【数据结构】经典 Leetcode 题
经典 Leetcode 题
- 一. 顺序表
- 27. 移除元素
- 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
- 88. 合并两个有序数组
- 189. 轮转数组
- 118. 杨辉三角
- 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
- JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 二. 链表
- 203. 移除链表元素
- 206. 反转链表
- 876. 链表的中间结点
- 21. 合并两个有序链表
- 160. 相交链表
- 234. 回文链表
- 141. 环形链表
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 138. 随机链表的复制
- 面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
- 面试题 02.04. 分割链表
- 三. 栈
- 20. 有效的括号
- 155. 最小栈
- 946. 验证栈序列
- 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 225. 用队列实现栈
- 四. 队列
- 232. 用栈实现队列
- 622. 设计循环队列
- 五. 二叉树
- 965. 单值二叉树
- 100. 相同的树
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 572. 另一棵树的子树
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 226. 翻转二叉树
- 110. 平衡二叉树
- 二叉树遍历
- 六. 字符串
- 387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
- 344. 反转字符串
- 541. 反转字符串 II
- 557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
- 125. 验证回文串
- 8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
- KY264 单词识别
一. 顺序表
27. 移除元素
27. 移除元素

解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {int n = nums.size();int slow = 0, fast = 0;while (fast < n) {if (nums[fast] == val) {fast++;} else {swap(nums[slow++], nums[fast++]);}}return slow;}
};
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项

解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();int slow = 0, fast = 0;while (fast < n) {if (nums[slow] == nums[fast]) {fast++;} else {swap(nums[++slow], nums[fast++]);}}return slow + 1;}
};
88. 合并两个有序数组
88. 合并两个有序数组

解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {int cur1 = m - 1, cur2 = n - 1, i = m + n - 1;while (cur1 >= 0 && cur2 >= 0) {if (nums1[cur1] >= nums2[cur2]) {nums1[i--] = nums1[cur1--];} else {nums1[i--] = nums2[cur2--];}}while (cur2 >= 0) {nums1[i--] = nums2[cur2--];}}
};
189. 轮转数组
189. 轮转数组

class Solution {
public:void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();k %= n;reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());reverse(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + k);reverse(nums.begin() + k, nums.end());}
};
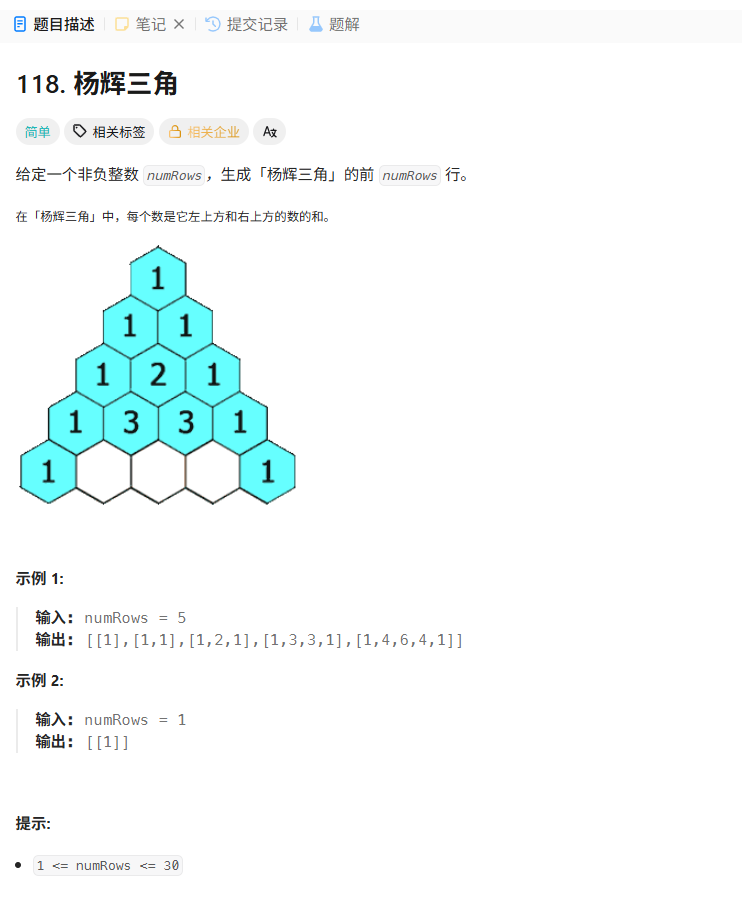
118. 杨辉三角
118. 杨辉三角
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {vector<vector<int>> ret(numRows);for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {ret[i].resize(i + 1, 1);for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {if (i >= 2) {ret[i][j] = ret[i - 1][j] + ret[i - 1][j - 1];}}}return ret;}
};
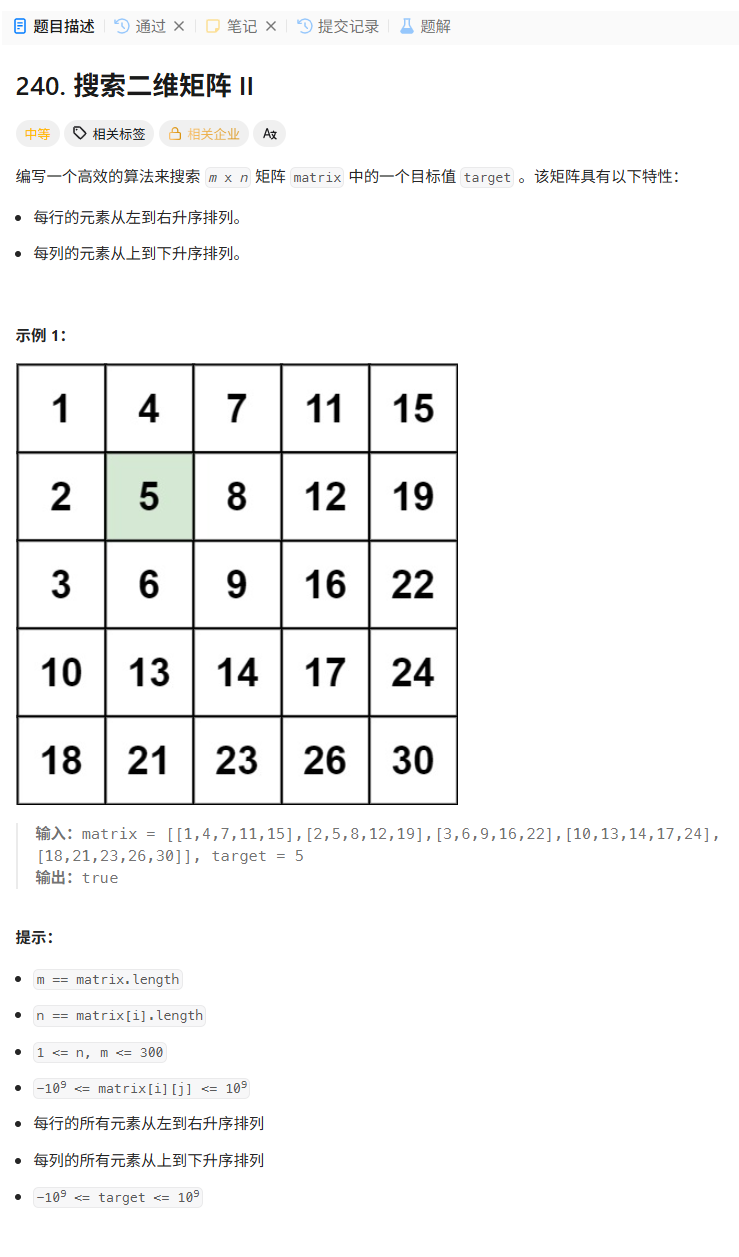
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
class Solution {
public:bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();int i = 0, j = n - 1;while (i < m && j >= 0) {if (matrix[i][j] < target) {i++;} else if (matrix[i][j] == target) {return true;} else {j--;}}return false;}
};
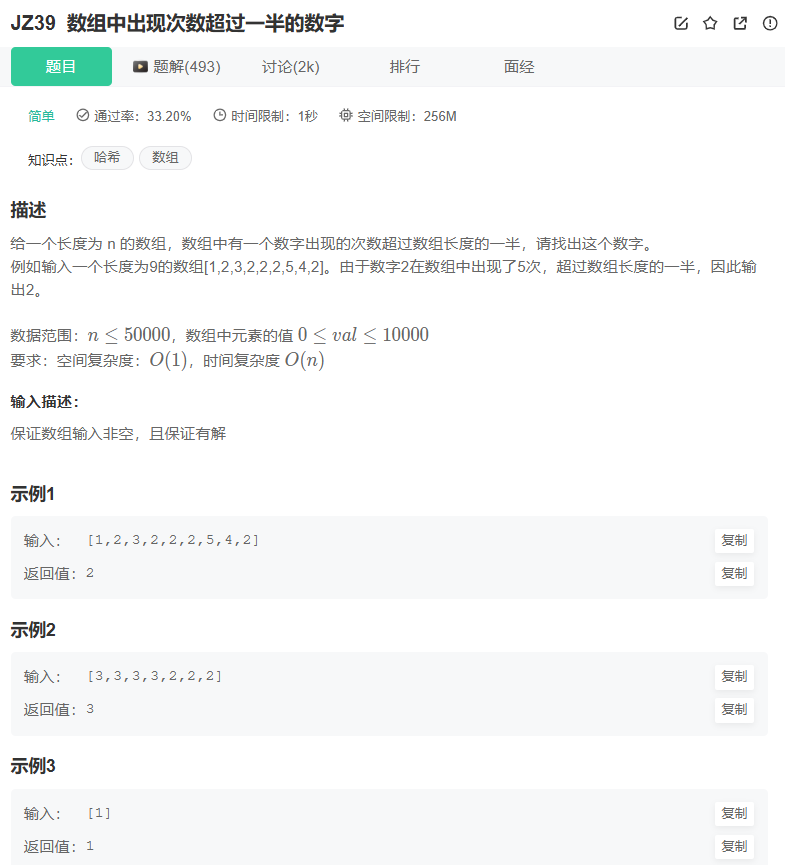
JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
解法:摩尔投票法
class Solution {
public:int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int>& numbers) {// 若存在这个数,则说明这个数出现的次数减去其余的数一定大于0int target = 0, count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) {if (count == 0) {target = numbers[i];count = 1;} else if (numbers[i] == target) {count++;} else {count--;}}// 判断这个数是否满足要求count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) {if (numbers[i] == target) {count++;}}return count > numbers.size() / 2 ? target : 0;}
};
二. 链表
203. 移除链表元素
203. 移除链表元素

解法一:迭代
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(), * tail = newHead;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur) {if (cur->val != val) {tail->next = cur;tail = tail->next;}cur = cur->next;}tail->next = nullptr;ListNode* ret = newHead->next;delete newHead;return ret;}
};
解法二:递归
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {if (head == nullptr) {return nullptr;}if (head->val != val) {head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);return head;} else {return removeElements(head->next, val);}}
};
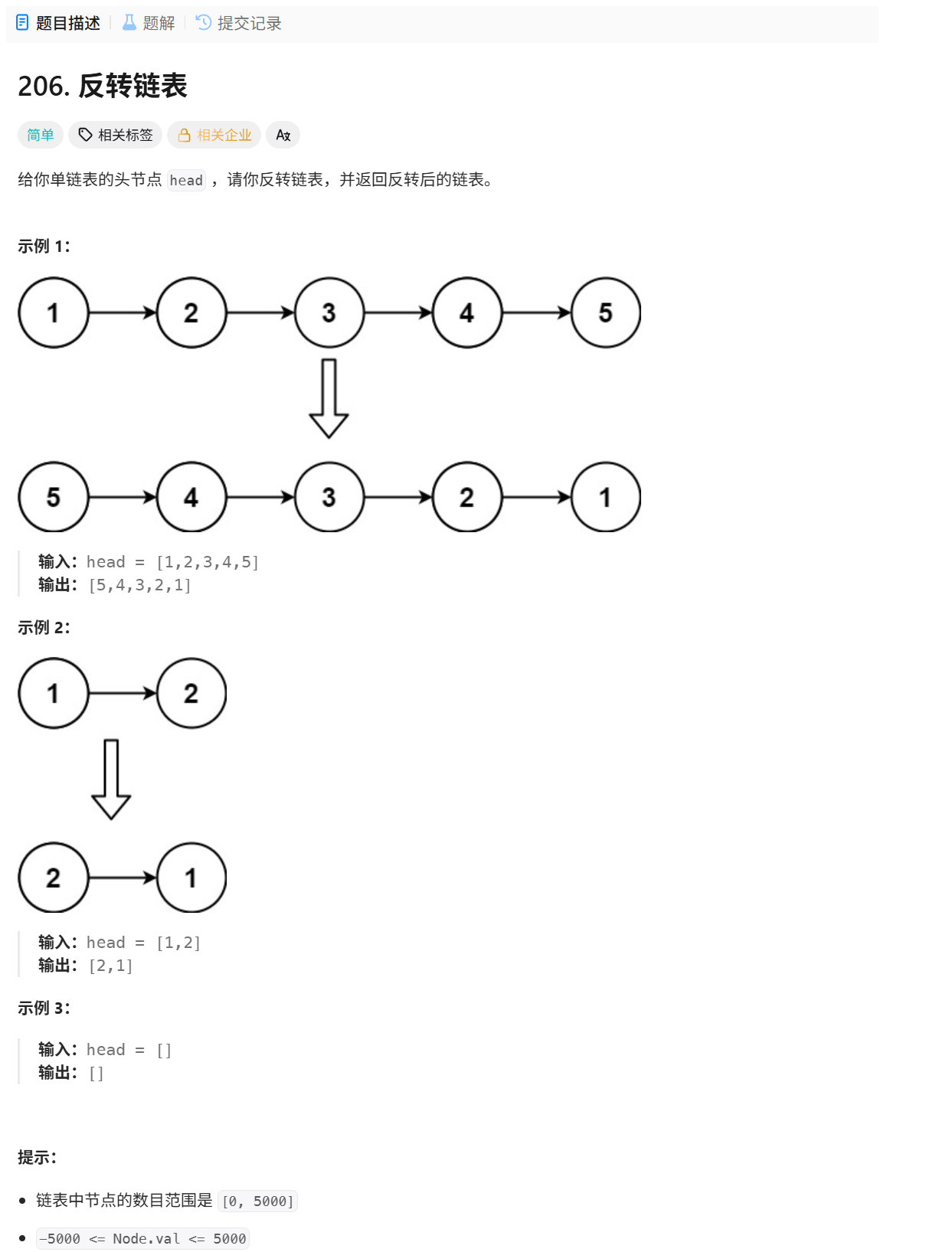
206. 反转链表
206. 反转链表
解法一:三指针
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if (head == nullptr) {return nullptr;}ListNode* p1 = nullptr, *p2 = head, *p3 = p2->next;while (p2) {p2->next = p1;p1 = p2;p2 = p3;if (p3) {p3 = p3->next;}}return p1;}
};
解法二:头插法
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* newHead = nullptr, *cur = head;while (cur) {ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newHead;newHead = cur;cur = next;}return newHead;}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(), *cur = head;while (cur) {ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = newHead->next;newHead->next = cur;cur = next;}ListNode* ret = newHead->next;delete newHead;return ret;}
};
876. 链表的中间结点
876. 链表的中间结点

解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}
};
21. 合并两个有序链表
21. 合并两个有序链表
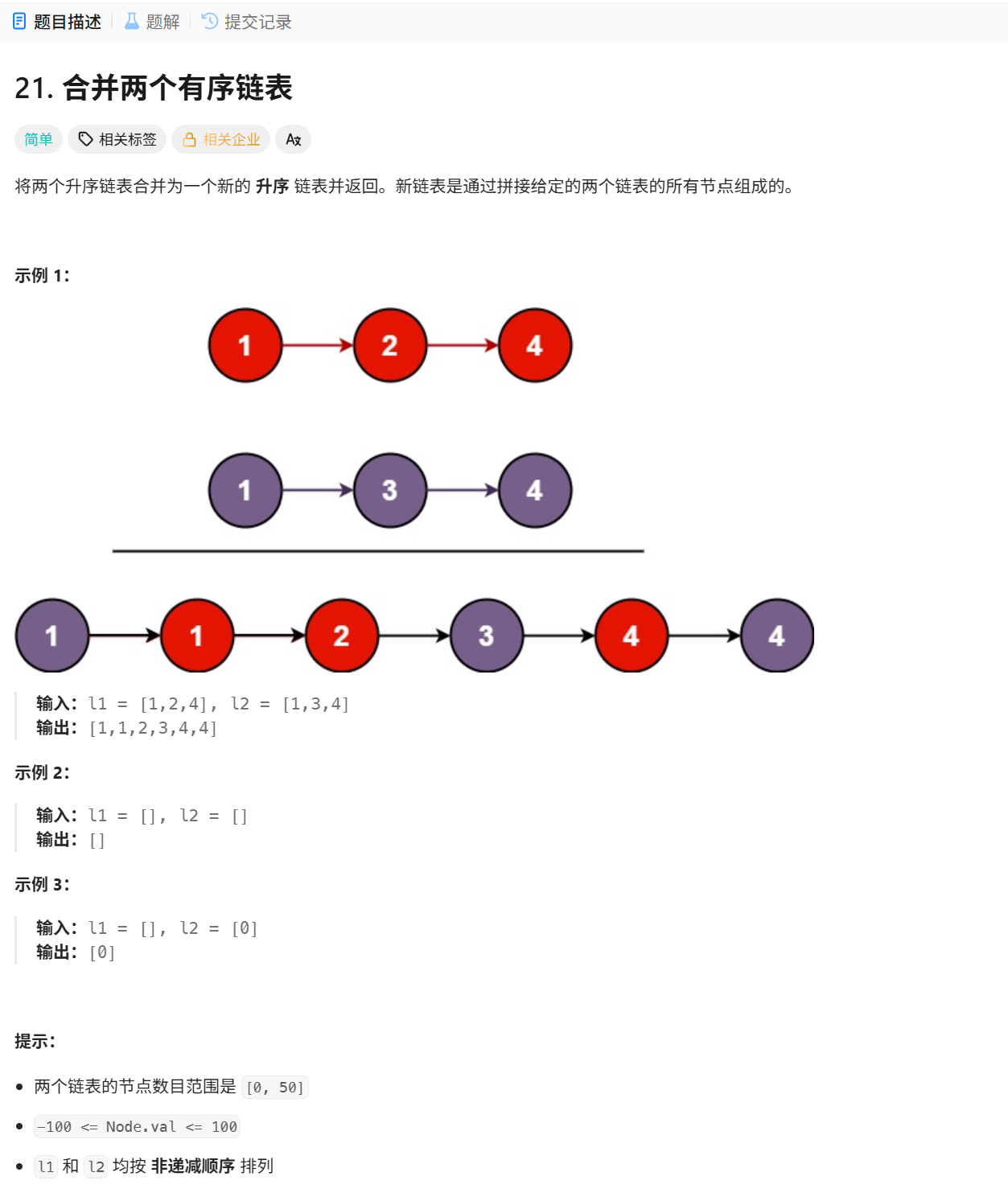
解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {if (list1 == nullptr) {return list2;}if (list2 == nullptr) {return list1;}ListNode* head = new ListNode(), *tail = head;ListNode* l1 = list1, *l2 = list2;while (l1 && l2) {if (l1->val <= l2->val) {tail->next = l1;l1 = l1->next;} else {tail->next = l2;l2 = l2->next;}tail = tail->next;}if (l1) {tail->next = l1;} else {tail->next = l2;}ListNode* ret = head->next;delete head;return ret;}
};
160. 相交链表
160. 相交链表

解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;ListNode* cur1 = headA, *cur2 = headB;while (cur1) {len1++;cur1 = cur1->next;}while (cur2) {len2++;cur2 = cur2->next;}ListNode* slow = nullptr, *fast = nullptr;if (len1 < len2) {slow = headA;fast = headB;} else {slow = headB;fast = headA;}for (int i = 0; i < abs(len1 - len2); i++) {fast = fast->next;}while (slow) {if (slow == fast) {return slow;}slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return nullptr;}
};
234. 回文链表
234. 回文链表

class Solution {
public:ListNode* findMid(ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {ListNode* p1 = nullptr, *p2 = head, *p3 = p2->next;while (p2) {p2->next = p1;p1 = p2;p2 = p3;if (p3) {p3 = p3->next;}}return p1;}bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {// 1.寻找中间节点ListNode* mid = findMid(head);// 2.逆序左右链表ListNode* left = head, *right = reverse(mid);// 3.判断是否回文while (right) {if (left->val != right->val) {return false;}left = left->next;right = right->next;}return true;}
};
141. 环形链表
141. 环形链表
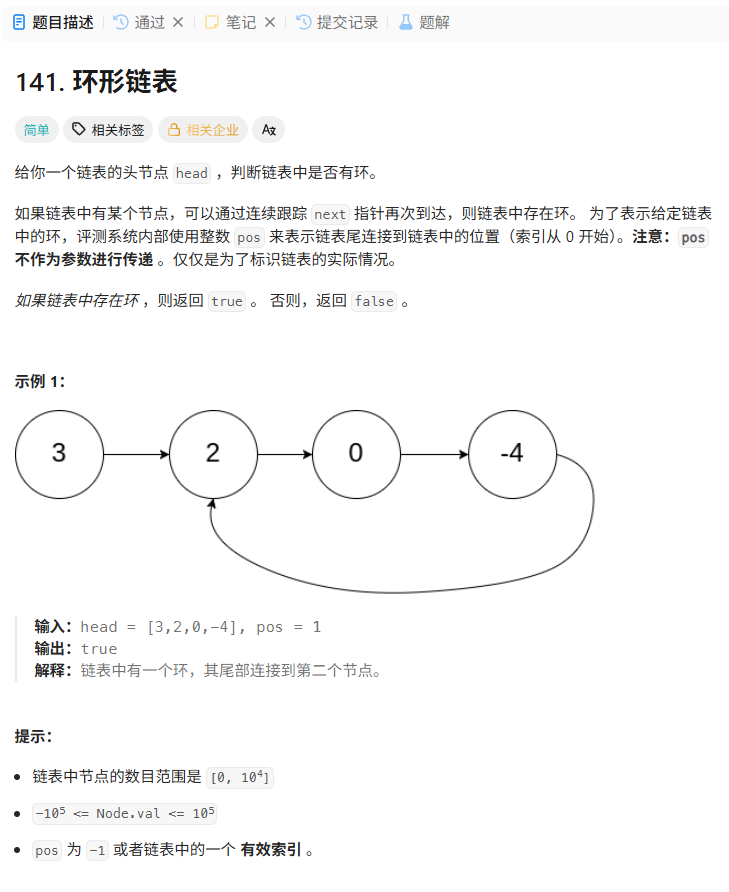
解法:快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,若为环型链表最终在环中相遇。
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {return true;}}return false;}
};
思考1:为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以相遇,有没有可能遇不上,请推理证明!

思考2:快指针一次走3步,走4步,…走n步,行吗?


思考:真的存在N是奇数,C是偶数这一条件?


142. 环形链表 II
142. 环形链表 II

解法:快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,若为环型链表最终在环中相遇,然后让一个指针从相遇点开始走,一个指针从起点开始走,一次走一步,最终在进环处相遇。

class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {ListNode* meet = slow, *cur = head;while (meet != cur) {meet = meet->next;cur = cur->next;}return meet;}}return nullptr;}
};
138. 随机链表的复制
138. 随机链表的复制

解法:迭代



class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {// 1.在原链表上拷贝链表Node* cur = head;while (cur) {Node* copy = new Node(cur->val);copy->next = cur->next;cur->next = copy;cur = copy->next;}// 2.处理randomcur = head;while (cur) {Node* copy = cur->next;if (cur->random == nullptr) {copy->random = nullptr;} else {copy->random = cur->random->next;}cur = copy->next;}// 3.分割链表Node* copyHead = nullptr, *copyTail = nullptr;cur = head;while (cur) {Node* copy = cur->next;Node* next = copy->next;if (copyTail == nullptr) {copyHead = copyTail = copy;} else {copyTail->next = copy;copyTail = copyTail->next;}cur->next = next;cur = next;}return copyHead;}
};
解法二:哈希表
为了控制随机指针,我们将拷贝结点链接在原节点的后面解决,后面拷贝节点还得解下来链接,非常麻烦。这里我们直接让 {原结点,拷贝结点} 建立映射关系放到map中,控制随机指针会非常简单方便,这里体现了map在解决一些问题时的价值,完全是降维打击。

class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {// 原节点映射拷贝节点unordered_map<Node*, Node*> hash;// 1.拷贝链表并添加映射关系Node* copyHead = nullptr, *copyTail = nullptr;Node* cur = head;while (cur) {Node* copy = new Node(cur->val);if (copyTail == nullptr) {copyHead = copyTail = copy;} else {copyTail->next = copy;copyTail = copyTail->next;}hash[cur] = copy;cur = cur->next;}// 2.通过哈希表处理randomcur = head;Node* copy = copyHead;while (cur) {if (cur->random == nullptr) {copy->random = nullptr;} else {copy->random = hash[cur->random];}cur = cur->next;copy = copy->next;}return copyHead;}
};
面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
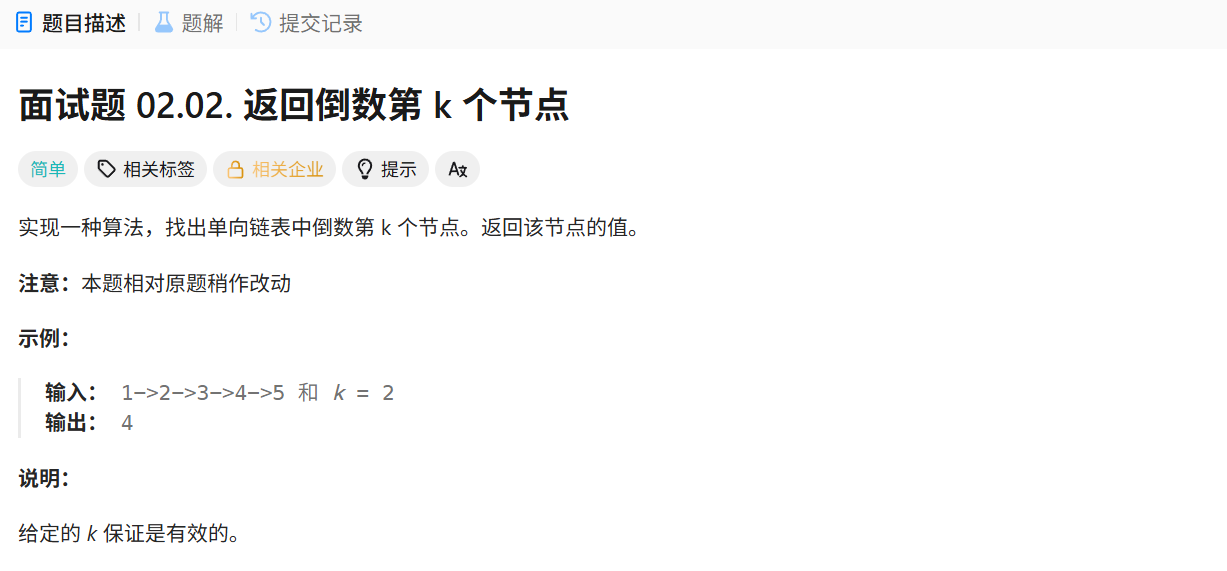
解法:双指针
class Solution {
public:int kthToLast(ListNode* head, int k) {ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {fast = fast->next;}while (fast) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return slow->val;}
};
面试题 02.04. 分割链表
面试题 02.04. 分割链表
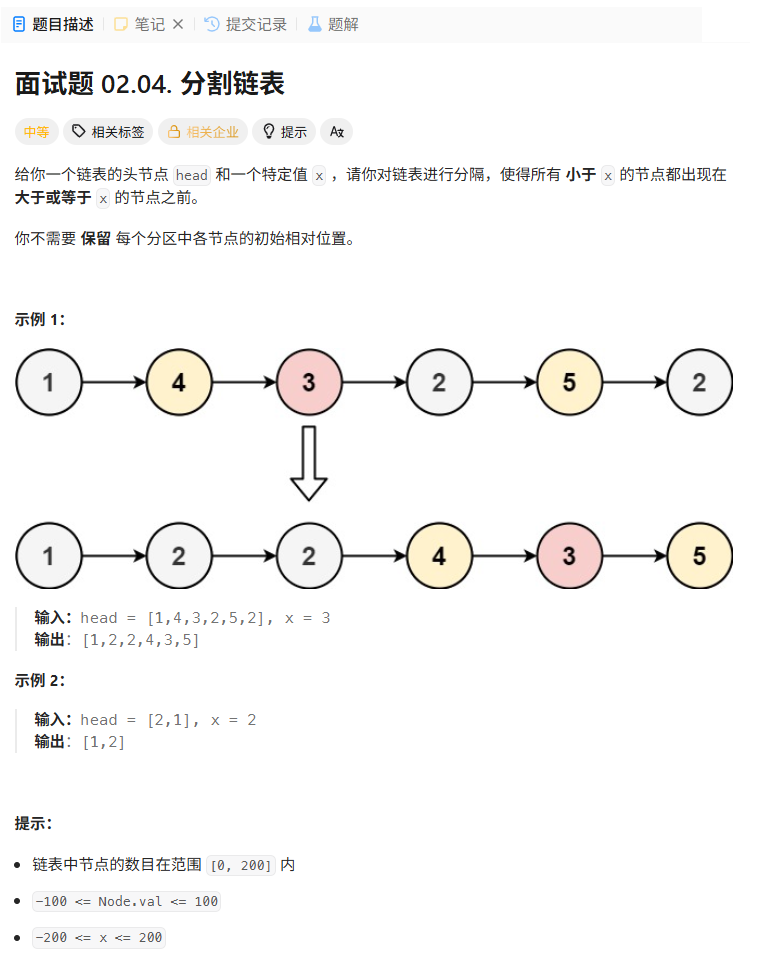
解法:创建大小链表
class Solution {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {ListNode* smallHead = new ListNode(), *smallTail = smallHead;ListNode* bigHead = new ListNode(), *bigTail = bigHead;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur) {if (cur->val < x) {smallTail->next = cur;smallTail = smallTail->next;} else {bigTail->next = cur;bigTail = bigTail->next;}cur = cur->next;}smallTail->next = bigHead->next;bigTail->next = nullptr;ListNode* ret = smallHead->next;delete smallHead;delete bigHead;return ret;}
};
三. 栈
20. 有效的括号
20. 有效的括号

解法:遍历括号,遇到左括号入栈、遇到右括号,判断是否与栈顶括号匹配 (若栈顶为空,则不是有效的括号),若匹配则出栈,若不匹配则不是有效的括号,遍历结束后,若栈中还有括号则不是有效的括号,否则是有效的括号。
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> st;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if (s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '{') { // 左括号进栈st.push(s[i]);} else { // 右括号判断if (st.empty()) { // 栈为空,则匹配失败return false;}char top = st.top(); // 栈不为空,进行括号匹配st.pop();if ((top == '(' && s[i] != ')') || (top == '[' && s[i] != ']') || (top == '{' && s[i] != '}')) { // 若括号不匹配,则匹配失败return false; }}}return st.empty();}
};
155. 最小栈
155. 最小栈

解法:双栈

class MinStack {stack<int> _st;stack<int> _min_st;
public:MinStack() {}void push(int val) {if (_min_st.empty() || _min_st.top() >= val) {_min_st.push(val);}_st.push(val);}void pop() {int top = _st.top();_st.pop();if (_min_st.top() == top) {_min_st.pop();}}int top() {return _st.top();}int getMin() {return _min_st.top();}
};
946. 验证栈序列
946. 验证栈序列

解法:入栈序列模拟出栈过程

class Solution {
public:bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {stack<int> st;for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < pushed.size(); i++) {st.push(pushed[i]);// 栈顶数据与出栈序列是否相等,判断是否出栈while (!st.empty() && popped[j] == st.top()) {st.pop();j++;}}return st.empty();}
};
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
150. 逆波兰表达式求值

解法:遍历序列,遇到数字直接入栈,遇到操作符,则取出栈顶两个数字 (注意:第一个栈顶是右操作数,第二个栈顶是左操作数),运算的结果入栈,遍历结束后,返回栈顶数字就是最终结果。
class Solution {
public:int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {stack<int> st;for (int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++) {string str = tokens[i];if (str == "+" || str == "-" || str == "*" || str == "/") {// 先取到的是右操作数,后取到的是左操作数int right = st.top();st.pop();int left = st.top();st.pop();if (str == "+") {st.push(left + right);} else if (str == "-") {st.push(left - right);} else if (str == "*") {st.push(left * right);} else if (str == "/") {st.push(left / right);}} else {st.push(stoi(str));}}return st.top();}
};
225. 用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈

解法一:双队列

class MyStack {queue<int> _q1;queue<int> _q2;
public:MyStack() {}void push(int x) {// 向非空队列中放置元素if (!_q1.empty()) {_q1.push(x);} else {_q2.push(x);}}int pop() {// 将非空队列中的前n-1个元素移动至空队列中if (_q1.empty()) {swap(_q1, _q2);}while (_q1.size() > 1) {int front = _q1.front();_q1.pop();_q2.push(front);}int ret = _q1.front();_q1.pop();return ret;}int top() {// 非空队列的最后一个元素就是栈顶元素if (_q1.empty()) {swap(_q1, _q2);}return _q1.back();}bool empty() {return _q1.empty() && _q2.empty();}
};
解法二:单队列
class MyStack {queue<int> q;
public:MyStack() {}void push(int x) {// 每一次入队列之前都需要将队列中的前n-1个元素移除重新入队列int n = q.size();q.push(x);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {q.push(q.front());q.pop();}}int pop() {int ret = q.front();q.pop();return ret;}int top() {return q.front();}bool empty() {return q.empty();}
};
四. 队列
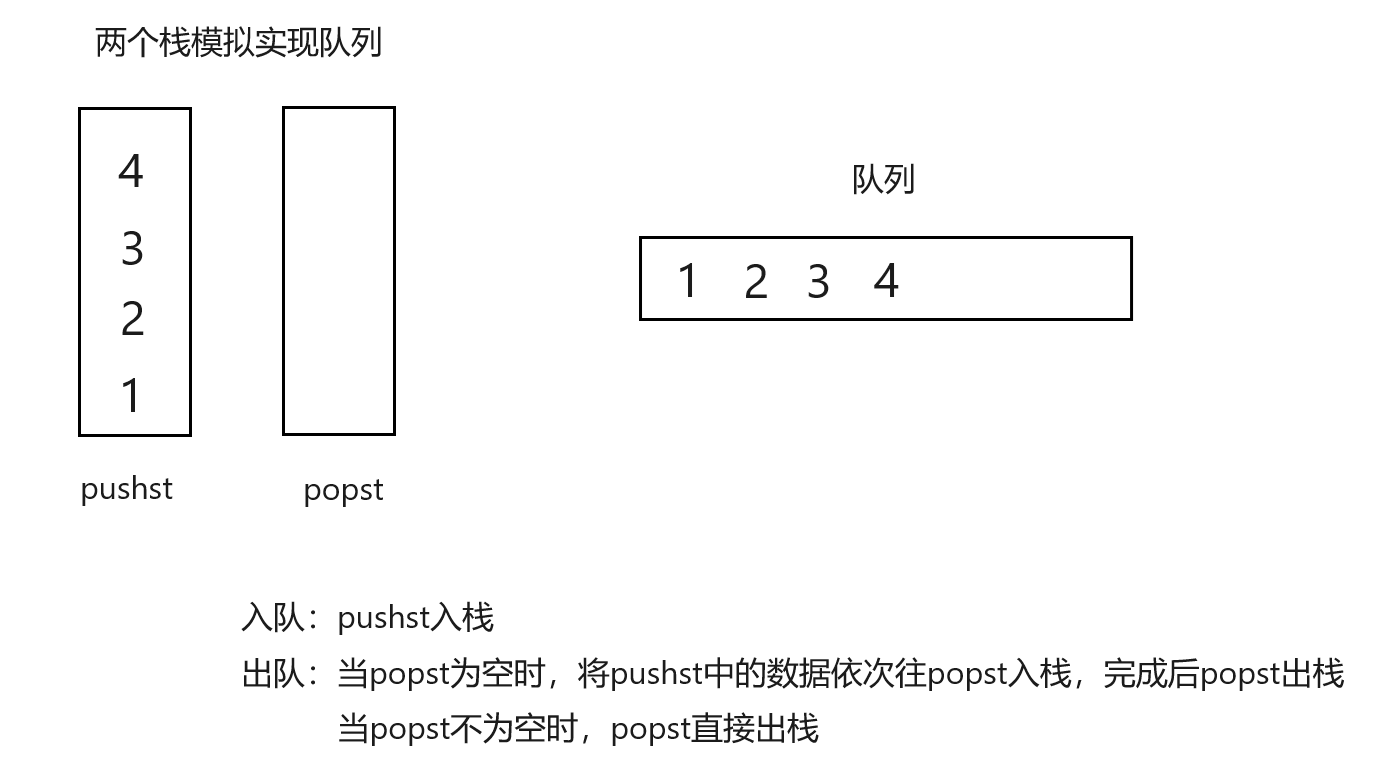
232. 用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列

解法:双栈
class MyQueue {stack<int> _push_st;stack<int> _pop_st;
public:MyQueue() {}void push(int x) {// 直接向_push_st中入栈_push_st.push(x);}int pop() {// 如果_pop_st非空,则出栈if (!_pop_st.empty()) {int ret = _pop_st.top();_pop_st.pop();return ret;}// 若_pop_st为空,则将_push_st中的元素不断出栈且入栈到_pop_st中while (_push_st.size() > 1) {int top = _push_st.top();_pop_st.push(top);_push_st.pop();}// _pop_st出栈int ret = _push_st.top();_push_st.pop();return ret;}int peek() {// 同pop()函数if (!_pop_st.empty()) {return _pop_st.top();}while (_push_st.size() > 0) {int top = _push_st.top();_pop_st.push(top);_push_st.pop();}return _pop_st.top();}bool empty() {return _push_st.empty() && _pop_st.empty();}
};
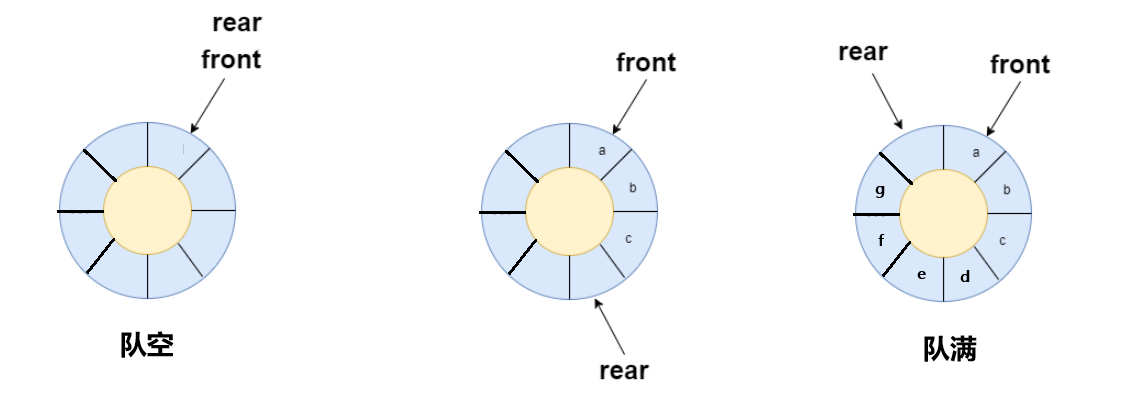
622. 设计循环队列
622. 设计循环队列

解法一:数组
class MyCircularQueue {int front; // 队头int rear; // 队尾int capacity; // 数据个数 + 1vector<int> arr;
public:MyCircularQueue(int k) {capacity = k + 1;arr = vector<int>(capacity);rear = front = 0;}bool enQueue(int value) {if (isFull()) {return false;}arr[rear] = value;rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;return true;}bool deQueue() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}front = (front + 1) % capacity;return true;}int Front() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return arr[front];}int Rear() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return arr[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];}bool isEmpty() {return rear == front;}bool isFull() {return ((rear + 1) % capacity) == front;}
};
解法二:链表
class MyCircularQueue {
private:ListNode *head;ListNode *tail;int capacity;int size;public:MyCircularQueue(int k) {this->capacity = k;this->size = 0;this->head = this->tail = nullptr;}bool enQueue(int value) {if (isFull()) {return false;}ListNode *node = new ListNode(value);if (!head) {head = tail = node;} else {tail->next = node;tail = node;}size++;return true;}bool deQueue() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}ListNode *node = head;head = head->next; size--;delete node;return true;}int Front() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return head->val;}int Rear() {if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}return tail->val;}bool isEmpty() {return size == 0;}bool isFull() {return size == capacity;}
};
五. 二叉树
965. 单值二叉树
965. 单值二叉树

class Solution {
public:bool dfs(TreeNode* root, int val) {if (root == nullptr) {return true;}if (root->val != val) {return false;}return dfs(root->left, val) && dfs(root->right, val);}bool isUnivalTree(TreeNode* root) {return dfs(root, root->val);}
};
100. 相同的树
100. 相同的树
class Solution {
public:bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if (p == nullptr && q == nullptr) {return true;} else if (p == nullptr || q == nullptr) {return false;} else if (p->val != q->val) {return false;} else {return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);}}
};
101. 对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树
class Solution {
public:bool dfs(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {if (root1 == nullptr && root2 == nullptr) {return true;} else if (root1 == nullptr || root2 == nullptr) {return false;} else if (root1->val != root2->val) {return false;} else {return dfs(root1->left, root2->right) && dfs(root1->right, root2->left);}}bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {return dfs(root->left, root->right);}
};
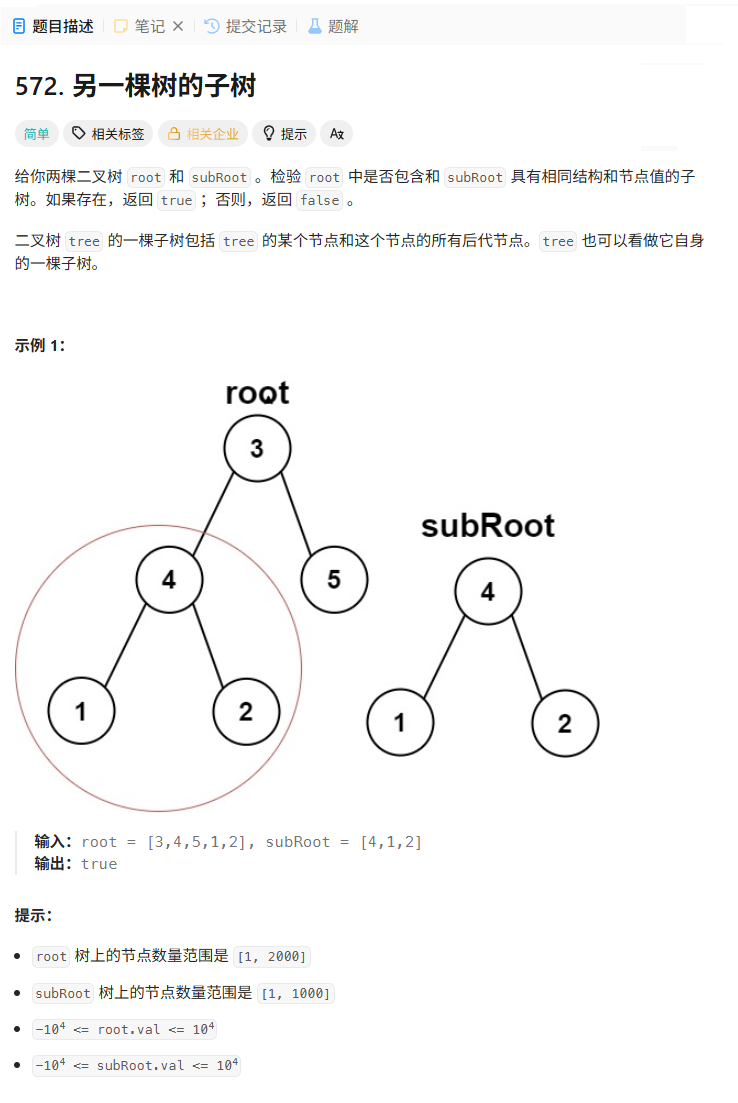
572. 另一棵树的子树
572. 另一棵树的子树
class Solution {
public:bool isSameTree(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {if (root1 == nullptr && root2 == nullptr) {return true;} else if (root1 == nullptr || root2 == nullptr) {return false;} else if (root1->val != root2->val) {return false;} else {return isSameTree(root1->left, root2->left) && isSameTree(root1->right, root2->right);}}bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {if (root == nullptr) {return false;} else if (root->val == subRoot->val && isSameTree(root, subRoot)) {return true;} else {return isSubtree(root->left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right, subRoot);}}
};
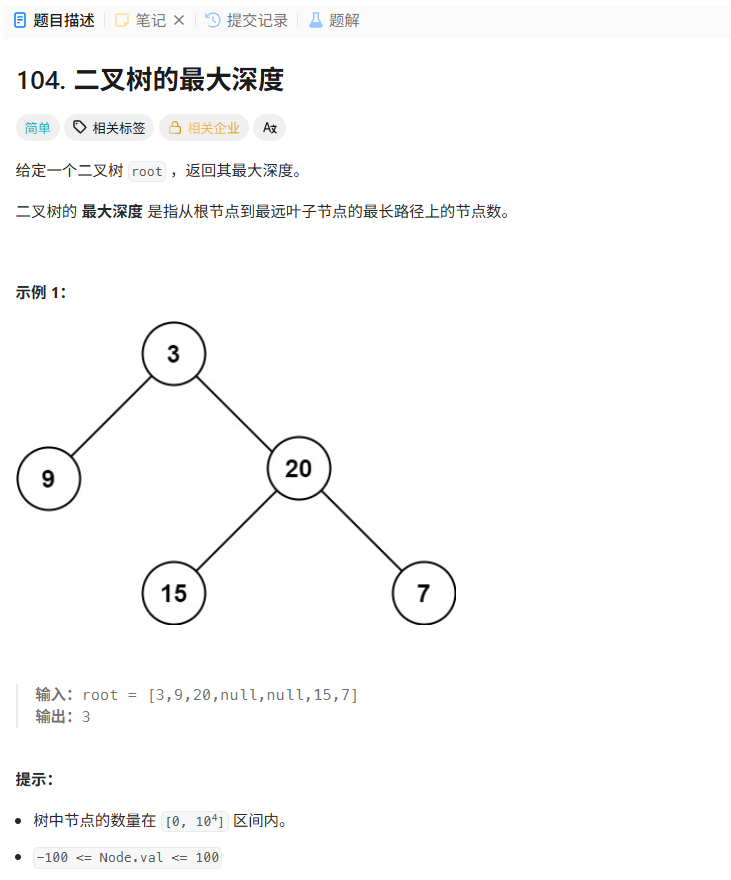
104. 二叉树的最大深度
104. 二叉树的最大深度
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return 0;}int leftHeight = maxDepth(root->left);int rightHeight = maxDepth(root->right);return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}
};class Solution {int ret = 0;
public:void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth) {if (root == nullptr) {return;}ret = max(ret, depth);dfs(root->left, depth + 1);dfs(root->right, depth + 1);}int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root, 1);return ret;}
};
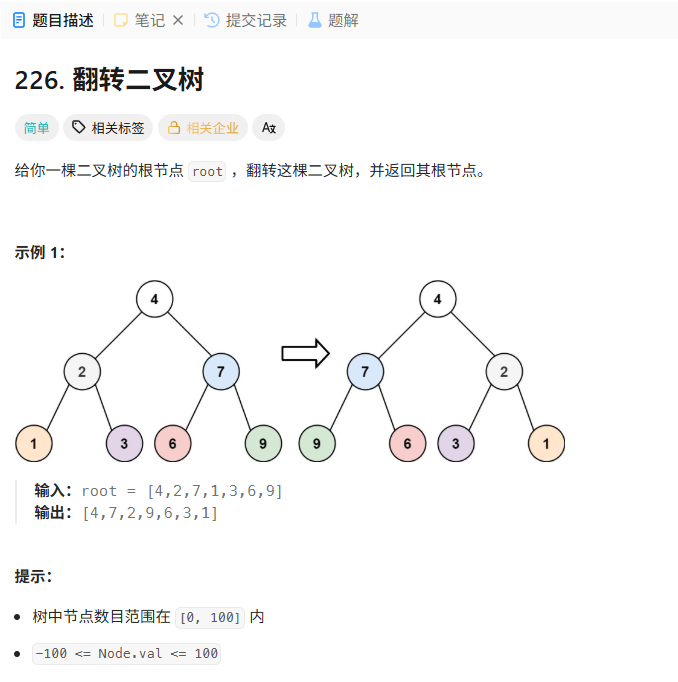
226. 翻转二叉树
226. 翻转二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return nullptr;}invertTree(root->left);invertTree(root->right);swap(root->left, root->right);return root;}
};class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return nullptr;} else if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {return root;} else if (root->left == nullptr) {root->left = invertTree(root->right);root->right = nullptr;return root;} else if (root->right == nullptr) {root->right = invertTree(root->left);root->left = nullptr;return root;} else {TreeNode* left = root->left;TreeNode* right = root->right;root->left = invertTree(right);root->right = invertTree(left);return root;}}
};
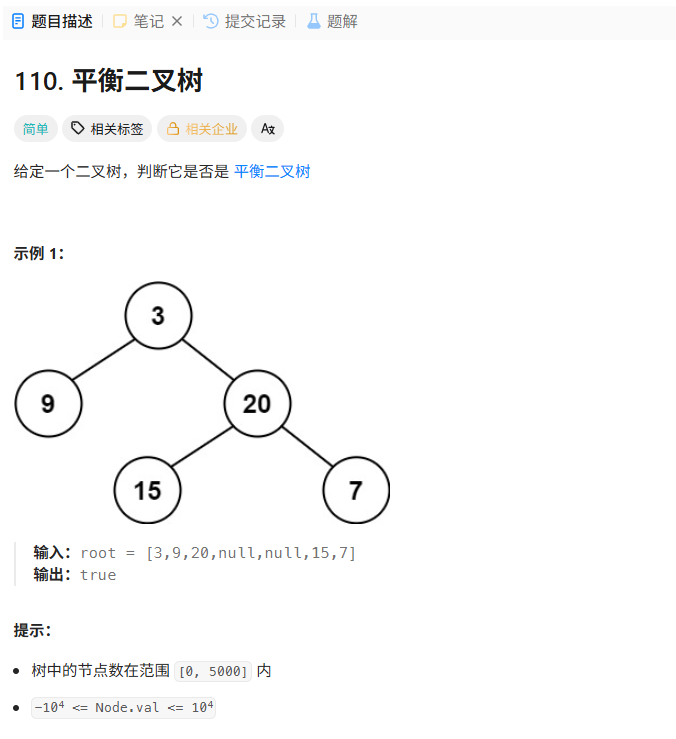
110. 平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树
class Solution {
public:int getHeight(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return 0;}int leftHeight = getHeight(root->left);if (leftHeight == -1) {return -1;}int rightHeight = getHeight(root->right);if (rightHeight == -1) {return -1;}if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {return -1;}return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {return getHeight(root) != -1;}
};
二叉树遍历
二叉树遍历
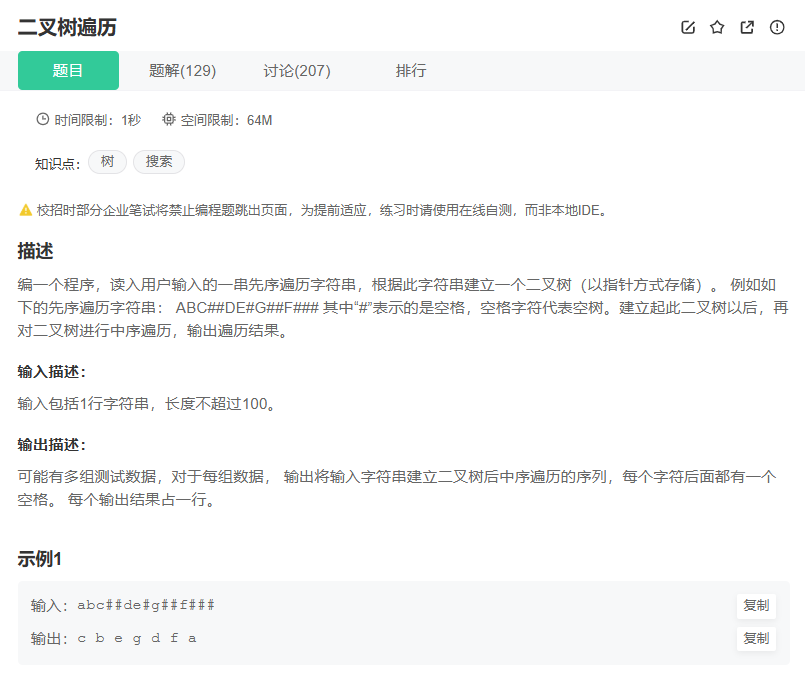

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;struct TreeNode {char val;TreeNode* left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode(char val) : val(val), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};TreeNode* CreateTree(string s, int& i) {if (s[i] == '#') {i++; // 注意:这里也需要自增return nullptr;}TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(s[i]);i++;root->left = CreateTree(s, i);root->right = CreateTree(s, i);return root;
}void inOrder(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return;}inOrder(root->left);cout << root->val << " ";inOrder(root->right);
}int main()
{string s;cin >> s;int i = 0;TreeNode* root = CreateTree(s, i);inOrder(root);return 0;
}
六. 字符串
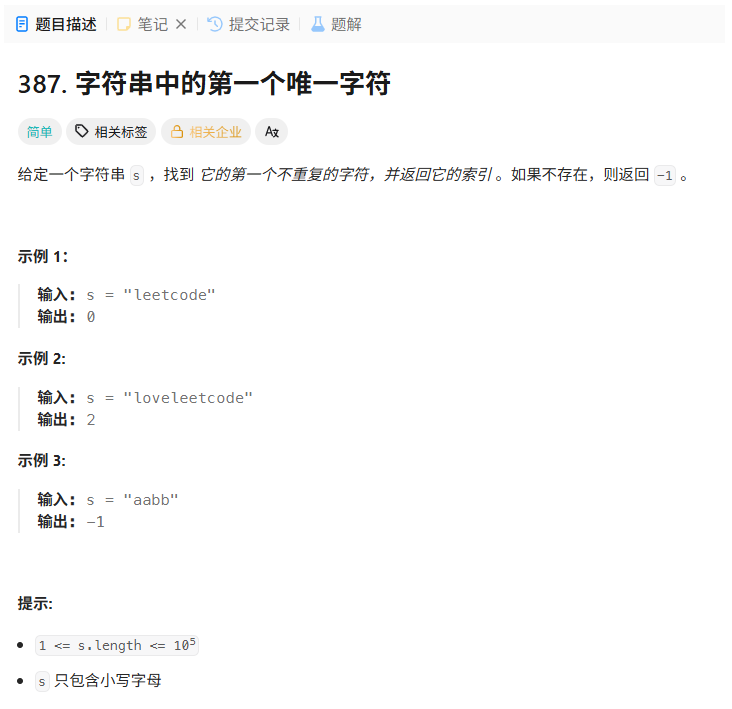
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {int count[26] = { 0 };for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {count[ch - 'a']++;}for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if(count[s[i] - 'a'] == 1) {return i;}}return -1;}
};
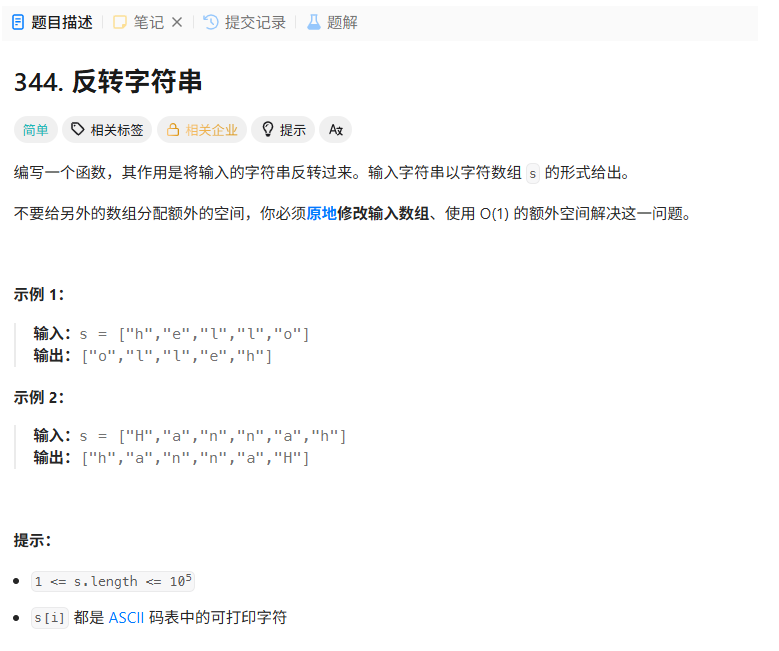
344. 反转字符串
344. 反转字符串
class Solution {
public:void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {int left = 0, right = s.size() - 1;while (left < right) {swap(s[left++], s[right--]);}}
};class Solution {
public:void dfs(vector<char>& s, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) {return;}swap(s[left], s[right]);dfs(s, left + 1, right - 1);}void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {dfs(s, 0, s.size() - 1);}
};
541. 反转字符串 II
541. 反转字符串 II

class Solution {
public:string reverseStr(string s, int k) {int n = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * k) {if (n - i > 2 * k) {reverse(s.begin() + i, s.begin() + i + k);} else if (n - i >= k) {reverse(s.begin() + i, s.begin() + i + k);} else {reverse(s.begin() + i, s.end());}}return s;}
};
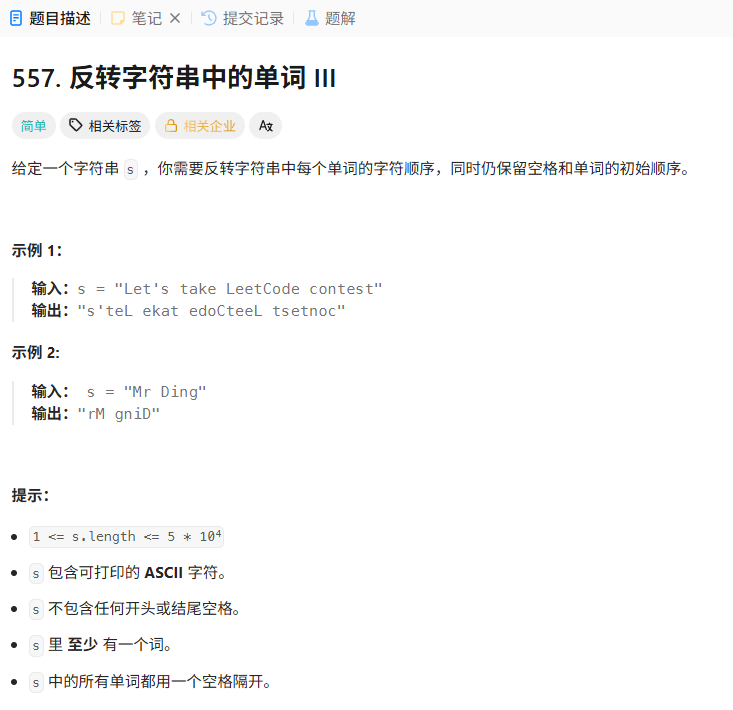
557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
class Solution {
public:string reverseWords(string s) {int prev = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if (s[i] == ' ') {reverse(s.begin() + prev, s.begin() + i);prev = i + 1;}}reverse(s.begin() + prev, s.end());return s;}
};
125. 验证回文串
125. 验证回文串


class Solution {
public:void toLower(string& s) {for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if ('A' <= s[i] && s[i] <= 'Z') {s[i] += 32;}}}bool isValid(char ch) {if (('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z') || ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9')) {return true;}return false;}bool isPalindrome(string s) {toLower(s);int left = 0, right = s.size() - 1;while (left < right) {while (left < right && !isValid(s[left])) {left++;}while (left < right && !isValid(s[right])) {right--;}if (s[left] != s[right]) {return false;}left++;right--;}return true;}
};
8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)

class Solution {
public:int myAtoi(const string& s) {int i = 0, n = s.size();// 1.跳过空格while (i < n && s[i] == ' ') i++;// 2.检验符号int sign = 1;if (i < n && (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-')) {if (s[i] == '-') sign = -1;i++;}// 3.开始转换int result = 0;while (i < n && isdigit(s[i])) {int digit = s[i] - '0';// 判断是否溢出if (result > INT_MAX / 10 || (result == INT_MAX / 10 && digit > INT_MAX % 10)) {return sign == 1 ? INT_MAX : INT_MIN;}result = result * 10 + digit;i++;}return result * sign;}
};
KY264 单词识别
KY264 单词识别
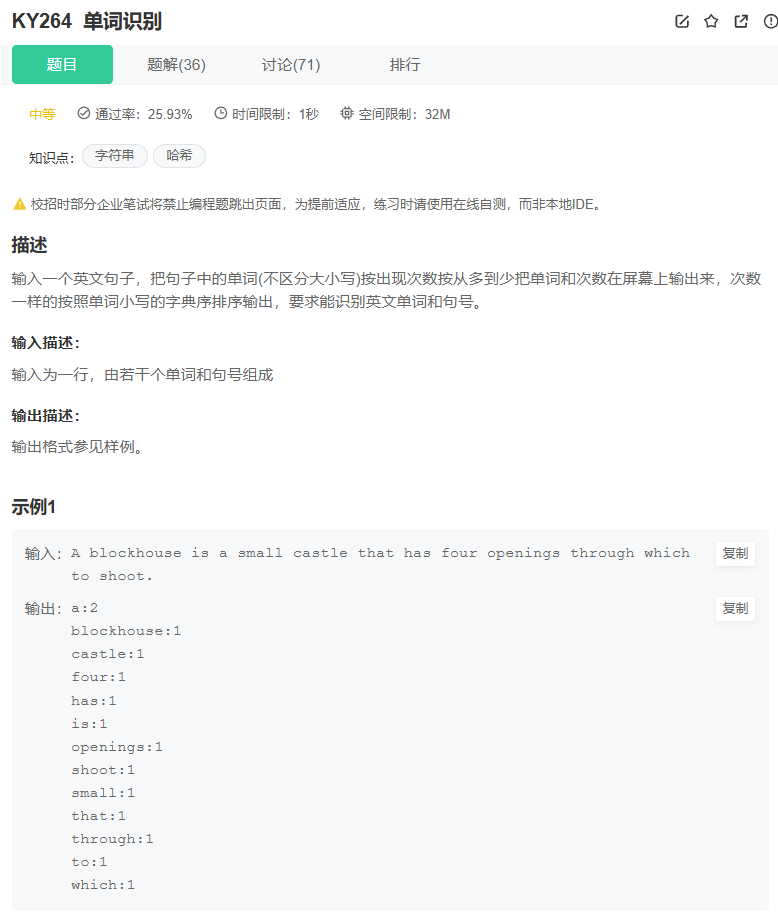
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s;getline(cin, s);map<string, int> hashMap;int prev = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if (s[i] == ' ' || s[i] == '.') {string key = s.substr(prev, i - prev);if ('A' <= key[0] && key[0] <= 'Z') {key[0] += 32;}hashMap[key]++;prev = i + 1;}}for (auto& [key, value] : hashMap) {cout << key << ":" << value << endl;}return 0;
}
