sk04.【scikit-learn基础】--『监督学习』之 线性回归
线性回归(Linear Regression)是机器学习中最基础且广泛应用的算法之一。
线性回归 (Linear Regression) 是一种用于预测连续值的最基本的机器学习算法,它假设目标变量 y 和特征变量 x 之间存在线性关系,并试图找到一条最佳拟合直线来描述这种关系。
其中:
y是预测值x是特征变量w是权重 (斜率)b是偏置 (截距)
线性回归的目标是找到最佳的 w 和 b,使得预测值 y 与真实值之间的误差最小。常用的误差函数是均方误差 (MSE):
其中:
是实际值。
是预测值。
- n 是数据点的数量。
我们的目标是通过调整 w 和 b ,使得 MSE 最小化。
如何求解线性回归?
1、最小二乘法
最小二乘法是一种常用的求解线性回归的方法,它通过求解以下方程来找到最佳的 ( w ) 和 ( b )。
最小二乘法的目标是最小化残差平方和(RSS),其公式为:
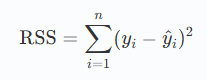
其中:
计算得到。
通过最小化 RSS,可以得到以下正规方程:
矩阵形式
将正规方程写成矩阵形式:
求解方法
通过求解上述矩阵方程,可以得到最佳的 w 和 b:
2、梯度下降法
梯度下降法的目标是最小化损失函数 J(w,b)。对于线性回归问题,通常使用均方误差(MSE)作为损失函数:
其中:
m是样本数量。
是预测值,由线性回归模型
计算得到。
梯度是损失函数对参数的偏导数,表示损失函数在参数空间中的变化方向。对于线性回归,梯度计算如下:
参数更新规则
梯度下降法通过以下规则更新参数 w 和 b:
其中:
α是学习率(learning rate),控制每次更新的步长。
梯度下降法的步骤
- 初始化参数:初始化
w和b的值(通常设为 0 或随机值)。 - 计算损失函数:计算当前参数下的损失函数值
- 计算梯度:计算损失函数对
w和b的偏导数。 - 更新参数:根据梯度更新
w和b。 - 重复迭代:重复步骤 2 到 4,直到损失函数收敛或达到最大迭代次数。
使用 Python 实现线性回归
下面我们通过一个简单的例子来演示如何使用 Python 实现线性回归。
# 1、导入必要的库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 2、生成模拟数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 生成一些随机数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
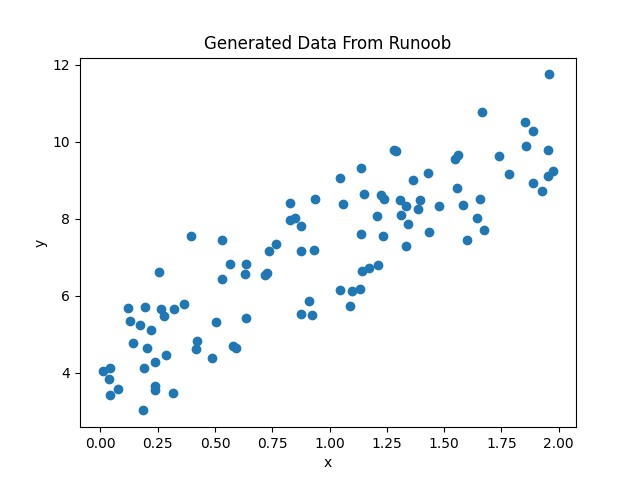
y = 4 + 3 * x + np.random.randn(100, 1)# 可视化数据
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Generated Data From Runoob')
plt.show()显示如下所示:
# 3、使用 Scikit-learn 进行线性回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 生成一些随机数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * x + np.random.randn(100, 1)# 创建线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()# 拟合模型
model.fit(x, y)# 输出模型的参数
print(f"斜率 (w): {model.coef_[0][0]}")
print(f"截距 (b): {model.intercept_[0]}")# 预测
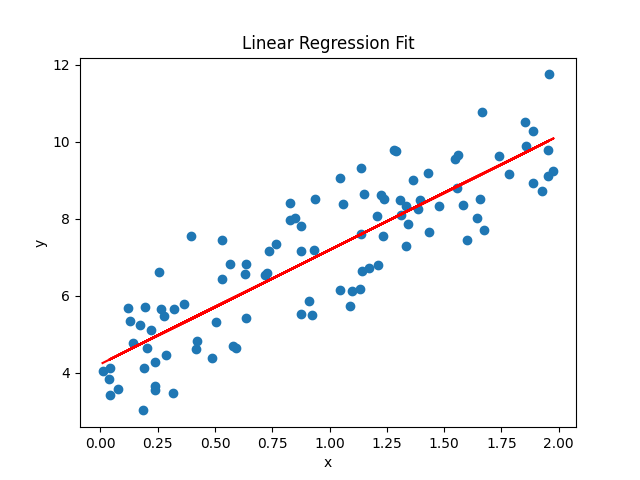
y_pred = model.predict(x)# 可视化拟合结果
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, y_pred, color='red')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Linear Regression Fit')
plt.show()输出结果:
斜率 (w): 2.968467510701019
截距 (b): 4.222151077447231显示如下所示:
我们可以使用 score() 方法来评估模型性能,返回 R^2 值。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 生成一些随机数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * x + np.random.randn(100, 1)# 创建线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()# 拟合模型
model.fit(x, y)
# 计算模型得分
score = model.score(x, y)
print("模型得分:", score)输出结果为:
模型得分: 0.74696299255047554、手动实现梯度下降法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression# 生成一些随机数据
np.random.seed(0)
x = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * x + np.random.randn(100, 1)# 初始化参数
w = 0
b = 0
learning_rate = 0.1
n_iterations = 1000# 梯度下降
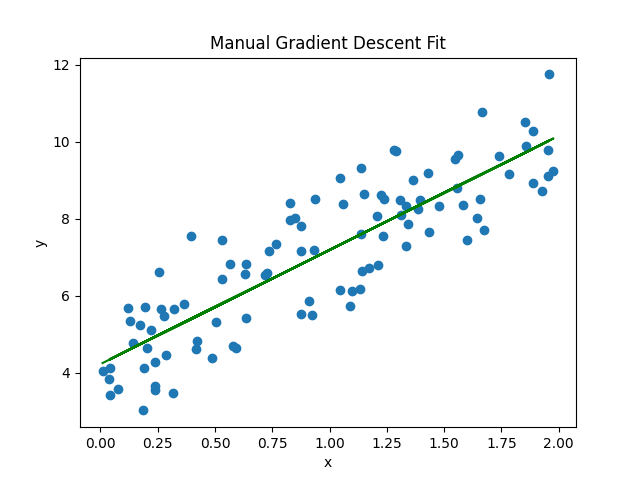
for i in range(n_iterations):y_pred = w * x + bdw = -(2/len(x)) * np.sum(x * (y - y_pred))db = -(2/len(x)) * np.sum(y - y_pred)w = w - learning_rate * dwb = b - learning_rate * db# 输出最终参数
print(f"手动实现的斜率 (w): {w}")
print(f"手动实现的截距 (b): {b}")# 可视化手动实现的拟合结果
y_pred_manual = w * x + b
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, y_pred_manual, color='green')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Manual Gradient Descent Fit')
plt.show()输出结果:
手动实现的斜率 (w): 2.968467510701028
手动实现的截距 (b): 4.222151077447219显示如下所示: