人工智能深度学习——多层感知器(人工神经网络)

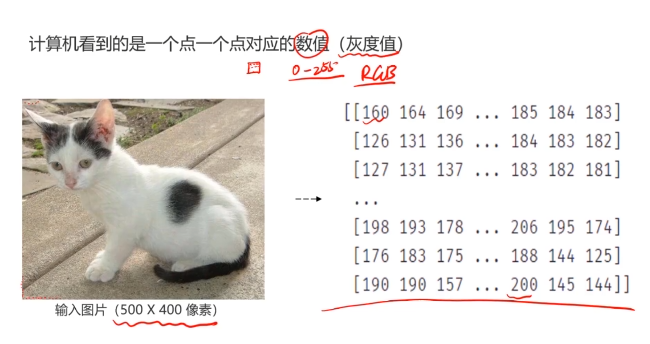
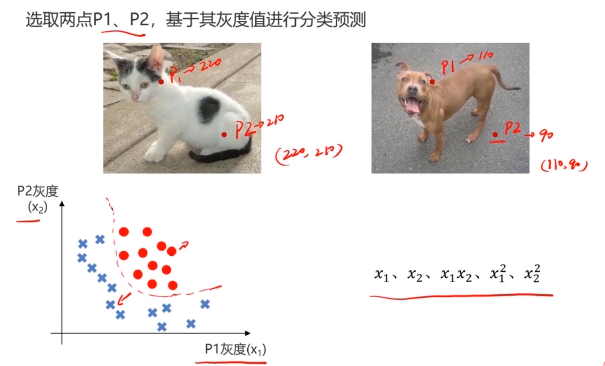
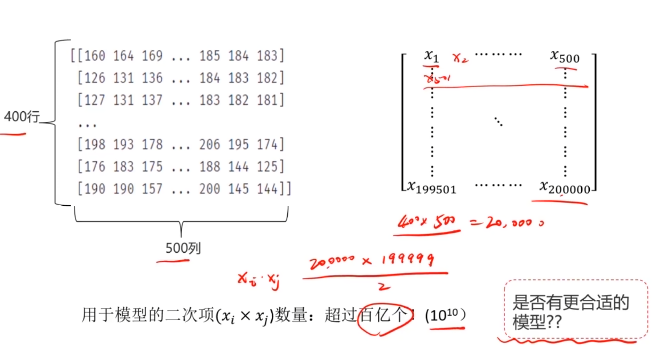
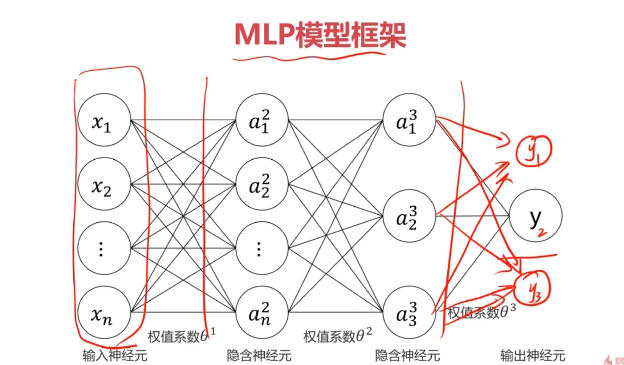
一、多层感知器(Multi-Layer Perceptron)(神经网络)(MLP)
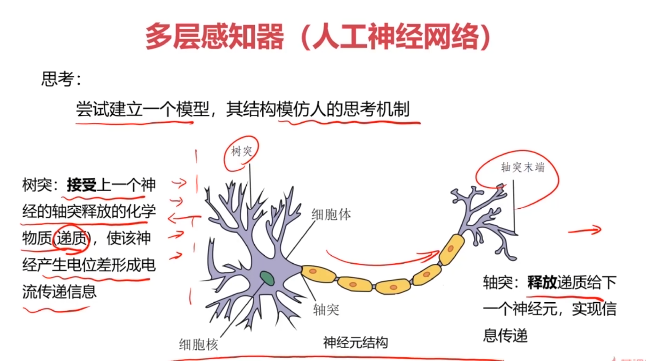
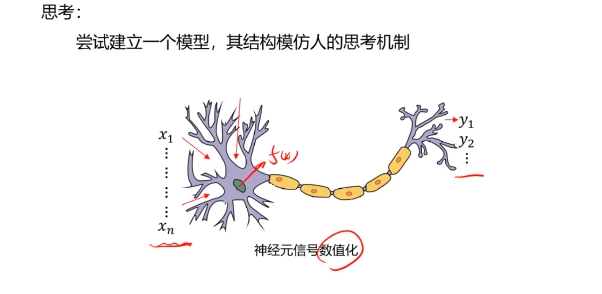
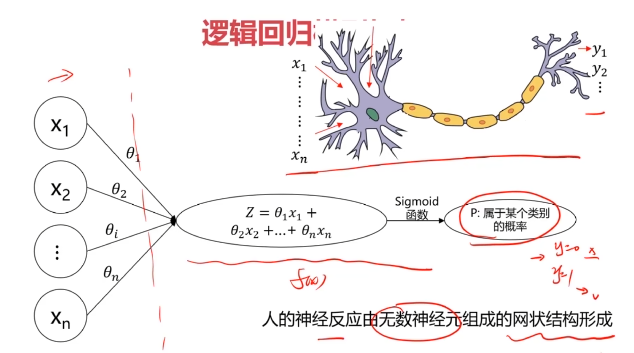
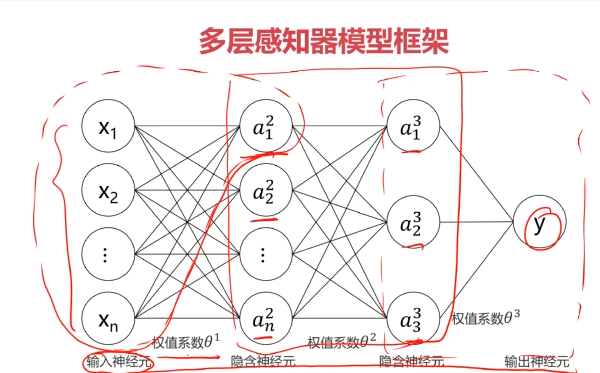
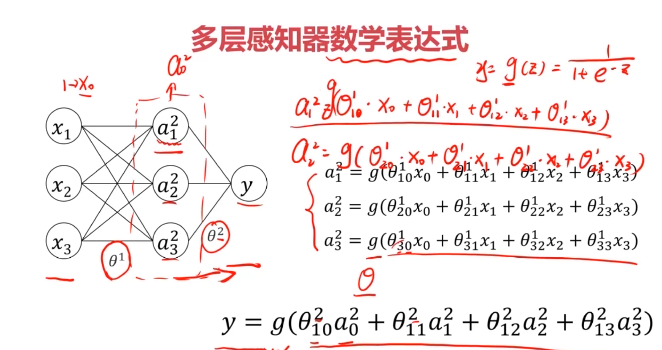
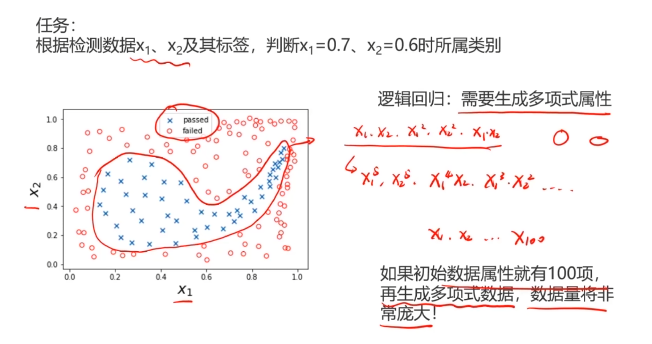
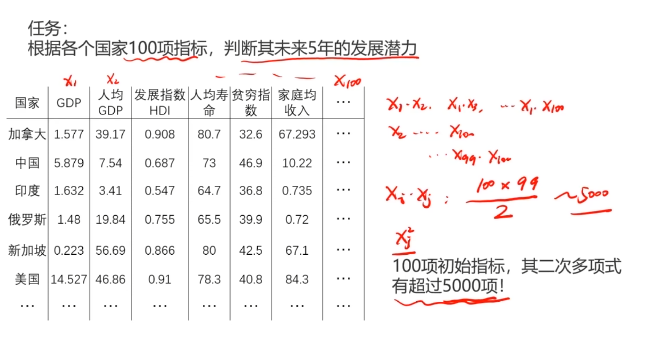
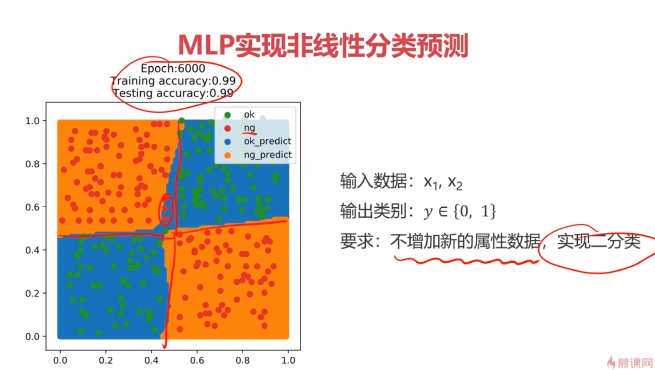
二、多层感知器(Multi-Layer Perceptron)(神经网络)(MLP)实现非线性分类
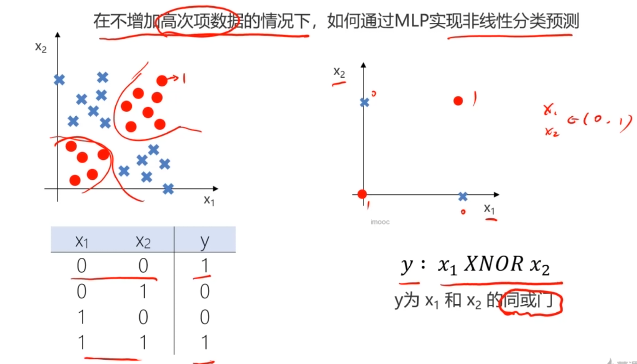
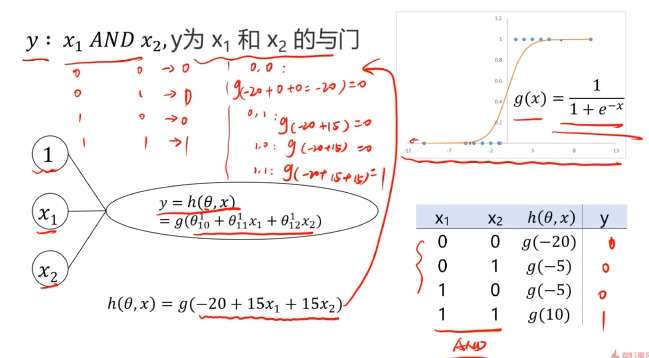
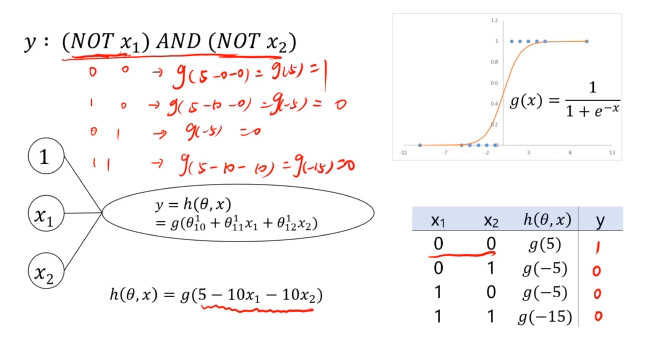
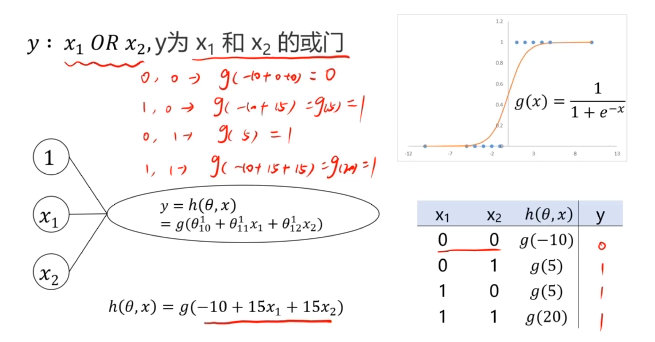
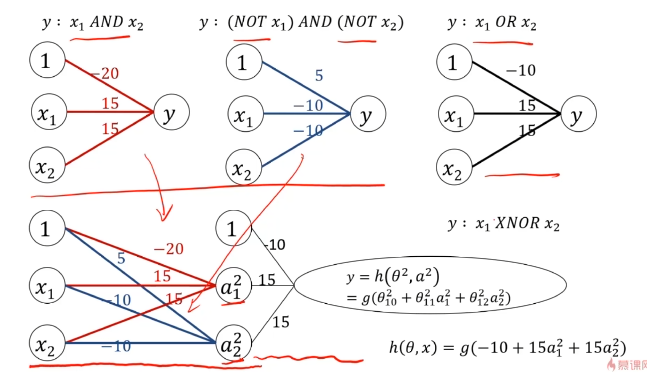
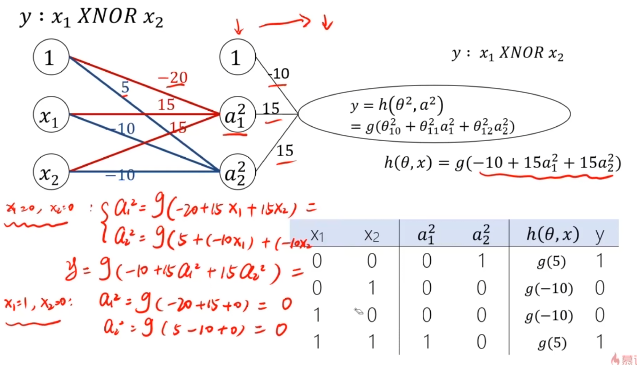
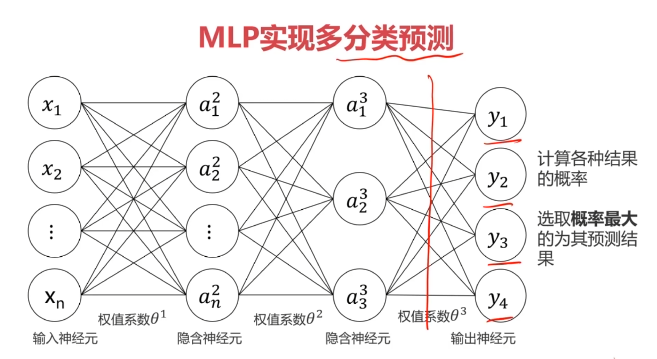
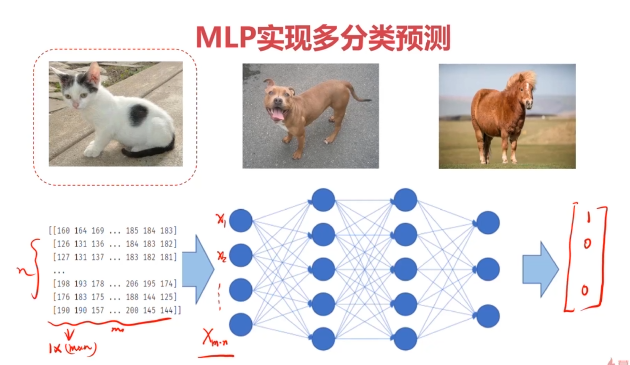
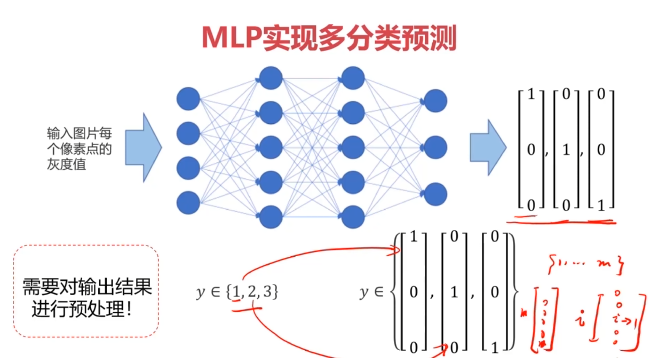
MLP用于多分类预测
三、Keras介绍与实战准备
Keras是一个用Python编写的用于神经网络开发的应用接口,调用开接囗可以实现神经网络、卷积神经网络、循环神经网络等常用深度学习算法的开发

pip install tensorflow -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
pip install keras -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
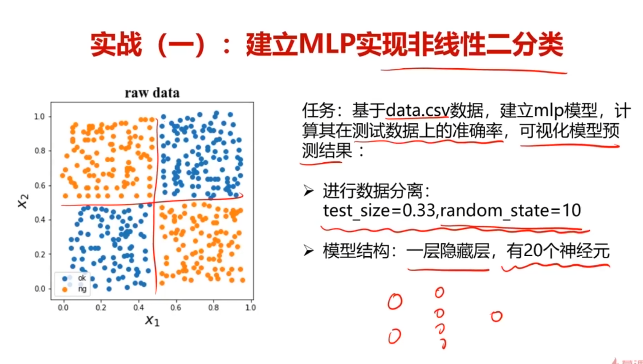
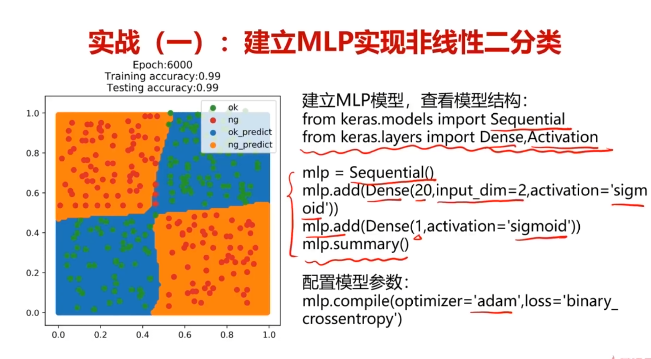




四、基于MLP_test_data.csv数据,建立mlp模型,计算其在测试数据上的准确率
#加载数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
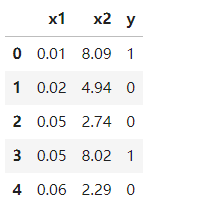
data = pd.read_csv('MLP_test_data.csv')
data.head()
#赋值x,y
x = data.drop(['y'],axis=1)
y = data.loc[:,'y']
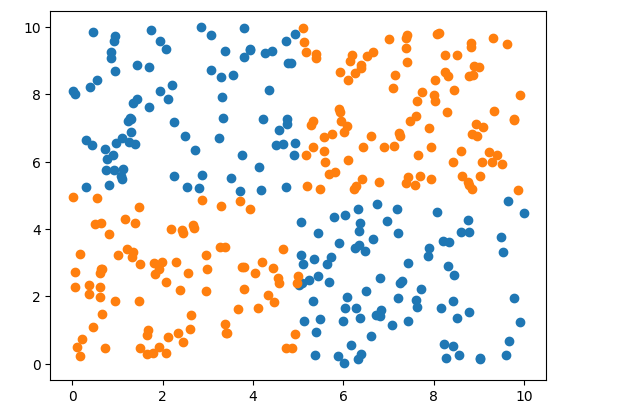
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig1 = plt.figure()
plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==1])
plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0])
plt.show()
#数据分离
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
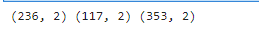
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.33,random_state=10)
print(x_train.shape,x_test.shape,x.shape)
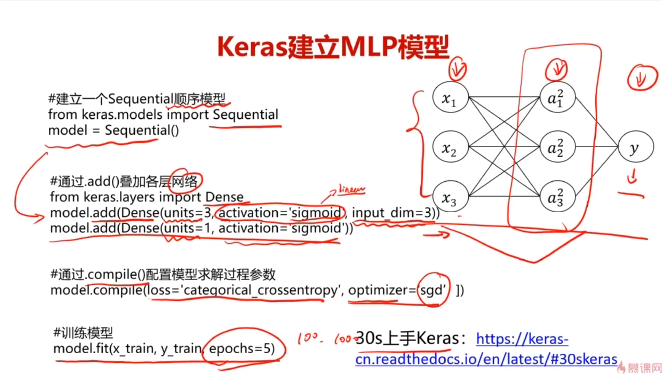
#创建一个Sequential顺序模型
from keras.models import Sequential
mlp = Sequential()#通过add()叠加各层网络
from keras.layers import Dense,Activation
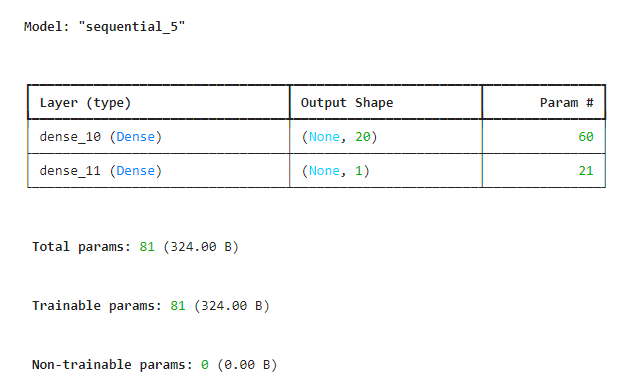
mlp.add(Dense(units=20,activation='sigmoid',input_dim=2))
mlp.add(Dense(units=1,activation='sigmoid'))
#查看模型结构
mlp.summary()
#通过compile()配置模型求解的过程参数
mlp.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='binary_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
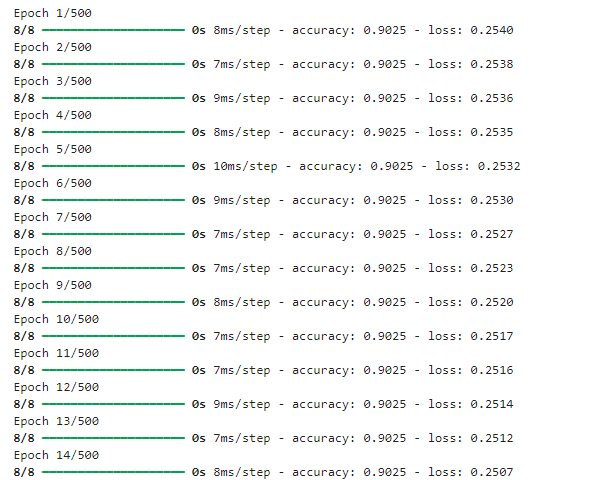
#训练模型
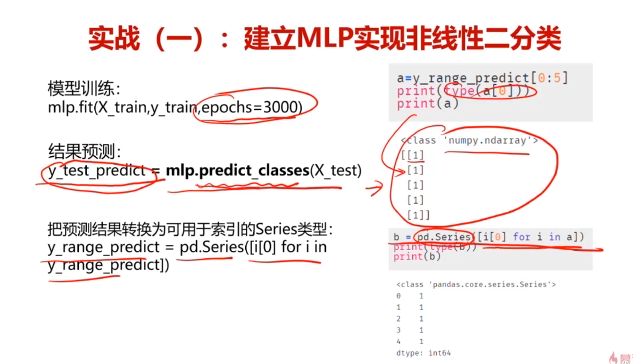
mlp.fit(x_train,y_train,epochs=500)
#计算准确率
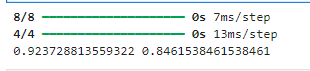
y_train_predict = mlp.predict(x_train)# 对于二分类问题(输出是0-1之间的概率)
y_train_predict = (y_train_predict > 0.5).astype("int32") # 使用0.5作为阈值from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_train = accuracy_score(y_train,y_train_predict)y_test_predict = mlp.predict(x_test)# 对于二分类问题(输出是0-1之间的概率)
y_test_predict = (y_test_predict > 0.5).astype("int32") # 使用0.5作为阈值
accuracy_test = accuracy_score(y_test,y_test_predict)
print(accuracy_train,accuracy_test)
print(type(y_train_predict))
y_train_predict_form = pd.Series(i[0] for i in y_train_predict)
print(type(y_train_predict_form),y_train_predict_form)

#可视化模型预测结果
xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0,10,0.05),np.arange(0,10,0.05))
x_range = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]
y_range_predict = mlp.predict(x_range)# 对于二分类问题(输出是0-1之间的概率)
y_range_predict = (y_range_predict > 0.5).astype("int32") # 使用0.5作为阈值
print(type(y_range_predict))y_range_predict_form = pd.Series(i[0] for i in y_range_predict)
print(type(y_range_predict_form),y_range_predict_form)
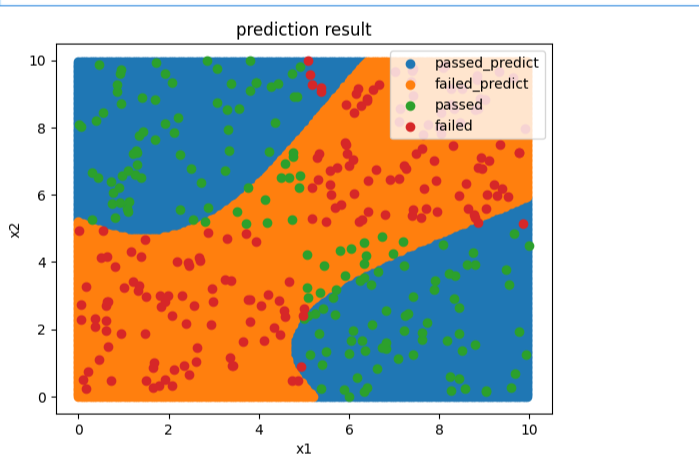
fig2 = plt.figure()passed_predict = plt.scatter(x_range[:,0][y_range_predict_form==1],x_range[:,1][y_range_predict_form==1])
failed_predict = plt.scatter(x_range[:,0][y_range_predict_form==0],x_range[:,1][y_range_predict_form==0])passed = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==1],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==1])
failed = plt.scatter(x.loc[:,'x1'][y==0],x.loc[:,'x2'][y==0])plt.title('prediction result')
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.legend((passed_predict,failed_predict,passed,failed),('passed_predict','failed_predict','passed','failed'))plt.show()
五、MLP实现图像多分类,使用mnist数据集(在keras里)
#加载数据
from keras.datasets import mnist
(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test) = mnist.load_data()

print(type(x_train),x_train.shape)

#可视化部分数据
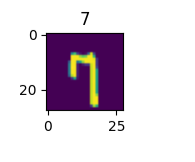
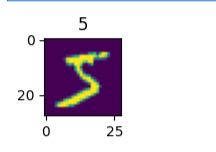
img1 = x_train[0]from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(1,1))
plt.imshow(img1)
plt.title(y_train[0])
plt.show()
img1.shape

feature_size = img1.shape[0]*img1.shape[1]
x_train_format = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],feature_size)
print(x_train_format.shape,x_train_format)x_test_format = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],feature_size)
#归一化处理
x_train_normal = x_train_format/255
x_test_normal = x_test_format/255# print(x_train_normal[0])
#转换输出结果
from keras.utils import to_categorical
y_train_format = to_categorical(y_train)
y_test_format = to_categorical(y_test)print(y_train[0],y_train_format[0])

#建立模型
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Input,Dense,Activation
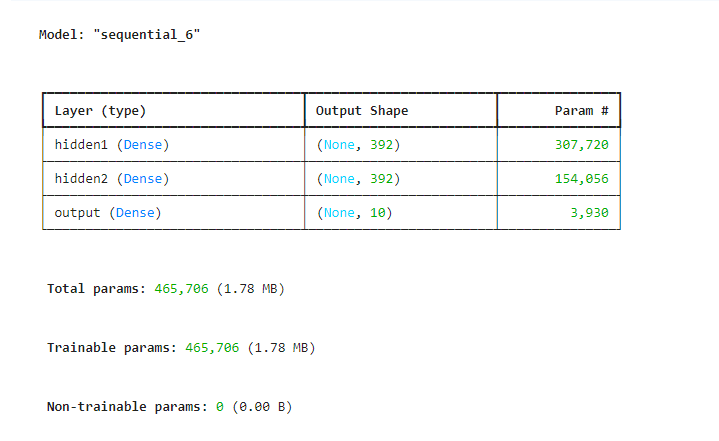
mlp = Sequential([Input(shape=(feature_size,), name='input_layer'),Dense(392, activation='sigmoid', name='hidden1'),Dense(392, activation='sigmoid', name='hidden2'),Dense(10, activation='softmax', name='output')
])mlp.summary()
#配置模型
mlp.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',optimizer='adam')
#模型训练
mlp.fit(x_train_format,y_train_format,epochs=10)

#计算训练集准确率
# 对于多分类问题(输出是概率分布)
probabilities = mlp.predict(x_train_normal)
y_train_predict = np.argmax(probabilities, axis=1) # 取概率最大的类别
print(y_train_predict)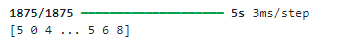
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_train = accuracy_score(y_train,y_train_predict)
print(accuracy_train)

#计算测试集准确率
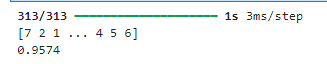
probabilities = mlp.predict(x_test_normal)
y_test_predict = np.argmax(probabilities, axis=1) # 取概率最大的类别
print(y_test_predict)accuracy_test = accuracy_score(y_test,y_test_predict)
print(accuracy_test)
#随机选取测试集图片进行验证
img2 = x_test[80]
fig2 = plt.figure(figsize=(1,1))
plt.imshow(img2)
plt.title(y_test_predict[80])
plt.show()