代码随想录算法训练营第十一天--二叉树2 || 226.翻转二叉树 / 101.对称二叉树 / 104.二叉树的最大深度 / 111.二叉树的最小深度
代码随想录算法训练营第十一天--二叉树2 || 226.翻转二叉树 / 101.对称二叉树 / 104.二叉树的最大深度 / 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 226.翻转二叉树(优先掌握递归)
- 解题思路
- 递归法
- 迭代法 -- 深度优先遍历
- 统一迭代法
- 层序遍历 -- 广度优先搜索
- 101.对称二叉树(优先掌握递归)
- 解题思路
- 递归法
- 完整代码
- 迭代法
- 练习1
- 练习2:
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 递归法
- 层序遍历--迭代法
- 练习:
- 迭代法--层序遍历
- 递归法
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 审题
- 递归法
- 迭代法--层序遍历
226.翻转二叉树(优先掌握递归)
解题思路
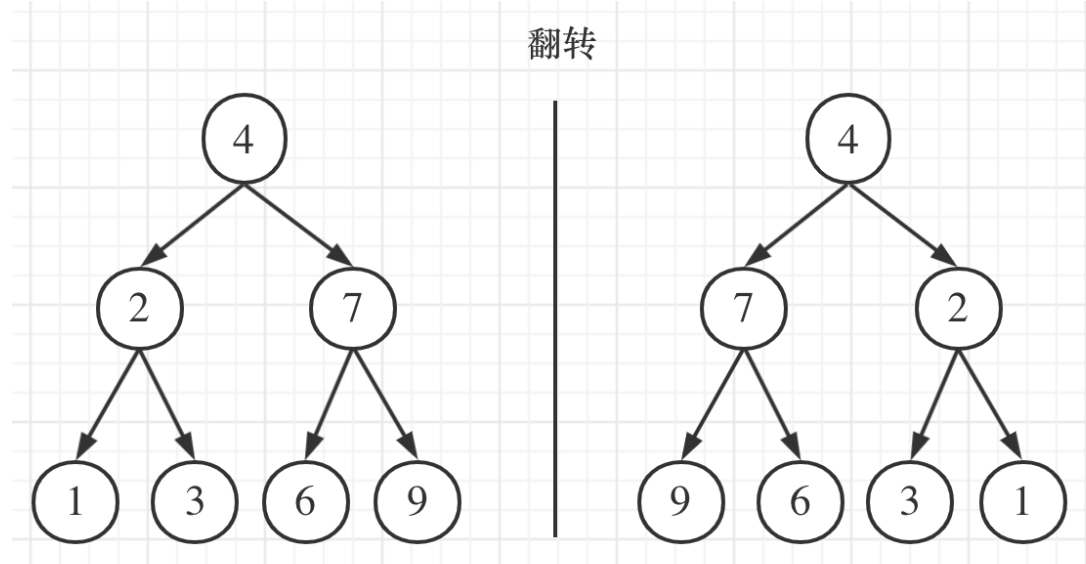
我们要翻转的不只是数字,而是指针。
递归法
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) return root;swap(root -> left, root -> right); // 中invertTree(root -> left); // 左invertTree(root -> right); // 右return root;}
};
上述代码使用的前序遍历法,当然也可以使用后序遍历法,但是**不能使用中序遍历法。
因为我们先翻转左子树,然后翻转中间节点,原来翻转过来的左子树翻转到右侧,我们又一次翻转右子树,那么把原来翻转过来的左子树又翻转回去了。而原来右子树没有进行翻转。
中序遍历代码如下:
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) return root;invertTree(root -> left); // 左swap(root -> left, root -> right); // 中invertTree(root -> left); // 右return root;}
};
迭代法 – 深度优先遍历
我们采用前序遍历
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return root;stack<TreeNode*> st;st.push(root);while (!st.empty()) {TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中st.pop();swap(node -> left, node -> right);if (node -> right) st.push(node -> right); // 右if (node -> left) st.push(node -> left); // 左}return root;}
};
统一迭代法
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;if (root != NULL) st.push(root);while (!st.empty()) {TreeNode* node = st.top();if (node != NULL) {st.pop();if (node -> right) st.push(node -> right); // 右if (node -> left) st.push(node -> left); // 左st.push(node); // 中st.push(NULL);} else {st.pop();node = st.top();st.pop();swap(node -> left, node -> right);}}return root;}
};
层序遍历 – 广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();while (size --) {TreeNode* node = que.front(); // 中que.pop();swap(node -> left, node -> right); // 节点处理if (node -> left) que.push(node -> left); // 左if (node -> right) que.push(node -> right); // 右}}return root;}
};
101.对称二叉树(优先掌握递归)
解题思路
对于要搜集左右孩子,返回到中间节点的情况,我们一般采取后序遍历,这个非常重要。
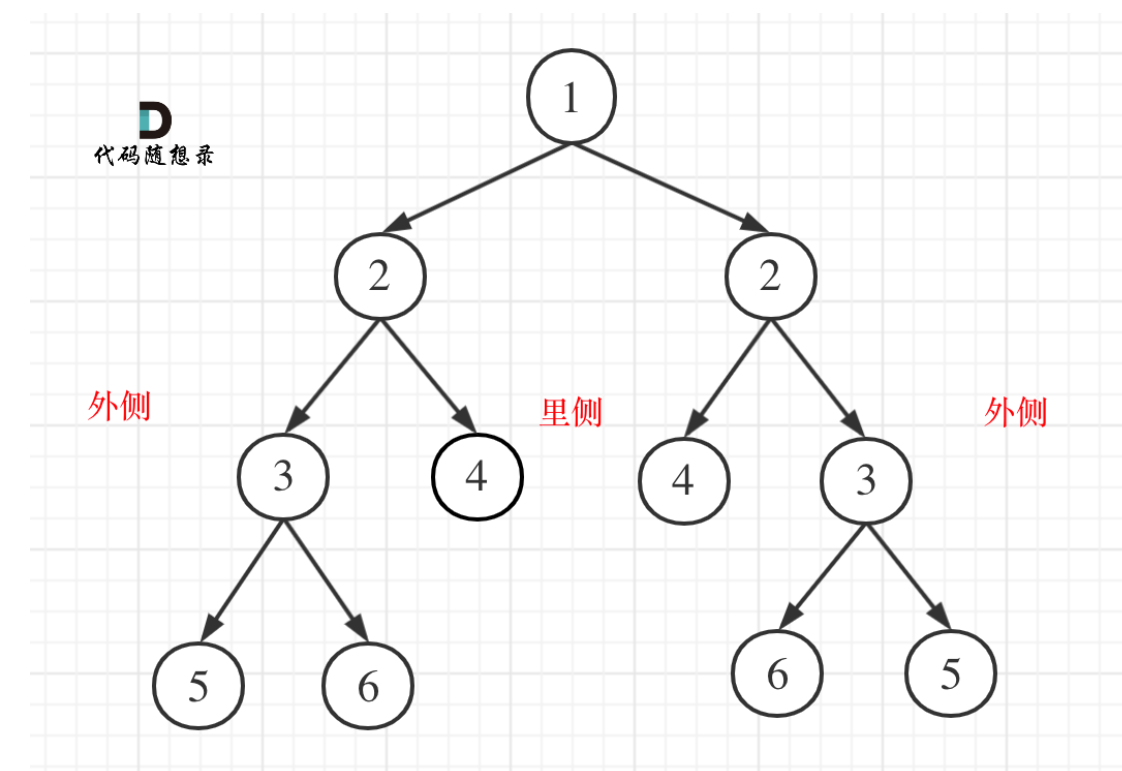
这道题的关键是要判断外侧相等,里侧相等,比较根节点的左右两棵子树能否互相翻转。
递归法
递归三部曲
1.先判断返回值和传入的参数:
返回bool类型,参数就是左右节点
2.确定终止条件:
- 左节点为空,右节点不为空,不对称,return false
- 左不为空,右为空,不对称 return false
- 左右都为空,对称,返回true
- 左右都不为空,左右值不同,return false
- 左右都不为空,左右值相同,进入单层递归
3.确定单层递归逻辑
- 比较二叉树外侧是否对称:传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子。
- 比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子。
- 如果左右都对称就返回true ,有一侧不对称就返回false 。
完整代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {// 分五种情况if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false; // 1.左空,右非空else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false; // 2.左非空,右空else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true; // 3.左空,右空else if (left -> val != right -> val) return false; // 4.左值 不等于 右值// 5.左值 = 右值bool outside = compare(left -> left, right -> right); // 左子树:左 右子树:右bool inside = compare(left -> right, right -> left); // 右 左bool issame = outside && inside; // 中 中return issame;}bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return true;return compare(root -> left, root -> right);}
};
迭代法
使用队列
class Solution {
public:bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return true;queue<TreeNode*> que;que.push(root -> left); // 将左子树头节点入队que.push(root -> right); // 将右子树头节点入队while (!que.empty()) { // 判断两个树是否相互翻转TreeNode* l = que.front(); que.pop();TreeNode* r = que.front(); que.pop();// 左右皆空,对称if (l == NULL && r == NULL) continue;// 左右一个为空 or 都不空但值不相等,不对称if (l == NULL || r == NULL || l -> val != r -> val)return false;que.push(l -> left); // 左节点左孩子que.push(r -> right); // 右节点右孩子que.push(l -> right); // 左节点右孩子que.push(r -> left); // 右节点左孩子}return true;}
};
练习1
100.相同的树
class Solution {
public:bool cmp(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if (p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;else if (p == NULL || q == NULL || p -> val != q -> val) return false;bool isl = cmp(p -> left, q -> left);bool isr = cmp(p -> right, q -> right);return isl && isr;}bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {return cmp(p, q);}
};
练习2:
572.另一棵树的子树
class Solution {
public:bool cmp(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {if (root == NULL && subRoot == NULL) return true;else if (root == NULL || subRoot == NULL || root -> val != subRoot -> val)return false;bool isl = cmp(root -> left, subRoot -> left);bool isr = cmp(root -> right, subRoot -> right);return isl && isr;}bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {if (root == NULL) return false;return cmp(root, subRoot) ||isSubtree(root -> left, subRoot) ||isSubtree(root -> right, subRoot);}
};
这道题首先要判断根节点非空,防止对空节点进行操作。
然后我们就像100.相同的树一样去比较是否相等,不相等我们就递归isSubtree函数,直到找到相等的子树。
104.二叉树的最大深度
递归法
我们要分清高度和深度的概念,对于一个二叉树,最上面的根节点的深度为1,高度就是深度的最大值,也就是说高度和深度是反转关系的。
一般使用后序遍历来求二叉树的最大高度,也就是二叉树的最大深度
public:int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0; // 终止条件,最底层的下一层高度为0int leftDepth = getDepth(node -> left); // 左int rightDepth = getDepth(node -> right); // 右int depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth); // 中return depth;}int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
代码可以精简
class Solution {
public:int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0; // 终止条件,最底层的下一层高度为0return 1 + max(getDepth(node -> left), getDepth(node -> right));}int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
层序遍历–迭代法
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();depth ++; // 记录深度while (size --) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (node -> left) que.push(node -> left);if (node -> right) que.push(node -> right);}}return ans;}
};
练习:
559.N叉树的最大深度
迭代法–层序遍历
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(Node* root) {queue<Node*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();depth ++;while (size --) {Node* node = que.front();que.pop();for (int i = 0; i < node -> children.size(); i++) {if (node -> children[i]) que.push(node -> children[i]);}}}return depth;}
};
递归法
class Solution {
public:int getDepth(Node* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int depth = 0;for (int i = 0; i < node -> children.size(); i++) {depth = max(depth, getDepth(node -> children[i]));}return depth + 1;}int maxDepth(Node* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
最后为什么要加1呢,想想之前的二叉树,是左右,然后中,中是1 + max(左,右)。这里for循环就先当于左右,最后到中需要加1。
111.二叉树的最小深度
审题
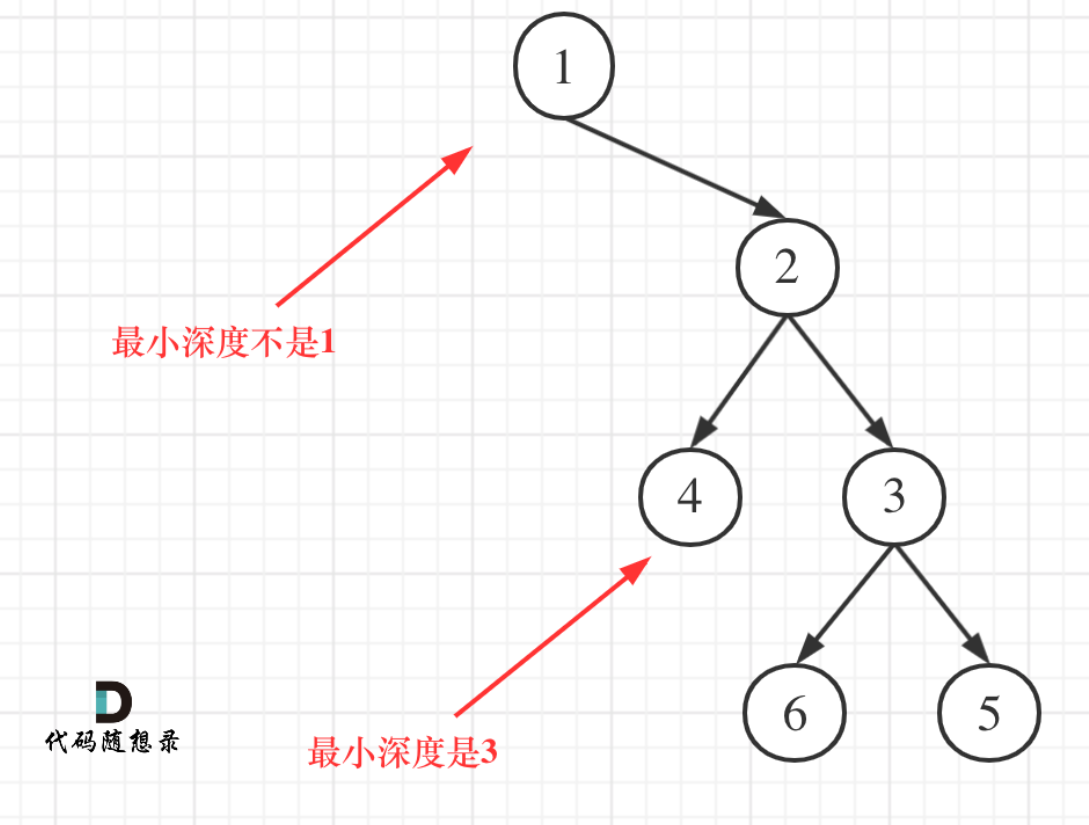
这道题的最小深度,指的是叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点,有一个节点的,不叫最小深度,必须左右两个节点都无才算。
递归法
class Solution {
public:int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {int res = 0;if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = getDepth(node -> left); // 左int right = getDepth(node -> right); // 右// 中// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点if (node -> left == NULL && node -> right != NULL) {res = 1 + right;} else if (node -> left != NULL && node -> right == NULL) {res = 1 + left;} else {res = 1 + min(left, right);}return res;}int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
迭代法–层序遍历
class Solution {
public:int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();depth ++;while (size --) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (node -> left) que.push(node -> left);if (node -> right) que.push(node -> right);if (!node -> left && !node -> right) return depth;}}return depth;}
};
注意一下depth的位置,层序遍历是从上到下遍历,当左右无节点,那就直接返回。
