第十六届蓝桥杯软件赛C组省赛C++题解(京津冀)
大家好,我们又见面了,今天是 2025 年 9 月 27 日,我来给大家分享的是:"第十六届蓝桥杯软件赛C组省赛C++题解(京津冀)",创作不易,大家多多支持,希望对大家有所帮助。
废话不多说,我们直接开始:
题目一:密密摆放
题目链接:密密摆放
【题目描述】

【算法原理】
数学
根据题目的名称:"密密摆放",再结合实际:"大箱子空间利用率越高的话,装的小盒子肯定是越多的",我们就不难得出,250 对应 50,240 对应 30,200 对应 40,这样的话,空间利用率能达到 100%,装入的小盒子的数量是最多的。
因此,本题只需要输出 250 / 50 * 240 / 30 * 200 / 40 即可。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{cout << 250 / 50 * 240 / 30 * 200 / 40 << endl;return 0;
}题目二:脉冲强度之和
题目链接:脉冲强度之和
【题目描述】

【算法原理】
数学 + 枚举
拿到这道题目之后,我们很容易想到枚举,但是如果暴力枚举的话是很麻烦的。我们根据条件1.:10个连续的正整数我们可以通过等差数列来求和:

因此,我们仅需要从小到大枚举 k,枚举出一个数就判断它的每一位是否相等即可。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;bool check(int x)
{int tmp = x % 10;while(x){if(tmp != x % 10) return false;x /= 10;}return true;
}int main()
{int ret = 0;for(int k = 1; ; k++){int p = 10 * k + 45;if(p > 20255202) break;if(check(p)) ret += p;}cout << ret << endl;return 0;
}题目三:25之和
题目链接:25之和
【题目描述】
【算法原理】
数学 模拟
送分题:一层 for 循环直接求和,或者数学等差数列求和都可以。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{int n, sum = 0; cin >> n;for(int i = 0; i < 25; i++)sum += n + i;cout << sum << endl;return 0;
}题目四:旗帜
题目链接:旗帜
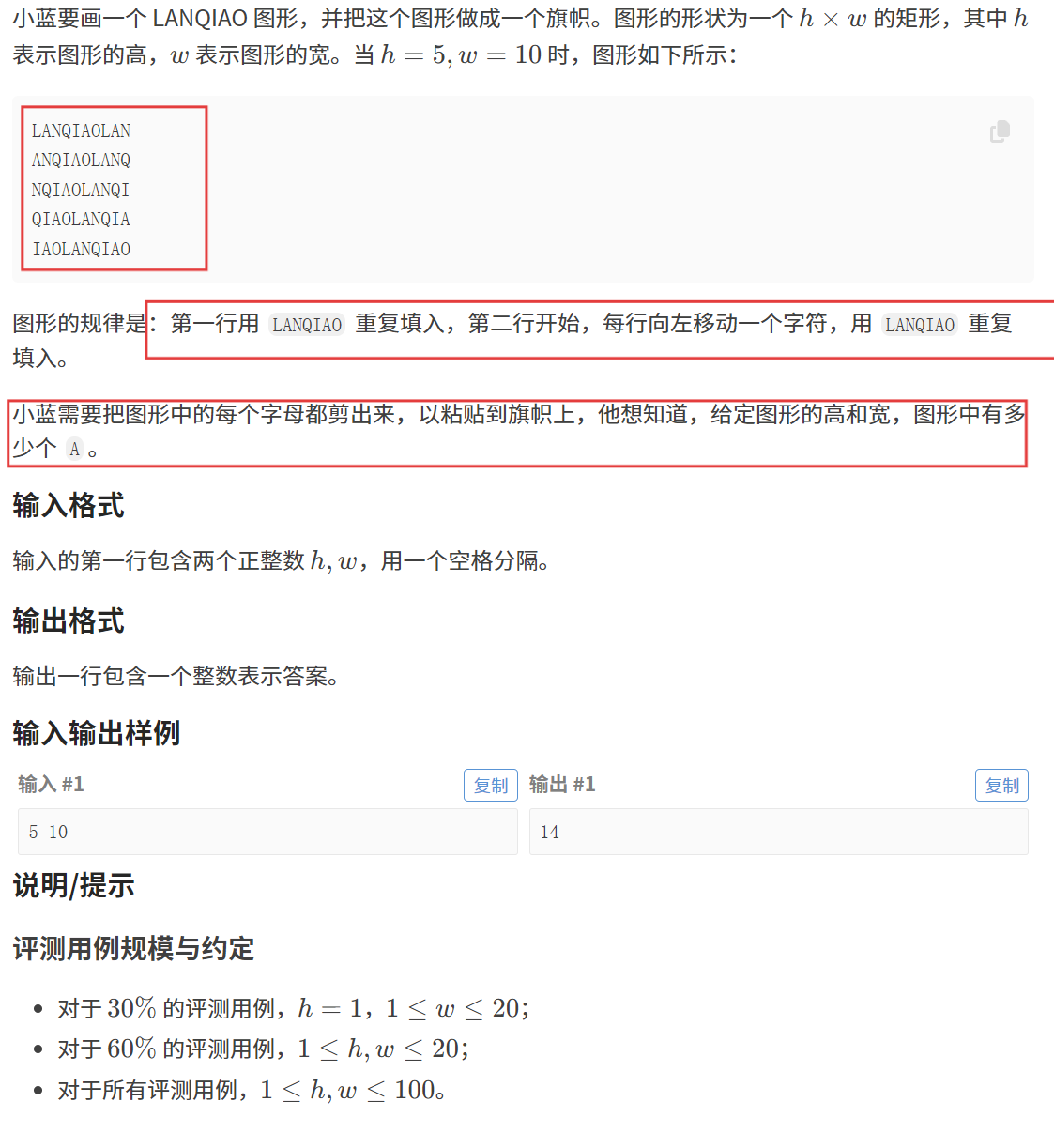
【题目描述】
【算法原理】
暴力模拟,找规律 + 周期
解法一:暴力模拟:
这道题数据范围较小,我们完全可以创建一个string,push_back 200个 "LANQIAO",再结合题意将二维字符数组填满,最后遍历一遍二维数组直接统计结果即可。
解法二:找规律:
我们手写几行尝试去找一下规律:

不难发现,(i + j) % 7 == 1 和 (i + j) % 7 == 5 的位置都是对应 'A' 字符的位置,直接统计即可。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{int n, m; cin >> n >> m;int ret = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)if((i + j) % 7 == 1 || (i + j) % 7 == 5)ret++;cout << ret << endl;return 0;
}题目五:消消乐
题目链接:消消乐
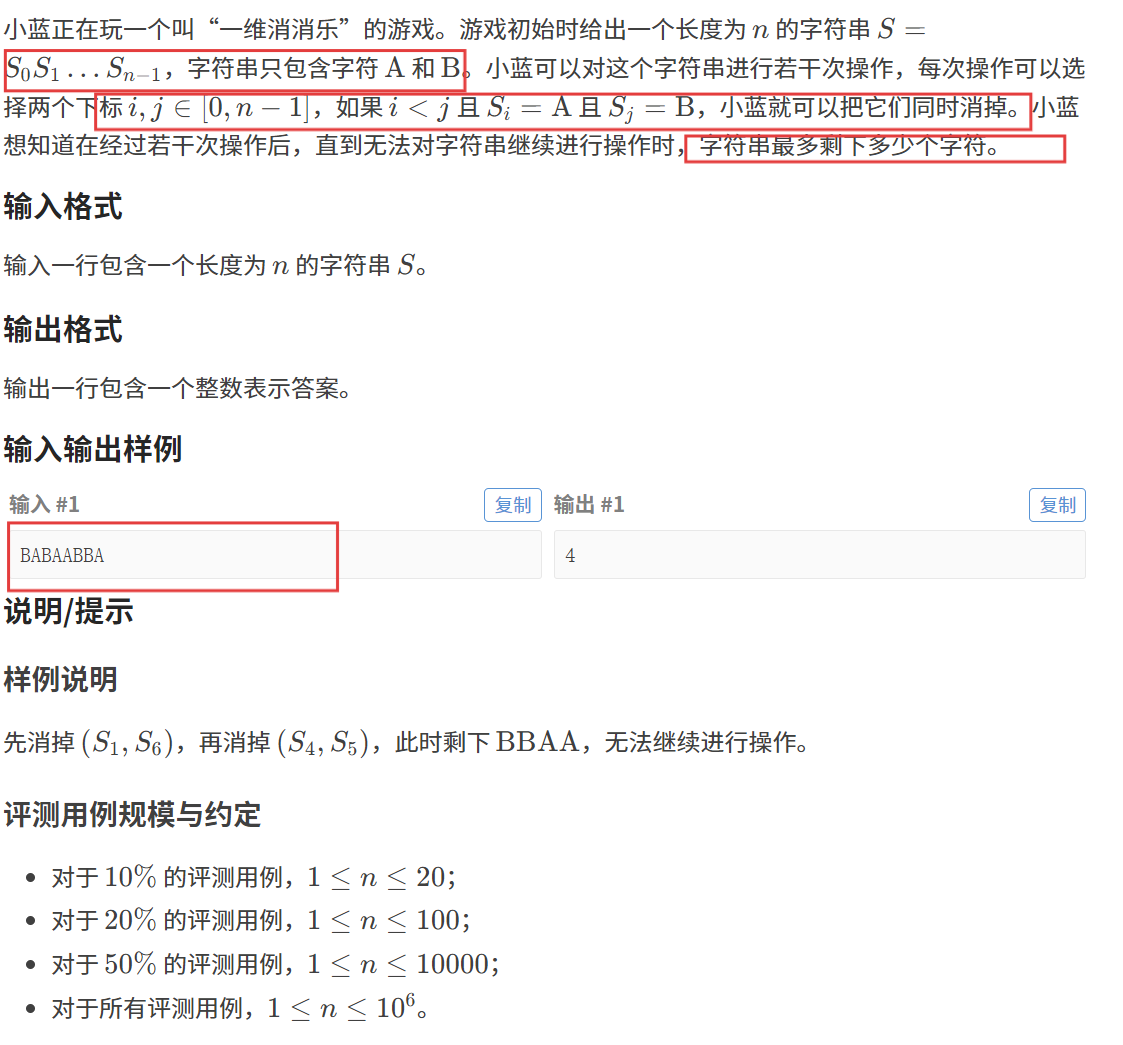
【题目描述】
【算法原理】
贪心 + 双指针
我们要做的是,让字符串中剩下的字符尽可能的多,如何做到呢???
对于左边的 'A' 可以消去右边的 'B',直到左边只剩下 'B',右边只剩下 'A' 时,就结束了,我们要保留下尽可能多的字符,因此,我们就要尽量多保留左边的 'B' 和 右边的 'A'。

贪心:对于左边的 'A' 尽量让它去消去最右边的 'B'。(贪心策略显然是正确的,不必证明)
那么,我们使用一头一尾双指针就可以解决这个问题。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string s; cin >> s;int n = s.size();int l = 0, r = n - 1;while(l < r){while(l < r && s[l] == 'B') l++; // 尽量保留左边的 Bwhile(l < r && s[r] == 'A') r--; // 尽量保留右边的 Aif(l < r){n -= 2;l++;r--;}}cout << n << endl;return 0;
}题目六:树上寻宝
题目链接:树上寻宝
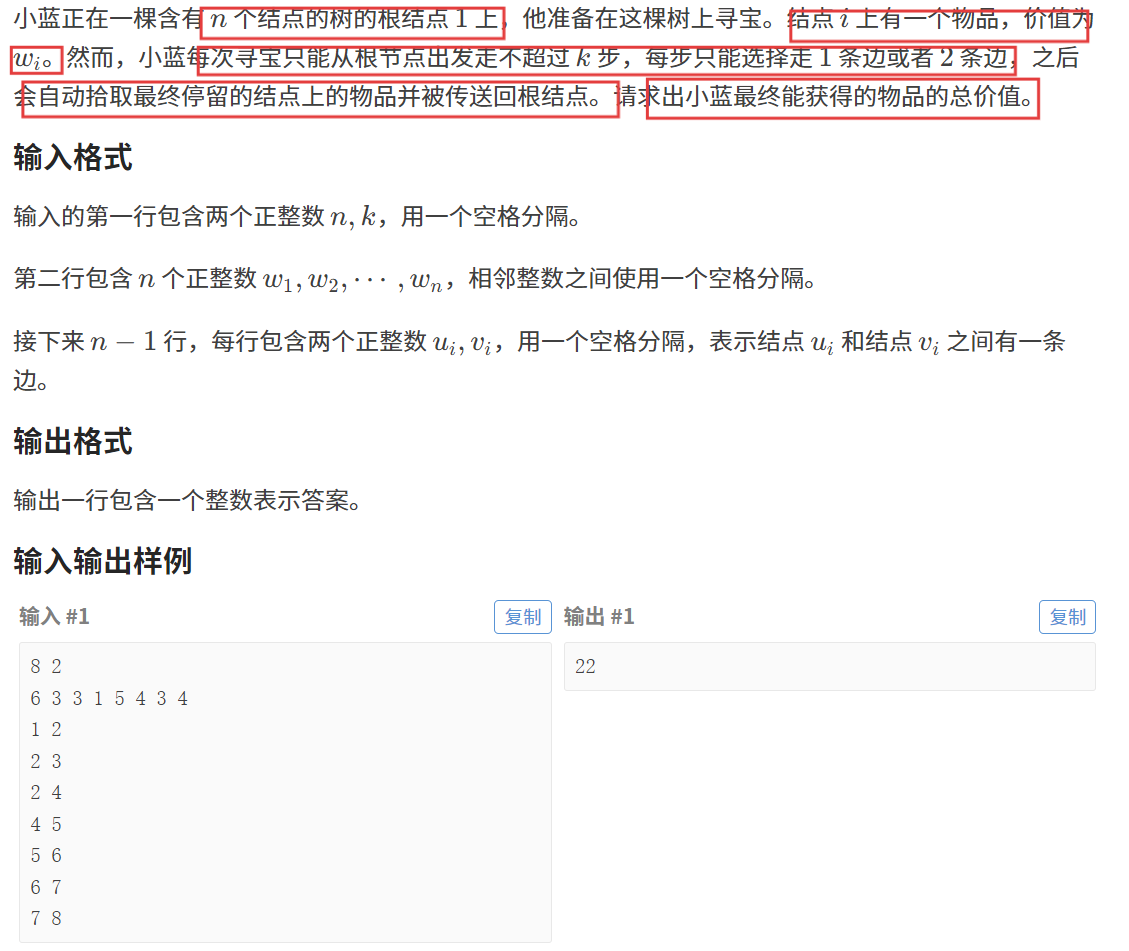
【题目描述】

【算法原理】
树的遍历 dfs / bfs
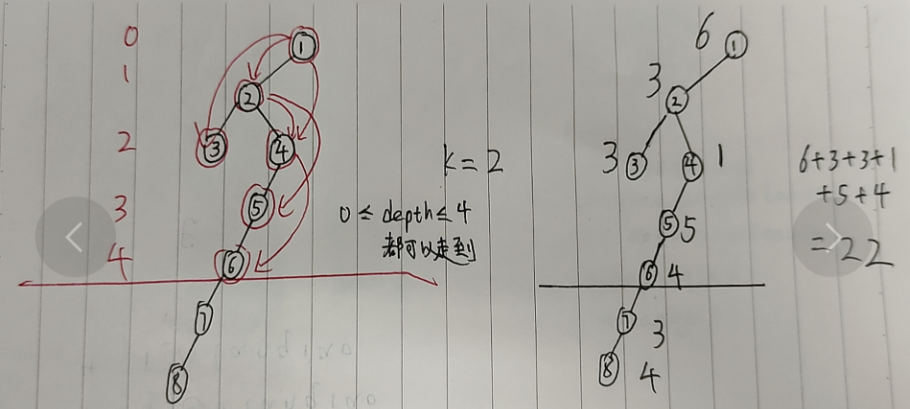
简单来说本题就求是树上所有深度不超过 2*k 的点的点权之和。
使用 dfs 或者 bfs (控制好深度)就可以解决。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;int n, k;
LL w[N];
vector<int> edges[N];
bool st[N]; // 标记哪些点已经遍历过
LL sum;void dfs(int x, int dep)
{sum += w[x];st[x] = true;if(dep == k) return;for(auto y : edges[x]){if(st[y]) continue;dfs(y, dep + 1);}
}int main()
{cin >> n >> k; k *= 2;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> w[i];for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){int a, b; cin >> a >> b;edges[a].push_back(b);edges[b].push_back(a);}dfs(1, 0);cout << sum << endl;return 0;
}题目七:基因配对
题目链接:基因配对
【题目描述】
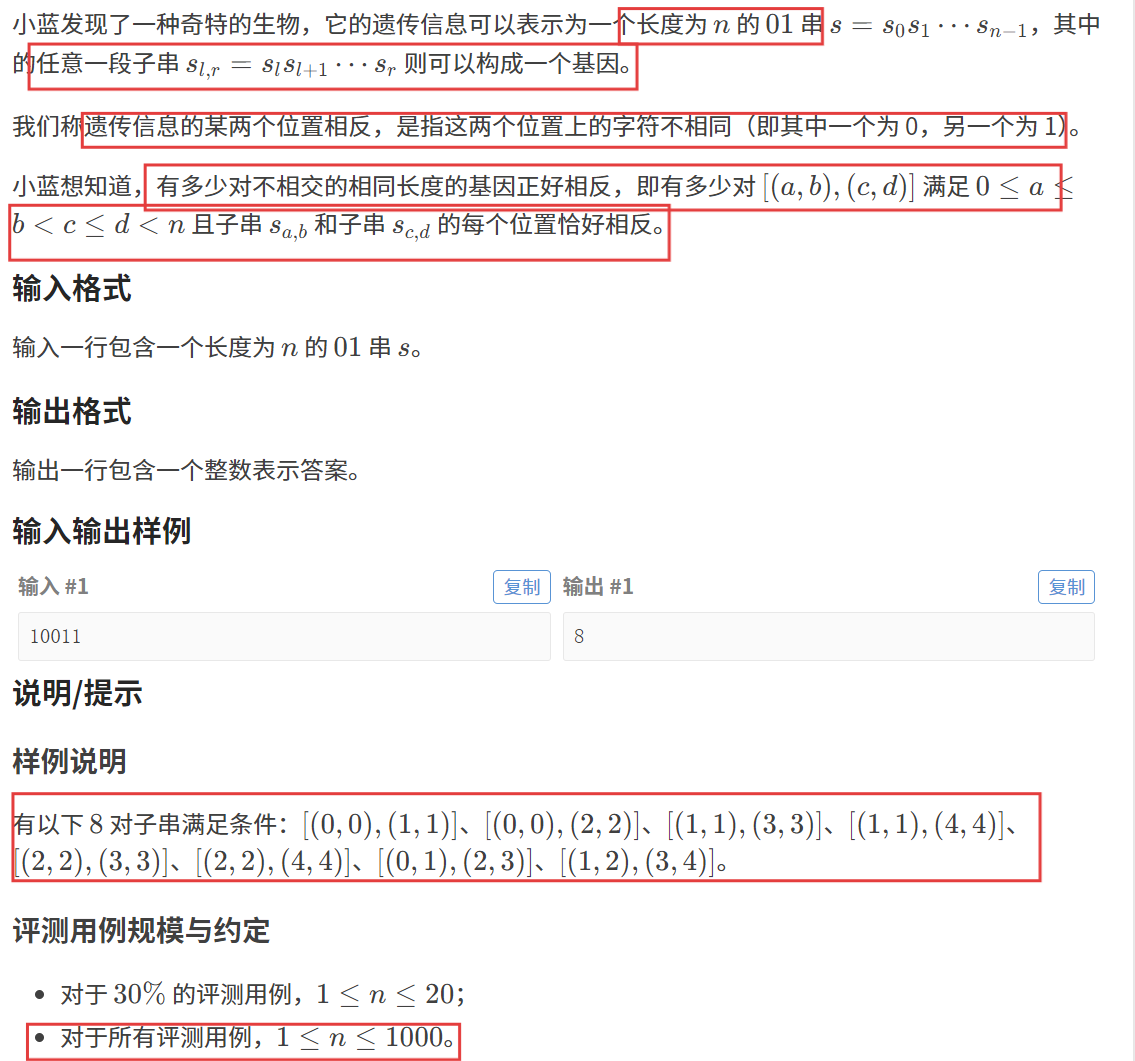
【算法原理】
动态规划(预处理)
看到数据范围比较小,我们可以先想一下暴力解法:
解法一:暴力解法:
1. 两层 for 循环枚举两个端点 i,j;
2. 然后从 i,j 出发,找出以 i,j 为起点的最长匹配的长度 len,那么 len 就是以 i,j 为起点时满足条件的基因对的数量。(len 可以,len - 1、len - 2、len - 3……都可以)
但是,这样暴力枚举的话,时间复杂度为 O(n^3),是会超时的。我们要另想办法去优化暴力解法。
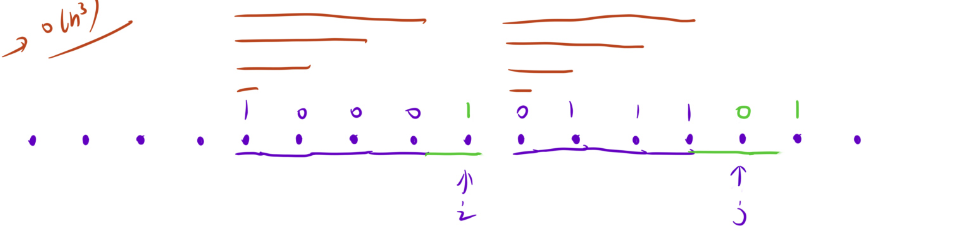
解法二:使用动态规划做预处理,优化暴力枚举
我们可以预处理出以 i,j 位置为结尾的最长的正好相反的基因的长度。
其实向后预处理也是可以的,但是我们习惯从前往后遍历~~~
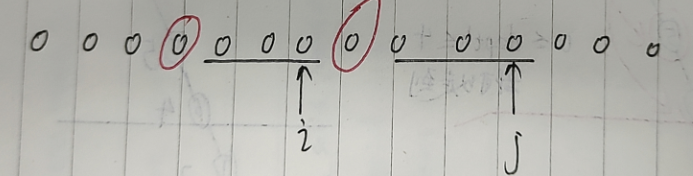
1. 状态表示:
f[i][j]:表示以 i,j 位置为起点,向前扩展时,所能匹配的最长的长度。
2. 状态转移方程:
如果 a[i] == a[j],f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;否则 f[i][j] = 0;
3. 初始化:
全0,f[0][0] = 0;
4. 填表顺序:
从上到下每一行,每一行从左往右;
预处理之后,我们就可以遍历一遍 f 表,表中有值的话就累加到结果中。
细节:有可能出现基因相交的情况,这样的话,就取 min(f[i][j],j - i)累加到结果中。

【代码实现】
#include <iostream>using namespace std;const int N = 1010;int n;
int f[N][N];int main()
{string s; cin >> s;n = s.size();s = ' ' + s;// 预处理for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)if(s[i] != s[j])f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;// 统计结果int ret = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)ret += min(j - i, f[i][j]); // 不能出现区间重叠的情况cout << ret << endl;return 0;
}题目八:栈与乘积
题目链接:栈与乘积
【题目描述】
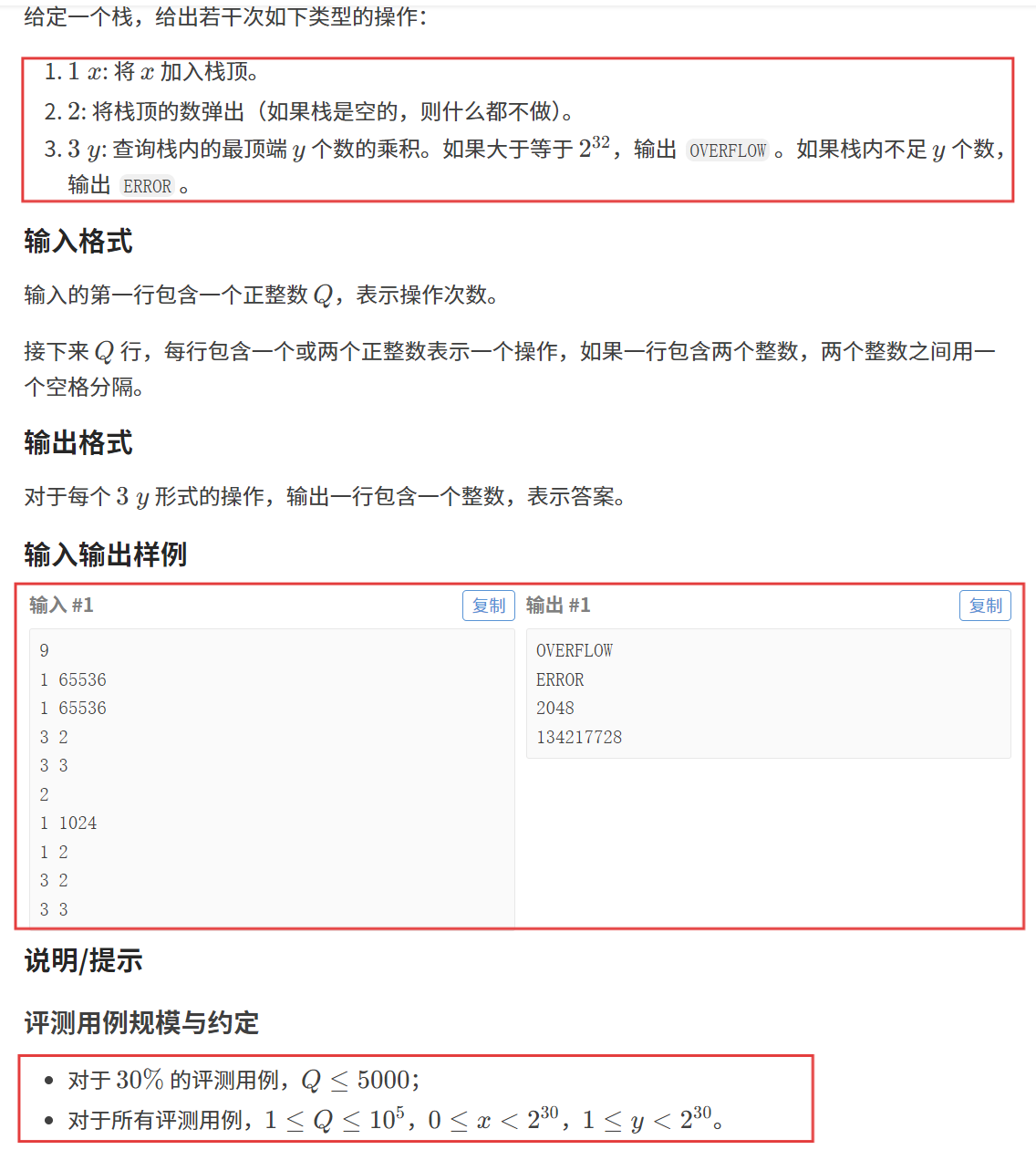
【算法原理】
线段树 / 栈 + 模拟 + 分类讨论
这道题目如果我们使用暴力模拟的话,时间复杂度为 O(Q*Q),超时。
解法一:线段树(模板)
对线段树敏感的同学,读完这道题目之后,肯定是可以想到线段树的。
我们可以用线段树来维护区间乘积的信息:
1. 进栈操作:线段树中的单点修改;
2. 出栈操作:仅需要让有效元素 -1 即可;
3. 查询操作:区间查询。[n - y + 1,n];
注意:区间合并的时候,一定要注意,乘积有可能会溢出。
如果 mul > 2^32 的话,我们就标记一下,最后输出 overflow 就可以了。

代码实现也很简单,就是一个线段树的模板。
解法二:栈 + 模拟 + 分类讨论

【代码实现】
解法一:线段树
#include <iostream>using namespace std;typedef unsigned long long LL;
#define lc p << 1
#define rc p << 1 | 1
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const LL M = (1ull << 32);struct node
{int l, r;LL mul;
}tr[N << 2];
int top;void pushup(int p)
{LL a = tr[lc].mul, b = tr[rc].mul;// 分情况讨论:if(a == 0 || a == 1 || b == 0 || b == 1) tr[p].mul = a * b; // 如果是特殊数字 0/1else if(a == M || b == M) tr[p].mul = M; // 如果有个区间已经无穷大else if(a * b >= M) tr[p].mul = M; // 相乘之后已经无穷大else tr[p].mul = a * b;
}void build(int p, int l, int r)
{tr[p] = {l, r, 0};if(l == r) return;int mid = (l + r) >> 1;build(lc, l, mid); build(rc, mid + 1, r);pushup(p);
}void modify(int p, int x, LL k)
{int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;if(l == x && x == r) {tr[p].mul = k;return;}int mid = (l + r) >> 1;if(x <= mid) modify(lc, x, k);else modify(rc, x, k);pushup(p);
}LL query(int p, int x, int y)
{int l = tr[p].l, r = tr[p].r;if(x <= l && r <= y) return tr[p].mul;int mid = (l + r) >> 1;LL L = 1, R = 1;if(x <= mid) L = query(lc, x, y);if(y > mid) R = query(rc, x, y);// 分情况讨论合并区间:if(L == 0 || L == 1 || R == 0 || R == 1) return L * R;else if(L == M || R == M) return M;else if(L * R >= M) return M;else return L * R;
}int main()
{build(1, 1, 1e5);int Q; cin >> Q;while(Q--){LL op, x; cin >> op;if(op == 1){cin >> x;top++;modify(1, top, x);}else if(op == 2){if(top) top--;}else if(op == 3){cin >> x;if(top < x) cout << "ERROR" << endl;else{LL ret = query(1, top - x + 1, top);if(ret == M) cout << "OVERFLOW" << endl;else cout << ret << endl;}}}return 0;
}解法二:栈 + 模拟 + 分类讨论
#include <iostream>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const LL INF = (1ull << 32);LL st0[N], top0;
struct node
{LL x, id;
}st[N];
int top;
int n; // 有多少个有效元素int main()
{int Q; cin >> Q;while(Q--){int op, x, y;cin >> op;if(op == 1) // 进栈{cin >> x;n++;if(x == 1) continue;else if(x == 0) st0[++top0] = n;else st[++top] = {x, n};}else if(op == 2) // 出栈{if(n == 0) continue; // 栈如果为空,什么也不做if(st0[top0] == n) top0--;else if(st[top].id == n) top--;n--;}else // 查询{cin >> y;int down = n - y + 1; // 查询区间 [down, n]if(y > n) cout << "ERROR" << endl;else if(top0 && down <= st0[top0]) cout << 0 << endl;else {LL ret = 1;for(int i = top; i >= 1 && st[i].id >= down; i--){ret *= st[i].x;if(ret >= INF) break;}if(ret >= INF) cout << "OVERFLOW" << endl;else cout << ret << endl;}}}return 0;
}好的,今天的分享就到这里了,希望对大家有所帮助~~~
创作不易,望多多支持~~~
