从Poller中删除,Poller就将该channel从ChannelMap中删除*/
void EpollPoller::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{const int index = channel->index();LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd=%d events=%d index=%d \n", __FUNCTION__, channel->fd(), channel->events(), index);if (index == kNew | index == kDeleted) // channel没有在Poller上注册过或已从Poller上删除{if (index == kNew){int fd = channel->fd();channels_[fd] = channel;}channel->set_index(kAdded);update(EPOLL_CTL_ADD, channel);}else // channel已经在Poller上注册过{int fd = channel->fd();if (channel->isNoneEvent()){update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);channel->set_index(kDeleted);}else{update(EPOLL_CTL_MOD, channel);}}
}
// 从Poller中删除channel
void EpollPoller::removeChannel(Channel *channel)
{int fd = channel->fd();channels_.erase(fd);LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd=%d \n", __FUNCTION__, fd);int index = channel->index();if (index == kAdded){update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);}channel->set_index(kNew);
}
// 更新channel通道 epoll_ctl add/del/mod
void EpollPoller::update(int operation, Channel *channel)
{struct epoll_event event;memset(&event, 0, sizeof event);int fd = channel->fd();event.events = channel->events();event.data.fd = fd;event.data.ptr = channel;if (epoll_ctl(epollfd_, operation, fd, &event) < 0){if (operation == EPOLL_CTL_DEL){LOG_ERROR("epoll_ctl del error:%d\n", errno);}else{LOG_FATAL("epoll_ctl add/mod error:%d\n", errno);}}
}将Channel通道和Poller抽象基类以及EpollPoller类实现完成,并理清了其之间的关系,下面我们再来实现EventLoop。
